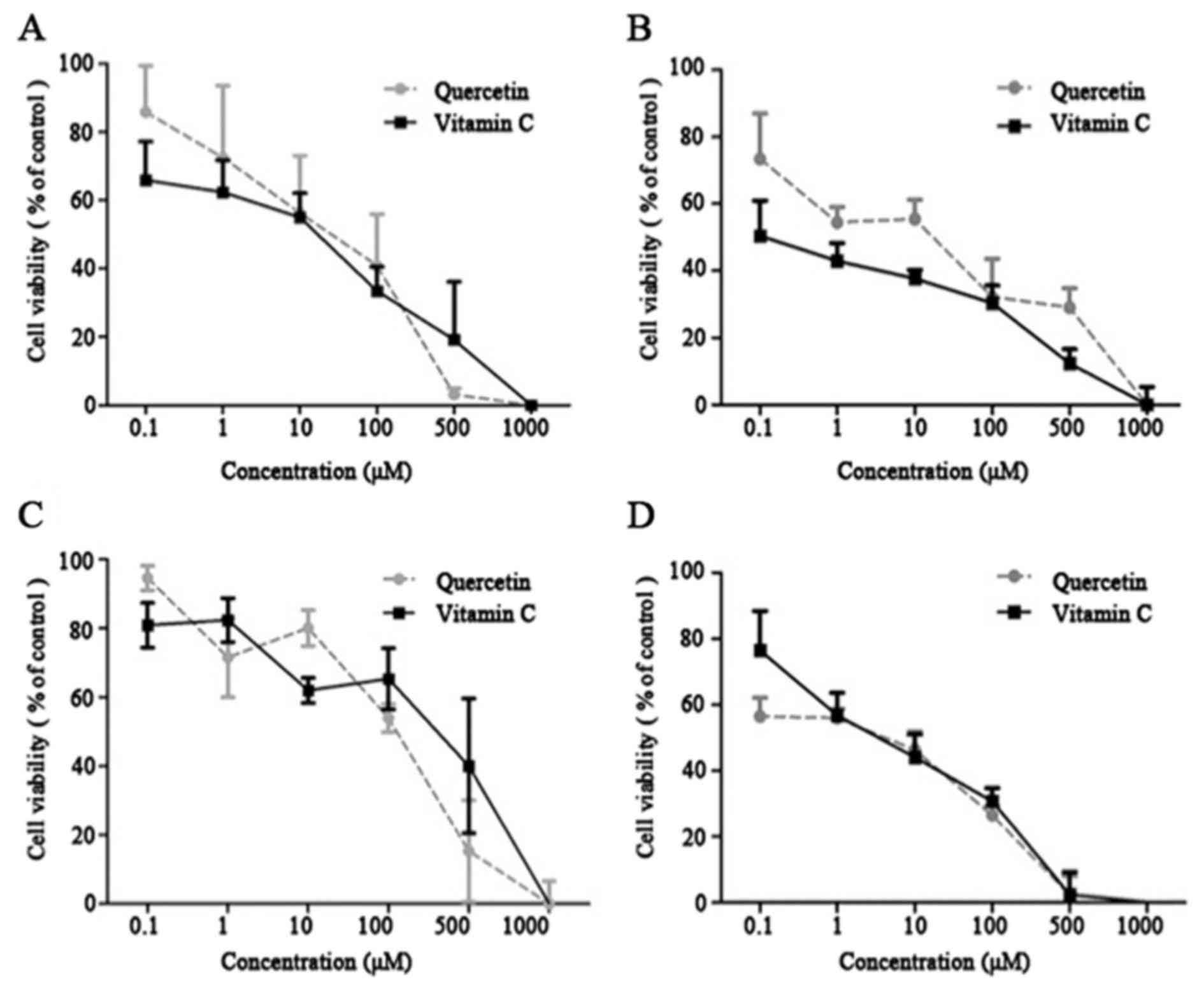
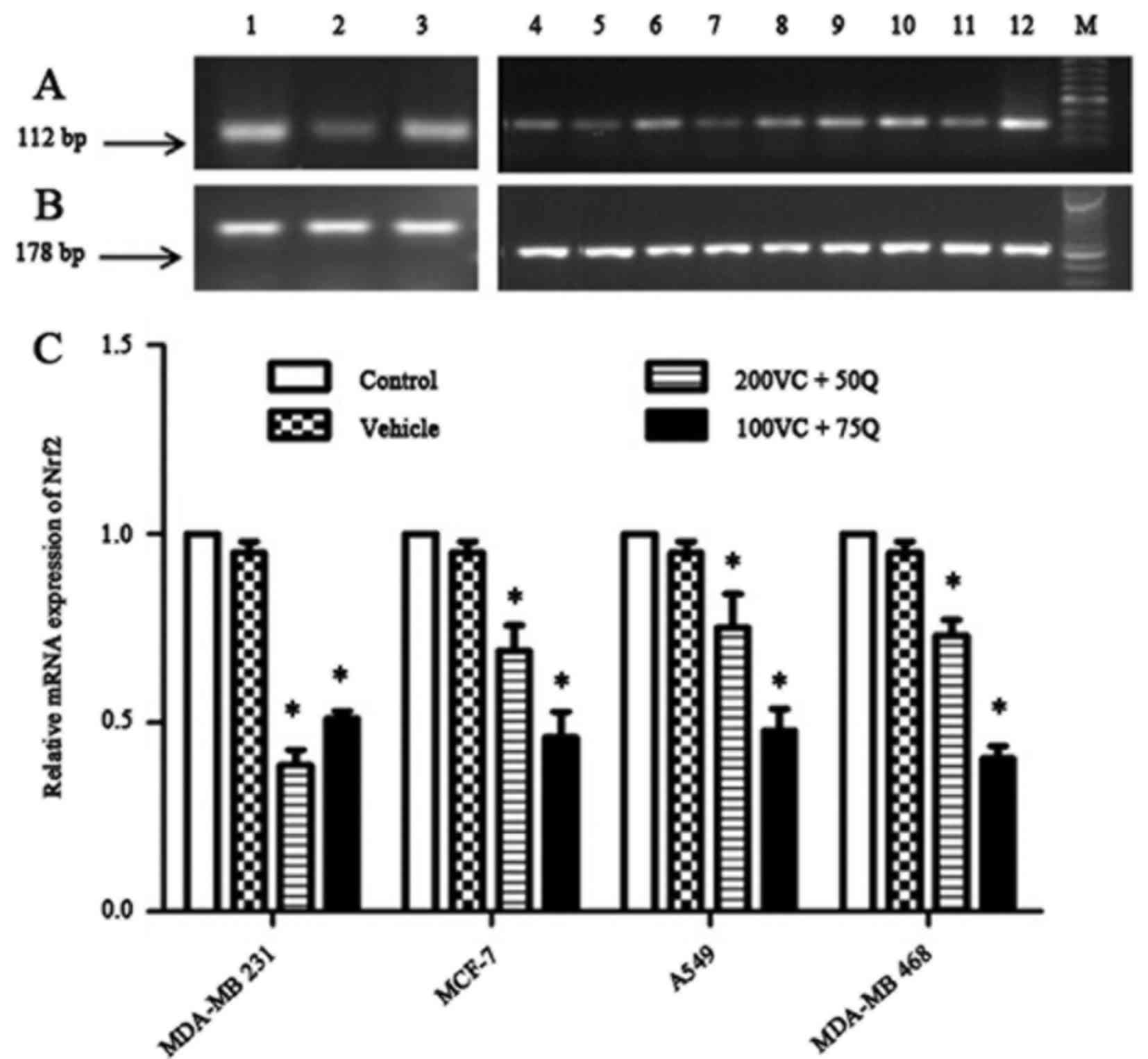
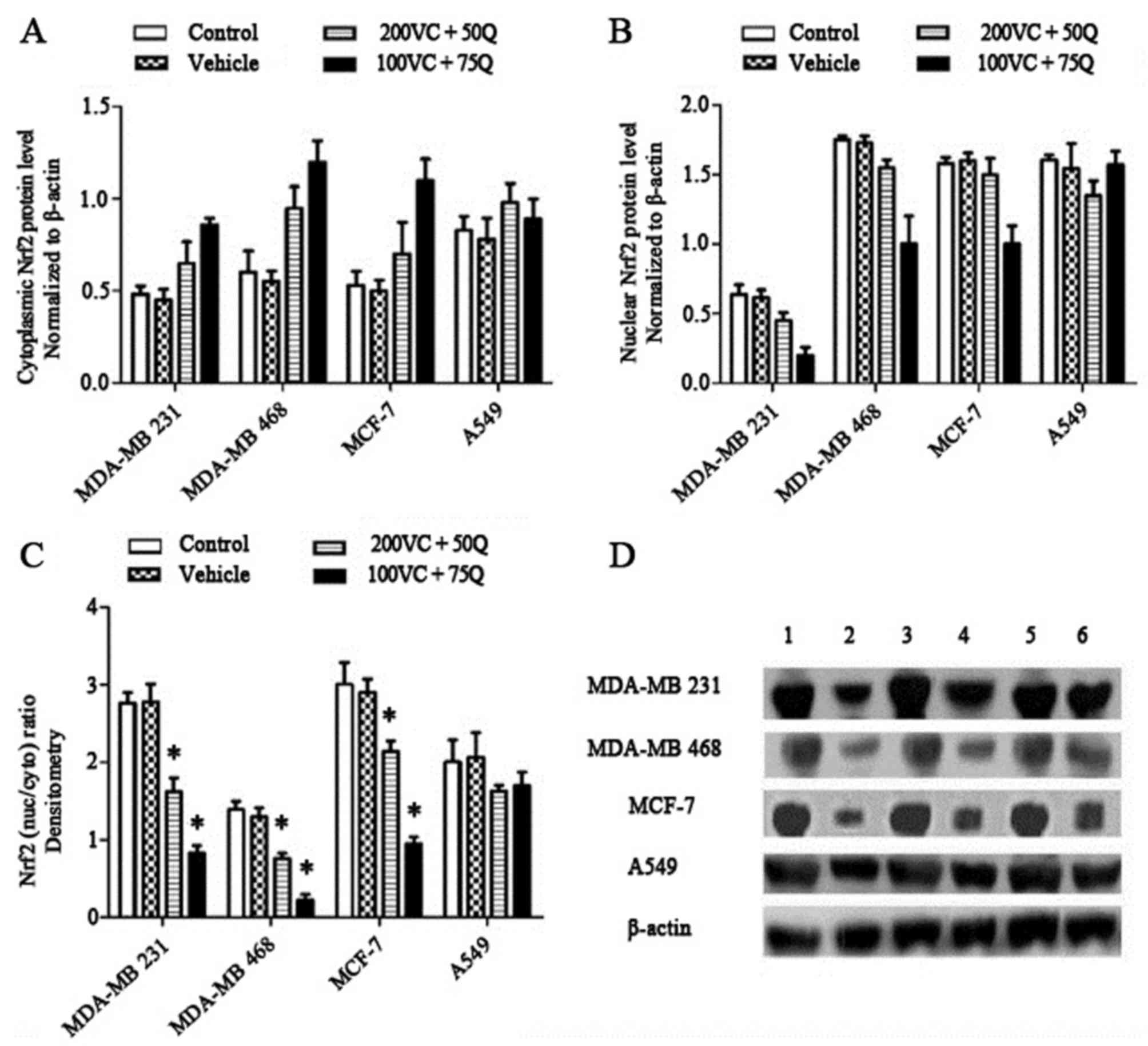
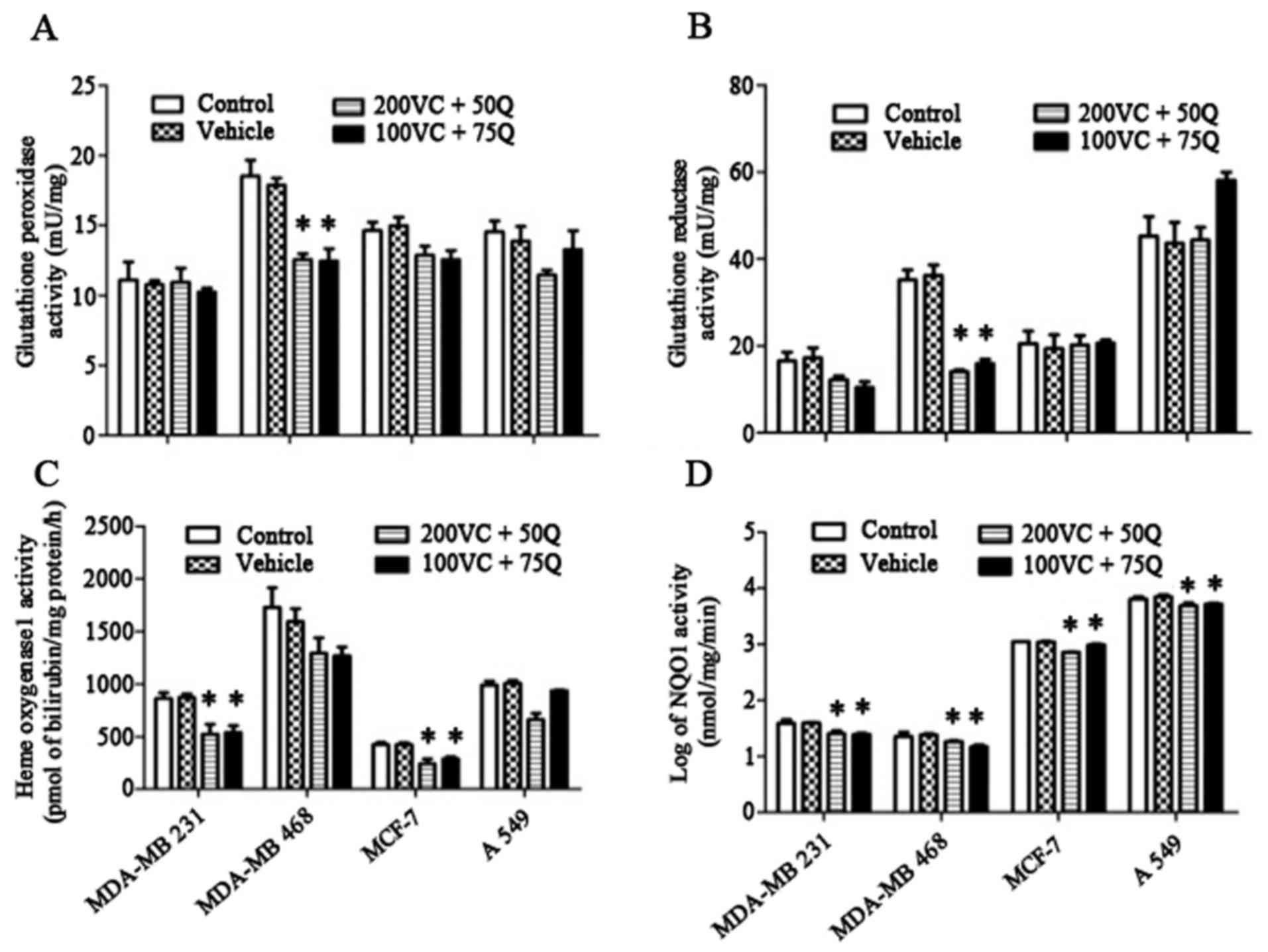
|
1
|
Ramos S: Effects of dietary flavonoids on
apoptotic pathways related to cancer chemoprevention. J Nutr
Biochem. 18:427–442. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
No JH, Kim YB and Song YS: Targeting nrf2
signaling to combat chemoresistance. J Cancer Prev. 19:111–117.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wu T, Harder BG, Wong PK, Lang JE and
Zhang DD: Oxidative stress, mammospheres and Nrf2-new implication
for breast cancer therapy? Mol Carcinog. 54:1494–1502. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Jaramillo MC and Zhang DD: The emerging
role of the Nrf2-Keap1 signaling pathway in cancer. Genes Dev.
27:2179–2191. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kensler TW, Wakabayashi N and Biswal S:
Cell survival responses to environmental stresses via the
Keap1-Nrf2-ARE pathway. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 47:89–116.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Foygel K, Sekar TV and Paulmurugan R:
Monitoring the antioxidant mediated chemosensitization and
ARE-signaling in triple negative breast cancer therapy. PloS One.
10:e01419132015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang XJ, Sun Z, Villeneuve NF, Zhang S,
Zhao F, Li Y, Chen W, Yi X, Zheng W, Wondrak GT, et al: Nrf2
enhances resistance of cancer cells to chemotherapeutic drugs, the
dark side of Nrf2. Carcinogenesis. 29:1235–1243. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Amadori D, Frassineti G, Zoli W, Milandri
C, Serra P, Tienghi A, Ravaioli A, Gentile A and Salzano E:
Doxorubicin and paclitaxel (sequential combination) in the
treatment of advanced breast cancer. Oncology (Williston Park).
11:(4 Suppl 3) 30–33. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Danesi R, Conte PF and Del Tacca M:
Pharmacokinetic optimisation of treatment schedules for
anthracyclines and paclitaxel in patients with cancer. Clin
Pharmacokinet. 37:195–211. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ibrahim T, Fabbri M, Frassineti GL, Zoli
W, Monti M, Ricotti L and Amadori D: Doxorubicin, paclitaxel and
gemcitabine: A Phase I study of a new sequential treatment in stage
III B-IV breast cancer. J Chemother. 15:488–494. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chou TC: Theoretical basis, experimental
design, and computerized simulation of synergism and antagonism in
drug combination studies. Pharmacol Rev. 58:621–681. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lee KW, Lee HJ, Surh YJ and Lee CY:
Vitamin C and cancer chemoprevention: Reappraisal. Am J Clin Nutr.
78:1074–1078. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zielinski CC: Gemcitabine, anthracycline,
and taxane combinations for advanced breast cancer. Oncology
(Williston Park). 17:(12 Suppl 14) 36–40. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chao MW, Lai MJ, Liou JP, Chang YL, Wang
JC, Pan SL and Teng CM: The synergic effect of vincristine and
vorinostat in leukemia in vitro and in vivo. J Hematol Oncol.
8:822015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Weiss RB, Woolf SH, Demakos E, Holland JF,
Berry DA, Falkson G, Cirrincione CT, Robbins A, Bothun S, Henderson
IC, et al: Natural history of more than 20 years of node-positive
primary breast carcinoma treated with cyclophosphamide,
methotrexate, and fluorouracil-based adjuvant chemotherapy: A study
by the cancer and leukemia group B. J Clin Oncol. 21:1825–1835.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Tarumoto T, Nagai T, Ohmine K, Miyoshi T,
Nakamura M, Kondo T, Mitsugi K, Nakano S, Muroi K, Komatsu N and
Ozawa K: Ascorbic acid restores sensitivity to imatinib via
suppression of Nrf2-dependent gene expression in the
imatinib-resistant cell line. Exp Hematol. 32:375–381. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Khanduja KL, Gandhi RK, Pathania V and
Syal N: Prevention of N-nitrosodiethylamine-induced lung
tumorigenesis by ellagic acid and quercetin in mice. Food Chem
Toxicol. 37:313–318. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Saw CL, Guo Y, Yang AY, Paredes-Gonzalez
X, Ramirez C, Pung D and Kong AN: The berry constituents quercetin,
kaempferol, and pterostilbene synergistically attenuate reactive
oxygen species: Involvement of the Nrf2-ARE signaling pathway. Food
Chem Toxicol. 72:303–311. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Borska S, Chmielewska M, Wysocka T,
Drag-Zalesinska M, Zabel M and Dziegiel P: In vitro effect of
quercetin on human gastric carcinoma: Targeting cancer cells death
and MDR. Food Chem Toxicol. 50:3375–3383. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Granado-Serrano AB, Martín MA, Bravo L,
Goya L and Ramos S: Quercetin induces apoptosis via caspase
activation, regulation of Bcl-2, and inhibition of PI-3-kinase/Akt
and ERK pathways in a human hepatoma cell line (HepG2). J Nutr.
136:2715–2721. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Li N, Sun C, Zhou B, Xing H, Ma D, Chen G
and Weng D: Low concentration of quercetin antagonizes the
cytotoxic effects of anti-neoplastic drugs in ovarian cancer. PloS
One. 9:e1003142014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Robaszkiewicz A, Balcerczyk A and Bartosz
G: Antioxidative and prooxidative effects of quercetin on A549
cells. Cell Biol Int. 31:1245–1250. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Samuel T, Fadlalla K, Mosley L, Katkoori
V, Turner T and Manne U: Dual-mode interaction between quercetin
and DNA-damaging drugs in cancer cells. Anticancer Res. 32:61–71.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Granado-Serrano AB, Martín MA, Bravo L,
Goya L and Ramos S: Quercetin modulates Nrf2 and
glutathione-related defenses in HepG2 cells: Involvement of p38.
Chem Biol Interact. 195:154–164. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Pfaffl MW: Quantification strategies in
real-time PCR. A-Z of quantitative PCR. 3:87–112. 2004.
|
|
26
|
Sabzichi M, Samadi N, Mohammadian J,
Hamishehkar H, Akbarzadeh M and Molavi O: Sustained release of
melatonin: A novel approach in elevating efficacy of tamoxifen in
breast cancer treatment. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 145:64–71.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Fecondo JV and Augusteyn RC: Superoxide
dismutase, catalase and glutathione peroxidase in the human
cataractous lens. Exp Eye Res. 36:15–23. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Maiani G, Mobarhan S, Nicastro A, Virgili
F, Scaccini C and Ferro-Luzzi A: Determination of glutathione
reductase activity in erythrocytes and whole blood as an indicator
of riboflavin nutrition. Acta Vitaminol Enzymol. 5:171–178.
1982.(In Italian).
|
|
29
|
Ellman GL: Tissue sulfhydryl groups. Arch
Biochem Biophys. 82:70–77. 1959. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Furfaro A, Traverso N, Domenicotti C,
Piras S, Moretta L, Marinari UM, Pronzato MA and Nitti M: The
Nrf2/HO-1 axis in cancer cell growth and chemoresistance. Oxid Med
Cell Longev. 2016:19581742016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
van der Wijst MG, Brown R and Rots MG:
Nrf2, the master redox switch: The Achilles' heel of ovarian
cancer? Biochim Biophys Acta. 1846:494–509. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Liu KC, Yen CY, Wu RS, Yang JS, Lu HF, Lu
KW, Lo C, Chen HY, Tang NY, Wu CC and Chung JG: The roles of
endoplasmic reticulum stress and mitochondrial apoptotic signaling
pathway in quercetin-mediated cell death of human prostate cancer
PC-3 cells. Environ Toxicol. 29:428–439. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lee WJ, Hsiao M, Chang JL, Yang SF, Tseng
TH, Cheng CW, Chow JM, Lin KH, Lin YW, Liu CC, et al: Quercetin
induces mitochondrial-derived apoptosis via reactive oxygen
species-mediated ERK activation in HL-60 leukemia cells and
xenograft. Arch Toxicol. 89:1103–1117. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Bournival J, Francoeur MA, Renaud J and
Martinoli MG: Quercetin and sesamin protect neuronal PC12 cells
from high-glucose-induced oxidation, nitrosative stress, and
apoptosis. Rejuvenation Res. 15:322–333. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Bouayed J and Bohn T: Exogenous
antioxidants-double-edged swords in cellular redox state: Health
beneficial effects at physiologic doses versus deleterious effects
at high doses. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 3:228–237. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Carr AC, Vissers MC and Cook JS: The
effect of intravenous vitamin C on cancer-and chemotherapy-related
fatigue and quality of life. Front Oncol. 4:2832014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Chen MF, Yang CM, Su CM and Hu ML: Vitamin
C protects against cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity and damage
without reducing its effectiveness in C57BL/6 mice xenografted with
Lewis lung carcinoma. Nutr Cancer. 66:1085–1091. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Wang X, Ye XL Liu R, Chen HL, Bai H, Liang
X, Zhang XD, Wang Z, Li WL and Hai CX: Antioxidant activities of
oleanolic acid in vitro: Possible role of Nrf2 and MAP kinases.
Chem Biol Interact. 184:328–337. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ding M, Zhao J, Bowman L, Lu Y and Shi X:
Inhibition of AP-1 and MAPK signaling and activation of Nrf2/ARE
pathway by quercitrin. Int J Oncol. 36:59–67. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Chun KS, Kundu J, Kundu JK and Surh YJ:
Targeting Nrf2-Keap1 signaling for chemoprevention of skin
carcinogenesis with bioactive phytochemicals. Toxicol Lett.
229:73–84. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Minaei A, Sabzichi M, Ramezani F,
Hamishehkar H and Samadi N: Co-delivery with nano-quercetin
enhances doxorubicin-mediated cytotoxicity against MCF-7 cells. Mol
Biol Rep. 43:99–105. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Ren D, Villeneuve NF, Jiang T, Wu T, Lau
A, Toppin HA and Zhang DD: Brusatol enhances the efficacy of
chemotherapy by inhibiting the Nrf2-mediated defense mechanism.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 108:1433–1438. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Wagner AE, Ernst I, Iori R, Desel C and
Rimbach G: Sulforaphane but not ascorbigen, indole-3-carbinole and
ascorbic acid activates the transcription factor Nrf2 and induces
phase-2 and antioxidant enzymes in human keratinocytes in culture.
Exp Dermatol. 19:137–144. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Scharf G, Prustomersky S, Knasmuller S,
Schulte-Hermann R and Huber WW: Enhancement of glutathione and
g-glutamylcysteine synthetase, the rate limiting enzyme of
glutathione synthesis, by chemoprotective plant-derived food and
beverage components in the human hepatoma cell line HepG2. Nutr
Cancer. 45:74–83. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Goldring CE, Kitteringham NR, Elsby R,
Randle LE, Clement YN, Williams DP, McMahon M, Hayes JD, Itoh K,
Yamamoto M and Park BK: Activation of hepatic Nrf2 in vivo by
acetaminophen in CD-1 mice. Hepatology. 39:1267–1276. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Hanneken A, Lin FF, Johnson J and Maher P:
Flavonoids protect human retinal pigment epithelial cells from
oxidative-stress-induced death. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci.
47:3164–3177. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Parrow NL, Leshin JA and Levine M:
Parenteral ascorbate as a cancer therapeutic: A reassessment based
on pharmacokinetics. Antioxid Redox Signal. 19:2141–2156. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|