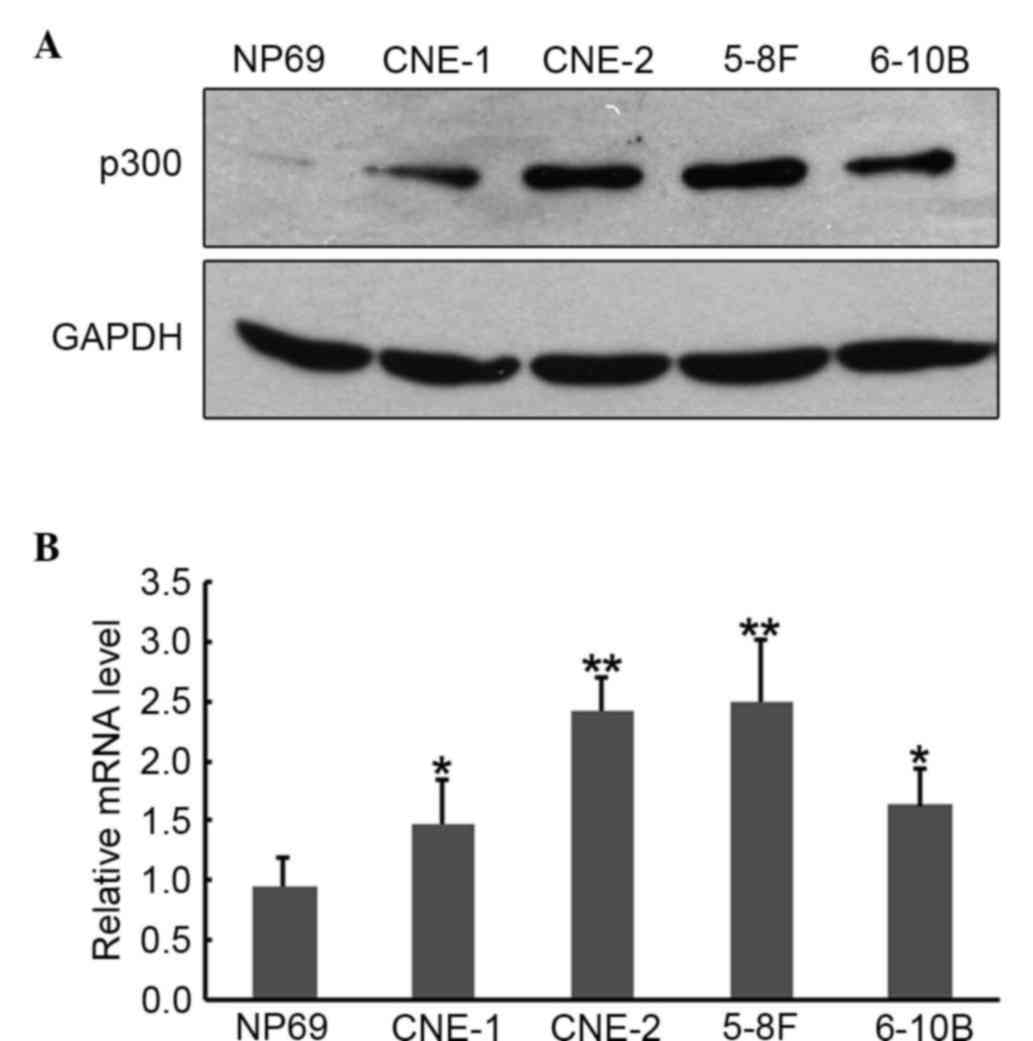
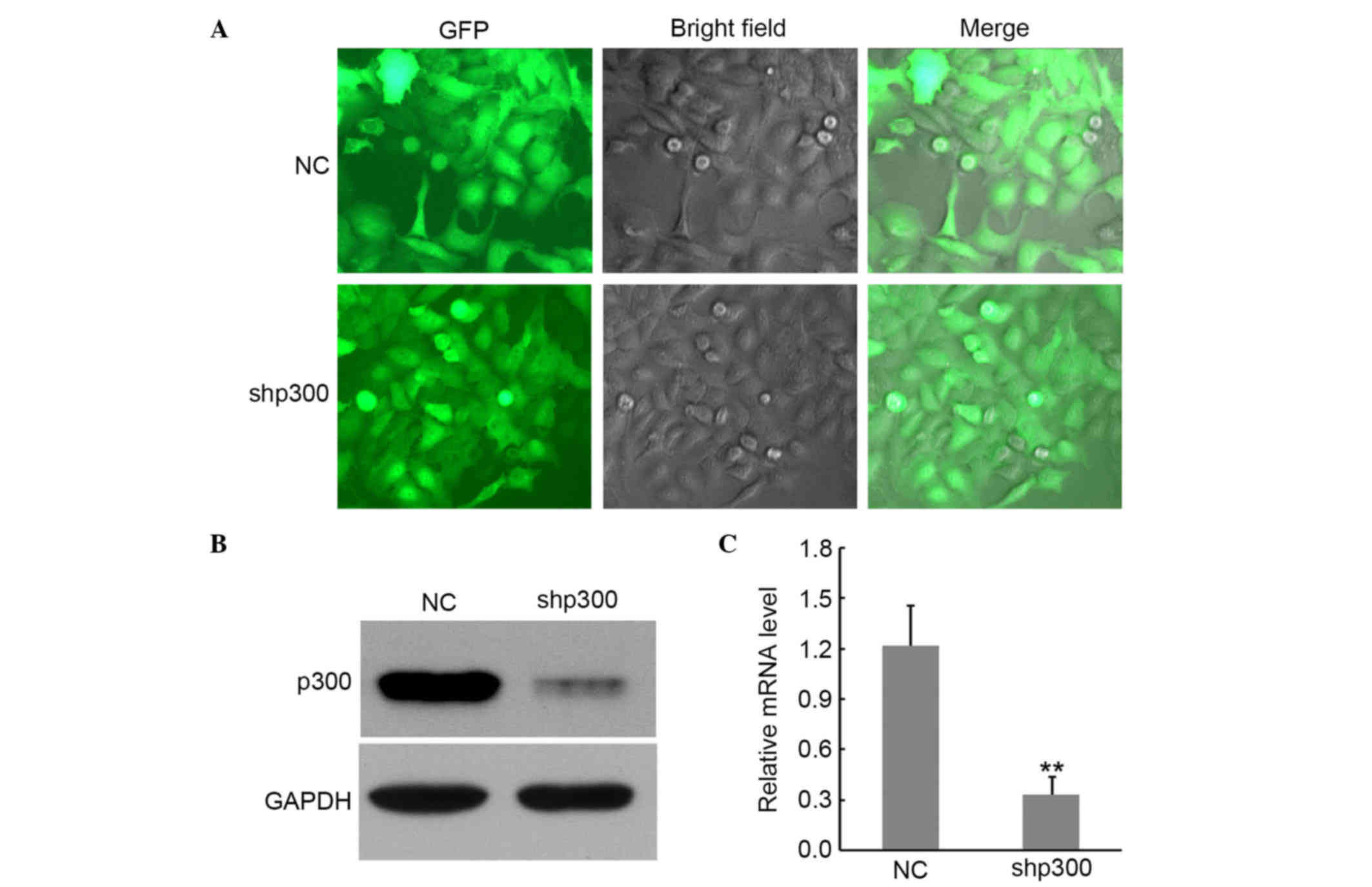
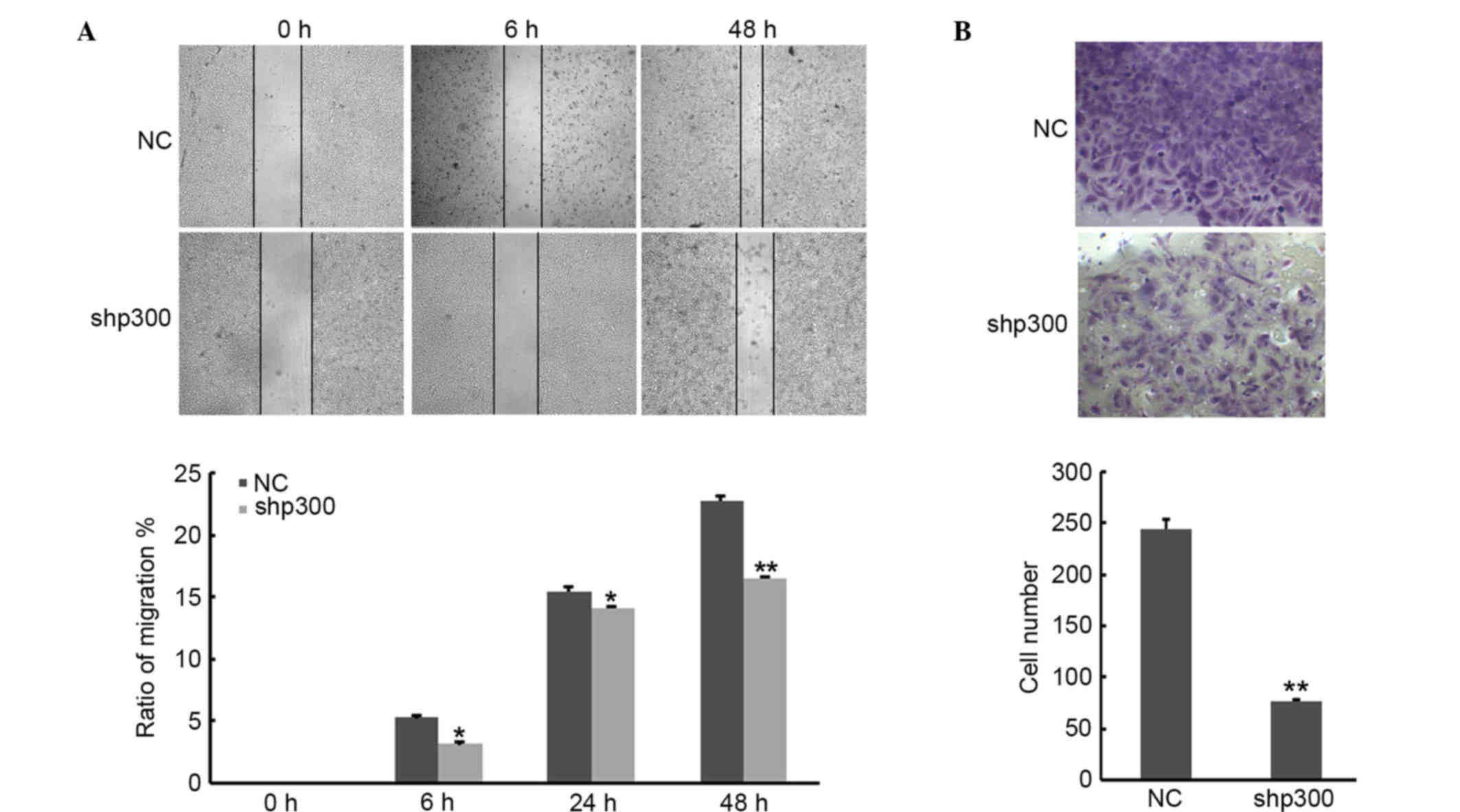
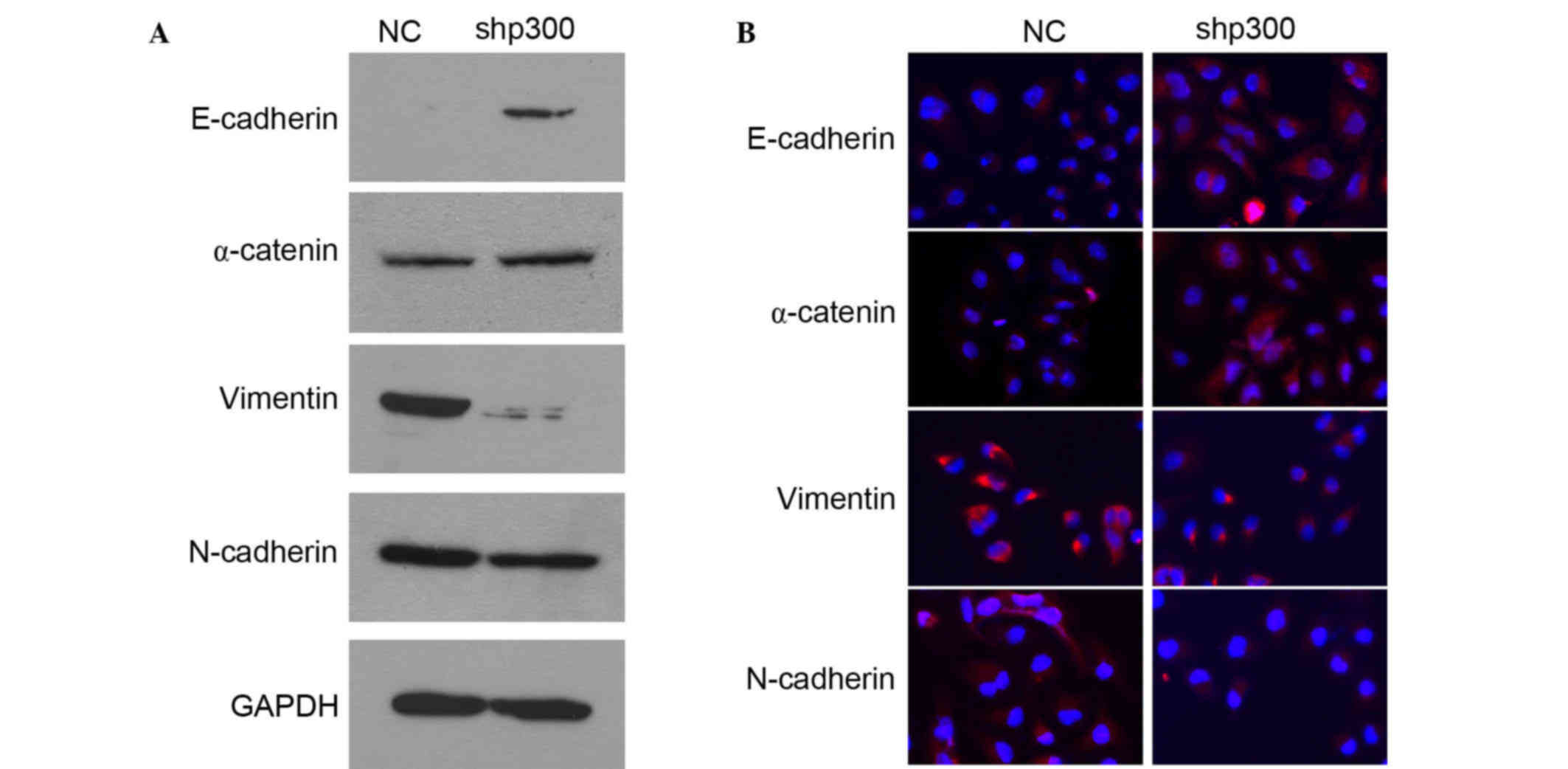
|
1
|
Yu MC and Yuan JM: Epidemiology of
nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Semin Cancer Biol. 12:421–429. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zhang L, Zhao C, Ghimire B, Hong MH, Liu
Q, Zhang Y, Guo Y, Huang YJ and Guan ZZ: The role of concurrent
chemoradiotherapy in the treatment of locoregionally advanced
nasopharyngeal carcinoma among endemic population: A meta-analysis
of the phase III randomized trials. BMC Cancer. 10:5582010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Goodman RH and Smolik S: CBP/p300 in cell
growth, transformation, and development. Genes Dev. 14:1553–1577.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Liao ZW, Zhou TC, Tan XJ, Song XL, Liu Y,
Shi XY, Huang WJ, Du LL, Tu BJ and Lin XD: High expression of p300
is linked to aggressive features and poor prognosis of
nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J Transl Med. 10:1102012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Xiao XS, Cai MY, Chen JW, Guan XY, Kung
HF, Zeng YX and Xie D: High Expression of p300 in human breast
cancer correlates with tumor recurrence and predicts adverse
prognosis. Chin J Cancer Res. 23:201–207. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ishihama K, Yamakawa M, Semba S, Takeda H,
Kawata S, Kimura S and Kimura W: Expression of HDAC1 and CBP/p300
in human colorectal carcinomas. J Clin Pathol. 60:1205–1210. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Li Y, Yang HX, Luo RZ, Zhang Y, Li M, Wang
X and Jia WH: High expression of p300 has an unfavorable impact on
survival in resectable esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Ann
Thorac Surg. 91:1531–1538. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Li M, Luo R, Chen JM, Cao Y, Lu JB, He JH,
Wu QL and Cai MY: High expression of transcriptional coactivator
p300 correlates with aggressive features and poor prognosis of
hepatocellular carcinoma. J Transl Med. 9:52011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Thiery JP, Acloque H, Huang RY and Nieto
MA: Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease.
Cell. 139:871–890. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Luo WR, Chen XY, Li SY, Wu AB and Yao KT:
Neoplastic spindle cells in nasopharyngeal carcinoma show features
of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Histopathology. 61:113–122.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Song LB, Li J, Liao WT, Feng Y, Yu CP, Hu
LJ, Kong QL, Xu LH, Zhang X, Liu WL, et al: The polycomb group
protein Bmi-1 represses the tumor suppressor PTEN and induces
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human nasopharyngeal
epithelial cells. J Clin Invest. 119:3626–3636. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yokomizo C, Yamaguchi K, Itoh Y, Nishimura
T, Umemura A, Minami M, Yasui K, Mitsuyoshi H, Fujii H, Tochiki N,
et al: High expression of p300 in HCC predicts shortened overall
survival in association with enhanced epithelial mesenchymal
transition of HCC cells. Cancer Lett. 310:140–147. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2−ΔΔCt method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ko H, So Y, Jeon H, Jeong MH, Choi HK, Ryu
SH, Lee SW, Yoon HG and Choi KC: TGF-β1-induced
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and acetylation of Smad2 and
Smad3 are negatively regulated by EGCG in human A549 lung cancer
cells. Cancer Lett. 335:205–213. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wei WI and Sham JS: Nasopharyngeal
carcinoma. Lancet. 365:2041–2054. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chang ET and Adami HO: The enigmatic
epidemiology of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Epidemiol
Biomarkers Prev. 15:1765–1777. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chen YF, Luo RZ, Li Y, Cui BK, Song M,
Yang AK and Chen WK: High expression levels of COX-2 and P300 are
associated with unfavorable survival in laryngeal squamous cell
carcinoma. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 270:1009–1017. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hou X, Li Y, Luo RZ, Fu JH, He JH, Zhang
LJ and Yang HX: High expression of the transcriptional co-activator
p300 predicts poor survival in resectable non-small cell lung
cancers. Eur J Surg Oncol. 38:523–530. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Gao Y, Geng J, Hong X, Qi J, Teng Y, Yang
Y, Qu D and Chen G: Expression of p300 and CBP is associated with
poor prognosis in small cell lung cancer. Int J Clin Exp Pathol.
7:760–767. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhou J, Zhan S, Tan W, Cheng R, Gong H and
Zhu Q: P300 binds to and acetylates MTA2 to promote colorectal
cancer cells growth. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 444:387–390. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Fermento ME, Gandini NA, Salomón DG,
Ferronato MJ, Vitale CA, Arévalo J, López Romero A, Nuñez M, Jung
M, Facchinetti MM and Curino AC: Inhibition of p300 suppresses
growth of breast cancer. Role of p300 subcellular localization. Exp
Mol Pathol. 97:411–424. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Peña C, García JM, García V, Silva J,
Domínguez G, Rodríguez R, Maximiano C, de Herreros A García, Muñoz
A and Bonilla F: The expression levels of the transcriptional
regulators p300 and CtBP modulate the correlations between SNAIL,
ZEB1, E-cadherin and vitamin D receptor in human colon carcinomas.
Int J Cancer. 119:2098–2104. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhao L, Lin L, Pan C, Shi M, Liao Y, Bin J
and Liao W: Flotillin-2 promotes nasopharyngeal carcinoma
metastasis and is necessary for the epithelial-mesenchymal
transition induced by transforming growth factor-β. Oncotarget.
6:9781–9793. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Xiao J, Xiang Q, Xiao YC, Su ZJ, Huang ZF,
Zhang QH, Tan Y, Li XK and Huang YD: The effect of transforming
growth factor-beta1 on nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells: Insensitive
to cell growth but functional to TGF-beta/Smad pathway. J Exp Clin
Cancer Res. 29:352010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Morrison CD, Parvani JG and Schiemann WP:
The relevance of the TGF-β paradox to EMT-MET programs. Cancer
Lett. 341:30–40. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Inoue Y, Itoh Y, Abe K, Okamoto T, Daitoku
H, Fukamizu A, Onozaki K and Hayashi H: Smad3 is acetylated by
p300/CBP to regulate its transactivation activity. Oncogene.
26:500–508. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|