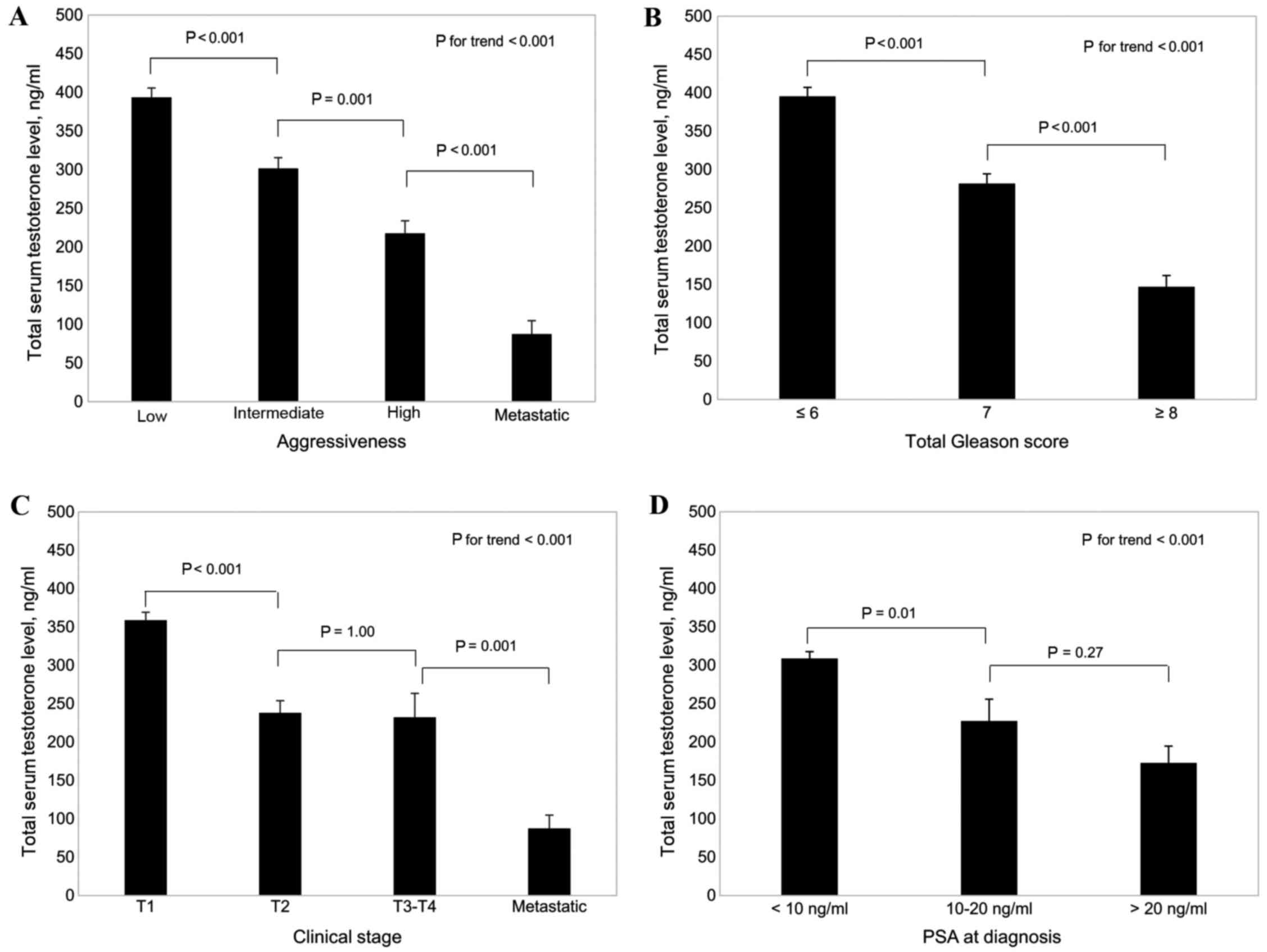
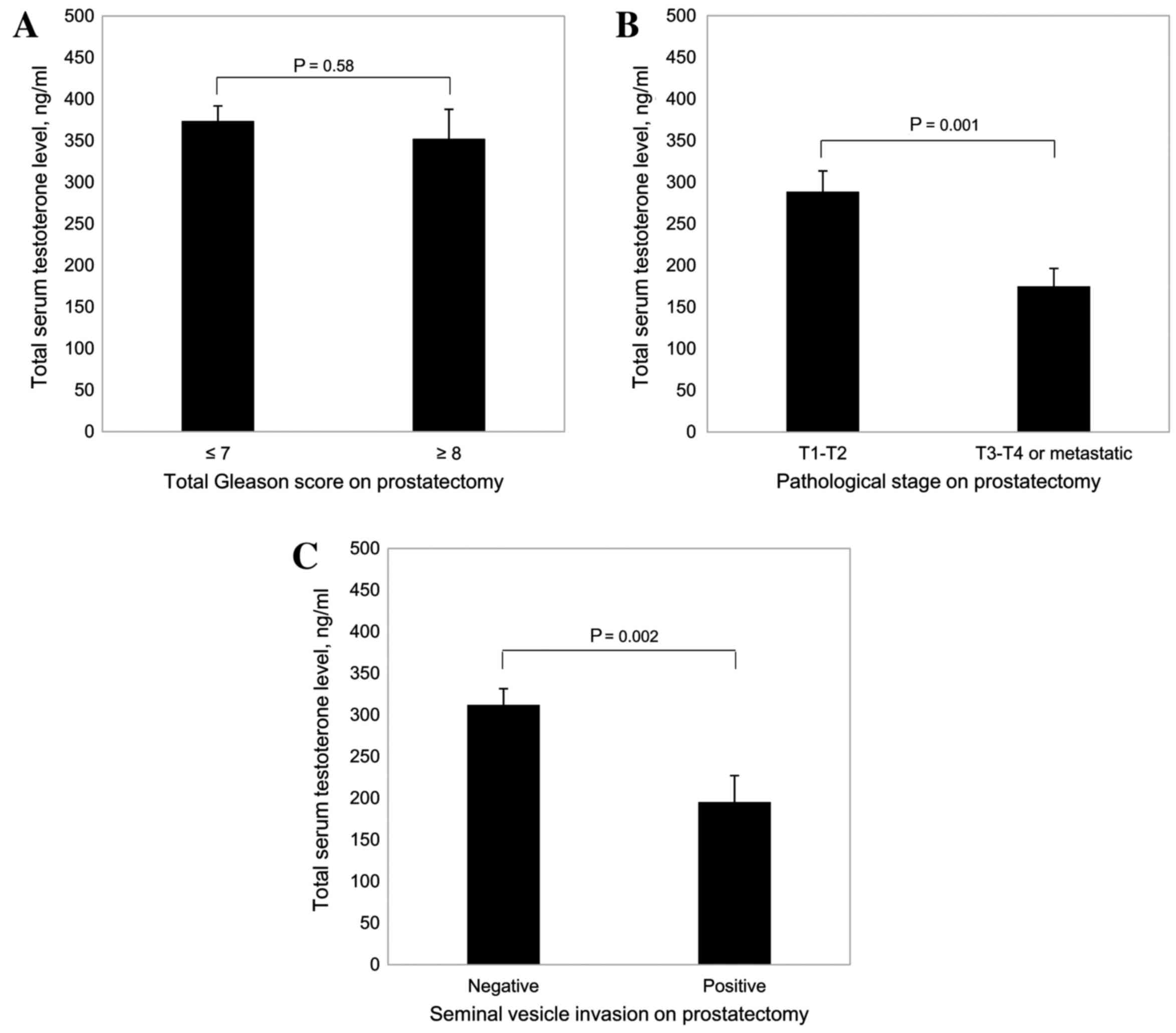
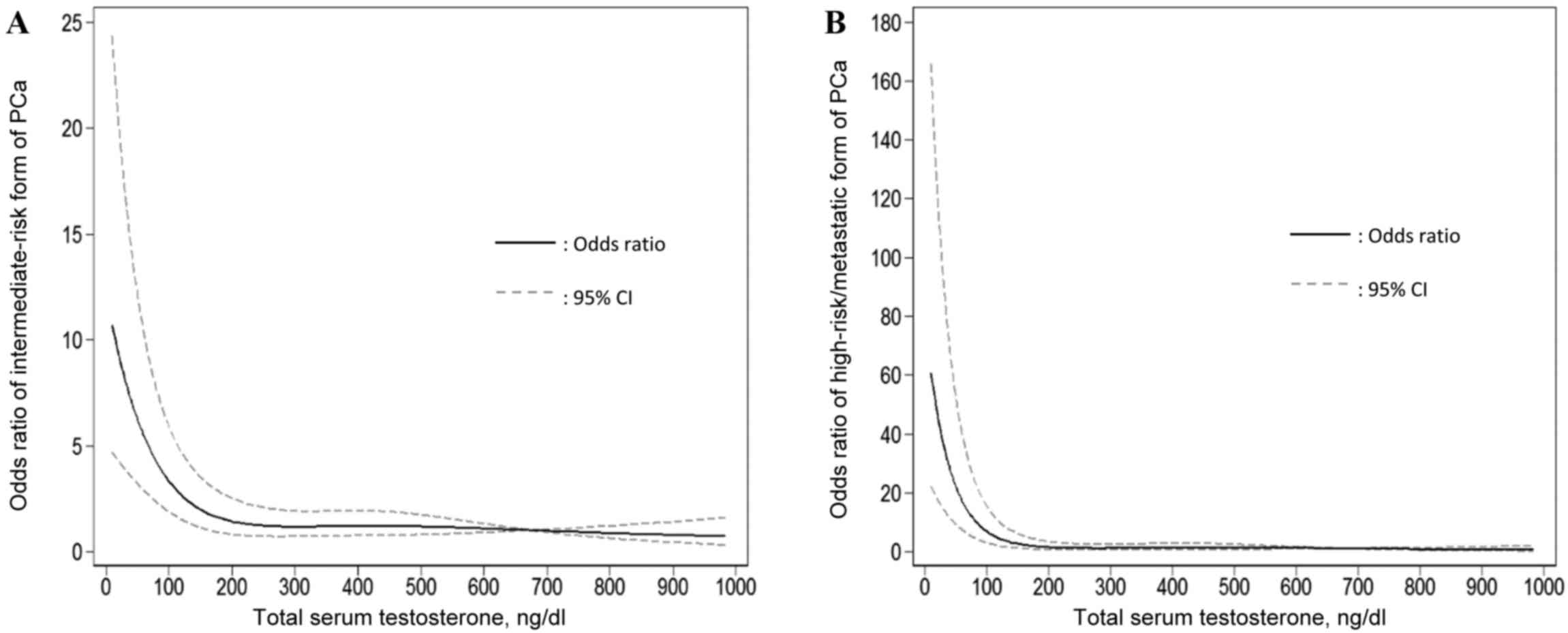
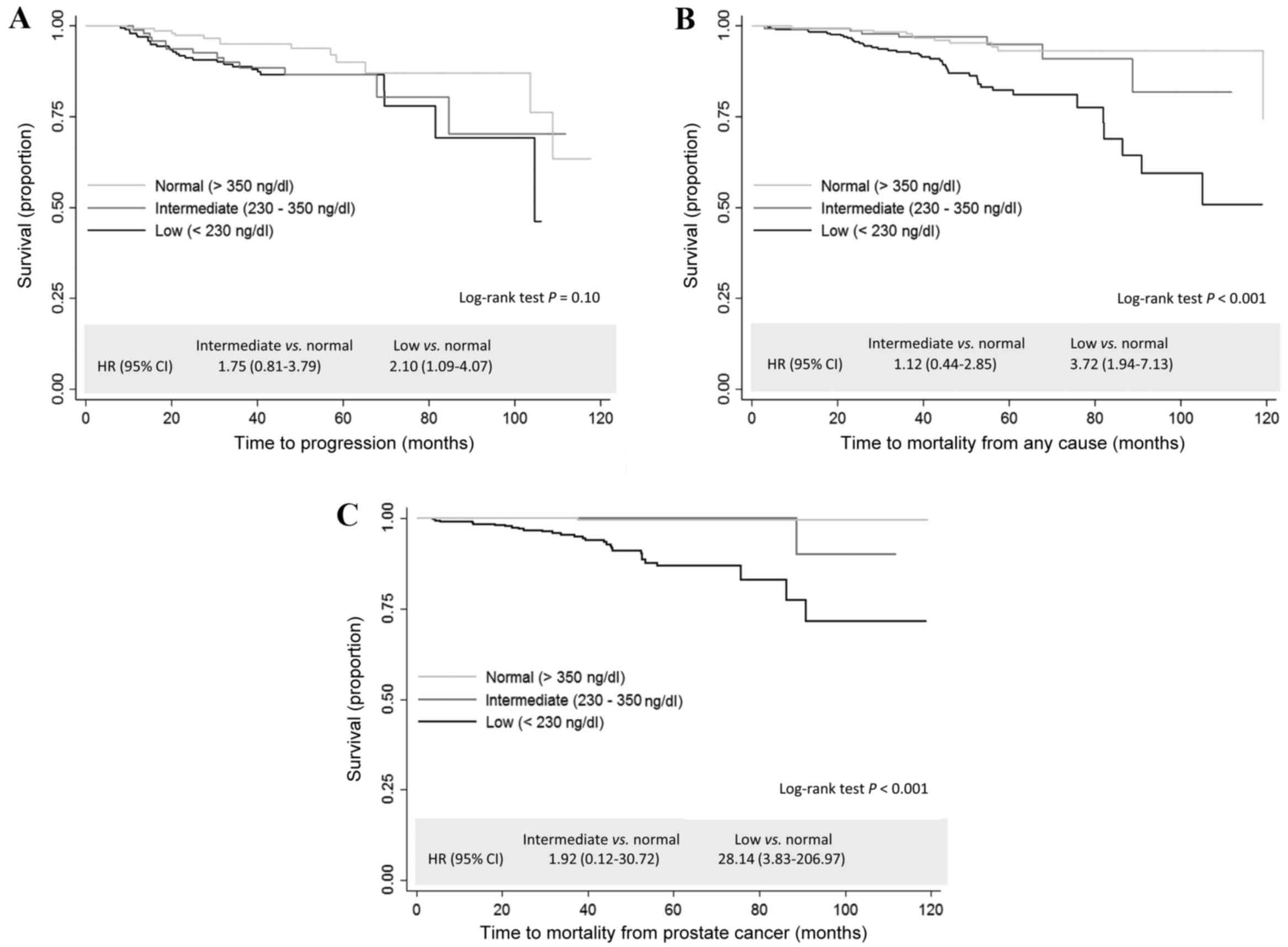
|
1
|
American Cancer Society, . Cancer Facts
& Figures 2015. American Cancer Society; Atlanta, GA: 2015
|
|
2
|
Barry MJ: Screening for prostate
cancer-the controversy that refuses to die. N Engl J Med.
360:1351–1354. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Welch HG and Albertsen PC: Prostate cancer
diagnosis and treatment after the introduction of prostate-specific
antigen screening: 1986–2005. J Natl Cancer Inst. 101:1325–1329.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zlotta AR, Egawa S, Pushkar D, Govorov A,
Kimura T, Kido M, Takahashi H, Kuk C, Kovylina M, Aldaoud N, et al:
Prevalence of prostate cancer on autopsy: Cross-sectional study on
unscreened Caucasian and Asian men. J Natl Cancer Inst.
105:1050–1058. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Welch HG and Black WC: Overdiagnosis in
cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 102:605–613. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Rodrigues G, Warde P, Pickles T, Crook J,
Brundage M, Souhami L and Lukka H: Genitourinary Radiation
Oncologists of Canada: Pre-treatment risk stratification of
prostate cancer patients: A critical review. Can Urol Assoc J.
6:121–127. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
D'Amico AV, Whittington R, Malkowicz SB,
Schultz D, Blank K, Broderick GA, Tomaszewski JE, Renshaw AA,
Kaplan I, Beard CJ and Wein A: Biochemical outcome after radical
prostatectomy, external beam radiation therapy, or interstitial
radiation therapy for clinically localized prostate cancer. JAMA.
280:969–974. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Isbarn H, Pinthus JH, Marks LS, Montorsi
F, Morales A, Morgentaler A and Schulman C: Testosterone and
prostate cancer: Revisiting old paradigms. Eur Urol. 56:48–56.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Klap J, Schmid M and Loughlin KR: The
relationship between total testosterone levels and prostate cancer:
A review of the continuing controversy. J Urol. 193:403–413. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Morgentaler A: Testosterone and prostate
cancer: An historical perspective on a modern myth. Eur Urol.
50:935–939. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
García-Cruz E, Piqueras M, Huguet J, Peri
L, Izquierdo L, Musquera M, Franco A, Alvarez-Vijande R, Ribal MJ
and Alcaraz A: Low testosterone levels are related to poor
prognosis factors in men with prostate cancer prior to treatment.
BJU Int. 110:E541–E546. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Morgentaler A: Turning conventional wisdom
upside-down: Low serum testosterone and high-risk prostate cancer.
Cancer. 117:3885–3888. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Imamoto T, Suzuki H, Fukasawa S, Shimbo M,
Inahara M, Komiya A, Ueda T, Shiraishi T and Ichikawa T:
Pretreatment serum testosterone level as a predictive factor of
pathological stage in localized prostate cancer patients treated
with radical prostatectomy. Eur Urol. 47:308–312. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Schatzl G, Madersbacher S, Thurridl T,
Waldmüller J, Kramer G, Haitel A and Marberger M: High-grade
prostate cancer is associated with low serum testosterone levels.
Prostate. 47:52–58. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yano M, Imamoto T, Suzuki H, Fukasawa S,
Kojima S, Komiya A, Naya Y and Ichikawa T: The clinical potential
of pretreatment serum testosterone level to improve the efficiency
of prostate cancer screening. Eur Urol. 51:375–380. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Massengill JC, Sun L, Moul JW, Wu H,
McLeod DG, Amling C, Lance R, Foley J, Sexton W, Kusuda L, et al:
Pretreatment total testosterone level predicts pathological stage
in patients with localized prostate cancer treated with radical
prostatectomy. J Urol. 169:1670–1675. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Isom-Batz G, Bianco FJ Jr, Kattan MW,
Mulhall JP, Lilja H and Eastham JA: Testosterone as a predictor of
pathological stage in clinically localized prostate cancer. J Urol.
173:1935–1937. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Teloken C, Da Ros CT, Caraver F, Weber FA,
Cavalheiro AP and Graziottin TM: Low serum testosterone levels are
associated with positive surgical margins in radical retropubic
prostatectomy: Hypogonadism represents bad prognosis in prostate
cancer. J Urol. 174:2178–2180. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
San Francisco IF, Regan MM, Dewolf WC and
Olumi AF: Low age adjusted free testosterone levels correlate with
poorly differentiated prostate cancer. J Urol. 175:1341–1346. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Leon P, Seisen T, Cussenot O, Drouin SJ,
Cattarino S, Compérat E, Renard-Penna R, Mozer P, Bitker MO and
Rouprêt M: Low circulating free and bioavailable testosterone
levels as predictors of high-grade tumors in patients undergoing
radical prostatectomy for localized prostate cancer. Urol Oncol.
33:384.r21-e27. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Salonia A, Gallina A, Briganti A, Abdollah
F, Suardi N, Capitanio U, Colombo R, Freschi M, Rigatti P and
Montorsi F: Preoperative hypogonadism is not an independent
predictor of high-risk disease in patients undergoing radical
prostatectomy. Cancer. 117:3953–3962. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ide H, Yasuda M, Nishio K, Saito K,
Isotani S, Kamiyama Y, Muto S and Horie S: Development of a
nomogram for predicting high-grade prostate cancer on biopsy: The
significance of serum testosterone levels. Anticancer Res.
28:2487–2492. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Dai B, Qu Y, Kong Y, Ye D, Yao X, Zhang S,
Wang C, Zhang H and Yang W: Low pretreatment serum total
testosterone is associated with a high incidence of Gleason score
8–10 disease in prostatectomy specimens: Data from ethnic Chinese
patients with localized prostate cancer. BJU Int. 110:E667–E672.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lane BR, Stephenson AJ, Magi-Galluzzi C,
Lakin MM and Klein EA: Low testosterone and risk of biochemical
recurrence and poorly differentiated prostate cancer at radical
prostatectomy. Urology. 72:1240–1245. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Botto H, Neuzillet Y, Lebret T, Camparo P,
Molinie V and Raynaud JP: High incidence of predominant Gleason
pattern 4 localized prostate cancer is associated with low serum
testosterone. J Urol. 186:1400–1405. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
He Y, Gu J, Strom S, Logothetis CJ, Kim J
and Wu X: The prostate cancer susceptibility variant rs2735839 near
KLK3 gene is associated with aggressive prostate cancer and can
stratify gleason score 7 patients. Clin Cancer Res. 20:5133–5139.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Tu H, Gu J, Meng QH, Kim J, Davis JW, He
Y, Wagar EA, Thompson TC, Logothetis CJ and Wu X: Mitochondrial DNA
copy number in peripheral blood leukocytes and the aggressiveness
of localized prostate cancer. Oncotarget. 6:41988–41996.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Howlader N, Noone AM, Krapcho M, Garshell
J, Miller D, Altekruse SF, Kosary CL, Yu M, Ruhl J, Tatalovich Z,
et al: SEER Cancer Statistics, Review 1975–2011. http://seer.cancer.gov/csr/1975_2013/Accessed.
September 12–2016.
|
|
29
|
Cookson MS, Aus G, Burnett AL,
Canby-Hagino ED, D'Amico AV, Dmochowski RR, Eton DT, Forman JD,
Goldenberg SL, Hernandez J, et al: Variation in the definition of
biochemical recurrence in patients treated for localized prostate
cancer: The American Urological Association Prostate Guidelines for
Localized Prostate Cancer Update Panel report and recommendations
for a standard in the reporting of surgical outcomes. J Urol.
177:540–545. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Roach M III, Hanks G, Thames H Jr,
Schellhammer P, Shipley WU, Sokol GH and Sandler H: Defining
biochemical failure following radiotherapy with or without hormonal
therapy in men with clinically localized prostate cancer:
Recommendations of the RTOG-ASTRO Phoenix Consensus Conference. Int
J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 65:965–974. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wang C, Nieschlag E, Swerdloff R, Behre
HM, Hellstrom WJ, Gooren LJ, Kaufman JM, Legros JJ, Lunenfeld B,
Morales A, et al: Investigation, treatment, and monitoring of
late-onset hypogonadism in males: ISA, ISSAM, EAU, EAA and ASA
recommendations. J Androl. 30:1–9. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Endogenous Hormones and Prostate Cancer
Collaborative Group, ; Roddam AW, Allen NE, Appleby P and Key TJ:
Endogenous sex hormones and prostate cancer: A collaborative
analysis of 18 prospective studies. J Natl Cancer Inst.
100:170–183. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ryan CJ, Molina A, Li J, Kheoh T, Small
EJ, Haqq CM, Grant RP, de Bono JS and Scher H: Serum androgens as
prognostic biomarkers in castration-resistant prostate cancer:
Results from an analysis of a randomized phase III trial. J Clin
Oncol. 31:2791–2798. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ribeiro M, Ruff P and Falkson G: Low serum
testosterone and a younger age predict for a poor outcome in
metastatic prostate cancer. Am J Clin Oncol. 20:605–608. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Imamoto T, Suzuki H, Akakura K, Komiya A,
Nakamachi H, Ichikawa T, Igarashi T and Ito H: Pretreatment serum
level of testosterone as a prognostic factor in Japanese men with
hormonally treated stage D2 prostate cancer. Endocr J. 48:573–578.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Yamamoto S, Yonese J, Kawakami S, Ohkubo
Y, Tatokoro M, Komai Y, Takeshita H, Ishikawa Y and Fukui I:
Preoperative serum testosterone level as an independent predictor
of treatment failure following radical prostatectomy. Eur Urol.
52:696–701. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
San Francisco IF, Rojas PA, DeWolf WC and
Morgentaler A: Low free testosterone levels predict disease
reclassification in men with prostate cancer undergoing active
surveillance. BJU Int. 114:229–235. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Furuya Y, Nozaki T, Nagakawa O and Fuse H:
Low serum testosterone level predicts worse response to endocrine
therapy in Japanese patients with metastatic prostate cancer.
Endocr J. 49:85–90. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Banach-Petrosky W, Jessen WJ, Ouyang X,
Gao H, Rao J, Quinn J, Aronow BJ and Abate-Shen C: Prolonged
exposure to reduced levels of androgen accelerates prostate cancer
progression in Nkx3.1; Pten mutant mice. Cancer Res. 67:9089–9096.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Karantanos T, Evans CP, Tombal B, Thompson
TC, Montironi R and Isaacs WB: Understanding the mechanisms of
androgen deprivation resistance in prostate cancer at the molecular
level. Eur Urol. 67:470–479. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|