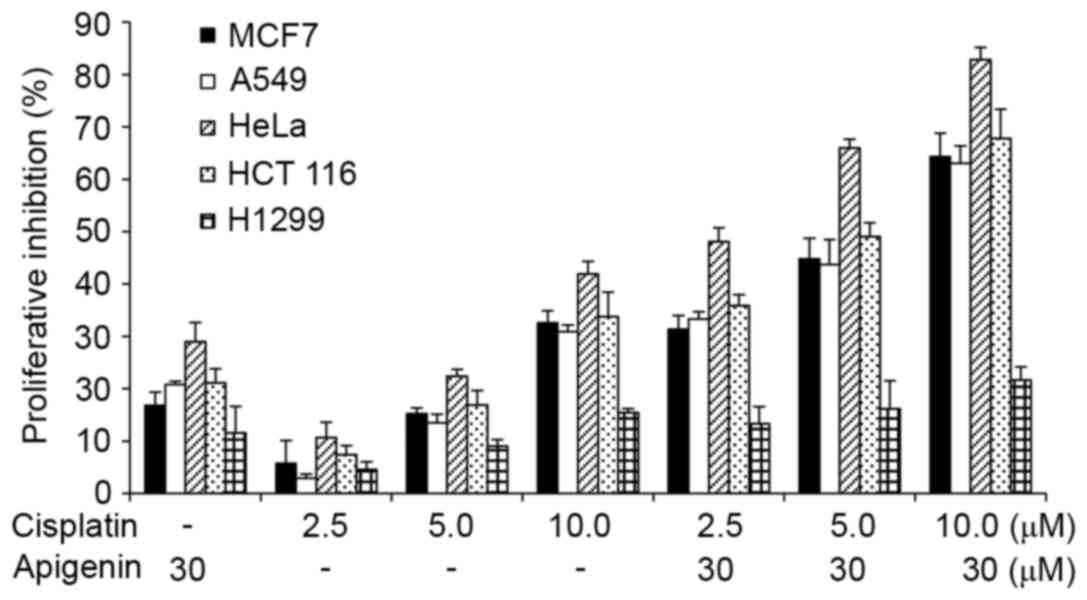
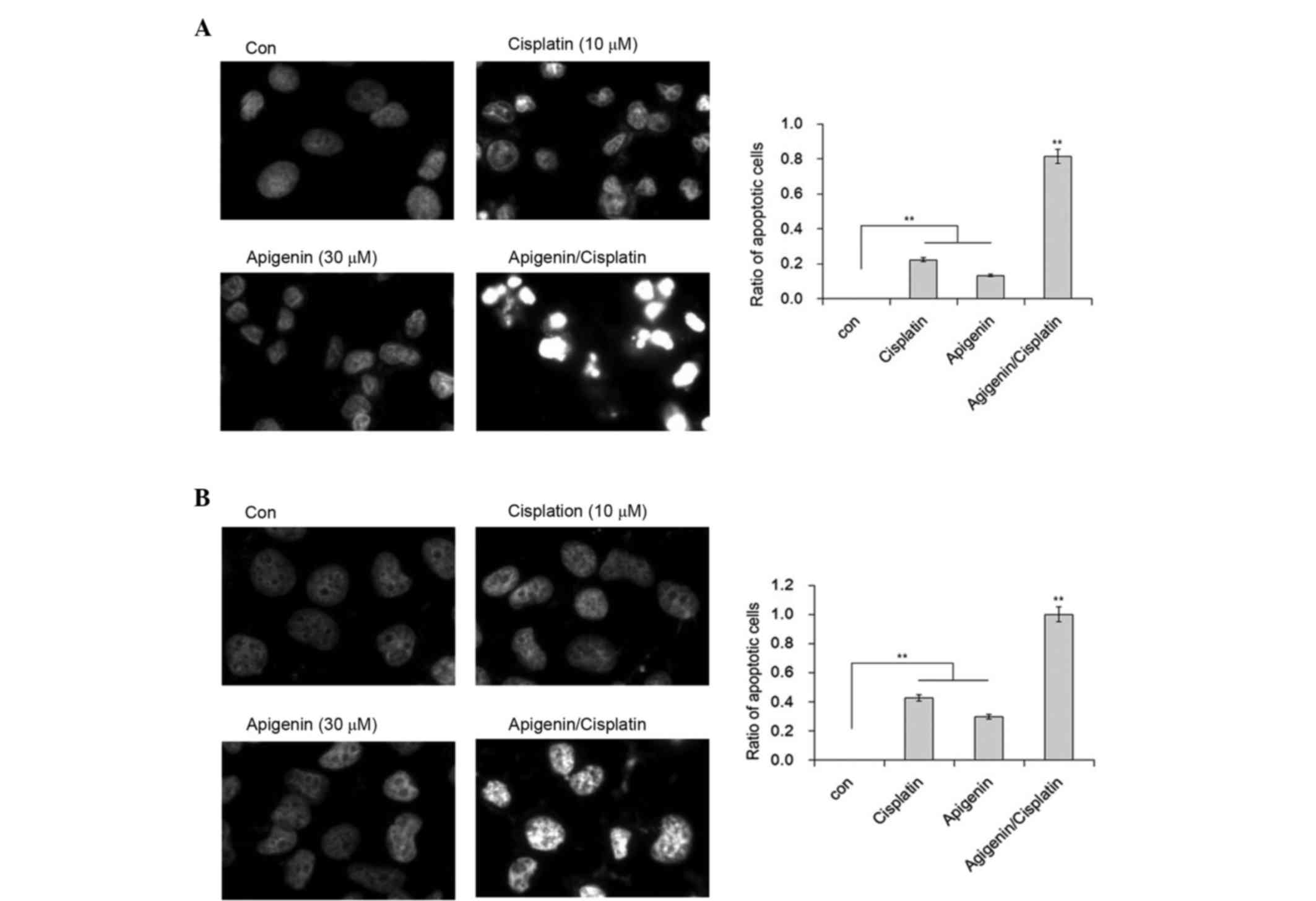
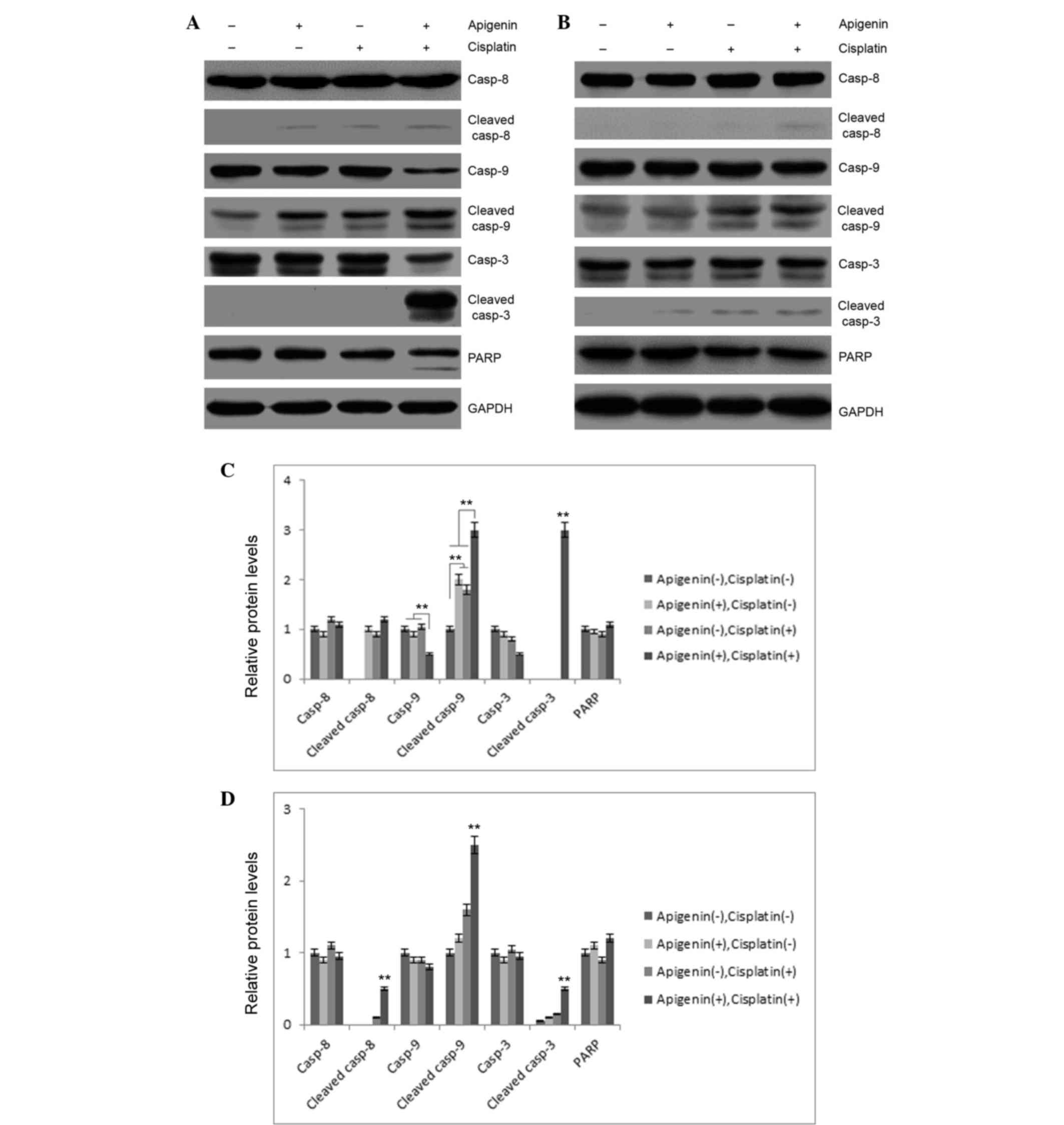
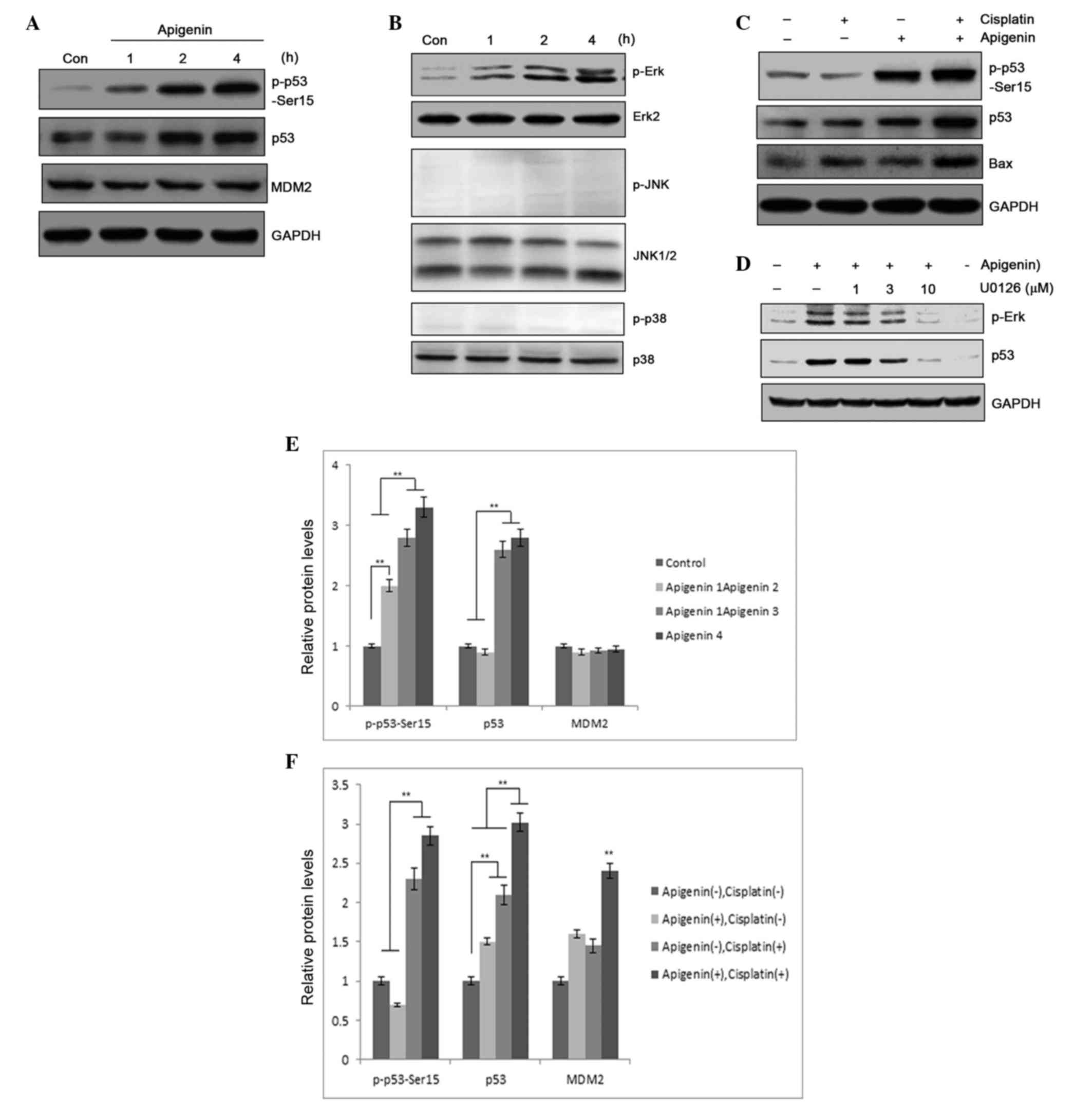
|
1
|
Afzal M, Safer AM and Menon M: Green tea
polyphenols and their potential role in health and disease.
Inflammopharmacology. 23:151–161. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Altemimi A, Watson DG, Kinsel M and
Lightfoot DA: Simultaneous extraction, optimization, and analysis
of flavonoids and polyphenols from peach and pumpkin extracts using
a TLC-densitometric method. Chem Cent J. 9:392015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Shukla S and Gupta S: Apigenin: A
promising molecule for cancer prevention. Pharm Res. 27:962–978.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kris-Etherton PM, Hecker KD, Bonanome A,
Coval SM, Binkoski AE, Hilpert KF, Griel AE and Etherton TD:
Bioactive compounds in foods: Their role in the prevention of
cardiovascular disease and cancer. Am J Med. 113:(Suppl 9B).
71S–88S. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yang S, Zhang H, Yang X, Zhu Y and Zhang
M: Evaluation of antioxidative and antitumor activities of
extracted flavonoids from Pink Lady apples in human colon and
breast cancer cell lines. Food Funct. 6:3789–3798. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Trudel D, Labbé DP, Bairati I, Fradet V,
Bazinet L and Têtu B: Green tea for ovarian cancer prevention and
treatment: A systematic review of the in vitro, in vivo and
epidemiological studies. Gynecol Oncol. 126:491–498. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Gupta SC, Kannappan R, Reuter S, Kim JH
and Aggarwal BB: Chemosensitization of tumors by resveratrol. Ann N
Y Acad Sci. 1215:150–160. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Nessa MU, Beale P, Chan C, Yu JQ and Huq
F: Synergism from combinations of cisplatin and oxaliplatin with
quercetin and thymoquinone in human ovarian tumour models.
Anticancer Res. 31:3789–3797. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Patel D, Shukla S and Gupta S: Apigenin
and cancer chemoprevention: Progress, potential and promise
(review). Int J Oncol. 30:233–245. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Torkin R, Lavoie JF, Kaplan DR and Yeger
H: Induction of caspase-dependent, p53-mediated apoptosis by
apigenin in human neuroblastoma. Mol Cancer Ther. 4:1–11. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ruela-de-Sousa RR, Fuhler GM, Blom N,
Ferreira CV, Aoyama H and Peppelenbosch MP: Cytotoxicity of
apigenin on leukemia cell lines: Implications for prevention and
therapy. Cell Death Dis. 1:e192010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Horinaka M, Yoshida T, Shiraishi T, Nakata
S, Wakada M and Sakai T: The dietary flavonoid apigenin sensitizes
malignant tumor cells to tumor necrosis factor-related
apoptosis-inducing ligand. Mol Cancer Ther. 5:945–951. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Strouch MJ, Milam BM, Melstrom LG, McGill
JJ, Salabat MR, Ujiki MB, Ding XZ and Bentrem DJ: The flavonoid
apigenin potentiates the growth inhibitory effects of gemcitabine
and abrogates gemcitabine resistance in human pancreatic cancer
cells. Pancreas. 38:409–415. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Xu Y, Xin Y, Diao Y, Lu C, Fu J, Luo L and
Yin Z: Synergistic effects of apigenin and paclitaxel on apoptosis
of cancer cells. PLoS One. 6:e291692011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Angelini A, Di Ilio C, Castellani ML,
Conti P and Cuccurullo F: Modulation of multidrug resistance
p-glycoprotein activity by flavonoids and honokiol in human
doxorubicin- resistant sarcoma cells (MES-SA/DX-5): Implications
for natural sedatives as chemosensitizing agents in cancer therapy.
J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 24:197–205. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Choi EJ and Kim GH: 5-Fluorouracil
combined with apigenin enhances anticancer activity through
induction of apoptosis in human breast cancer MDA-MB-453 cells.
Oncol Rep. 22:1533–1537. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wong IL, Chan KF, Tsang KH, Lam CY, Zhao
Y, Chan TH and Chow LM: Modulation of multidrug resistance protein
1 (MRP1/ABCC1)-mediated multidrug resistance by bivalent apigenin
homodimers and their derivatives. J Med Chem. 52:5311–5322. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Cai X and Liu X: Inhibition of Thr-55
phosphorylation restores p53 nuclear localization and sensitizes
cancer cells to DNA damage. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
105:16958–16963. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chabner BA and Roberts TG Jr: Timeline
Chemotherapy and the war on cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 5:65–72. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Billecke C, Finniss S, Tahash L, Miller C,
Mikkelsen T, Farrell NP and Bögler O: Polynuclear platinum
anticancer drugs are more potent than cisplatin and induce cell
cycle arrest in glioma. Neuro Oncol. 8:215–226. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Mendes F, Groessl M, Nazarov AA, Tsybin
YO, Sava G, Santos I, Dyson PJ and Casini A: Metal-based inhibition
of poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase-the guardian angel of DNA. J Med
Chem. 54:2196–2206. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Galluzzi L, Senovilla L, Vitale I, Michels
J, Martins I, Kepp O, Castedo M and Kroemer G: Molecular mechanisms
of cisplatin resistance. Oncogene. 31:1869–1883. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Dhandapani KM, Mahesh VB and Brann DW:
Curcumin suppresses growth and chemoresistance of human
glioblastoma cells via AP-1 and NFκB transcription factors. J
Neurochem. 102:522–538. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Li Z, Musich PR and Zou Y: Differential
DNA damage responses in p53 proficient and deficient cells:
Cisplatin-induced nuclear import of XPA is independent of ATR
checkpoint in p53-deficient lung cancer cells. Int J Biochem Mol
Biol. 2:138–145. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Losert D, Pratscher B, Soutschek J, Geick
A, Vornlocher HP, Müller M and Wacheck V: Bcl-2 downregulation
sensitizes nonsmall cell lung cancer cells to cisplatin, but not to
docetaxel. Anticancer Drugs. 18:755–761. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
He F, Wang Q, Zheng XL, Yan JQ, Yang L,
Sun H, Hu LN, Lin Y and Wang X: Wogonin potentiates
cisplatin-induced cancer cell apoptosis through accumulation of
intracellular reactive oxygen species. Oncol Rep. 28:601–605.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chen X, Wang Z, Yang Z, Wang J, Xu Y, Tan
RX and Li E: Houttuynia cordata blocks HSV infection through
inhibition of NF-κB activation. Antiviral Res. 92:341–345. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yang Z, Lee J, Ahn HJ, Chong CK, Dias RF
and Nam HW: Western Blot Detection of Human Anti-Chikungunya Virus
Antibody with Recombinant Envelope 2 Protein. Korean J Parasitol.
54:239–241. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lin DL and Chang C: p53 is a mediator for
radiation-repressed human TR2 orphan receptor expression in MCF-7
cells, a new pathway from tumor suppressor to member of the steroid
receptor superfamily. J Biol Chem. 271:14649–14652. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Stindt MH, Muller PA, Ludwig RL,
Kehrloesser S, Dötsch V and Vousden KH: Functional interplay
between MDM2, p63/p73 and mutant p53. Oncogene. 34:4300–4310. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Heyne K, Förster J, Schüle R and Roemer K:
Transcriptional repressor NIR interacts with the p53-inhibiting
ubiquitin ligase MDM2. Nucleic Acids Res. 42:3565–3579. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ahn HJ, Kim KS, Shin KW, Lim KH, Kim JO,
Lee JY, Kim J, Park JH, Yang KM, Baek KH, et al: Ell3 stabilizes
p53 following CDDP treatment via its effects on ubiquitin-dependent
and -independent proteasomal degradation pathways in breast cancer
cells. Oncotarget. 6:44523–44537. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhao Z, Wu L, Shi H and Wu C: p53
N-terminal binding and stabilisation by PIAS3 inhibits MDM2-induced
p53 ubiquitination and regulates cell growth. Mol Med Rep.
9:1903–1908. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wang L, Wang L, Zhang S, Qu G, Zhang D, Li
S and Liu S: Downregulation of ubiquitin E3 ligase TNF
receptor-associated factor 7 leads to stabilization of p53 in
breast cancer. Oncol Rep. 29:283–287. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kitamura T, Fukuyo Y, Inoue M, Horikoshi
NT, Shindoh M, Rogers BE, Usheva A and Horikoshi N: Mutant p53
disrupts the stress MAPK activation circuit induced by
ASK1-dependent stabilization of Daxx. Cancer Res. 69:7681–7688.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Cui C, Wang P, Cui N, Song S, Liang H and
Ji A: Sulfated polysaccharide isolated from the sea cucumber
Stichopus japonicas promotes the SDF-1α/CXCR4 axis-induced NSC
migration via the PI3K/Akt/FOXO3a, ERK/MAPK, and NF-κB signaling
pathways. Neurosci Lett. 616:57–64. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kim B, Jung N, Lee S, Sohng JK and Jung
HJ: Apigenin Inhibits Cancer Stem Cell-Like Phenotypes in Human
Glioblastoma Cells via Suppression of c-Met Signaling. Phytother
Res. 30:1833–1840. 2016. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Seo HS, Ku JM, Choi HS, Woo JK, Jang BH,
Go H, Shin YC and Ko SG: Apigenin induces caspase-dependent
apoptosis by inhibiting signal transducer and activator of
transcription 3 signaling in HER2-overexpressing SKBR3 breast
cancer cells. Mol Med Rep. 12:2977–2984. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Cho Y, Gorina S, Jeffrey PD and Pavletich
NP: Crystal structure of a p53 tumor suppressor-DNA complex:
Understanding tumorigenic mutations. Science. 265:346–355. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Vazquez A, Bond EE, Levine AJ and Bond GL:
The genetics of the p53 pathway, apoptosis and cancer therapy. Nat
Rev Drug Discov. 7:979–987. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Vucic D, Dixit VM and Wertz IE:
Ubiquitylation in apoptosis: A post-translational modification at
the edge of life and death. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 12:439–452.
2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Meek DW: Tumour suppression by p53: A role
for the DNA damage response? Nat Rev Cancer. 9:714–723.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Guo H, Kong S, Chen W, Dai Z, Lin T, Su J,
Li S, Xie Q, Su Z, Xu Y and Lai X: Apigenin mediated protection of
OGD-evoked neuron-like injury in differentiated PC12 cells.
Neurochem Res. 39:2197–2210. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Gazzani G, Daglia M and Papetti A: Food
components with anticaries activity. Curr Opin Biotechnol.
23:153–159. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Tang D, Chen K, Huang L and Li J:
Pharmacokinetic properties and drug interactions of apigenin, a
natural flavone. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2:1–8. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Chen L and Zhao W: Apigenin protects
against bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis in rats. Exp Ther Med.
11:230–234. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Gates MA, Vitonis AF, Tworoger SS, Rosner
B, TitusErnstoff L, Hankinson SE and Cramer DW: Flavonoid intake
and ovarian cancer risk in a population-based case-control study.
Int J Cancer. 124:1918–1925. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|