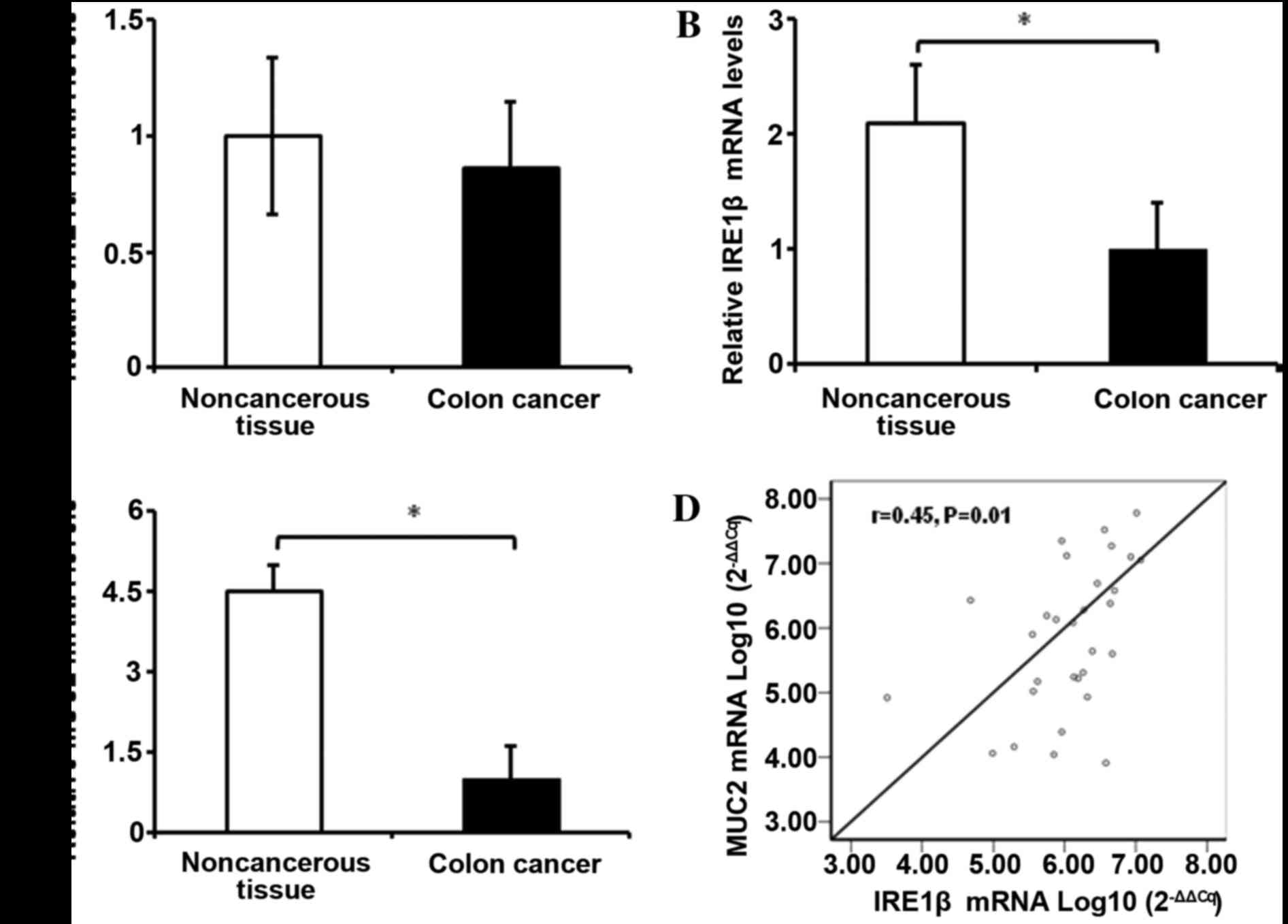
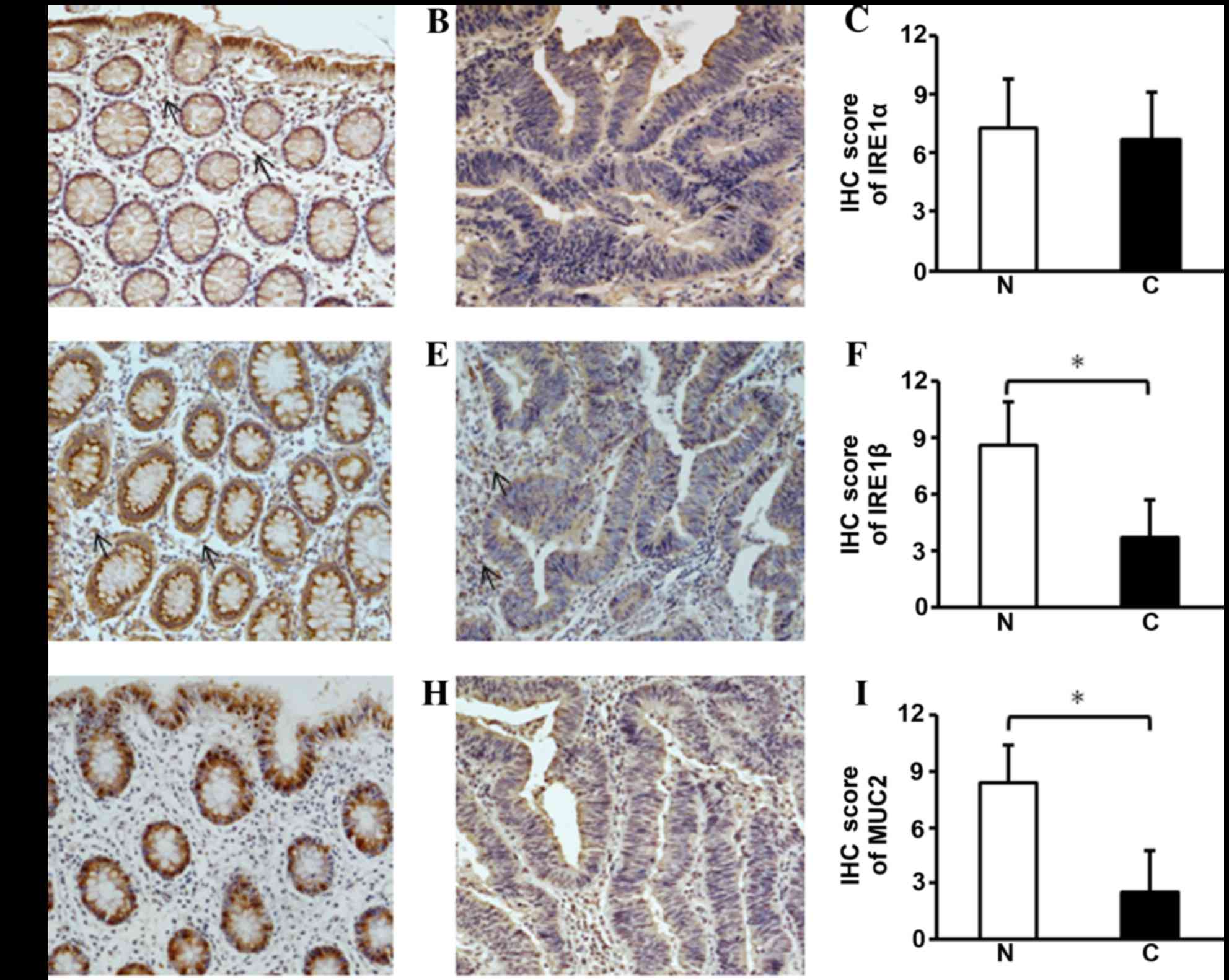
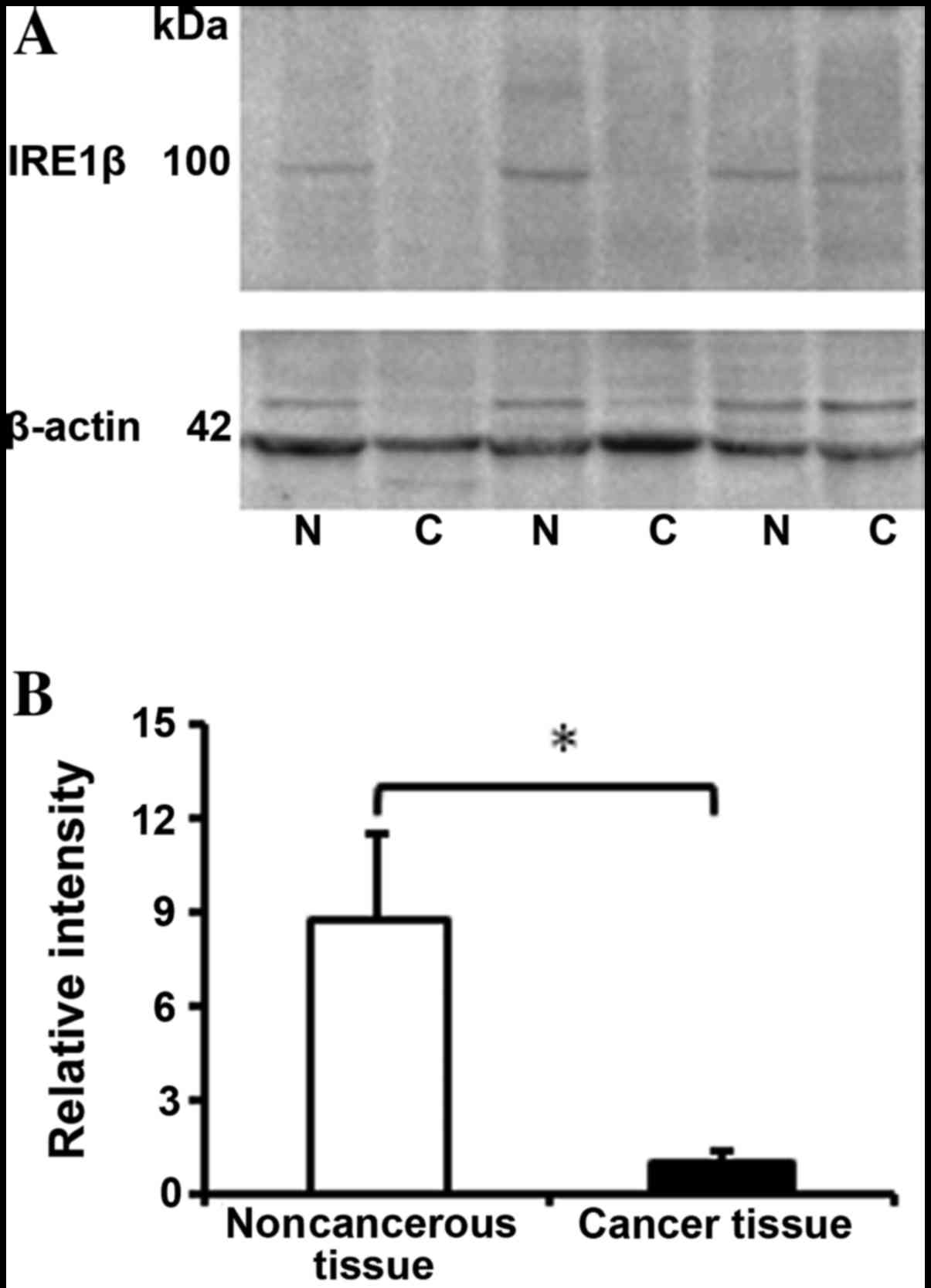
|
1
|
Fleming M, Ravula S, Tatishchev SF and
Wang HL: Colorectal carcinoma: Pathologic aspects. J Gastrointest
Oncol. 3:153–173. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zhao P, Dai M, Chen W and Li N: Cancer
trends in China. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 40:281–285. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Li L and Ma BB: Colorectal cancer in
Chinese patients: Current and emerging treatment options. Onco
Targets Ther. 7:1817–1828. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Dai Z, Zheng RS, Zou XN, Zhang SW, Zeng
HM, Li N and Chen WQ: Analysis and prediction of colorectal cancer
incidence trend in China. Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi.
46:598–603. 2012.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Stintzing S: Management of colorectal
cancer. F1000Prime Rep. 6:1082014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kim ER and Kim YH: Clinical application of
genetics in management of colorectal cancer. Intest Res.
12:184–193. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
SEER Stat Fact Sheets: Colon and Rectum
Cancer). National Cancer Institute; Bethesda, MD: https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/colorect.htmlSeptember
1–2015
|
|
8
|
Manié SN, Lebeau J and Chevet E: Cellular
mechanisms of endoplasmic reticulum stress signaling in health and
disease. 3. Orchestrating the unfolded protein response in
oncogenesis: An update. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 307:C901–C907.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Dicks N, Gutierrez K, Michalak M,
Bordignon V and Agellon LB: Endoplasmic reticulum stress, genome
damage, and cancer. Front Oncol. 5:112015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Parmar VM and Schröder M: Sensing
endoplasmic reticulum stress. Adv Exp Med Biol. 738:153–168. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gardner BM, Pincus D, Gotthardt K,
Gallagher CM and Walter P: Endoplasmic reticulum stress sensing in
the unfolded protein response. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol.
5:a0131692013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gao Q, Esworthy RS, Kim BW, Synold TW,
Smith DD and Chu FF: Atherogenic diets exacerbate colitis in mice
deficient in glutathione peroxidase. Inflamm Bowel Dis.
16:2043–2054. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
McMillan DR, Gething MJ and Sambrook J:
The cellular response to unfolded proteins: Intercompartmental
signaling. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 5:540–545. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Papandreou I, Denko NC, Olson M, Van
Melckebeke H, Lust S, Tam A, Solow-Cordero DE, Bouley DM, Offner F,
Niwa M and Koong AC: Identification of an Ire1alpha endonuclease
specific inhibitor with cytotoxic activity against human multiple
myeloma. Blood. 117:1311–1314. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Greenman C, Stephens P, Smith R, Dalgliesh
GL, Hunter C, Bignell G, Davies H, Teague J, Butler A, Stevens C,
et al: Patterns of somatic mutation in human cancer genomes.
Nature. 446:153–158. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Nakamura D, Tsuru A, Ikegami K, Imagawa Y,
Fujimoto N and Kohno K: Mammalian ER stress sensor IRE1β
specifically down-regulates the synthesis of secretory pathway
proteins. FEBS Lett. 585:133–138. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Koong AC, Chauhan V and Romero-Ramirez L:
Targeting XBP-1 as a novel anti-cancer strategy. Cancer Biol Ther.
5:756–759. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yoshida H, Oku M, Suzuki M and Mori K:
pXBP1(U) encoded in XBP1 pre-mRNA negatively regulates unfolded
protein response activator pXBP1(S) in mammalian ER stress
response. J Cell Biol. 172:565–575. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Fujimoto T, Onda M, Nagai H, Nagahata T,
Ogawa K and Emi M: Upregulation and overexpression of human X-box
binding protein 1 (hXBP-1) gene in primary breast cancers. Breast
Cancer. 10:301–306. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Shuda M, Kondoh N, Imazeki N, Tanaka K,
Okada T, Mori K, Hada A, Arai M, Wakatsuki T, Matsubara O, et al:
Activation of the ATF6, XBP1 and grp78 genes in human
hepatocellular carcinoma: A possible involvement of the ER stress
pathway in hepatocarcinogenesis. J Hepatol. 38:605–614. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Fujimoto T, Yoshimatsu K, Watanabe K,
Yokomizo H, Otani T, Matsumoto A, Osawa G, Onda M and Ogawa K:
Overexpression of human X-box binding protein 1 (XBP-1) in
colorectal adenomas and adenocarcinomas. Anticancer Res.
27:127–131. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Takahashi S, Suzuki S, Inaguma S, Ikeda Y,
Cho YM, Nishiyama N, Fujita T, Inoue T, Hioki T, Sugimura Y, et al:
Down-regulation of human X-box binding protein 1 (hXBP-1)
expression correlates with tumor progression in human prostate
cancers. Prostate. 50:154–161. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Chen Y and Brandizzi F: IRE1: ER stress
sensor and cell fate executor. Trends Cell Biol. 23:547–555. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Coelho DS and Domingos PM: Physiological
roles of regulated Ire1 dependent decay. Front Genet. 5:762014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Welihinda AA, Tirasophon W and Kaufman RJ:
The cellular response to protein misfolding in the endoplasmic
reticulum. Gene Expr. 7:293–300. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Bertolotti A, Wang X, Novoa I, Jungreis R,
Schlessinger K, Cho JH, West AB and Ron D: Increased sensitivity to
dextran sodium sulfate colitis in IRE1beta-deficient mice. J Clin
Invest. 107:585–593. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Martino MB, Jones L, Brighton B, Ehre C,
Abdulah L, Davis CW, Ron D, O'Neal WK and Ribeiro CM: The ER stress
transducer IRE1β is required for airway epithelial mucin
production. Mucosal Immunol. 6:639–654. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhang HS, Chen Y, Fan L, Xi QL, Wu GH, Li
XX, Yuan TL, He SQ, Yu Y, Shao ML, et al: The Endoplasmic Reticulum
Stress Sensor IRE1α in Intestinal Epithelial Cells Is Essential for
Protecting against Colitis. J Biol Chem. 290:15327–15336. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lin JH, Li H, Yasumura D, Cohen HR, Zhang
C, Panning B, Shokat KM, Lavail MM and Walter P: IRE1 signaling
affects cell fate during the unfolded protein response. Science.
318:944–949. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hetz C: The unfolded protein response:
Controlling cell fate decisions under ER stress and beyond. Nat Rev
Mol Cell Biol. 13:89–1026. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hetz C and Glimcher LH: Fine-tuning of the
unfolded protein response: Assembling the IRE1alpha interactome.
Mol Cell. 35:551–561. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Iwawaki T, Hosoda A, Okuda T, Kamigori Y,
Nomura-Furuwatari C, Kimata Y, Tsuru A and Kohno K: Translational
control by the ER transmembrane kinase/ribonuclease IRE1 under ER
stress. Nat Cell Biol. 3:158–164. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Tsuru A, Fujimoto N, Takahashi S, Saito M,
Nakamura D, Iwano M, Iwawaki T, Kadokura H, Ron D and Kohno K:
Negative feedback by IRE1β optimizes mucin production in goblet
cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 110:2864–2869. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Johansson ME and Hansson GC: Mucus and the
goblet cell. Dig Dis. 31:305–309. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Johansson ME, Phillipson M, Petersson J,
Velcich A, Holm L and Hansson GC: The inner of the two Muc2
mucin-dependent mucus layers in colon is devoid of bacteria. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 105:15064–15069. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kawashima H: Roles of the gel-forming MUC2
mucin and its O-glycosylation in the protection against colitis and
colorectal cancer. Biol Pharm Bull. 35:1637–1641. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Van der Sluis M, De Koning BA, De Bruijn
AC, Velcich A, Meijerink JP, Van Goudoever JB, Büller HA, Dekker J,
Van Seuningen I, Renes IB and Einerhand AW: Muc2-deficient mice
spontaneously develop colitis, indicating that MUC2 is critical for
colonic protection. Gastroenterology. 131:117–129. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Velcich A, Yang W, Heyer J, Fragale A,
Nicholas C, Viani S, Kucherlapati R, Lipkin M, Yang K and
Augenlicht L: Colorectal cancer in mice genetically deficient in
the mucin Muc2. Science. 295:1726–1729. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Imai Y, Yamagishi H, Fukuda K, Ono Y,
Inoue T and Ueda Y: Differential mucin phenotypes and their
significance in a variation of colorectal carcinoma. World J
Gastroenterol. 19:3957–3968. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Debunne H and Ceelen W: Mucinous
differentiation in colorectal cancer: Molecular, histological and
clinical aspects. Acta Chir Belg. 113:385–390. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Edge SB and Compton CC: The American Joint
Committee on Cancer: The 7th edition of the AJCC cancer staging
manual and the future of TNM. Ann Surg Oncol. 17:1471–1474. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Untergasser A, Cutcutache I, Koressaar T,
Ye J, Faircloth BC, Remm M and Rozen SG: Primer3-new capabilities
and interfaces. Nucleic Acids Res. 40:e1152012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Xu FX, Su YL, Zhang H, Kong JY, Yu H and
Qian BY: Prognostic implications for high expression of MiR-25 in
lung adenocarcinomas of female non-smokers. Asian Pac J Cancer
Prev. 15:1197–1203. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Gao Q, Meijer MJ, Kubben FJ, Sier CF,
Kruidenier L, van Duijn W, van den Berg M, van Hogezand RA, Lamers
CB and Verspaget HW: Expression of matrix metalloproteinases-2 and
−9 in intestinal tissue of patients with inflammatory bowel
diseases. Dig Liver Dis. 37:584–592. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Liu C, Huang Z, Jiang H and Shi F: The
sirtuin 3 expression profile is associated with pathological and
clinical outcomes in colon cancer patients. Biomed Res Int.
2014:8712632014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Liu S, Zheng R, Zhang M, Zhang S, Sun X
and Chen W: Incidence and mortality of colorectal cancer in China,
2011. Chin J Cancer Res. 27:22–28. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Imagawa Y, Hosoda A, Sasaka S, Tsuru A and
Kohno K: RNase domains determine the functional difference between
IRE1alpha and IRE1beta. FEBS Lett. 582:656–660. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Piemonte M: [TNM - classification of
malignant tumors (VI edition - 2002). Innovations in the
classification of head and neck neoplasms]. Acta Otorhinolaryngol
Ital. 23:132–135. 2003.(In Italian). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Wei Q, Huang X, Fu B, Liu J, Zhong L, Yang
Q and Zhao T: IMP3 expression in biopsy specimens of colorectal
cancer predicts lymph node metastasis and TNM stage. Int J Clin Exp
Pathol. 8:11024–3213. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Kesari MV, Gaopande VL, Joshi AR,
Babanagare SV, Gogate BP and Khadilkar AV: Immunohistochemical
study of MUC1, MUC2 and MUC5AC in colorectal carcinoma and review
of literature. Indian J Gastroenterol. 34:63–67. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Walsh MD, Clendenning M, Williamson E,
Pearson SA, Walters RJ, Nagler B, Packenas D, Win AK, Hopper JL,
Jenkins MA, et al: Expression of MUC2, MUC5AC, MUC5B, and MUC6
mucins in colorectal cancers and their association with the CpG
island methylator phenotype. Mod Pathol. 26:1642–1656. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Okudaira K, Kakar S, Cun L, Choi E, Wu
Decamillis R, Miura S, Sleisenger MH, Kim YS and Deng G: MUC2 gene
promoter methylation in mucinous and non-mucinous colorectal cancer
tissues. Int J Oncol. 36:765–775. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Iqbal J, Dai K, Seimon T, Jungreis R,
Oyadomari M, Kuriakose G, Ron D, Tabas I and Hussain MM: IRE1beta
inhibits chylomicron production by selectively degrading MTP mRNA.
Cell Metab. 7:445–455. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Terzić J, Grivennikov S, Karin E and Karin
M: Inflammation and colon cancer. Gastroenterology.
138:2101–2114.e5. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Dai K, Khatun I and Hussain MM: NR2F1 and
IRE1beta suppress microsomal triglyceride transfer protein
expression and lipoprotein assembly in undifferentiated intestinal
epithelial cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 30:568–574. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Heazlewood CK, Cook MC, Eri R, Price GR,
Tauro SB, Taupin D, Thornton DJ, Png CW, Crockford TL, Cornall RJ,
et al: Aberrant mucin assembly in mice causes endoplasmic reticulum
stress and spontaneous inflammation resembling ulcerative colitis.
PLoS Med. 5:e542008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Manne U, Weiss HL and Grizzle WE: Racial
differences in the prognostic usefulness of MUC1 and MUC2 in
colorectal adenocarcinomas. Clin Cancer Res. 6:4017–4025.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Matsuda K, Masaki T, Watanabe T, Kitayama
J, Nagawa H, Muto T and Ajioka Y: Clinical significance of MUC1 and
MUC2 mucin and p53 protein expression in colorectal carcinoma. Jpn
J Clin Oncol. 30:89–94. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Gratchev A, Siedow A, Bumke-Vogt C, Hummel
M, Foss HD, Hanski ML, Kobalz U, Mann B, Lammert H, Mansmann U, et
al: Regulation of the intestinal mucin MUC2 gene expression in
vivo: Evidence for the role of promoter methylation. Cancer Lett.
168:71–80. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Ookawa K, Kudo T, Aizawa S, Saito H and
Tsuchida S: Transcriptional activation of the MUC2 gene by p53. J
Biol Chem. 277:48270–48275. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|