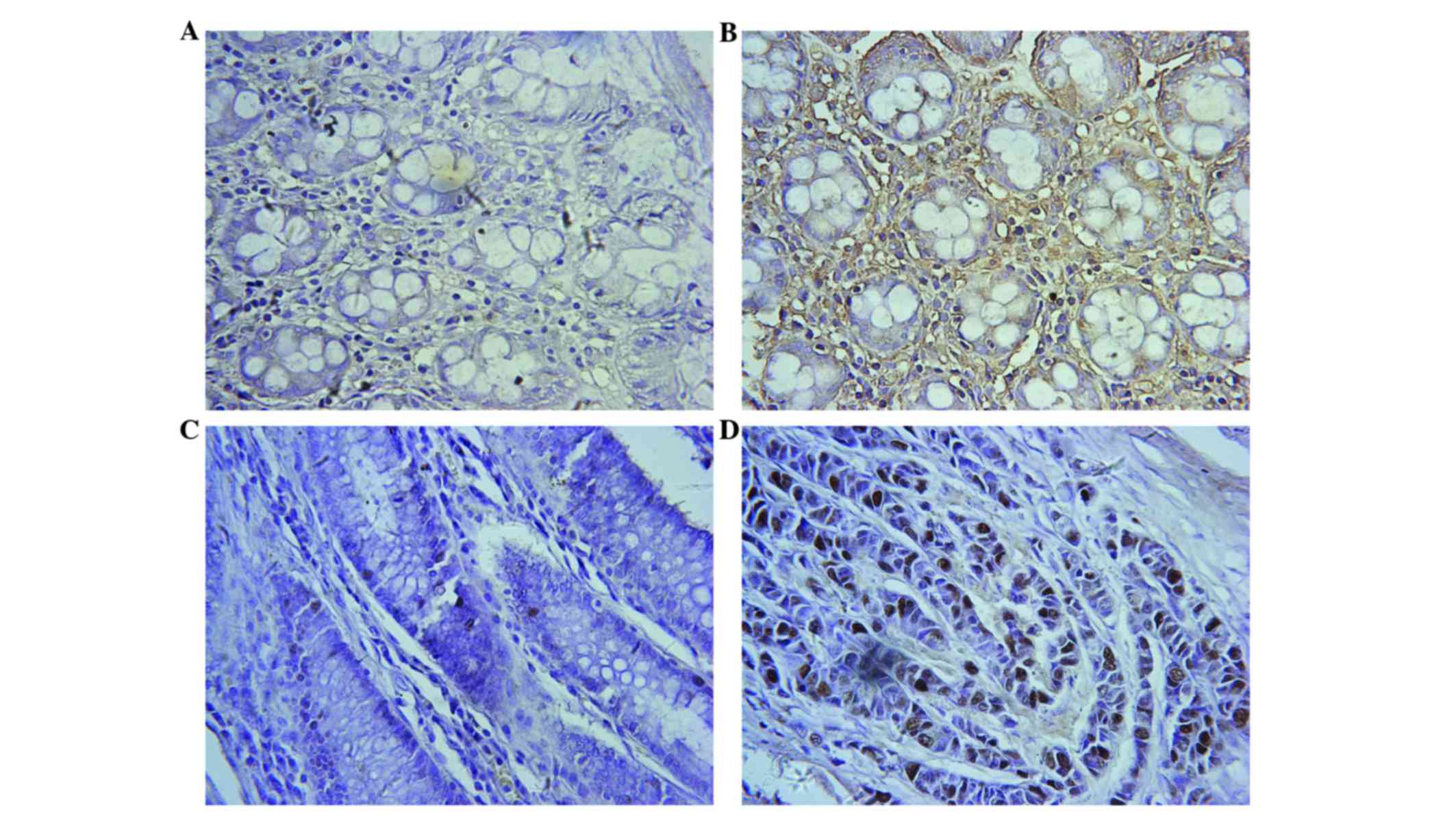
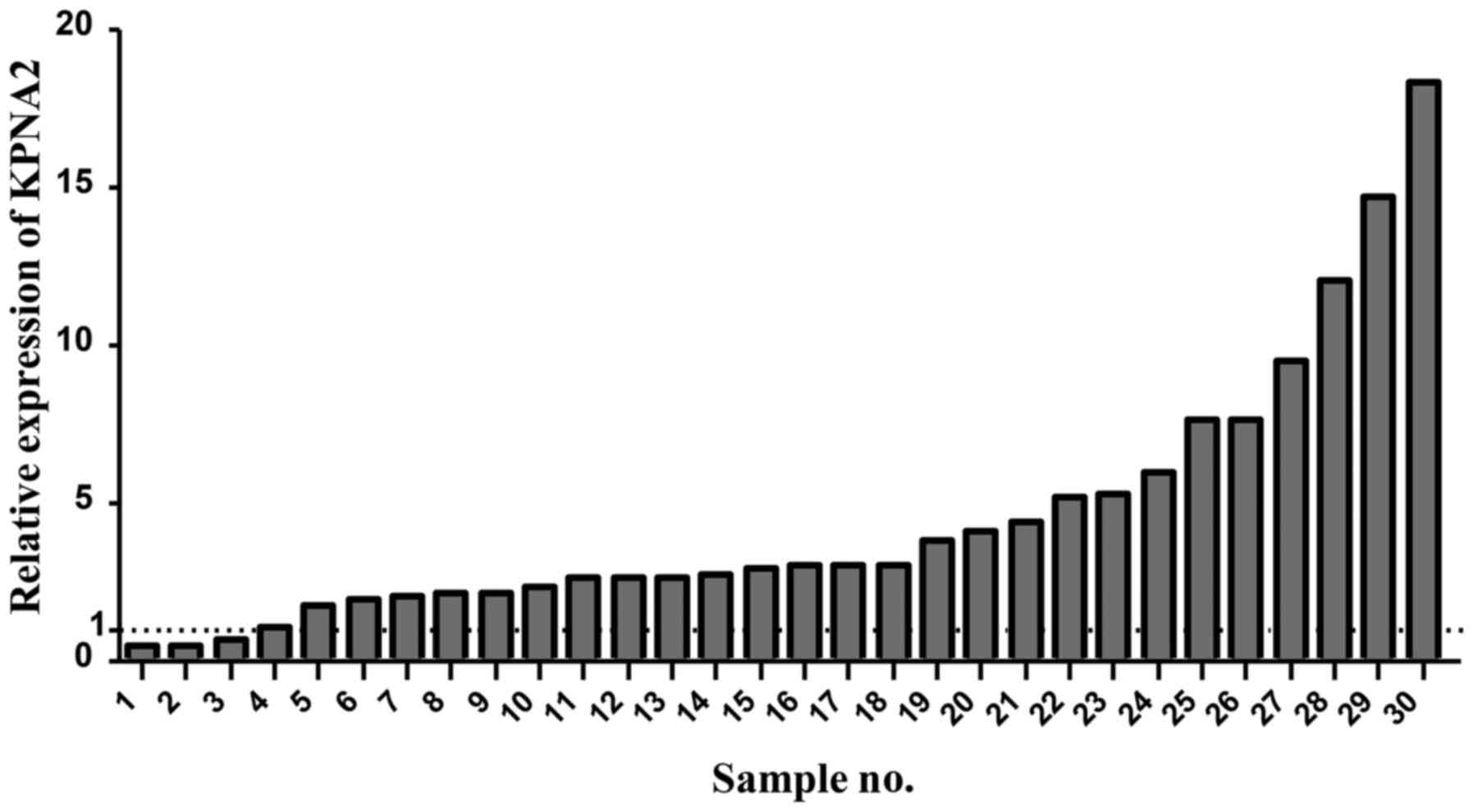
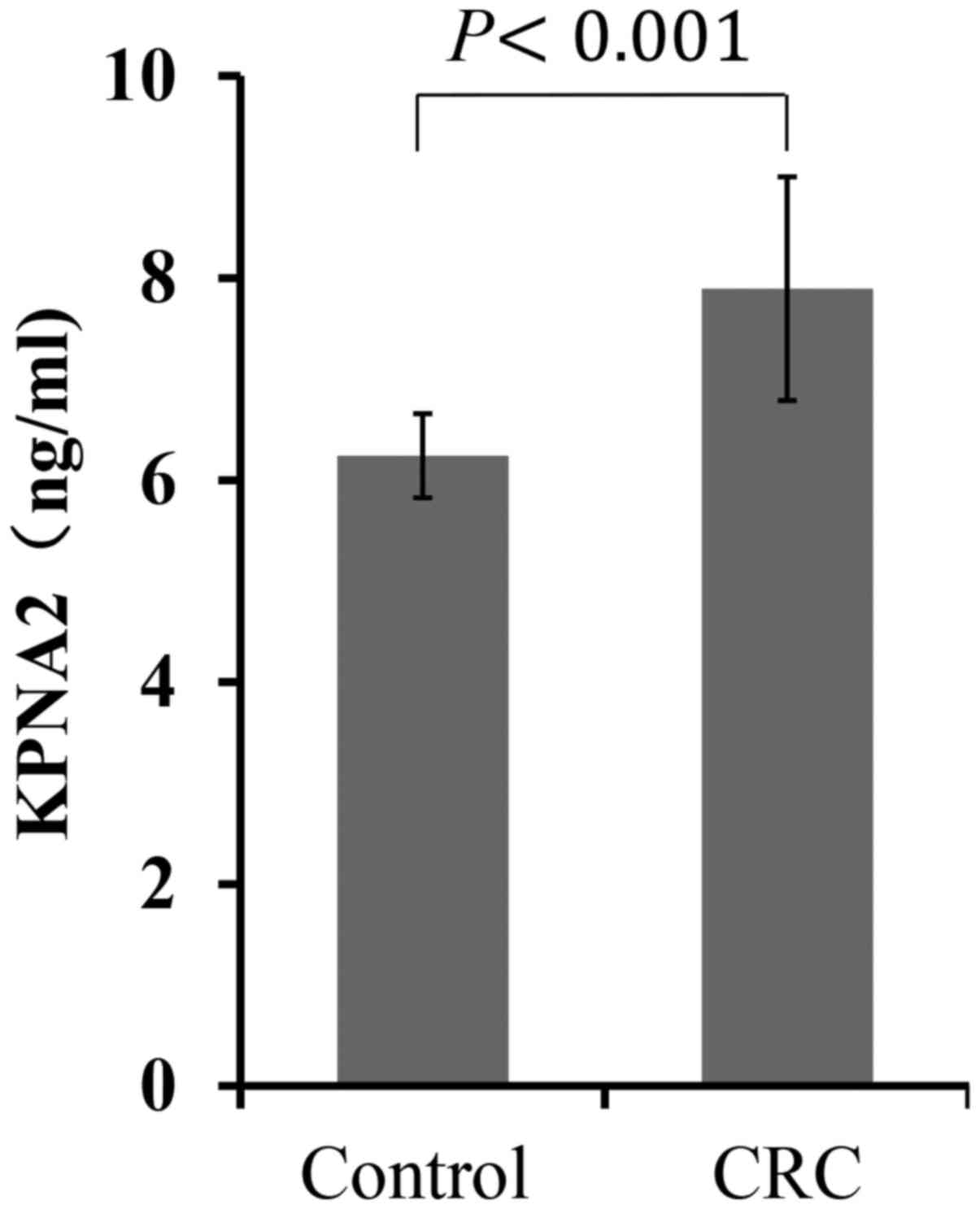
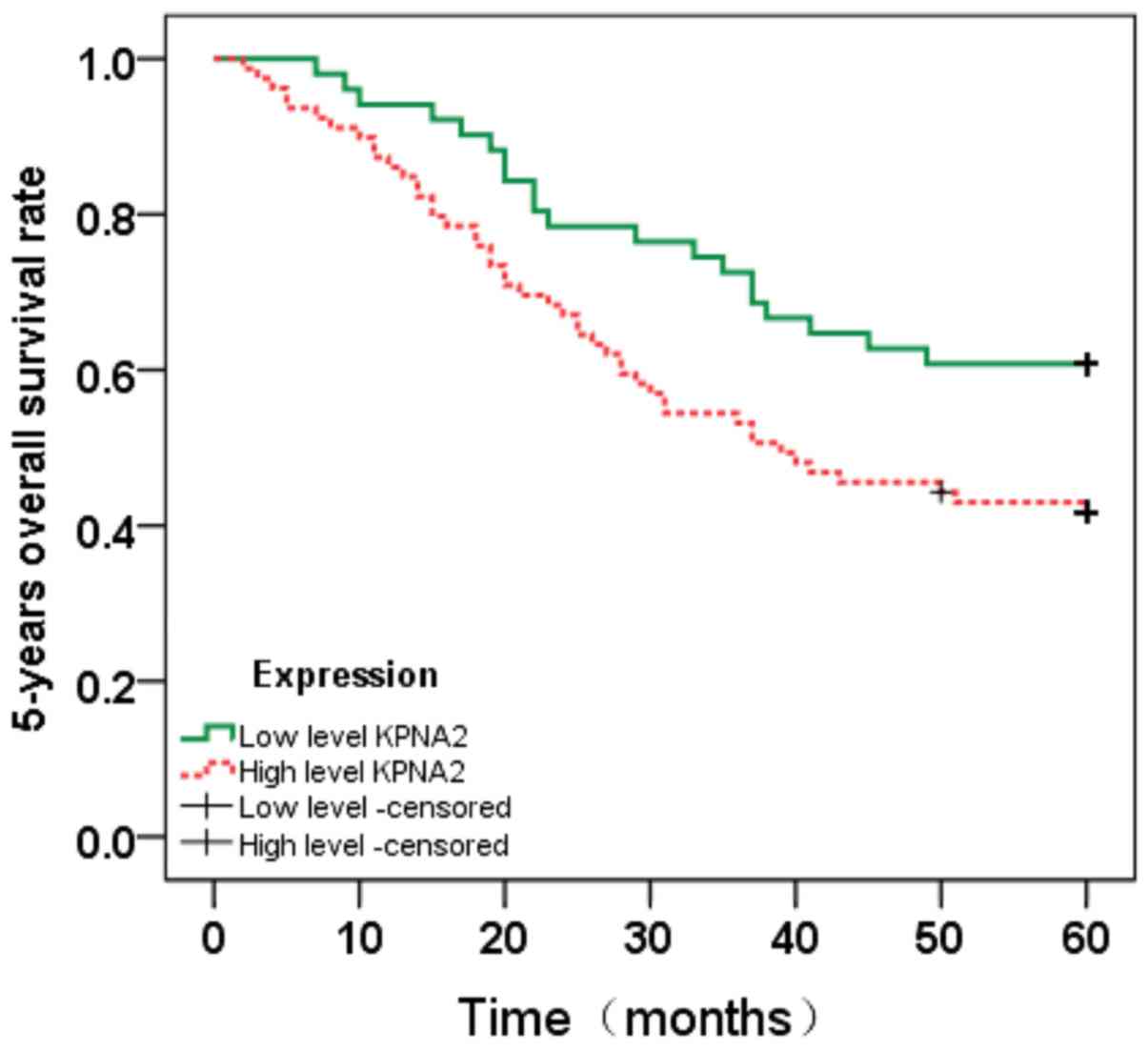
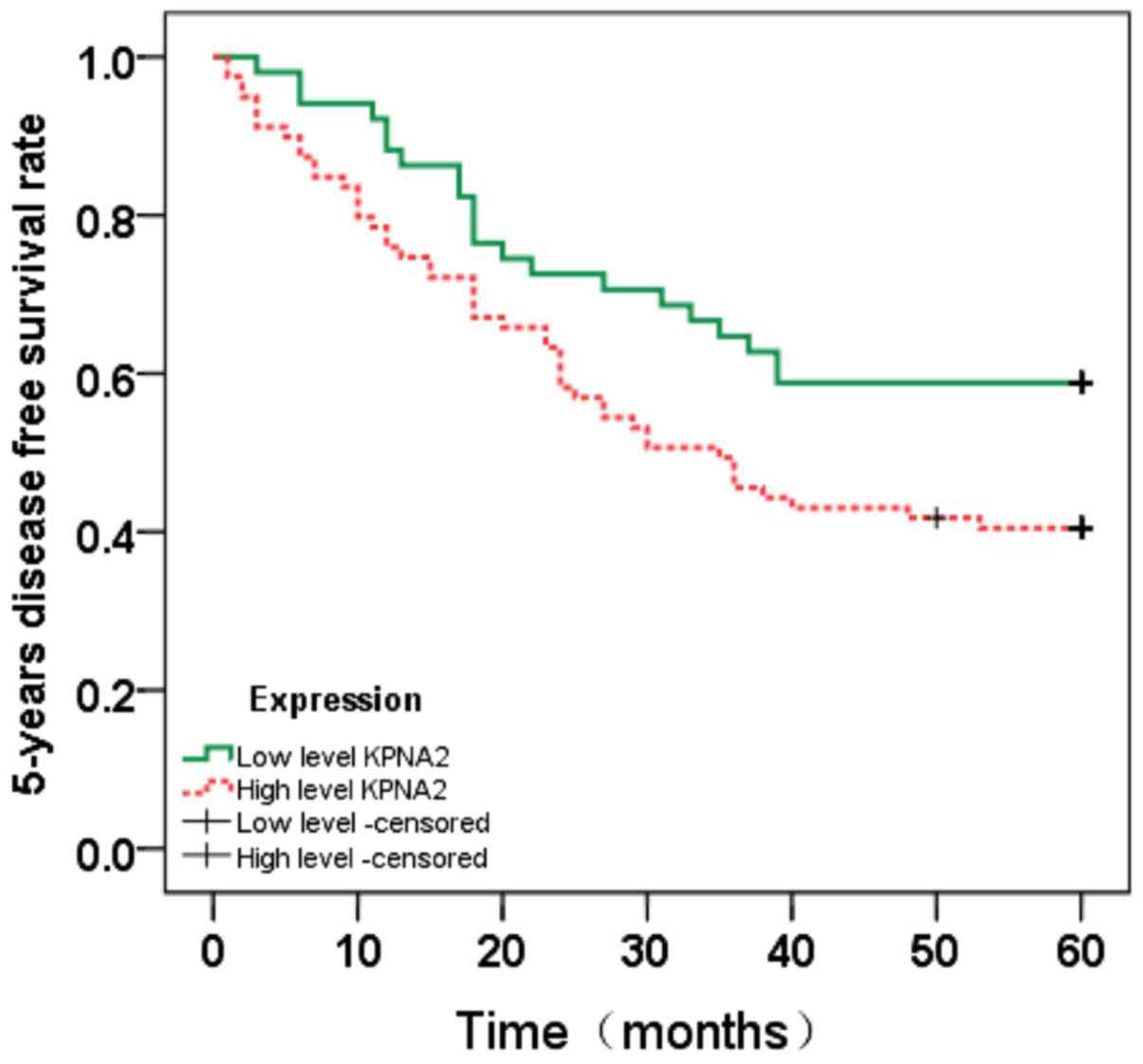
|
1
|
Brenner H, Kloor M and Pox CP: Colorectal
cancer. Lancet. 65:1490–1502. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Kau TR, Way JC and Silver PA: Nuclear
transport and cancer: From mechanism to intervention. Nat Rev
Cancer. 4:106–117. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Goldfarb DS, Corbett AH, Mason DA,
Harreman MT and Adam SA: Importin alpha: A multipurpose
nuclear-transport receptor. Trends Cell Biol. 14:505–514. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Christiansen A and Dyrskjøt L: The
functional role of the novel biomarker karyopherin α 2 (KPNA2) in
cancer. Cancer Lett. 331:18–23. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Radu A, Blobel G and Moore MS:
Identification of a protein complex that is required for nuclear
protein import and mediates docking of import substrate to distinct
nucleoporins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 92:1769–1773. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kotera I, Sekimoto T, Miyamoto Y, Saiwaki
T, Nagoshi E, Sakagami H, Kondo H and Yoneda Y: Importin alpha
transports CaMKIV to the nucleus without utilizing importin beta.
EMBO J. 24:942–951. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Stewart M: Molecular mechanism of the
nuclear protein import cycle. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 8:195–208.
2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Livak and Schmittgen, . Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2-ΔΔCt method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Dahl E, Kristiansen G, Gottlob K, Klaman
I, et al: Molecular profiling of laser-microdissected matched tumor
and normal breast tissue identifies karyopherin alpha2 as a
potential novel prognostic marker in breast cancer. Clin Cancer
Res. 12:3950–3960. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
van der Watt PJ, Maske CP, Hendricks DT,
Parker MI, Denny L, Govender D, Birrer MJ and Leaner VD: The
Karyopherin proteins, Crm1 and Karyopherin beta1, are overexpressed
in cervical cancer and are critical for cancer cell survival and
proliferation. Int J Cancer. 124:1829–1840. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sakai M, Sohda M, Miyazaki T, Suzuki S,
Sano A, Tanaka N, Inose T, Nakajima M, Kato H and Kuwano H:
Significance of karyopherin-{alpha} 2 (KPNA2) expression in
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 30:851–856.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Winnepenninckx V, Lazar V, Michiels S,
Dessen P, Stas M, Alonso SR, Avril MF, Romero PL Ortiz, Robert T,
Balacescu O, et al: Gene expression profiling of primary cutaneous
melanoma and clinical outcome. J Natl Cancer Inst. 98:472–482.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang CI, Wang CL, Wang CW, Chen CD, Wu CC,
Liang Y, Tsai YH, Chang YS, Yu JS and Yu CJ: Importin subunit
alpha-2 is identified as a potential biomarker for non-small cell
lung cancer by integration of the cancer cell secretome and tissue
transcriptome. Int J Cancer. 128:2364–2372. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Li C, Ji L, Ding ZY, Zhang QD and Huang
GR: Overexpression of KPNA2 correlates with poor prognosis in
patients with gastric adenocarcinoma. Tumour Biol. 34:1021–1026.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Mortezavi A, Hermanns T, Seifert HH, et
al: KPNA2 expression is an independent adverse predictor of
biochemical recurrence after radical prostatectomy. Clin Cancer
Res. 17:1111–1121. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gousias K, Becker AJ, Simon M and
Niehusmann P: Nuclear karyopherin a2: A novel biomarker for
infiltrative astrocytomas. J Neurooncol. 109:545–553. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yoshitake K, Tanaka S, Mogushi K, et al:
Importin-α1 as a novel prognostic target for hepatocellular
carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol. 18:2093–2103. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
He L, Ding H, Wang JH, et al:
Overexpression of karyopherin 2 in human ovarian malignant germ
cell tumor correlates with poor prognosis. PLoS One. 7:e429922012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Stochaj U, Rassadi R and Chiu J:
Stress-mediated inhibition of the classical nuclear protein import
pathway and nuclear accumulation of the small GTPase Gsp1p. FASEB
J. 14:2130–2132. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Furuta M, Kose S, Koike M, et al:
Heat-shock induced nuclear retention and recycling inhibition of
importin alpha. Genes Cells. 9:429–441. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kodiha M, Chu A, Matusiewicz N and Stochaj
U: Multiple mechanisms promote the inhibition of classical nuclear
import upon exposure to severe oxidative stress. Cell Death Differ.
11:862–874. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Miyamoto Y, Saiwaki T, Yamashita J, Yasuda
Y, Kotera I, Shibata S, Shigeta M, Hiraoka Y, Haraguchi T and
Yoneda Y: Cellular stresses induce the nuclear accumulation of
importin alpha and cause a conventional nuclear import block. J
Cell Biol. 165:617–623. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Trachootham D, Alexandre J and Huang P:
Targeting cancer cells by ROS-mediated mechanisms: A radical
therapeutic approach? Nat Rev Drug Discov. 8:579–591. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yasuda Y, Miyamoto Y, Yamashiro T, Asally
M, Masui A, Wong C, Loveland KL and Yoneda Y: Nuclear retention of
importin α coordinates cell fate through changes in gene
expression. EMBO J. 31:83–94. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Miyamoto Y, Loveland KL and Yoneda Y:
Nuclear importin α and its physiological importance. Commun Integr
Biol. 5:220–222. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Umegaki N, Tamai K, Nakano H, Moritsugu R,
Yamazaki T, Hanada K, Katayama I and Kaneda Y: Differential
regulation of karyopherin alpha 2 expression by TGF-beta1 and
IFN-gamma in normal human epidermal keratinocytes: Evident
contribution of KPNA2 for nuclear translocation of IRF-1. J Invest
Dermatol. 127:1456–1464. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Noetzel E, Rose M, Bornemann J, Gajewski
M, Knüchel R and Dahl E: Nuclear transport receptor karyopherin-α2
promotes malignant breast cancer phenotypes in vitro. Oncogene.
31:2101–2114. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hall MN, Griffin CA, Simionescu A, Corbett
AH and Pavlath GK: Distinct roles for classical nuclear import
receptors in the growth of multinucleated muscle cells. Dev Biol.
357:248–258. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Giuliani L, Ronci C, Bonifacio D, Di
Bonito L, Favalli C, Perno CF, Syrjänen K and Ciotti M: Detection
of oncogenic DNA viruses in colorectal cancer. Anticancer Res.
28:1405–1410. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Fischer N, Kremmer E, Lautscham G,
Mueller-Lantzsch N and Grässer FA: Epstein-Barr virus nuclear
antigen 1 forms a complex with the nuclear transporter karyopherin
alpha2. J Biol Chem. 272:3999–4005. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Nelson LM, Rose RC, LeRoux L, Lane C,
Bruya K and Moroianu J: Nuclear import and DNA binding of human
papillomavirus type 45 L1 capsid protein. J Cell Biochem.
79:225–238. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Le Roux LG and Moroianu J: Nuclear entry
of high-risk human papillomavirus type 16 E6 oncoprotein occurs via
several pathways. J Virol. 77:2330–2337. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Qu Q, Sawa H, Suzuki T, Semba S, Henmi C,
Okada Y, Tsuda M, Tanaka S, Atwood WJ and Nagashima K: Nuclear
entry mechanism of the human polyomavirus JC virus-like particle:
Role of importins and the nuclear pore complex. J Biol Chem.
279:27735–27742. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Gallay P, Stitt V, Mundy C, Oettinger M
and Trono D: Role of the karyopherin pathway in human
immunodeficiency virus type 1 nuclear import. J Virol.
70:1027–1032. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Bird G, O'Donnell M, Moroianu J and Garcea
RL: Possible role for cellular karyopherins in regulating
polyomavirus and papillomavirus capsid assembly. J Virol.
82:9848–9857. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Narod SA and Foulkes WD: BRCA1 and BRCA2:
1994 and beyond. Nat Rev Cancer. 4:665–676. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Teng SC, Wu KJ, Tseng SF, Wong CW and Kao
L: Importin KPNA2, NBS1, DNA repair and tumorigenesis. J Mol
Histol. 37:293–299. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Cutress ML, Whitaker HC, Mills IG, Stewart
M and Neal DE: Structural basis for the nuclear import of the human
androgen receptor. J Cell Sci. 121:957–968. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kamikawa Y, Yasuhara N and Yoneda Y: Cell
type-specific transcriptional regulation of the gene encoding
importin-alpha1. Exp Cell Res. 317:1970–1978. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Dankof A, Fritzsche FR, Dahl E, Pahl S,
Wild P, Dietel M, Hartmann A and Kristiansen G: KPNA2 protein
expression in invasive breast carcinoma and matched peritumoral
ductal carcinoma in situ. Virchows Arch. 451:877–881. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Gluz O, Wild P, Meiler R, Diallo-Danebrock
R, Ting E, Mohrmann S, Schuett G, Dahl E, Fuchs T, Herr A, et al:
Nuclear karyopherin alpha2 expression predicts poor survival in
patients with advanced breast cancer irrespective of treatment
intensity. Int J Cancer. 123:1433–1438. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Altan B, Yokobori T, Mochiki E, Ohno T,
Ogata K, Ogawa A, Yanai M, Kobayashi T, Luvsandagva B, Asao T and
Kuwano H: Nuclear karyopherin-α2 expression in primary lesions and
metastatic lymph nodes was associated with poor prognosis and
progression in gastric cancer. Carcinogenesis. 34:2314–2321. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|