|
1
|
Alam M and Ratner D: Cutaneous
squamous-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 344:975–983. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ratushny V, Gober MD, Hick R, Ridky TW and
Seykora JT: From keratinocyte to cancer: The pathogenesis and
modeling of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. J Clin Invest.
122:464–472. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bushati N and Cohen SM: MicroRNA
functions. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 23:175–205. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zhang Y, Yang Q and Wang S: MicroRNAs: A
new key in lung cancer. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 74:1105–1111.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Xue J, Niu J, Wu J and Wu ZH: MicroRNAs in
cancer therapeutic response: Friend and foe. World J Clin Oncol.
5:730–743. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kent OA and Mendell JT: A small piece in
the cancer puzzle: MicroRNAs as tumor suppressors and oncogenes.
Oncogene. 25:6188–6196. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Acunzo M, Romano G, Wernicke D and Croce
CM: MicroRNA and cancer-a brief overview. Adv Biol Regul. 57:1–9.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lee JW, Choi CH, Choi JJ, Park YA, Kim SJ,
Hwang SY, Kim WY, Kim TJ, Lee JH, Kim BG and Bae DS: Altered
MicroRNA expression in cervical carcinomas. Clin Cancer Res.
14:2535–2542. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bruegger C, Kempf W, Spoerri I, Arnold AW,
Itin PH and Burger B: MicroRNA expression differs in cutaneous
squamous cell carcinomas and healthy skin of immunocompetent
individuals. Exp Dermatol. 22:426–428. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sand M, Skrygan M, Georgas D, Sand D, Hahn
SA, Gambichler T, Altmeyer P and Bechara FG: Microarray analysis of
microRNA expression in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. J
Dermatol Sci. 68:119–126. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhou M, Liu W, Ma S, Cao H, Peng X, Guo L,
Zhou X, Zheng L, Guo L, Wan M, et al: A novel onco-miR-365 induces
cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. Carcinogenesis. 34:1653–1659.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gastaldi C, Bertero T, Xu N,
Bourget-Ponzio I, Lebrigand K, Fourre S, Popa A, Cardot-Leccia N,
Meneguzzi G, Sonkoly E, et al: MiR-193b/365a cluster controls
progression of epidermal squamous cell carcinoma. Carcinogenesis.
35:1110–1120. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang SH, Zhou JD, He QY, Yin ZQ, Cao K and
Luo CQ: MiR-199a inhibits the ability of proliferation and
migration by regulating CD44-Ezrin signaling in cutaneous squamous
cell carcinoma cells. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 7:7131–7141.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Liu X, Sempere LF, Ouyang H, Memoli VA,
Andrew AS, Luo Y, Demidenko E, Korc M, Shi W, Preis M, et al:
MicroRNA-31 functions as an oncogenic microRNA in mouse and human
lung cancer cells by repressing specific tumor suppressors. J Clin
Invest. 120:1298–1309. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sun D, Yu F, Ma Y, Zhao R, Chen X, Zhu J,
Zhang CY, Chen J and Zhang J: MicroRNA-31 activates the RAS pathway
and functions as an oncogenic MicroRNA in human colorectal cancer
by repressing RAS p21 GTPase activating protein 1 (RASA1). J Biol
Chem. 288:9508–9518. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang S, Li Q, Wang K, Dai Y, Yang J, Xue
S, Han F, Zhang Q, Liu J and Wu W: Decreased expression of
microRNA-31 associates with aggressive tumor progression and poor
prognosis in patients with bladder cancer. Clin Transl Oncol.
15:849–854. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Xu XM, Qian JC, Deng ZL, Cai Z, Tang T,
Wang P, Zhang KH and Cai JP: Expression of miR-21, miR-31, miR-96
and miR-135b is correlated with the clinical parameters of
colorectal cancer. Oncol Lett. 4:339–345. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yang MH, Yu J, Chen N, Wang XY, Liu XY,
Wang S and Ding YQ: Elevated microRNA-31 expression regulates
colorectal cancer progression by repressing its target gene SATB2.
PLoS One. 8:e853532013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang T, Wang Q, Zhao D, Cui Y, Cao B, Guo
L and Lu SH: The oncogenetic role of microRNA-31 as a potential
biomarker in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Sci (Lond).
121:437–447. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Viré E, Curtis C, Davalos V, Git A, Robson
S, Villanueva A, Vidal A, Barbieri I, Aparicio S, Esteller M, et
al: The breast cancer oncogene EMSY represses transcription of
antimetastatic microRNA miR-31. Mol Cell. 53:806–818. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Körner C, Keklikoglou I, Bender C, Wörner
A, Münstermann E and Wiemann S: MicroRNA-31 sensitizes human breast
cells to apoptosis by direct targeting of protein kinase C epsilon
(PKCepsilon). J Biol Chem. 288:8750–8761. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ivanov SV, Goparaju CM, Lopez P, Zavadil
J, Toren-Haritan G, Rosenwald S, Hoshen M, Chajut A, Cohen D and
Pass HI: Pro-tumorigenic effects of miR-31 loss in mesothelioma. J
Biol Chem. 285:22809–22817. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Guo J, Miao Y, Xiao B, Huan R, Jiang Z,
Meng D and Wang Y: Differential expression of microRNA species in
human gastric cancer versus non-tumorous tissues. J Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 24:652–657. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Papaconstantinou IG, Manta A, Gazouli M,
Lyberopoulou A, Lykoudis PM, Polymeneas G and Voros D: Expression
of microRNAs in patients with pancreatic cancer and its prognostic
significance. Pancreas. 42:67–71. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang A, Landén NX, Meisgen F,
Lohcharoenkal W, Ståhle M, Sonkoly E and Pivarcsi A: MicroRNA-31 is
overexpressed in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma and regulates
cell motility and colony formation ability of tumor cells. PLoS
One. 9:e1032062014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Bhatnagar N, Li X, Padi SK, Zhang Q, Tang
MS and Guo B: Downregulation of miR-205 and miR-31 confers
resistance to chemotherapy-induced apoptosis in prostate cancer
cells. Cell Death Dis. 1:e1052010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chen T, Yao LQ, Shi Q, Ren Z, Ye LC, Xu
JM, Zhou PH and Zhong YS: MicroRNA-31 contributes to colorectal
cancer development by targeting factor inhibiting HIF-1α (FIH-1).
Cancer Biol Ther. 15:516–523. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hamaguchi M, Meth JL, von Klitzing C, Wei
W, Esposito D, Rodgers L, Walsh T, Welcsh P, King MC and Wigler MH:
DBC2, a candidate for a tumor suppressor gene involved in breast
cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 99:13647–13652. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Knowles MA, Aveyard JS, Taylor CF, Harnden
P and Bass S: Mutation analysis of the 8p candidate tumour
suppressor genes DBC2 (RHOBTB2) and LZTS1 in bladder cancer. Cancer
Lett. 225:121–130. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Cho YG, Choi BJ, Kim CJ, Song JH, Zhang C,
Nam SW, Lee JY and Park WS: Genetic analysis of the DBC2 gene in
gastric cancer. Acta Oncol. 47:366–371. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Beder LB, Gunduz M, Ouchida M, Gunduz E,
Sakai A, Fukushima K, Nagatsuka H, Ito S, Honjo N, Nishizaki K and
Shimizu K: Identification of a candidate tumor suppressor gene
RHOBTB1 located at a novel allelic loss region 10q21 in head and
neck cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 132:19–27. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
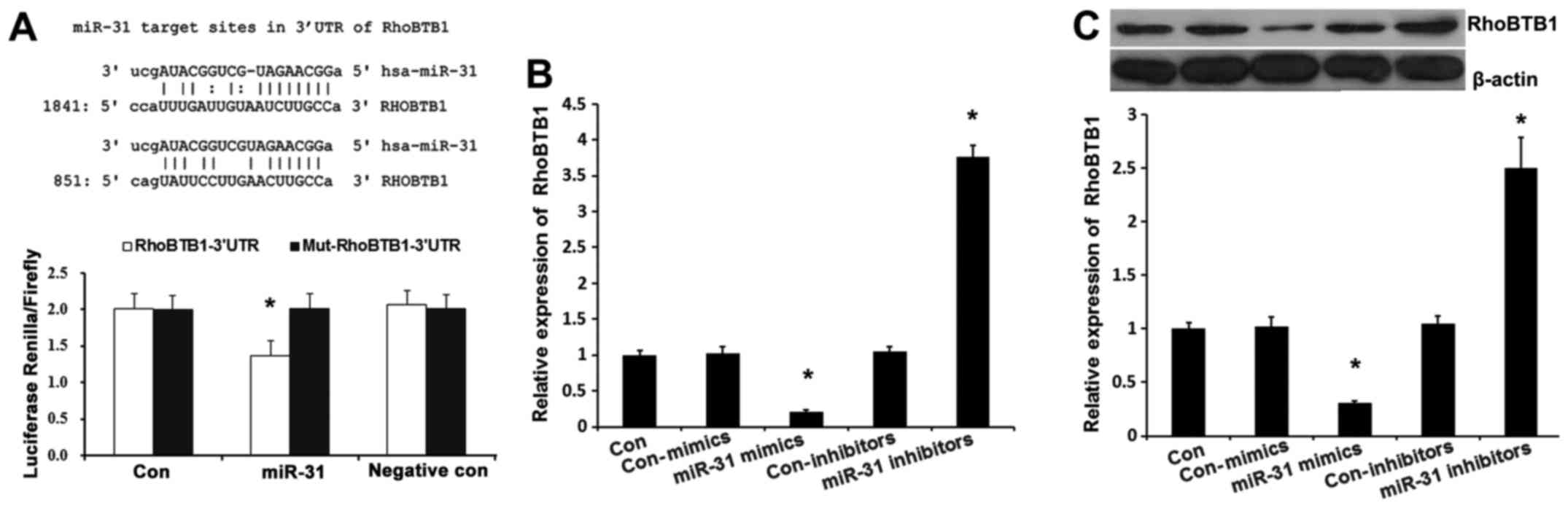
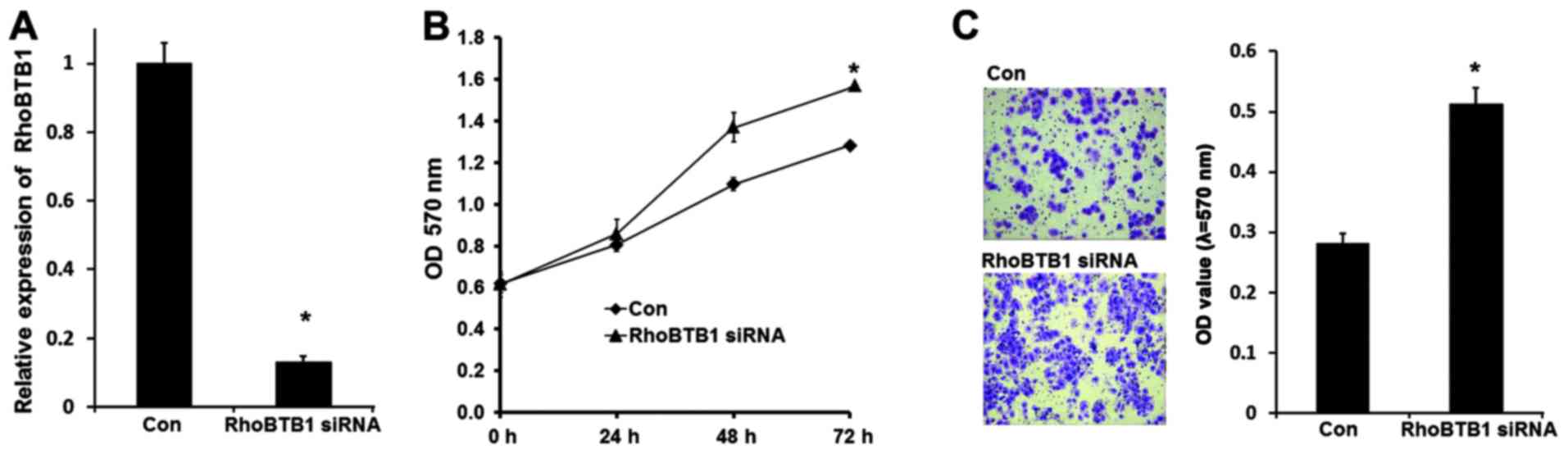
Xu RS, Wu XD, Zhang SQ, Li CF, Yang L, Li
DD, Zhang BG, Zhang Y, Jin JP and Zhang B: The tumor suppressor
gene RhoBTB1 is a novel target of miR-31 in human colon cancer. Int
J Oncol. 42:676–682. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|