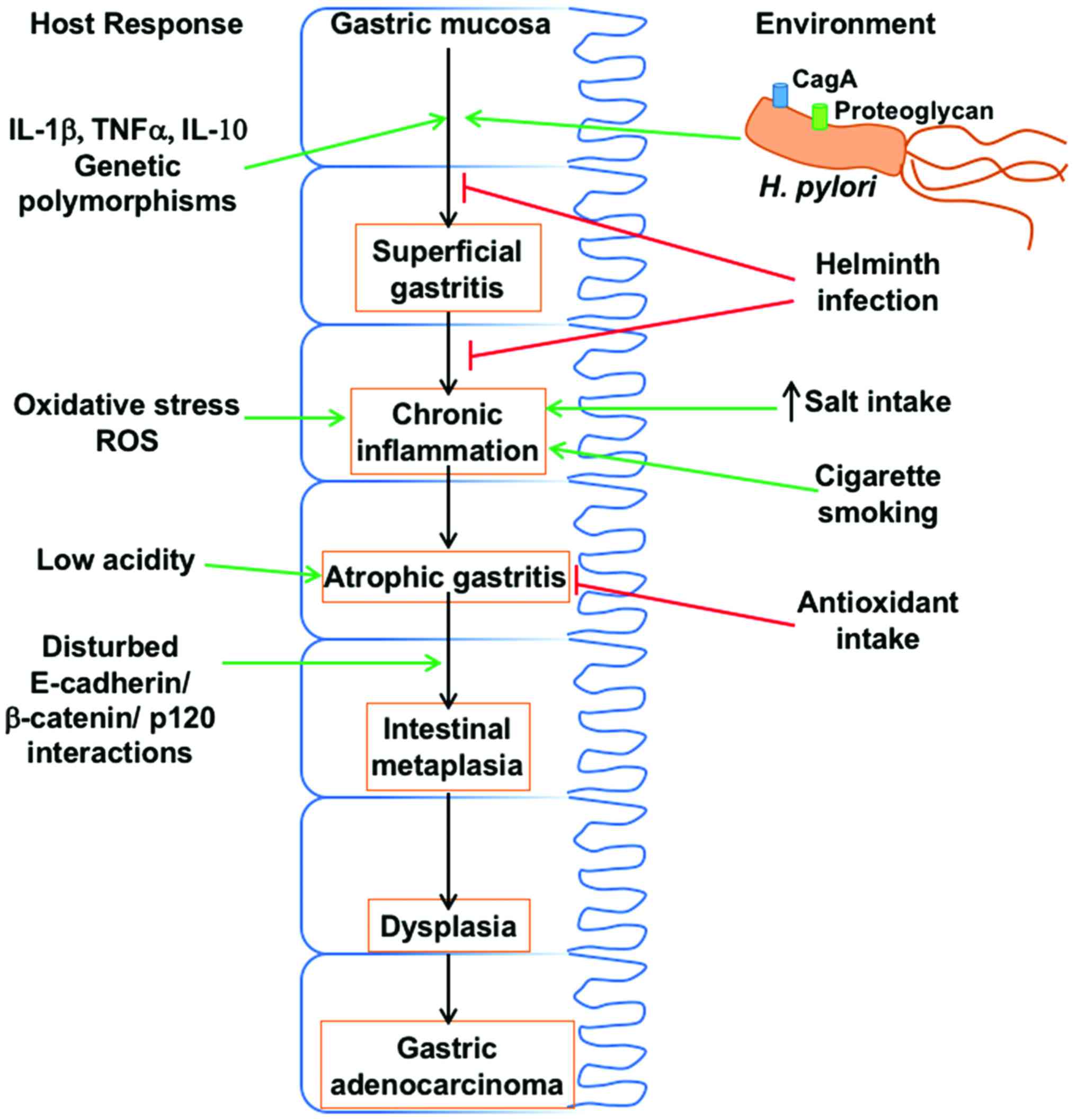
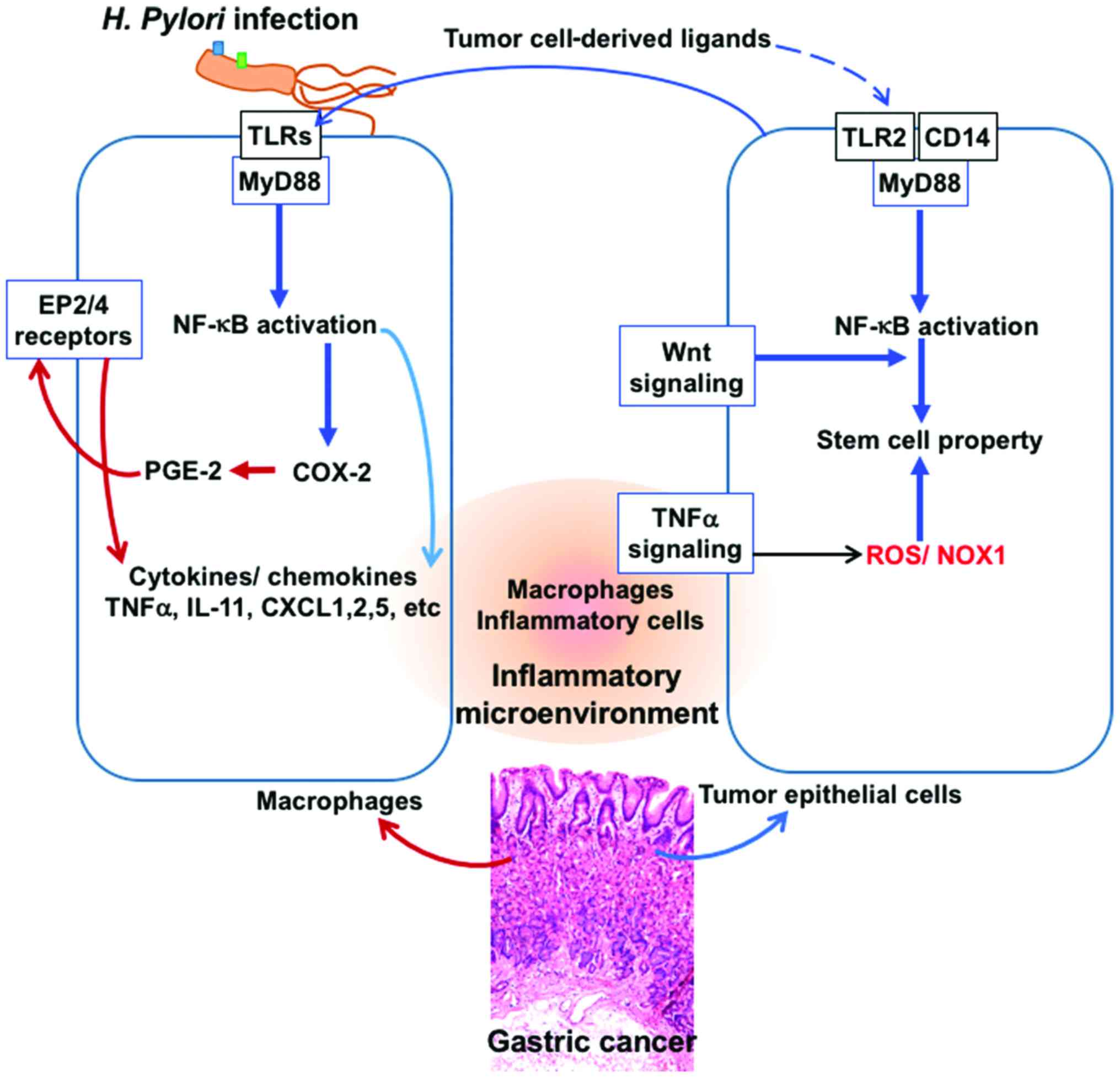
|
1
|
Ferro A, Peleteiro B, Malvezzi M, Bosetti
C, Bertuccio P, Levi F, Negri E, La Vecchia C and Lunet N:
Worldwide trends in gastric cancer mortality (1980–2011), with
predictions to 2015, and incidence by subtype. Eur J Cancer.
50:1330–1344. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Correa P: Human gastric carcinogenesis: a
multistep and multifactorial process - first American cancer
society award lecture on cancer epidemiology and prevention. Cancer
Res. 52:6735–6740. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Herrera V and Parsonnet J: Helicobacter
pylori and gastric adenocarcinoma. Clin Microbiol Infect.
15:971–976. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
He C, Tu H, Sun L, Xu Q, Li P, Gong Y,
Dong N and Yuan Y: Helicobacter pylori-related host gene
polymorphisms associated with susceptibility of gastric
carcinogenesis: a two-stage case-control study in Chinese.
Carcinogenesis. 34:1450–1457. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Souza RF and Spechler SJ: Concepts in the
prevention of adenocarcinoma of the distal esophagus and proximal
stomach. CA Cancer J Clin. 55:334–351. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Marshall BJ and Warren JR: Unidentified
curved bacilli in the stomach of patients with gastritis and peptic
ulceration. Lancet. 1:1311–1315. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J and Pisani P:
Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 55:74–108. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Weeks DL, Eskandari S, Scott DR and Sachs
G: A H+-gated urea channel: the link between
Helicobacter pylori urease and gastric colonization. Science.
287:482–485. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Peek RM Jr and Blaser MJ: Helicobacter
pylori and gastrointestinal tract adenocarcinomas. Nat Rev Cancer.
2:28–37. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Peek RM Jr and Crabtree JE: Helicobacter
infection and gastric neoplasia. J Pathol. 208:233–248. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sipponen P and Marshall BJ: Gastritis and
gastric cancer. Western countries. Gastroenterol Clin North Am.
29:579–592. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Correa P and Houghton J: Carcinogenesis of
Helicobacter pylori. Gastroenterology. 133:659–672. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Atherton JC: The pathogenesis of
Helicobacter pylori-induced gastro-duodenal diseases. Annu Rev
Pathol. 1:63–96. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Shimoyama T, Fukuda S, Tanaka M, Mikami T,
Munakata A and Crabtree JE: CagA seropositivity associated with
development of gastric cancer in a Japanese population. J Clin
Pathol. 51:225–228. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Torres J, Pérez-Pérez GI, Leal-Herrera Y
and Muñoz O: Infection with CagA+ Helicobacter pylori
strains as a possible predictor of risk in the development of
gastric adenocarcinoma in Mexico. Int J Cancer. 78:298–300. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Stein M, Bagnoli F, Halenbeck R, Rappuoli
R, Fantl WJ and Covacci A: c-Src/Lyn kinases activate Helicobacter
pylori CagA through tyrosine phosphorylation of the EPIYA motifs.
Mol Microbiol. 43:971–980. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Segal ED, Cha J, Lo J, Falkow S and
Tompkins LS: Altered states: involvement of phosphorylated CagA in
the induction of host cellular growth changes by Helicobacter
pylori. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 96:14559–14564. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Basso D, Zambon CF, Letley DP, Stranges A,
Marchet A, Rhead JL, Schiavon S, Guariso G, Ceroti M, Nitti D, et
al: Clinical relevance of Helicobacter pylori cagA and vacA gene
polymorphisms. Gastroenterology. 135:91–99. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Higashi H, Tsutsumi R, Muto S, Sugiyama T,
Azuma T, Asaka M and Hatakeyama M: SHP-2 tyrosine phosphatase as an
intracellular target of Helicobacter pylori CagA protein. Science.
295:683–686. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wroblewski LE, Peek RM Jr and Wilson KT:
Helicobacter pylori and gastric cancer: factors that modulate
disease risk. Clin Microbiol Rev. 23:713–739. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bagnoli F, Buti L, Tompkins L, Covacci A
and Amieva MR: Helicobacter pylori CagA induces a transition from
polarized to invasive phenotypes in MDCK cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 102:16339–16344. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Murata-Kamiya N, Kurashima Y, Teishikata
Y, Yamahashi Y, Saito Y, Higashi H, Aburatani H, Akiyama T, Peek RM
Jr, Azuma T, et al: Helicobacter pylori CagA interacts with
E-cadherin and deregulates the beta-catenin signal that promotes
intestinal transdifferentiation in gastric epithelial cells.
Oncogene. 26:4617–4626. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ohnishi N, Yuasa H, Tanaka S, Sawa H,
Miura M, Matsui A, Higashi H, Musashi M, Iwabuchi K, Suzuki M, et
al: Transgenic expression of Helicobacter pylori CagA induces
gastrointestinal and hematopoietic neoplasms in mouse. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 105:1003–1008. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Viala J, Chaput C, Boneca IG, Cardona A,
Girardin SE, Moran AP, Athman R, Mémet S, Huerre MR, Coyle AJ, et
al: Nod1 responds to peptidoglycan delivered by the Helicobacter
pylori cag pathogenicity island. Nat Immunol. 5:1166–1174. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Nagy TA, Frey MR, Yan F, Israel DA, Polk
DB and Peek RM Jr: Helicobacter pylori regulates cellular migration
and apoptosis by activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase
signaling. J Infect Dis. 199:641–651. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Miehlke S, Kirsch C, AghaAmiri K, Günther
T, Lehn N, Malfertheiner P, Stolte M, Ehninger G and Bayerdörffer
E: The Helicobacter pylori vacA s1, m1 genotype and cagA is
associated with gastric carcinoma in Germany. Int J Cancer.
87:322–327. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Dossumbekova A, Prinz C, Gerhard M,
Brenner L, Backert S, Kusters JG, Schmid RM and Rad R: Helicobacter
pylori outer membrane proteins and gastric inflammation. Gut.
55:1360–1361. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Echizen K, Hirose O, Maeda Y and Oshima M:
Inflammation in gastric cancer: interplay of the
COX-2/prostaglandin E2 and Toll-like receptor/MyD88 pathways.
Cancer Sci. 107:391–397. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Grivennikov SI, Greten FR and Karin M:
Immunity, inflammation, and cancer. Cell. 140:883–899. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Pradere JP, Dapito DH and Schwabe RF: The
yin and yang of toll-like receptors in cancer. Oncogene.
33:3485–3495. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Maeda Y, Echizen K, Oshima H, Yu L,
Sakulsak N, Hirose O, Yamada Y, Taniguchi T, Jenkins BJ, Saya H, et
al: Myeloid differentiation factor 88 signaling in bone
marrow-derived cells promotes gastric tumorigenesis by generation
of inflammatory microenvironment. Cancer Prev Res (Phila).
9:253–263. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Saukkonen K, Rintahaka J, Sivula A,
Buskens CJ, Van Rees BP, Rio MC, Haglund C, Van Lanschot JJ,
Offerhaus GJ and Ristimaki A: Cyclooxygenase-2 and gastric
carcinogenesis. APMIS. 111:915–925. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Sung JJ, Leung WK, Go MY, To KF, Cheng AS,
Ng EK and Chan FK: Cyclooxygenase-2 expression in Helicobacter
pylori-associated premalignant and malignant gastric lesions. Am J
Pathol. 157:729–735. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Oshima H, Matsunaga A, Fujimura T,
Tsukamoto T, Taketo MM and Oshima M: Carcinogenesis in mouse
stomach by simultaneous activation of the Wnt signaling and
prostaglandin E2 pathway. Gastroenterology. 131:1086–1095. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wang D, Fu L, Sun H, Guo L and DuBois RN:
Prostaglandin E2 promotes colorectal cancer stem cell expansion and
metastasis in mice. Gastroenterology. 149:1884–1895. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Jayaraman P, SadaOvalle I, Nishimura T,
Anderson AC, Kuchroo VK, Remold HG and Behar SM: IL-1β promotes
antimicrobial immunity in macrophages by regulating TNFR signaling
and caspase-3 activation. J Immunol. 190:4196–4204. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kumar S, Kumar A and Dixit VK: Evidences
showing association of interleukin-1B polymorphisms with increased
risk of gastric cancer in an Indian population. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 387:456–460. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Garza-González E, BosquesPadilla FJ,
ElOmar E, Hold G, TijerinaMenchaca R, MaldonadoGarza HJ and
Pérez-Pérez GI: Role of the polymorphic IL-1B, IL-1RN and TNF-A
genes in distal gastric cancer in Mexico. Int J Cancer.
114:237–241. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Peleteiro B, Lunet N, Carrilho C, Durães
C, Machado JC, La Vecchia C and Barros H: Association between
cytokine gene polymorphisms and gastric precancerous lesions:
systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers
Prev. 19:762–776. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Marcos-Pinto R, DinisRibeiro M, Carneiro
F, Wen X, Lopes C, Figueiredo C, Machado JC, Ferreira RM, Reis CA,
Canedo P, et al: First-degree relatives of early-onset gastric
cancer patients show a high risk for gastric cancer: phenotype and
genotype profile. Virchows Arch. 463:391–399. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Kamangar F, Cheng C, Abnet CC and Rabkin
CS: Interleukin-1B polymorphisms and gastric cancer risk - a
meta-analysis. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 15:1920–1928.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Waghray M, Zavros Y, SaquiSalces M,
ElZaatari M, Alamelumangapuram CB, Todisco A, Eaton KA and Merchant
JL: Interleukin-1beta promotes gastric atrophy through suppression
of Sonic Hedgehog. Gastroenterology. 138:562–572. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Wang M, Furuta T, Takashima M, Futami H,
Shirai N, Hanai H and Kaneko E: Relation between interleukin-1beta
messenger RNA in gastric fundic mucosa and gastric juice pH in
patients infected with Helicobacter pylori. J Gastroenterol.
34:(Suppl 11). 10–17. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Zeng ZR, Hu PJ, Hu S, Pang RP, Chen MH, Ng
M and Sung JJ: Association of interleukin 1B gene polymorphism and
gastric cancers in high and low prevalence regions in China. Gut.
52:1684–1689. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Shigematsu Y, Niwa T, Rehnberg E, Toyoda
T, Yoshida S, Mori A, Wakabayashi M, Iwakura Y, Ichinose M, Kim YJ,
et al: Interleukin-1β induced by Helicobacter pylori infection
enhances mouse gastric carcinogenesis. Cancer Lett. 340:141–147.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Furuta T, ElOmar EM, Xiao F, Shirai N,
Takashima M and Sugimura H: Interleukin 1beta polymorphisms
increase risk of hypochlorhydria and atrophic gastritis and reduce
risk of duodenal ulcer recurrence in Japan. Gastroenterology.
123:92–105. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Farinati F, Cardin R, Degan P, Rugge M,
Mario FD, Bonvicini P and Naccarato R: Oxidative DNA damage
accumulation in gastric carcinogenesis. Gut. 42:351–356. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Obst B, Wagner S, Sewing KF and Beil W:
Helicobacter pylori causes DNA damage in gastric epithelial cells.
Carcinogenesis. 21:1111–1115. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Ding SZ, Minohara Y, Fan XJ, Wang J, Reyes
VE, Patel J, DirdenKramer B, Boldogh I, Ernst PB and Crowe SE:
Helicobacter pylori infection induces oxidative stress and
programmed cell death in human gastric epithelial cells. Infect
Immun. 75:4030–4039. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Cheng Y, Chaturvedi R, Asim M, Bussière
FI, Scholz A, Xu H, Casero RA Jr and Wilson KT: Helicobacter
pylori-induced macrophage apoptosis requires activation of
ornithine decarboxylase by c-Myc. J Biol Chem. 280:22492–22496.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Xu H, Chaturvedi R, Cheng Y, Bussiere FI,
Asim M, Yao MD, Potosky D, Meltzer SJ, Rhee JG, Kim SS, et al:
Spermine oxidation induced by Helicobacter pylori results in
apoptosis and DNA damage: implications for gastric carcinogenesis.
Cancer Res. 64:8521–8525. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Chaturvedi R, Cheng Y, Asim M, Bussière
FI, Xu H, Gobert AP, Hacker A, Casero RA Jr and Wilson KT:
Induction of polyamine oxidase 1 by Helicobacter pylori causes
macrophage apoptosis by hydrogen peroxide release and mitochondrial
membrane depolarization. J Biol Chem. 279:40161–40173. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Jo TY, Jeon TY, Chae KH, Kim DH, Sim MS,
Park DY and Suh KS: RImmunohistochemical evaluation of
E-cadherin/catenin (alpha-, beta-, gamma-catenin and p120CTN)
complex expression in early gastric cancer. Cancer Res Treat.
35:16–24. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Perri F, Cotugno R, Piepoli A, Merla A,
Quitadamo M, Gentile A, Pilotto A, Annese V and Andriulli A:
Aberrant DNA methylation in non-neoplastic gastric mucosa of H.
pylori infected patients and effect of eradication. Am J
Gastroenterol. 102:1361–1371. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Oliveira MJ, Costa AM, Costa AC, Ferreira
RM, Sampaio P, Machado JC, Seruca R, Mareel M and Figueiredo C:
CagA associates with c-Met, E-cadherin, and p120-catenin in a
multiproteic complex that suppresses Helicobacter pylori-induced
cell-invasive phenotype. J Infect Dis. 200:745–755. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Jawhari AU, Noda M, Pignatelli M and
Farthing M: Up-regulated cytoplasmic expression, with reduced
membranous distribution, of the src substrate p120(ctn) in gastric
carcinoma. J Pathol. 189:180–185. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Noren NK, Liu BP, Burridge K and Kreft B:
p120 catenin regulates the actin cytoskeleton via Rho family
GTPases. J Cell Biol. 150:567–580. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Ogden SR, Wroblewski LE, Weydig C,
RomeroGallo J, O'Brien DP, Israel DA, Krishna US, Fingleton B,
Reynolds AB, Wessler S, et al: p120 and Kaiso regulate Helicobacter
pylori-induced expression of matrix metalloproteinase-7. Mol Biol
Cell. 19:4110–4121. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Tsugane S: Salt, salted food intake, and
risk of gastric cancer: epidemiologic evidence. Cancer Sci. 96:1–6.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Beevers DG, Lip GY and Blann AD: Salt
intake and Helicobacter pylori infection. J Hypertens.
22:1475–1477. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Shikata K, Kiyohara Y, Kubo M, Yonemoto K,
Ninomiya T, Shirota T, Tanizaki Y, Doi Y, Tanaka K, Oishi Y, et al:
A prospective study of dietary salt intake and gastric cancer
incidence in a defined Japanese population: the Hisayama study. Int
J Cancer. 119:196–201. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Gamboa-Dominguez A, Ubbelohde T,
SaquiSalces M, RomanoMazzoti L, Cervantes M, Domínguez-Fonseca C,
de la Luz Estreber M and Ruíz-Palacios GM: Salt and stress
synergize H. pylori-induced gastric lesions, cell proliferation,
and p21 expression in Mongolian gerbils. Dig Dis Sci. 52:1517–1526.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Sun J, Aoki K, Zheng JX, Su BZ, Ouyang XH
and Misumi J: Effect of NaCl and Helicobacter pylori vacuolating
cytotoxin on cytokine expression and viability. World J
Gastroenterol. 12:2174–2180. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Gancz H, Jones KR and Merrell DS: Sodium
chloride affects Helicobacter pylori growth and gene expression. J
Bacteriol. 190:4100–4105. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|