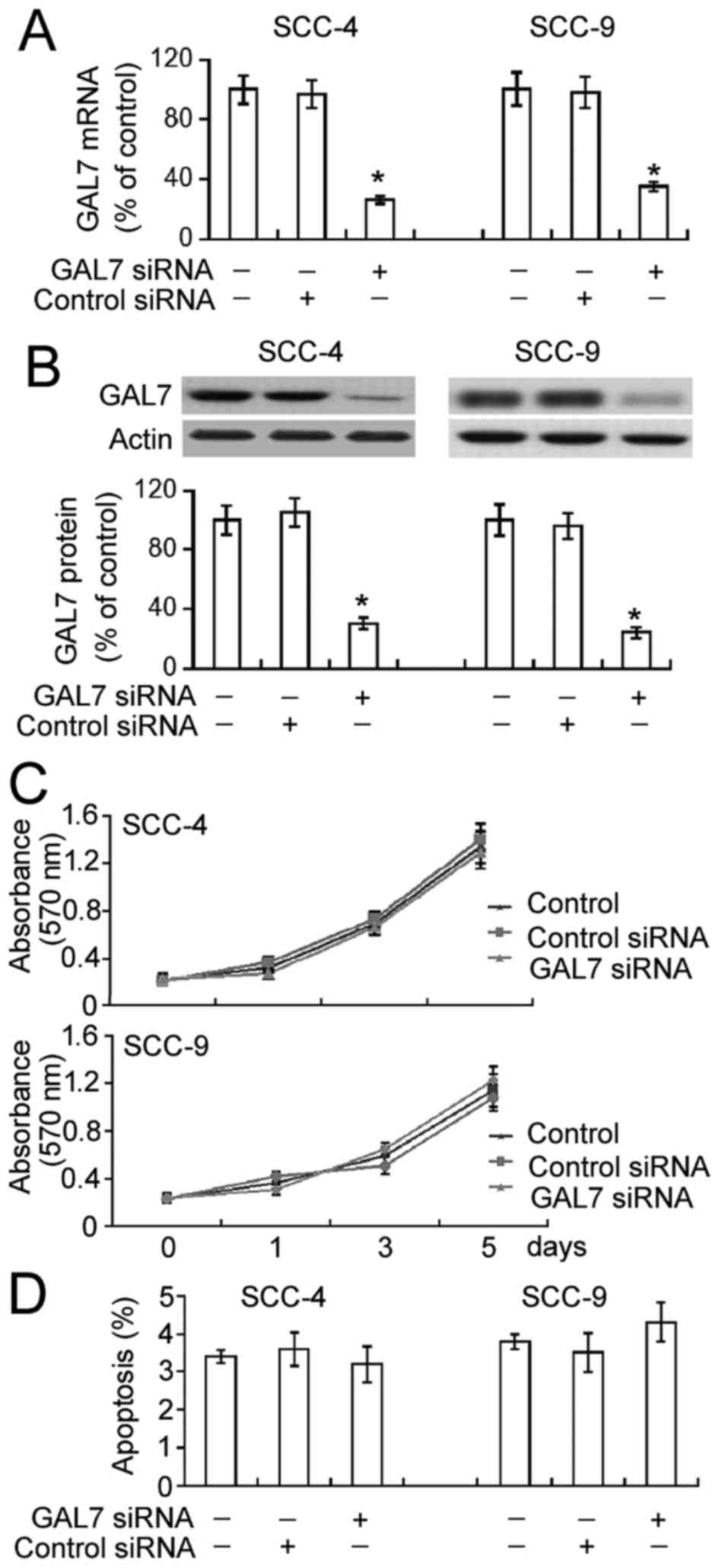
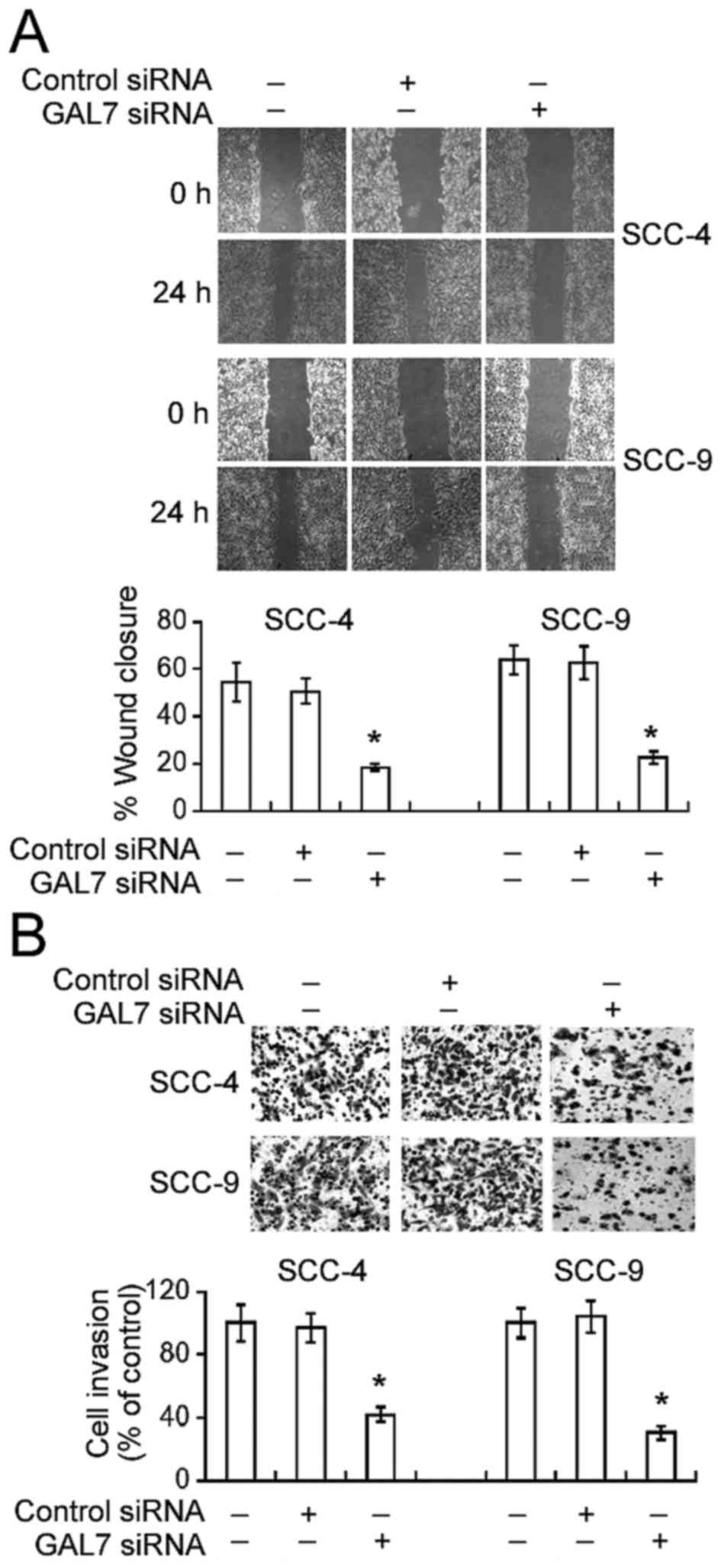
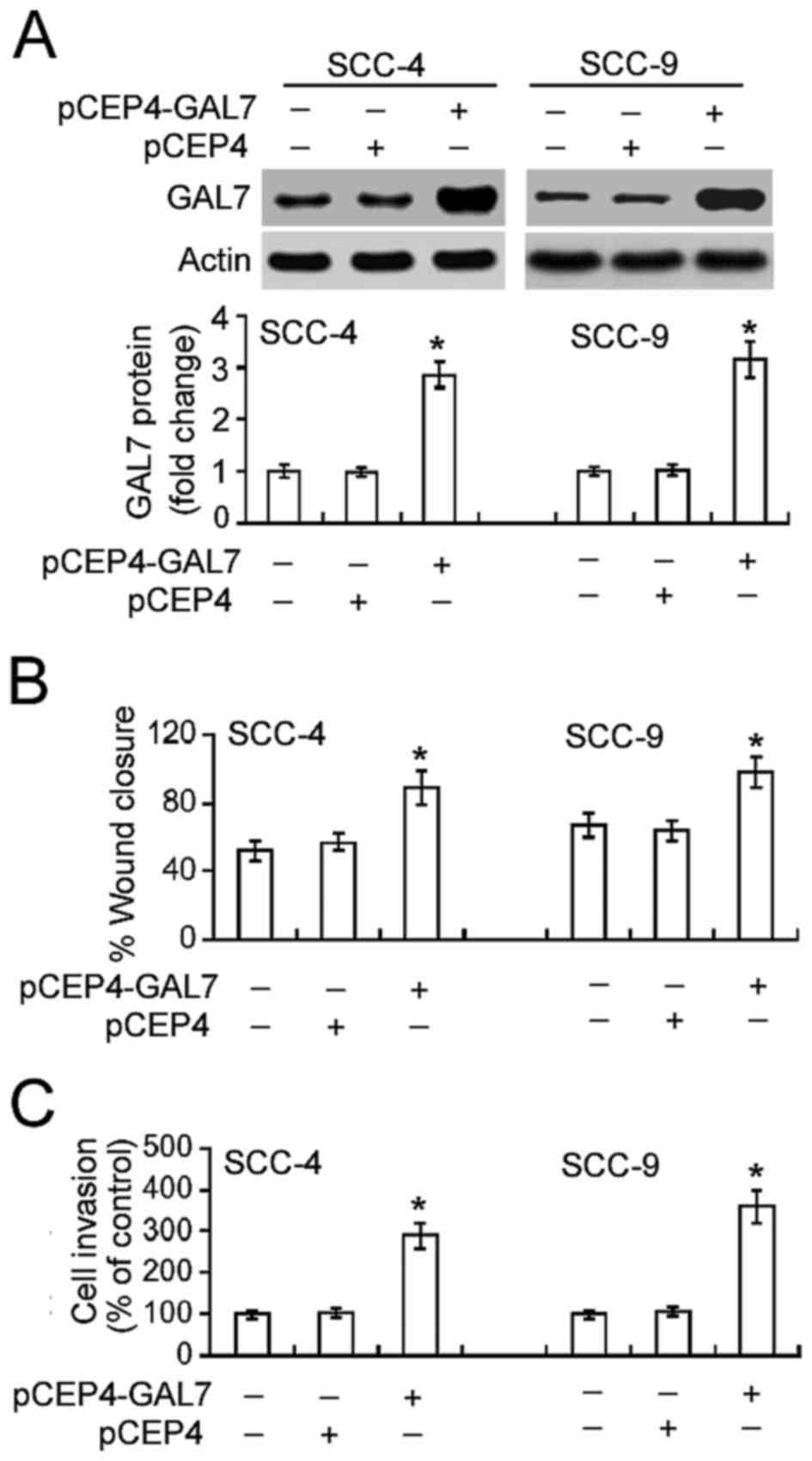
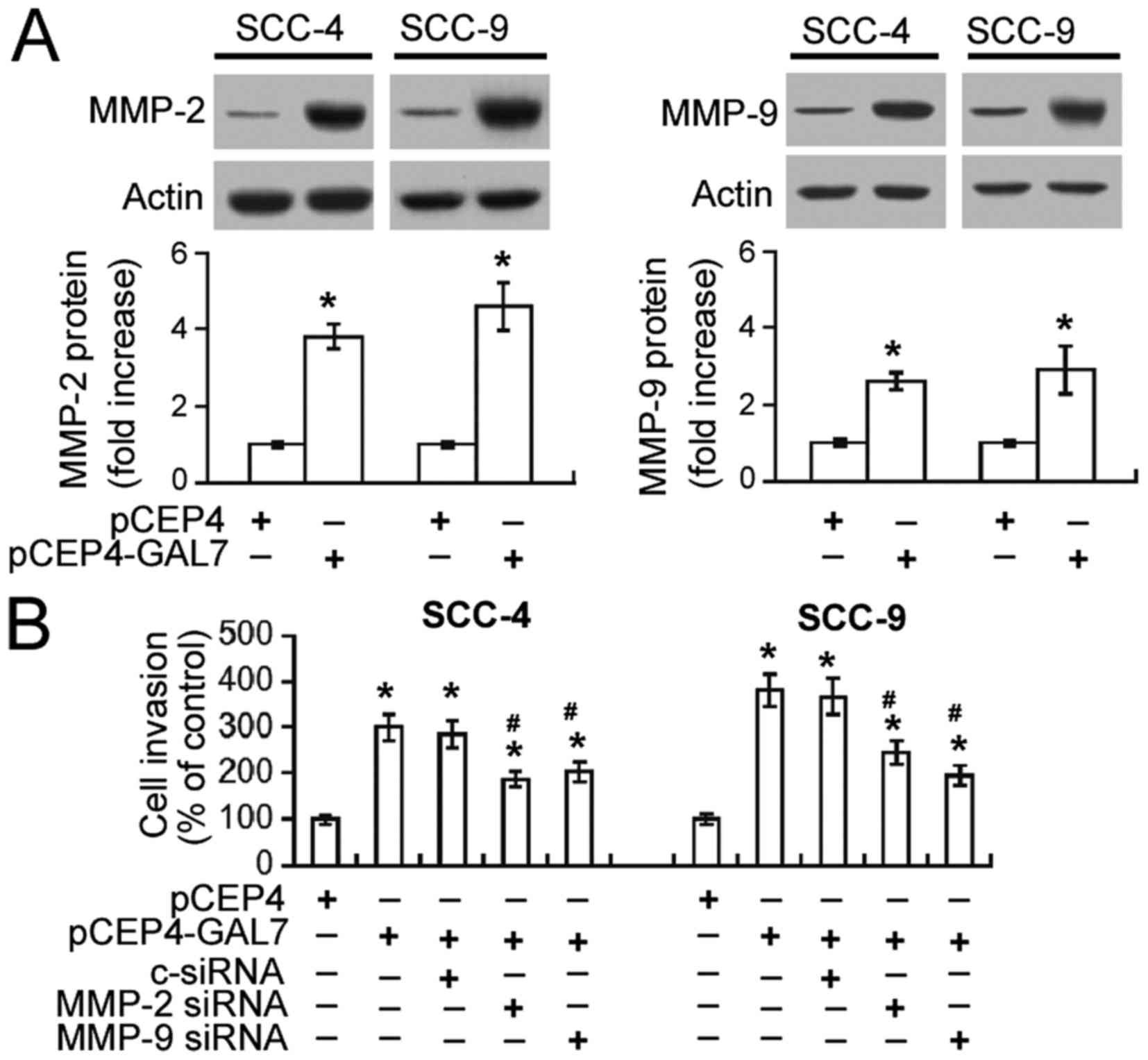
|
1
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ziober AF, Falls EM and Ziober BL: The
extracellular matrix in oral squamous cell carcinoma: Friend or
foe? Head Neck. 28:740–749. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Künzel J, Mantsopoulos K, Psychogios G,
Grundtner P, Koch M and Iro H: Lymph node ratio as a valuable
additional predictor of outcome in selected patients with oral
cavity cancer. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol.
117:677–684. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kim SY, Nam SY, Choi SH, Cho KJ and Roh
JL: Prognostic value of lymph node density in node-positive
patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol.
18:2310–2317. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sasahira T, Kirita T and Kuniyasu H:
Update of molecular pathobiology in oral cancer: A review. Int J
Clin Oncol. 19:431–436. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Magnaldo T, Fowlis D and Darmon M:
Galectin-7, a marker of all types of stratified epithelia.
Differentiation. 63:159–168. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Rondanino C, Poland PA, Kinlough CL, Li H,
Rbaibi Y, Myerburg MM, Al-bataineh MM, Kashlan OB, Pastor-Soler NM,
Hallows KR, et al: Galectin-7 modulates the length of the primary
cilia and wound repair in polarized kidney epithelial cells. Am J
Physiol Renal Physiol. 301:F622–F633. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
St-Pierre Y, Campion CG and Grosset AA: A
distinctive role for galectin-7 in cancer? Front Biosci (Landmark
Ed). 17:438–450. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kim SJ, Hwang JA, Ro JY, Lee YS and Chun
KH: Galectin-7 is epigenetically-regulated tumor suppressor in
gastric cancer. Oncotarget. 4:1461–1471. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Demers M, Rose AA, Grosset AA, Biron-Pain
K, Gaboury L, Siegel PM and St-Pierre Y: Overexpression of
galectin-7, a myoepithelial cell marker, enhances spontaneous
metastasis of breast cancer cells. Am J Pathol. 176:3023–3031.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Labrie M, Vladoiu MC, Grosset AA, Gaboury
L and St-Pierre Y: Expression and functions of galectin-7 in
ovarian cancer. Oncotarget. 5:7705–7721. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Park JE, Chang WY and Cho M: Induction of
matrix metalloproteinase-9 by galectin-7 through p38 MAPK signaling
in HeLa human cervical epithelial adenocarcinoma cells. Oncol Rep.
22:1373–1379. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Patel BP, Shah PM, Rawal UM, Desai AA,
Shah SV, Rawal RM and Patel PS: Activation of MMP-2 and MMP-9 in
patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma. J Surg Oncol. 90:81–88.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Thomas GT, Lewis MP and Speight PM: Matrix
metalloproteinases and oral cancer. Oral Oncol. 35:227–233. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Alves PM, Godoy GP, Gomes DQ, Medeiros AM,
de Souza LB, da Silveira EJ, Vasconcelos MG and Queiroz LM:
Significance of galectins-1, −3, −4 and −7 in the progression of
squamous cell carcinoma of the tongue. Pathol Res Pract.
207:236–240. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Demers M, Biron-Pain K, Hébert J, Lamarre
A, Magnaldo T and St-Pierre Y: Galectin-7 in lymphoma: Elevated
expression in human lymphoid malignancies and decreased lymphoma
dissemination by antisense strategies in experimental model. Cancer
Res. 67:2824–2829. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Giulietti A, Overbergh L, Valckx D,
Decallonne B, Bouillon R and Mathieu C: An overview of real-time
quantitative PCR: Applications to quantify cytokine gene
expression. Methods. 25:386–401. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Matsukawa S, Morita K, Negishi A, Harada
H, Nakajima Y, Shimamoto H, Tomioka H, Tanaka K, Ono M, Yamada T
and Omura K: Galectin-7 as a potential predictive marker of chemo-
and/or radio-therapy resistance in oral squamous cell carcinoma.
Cancer Med. 3:349–361. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ueda S, Kuwabara I and Liu FT: Suppression
of tumor growth by galectin-7 gene transfer. Cancer Res.
64:5672–5676. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kim HJ, Jeon HK, Lee JK, Sung CO, Do IG,
Choi CH, Kim TJ, Kim BG, Bae DS and Lee JW: Clinical significance
of galectin-7 in epithelial ovarian cancer. Anticancer Res.
33:1555–1561. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Demers M, Magnaldo T and St-Pierre Y: A
novel function for galectin-7: Promoting tumorigenesis by
up-regulating MMP-9 gene expression. Cancer Res. 65:5205–5210.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bedal KB, Grässel S, Oefner PJ, Reinders
J, Reichert TE and Bauer R: Collagen XVI induces expression of MMP9
via modulation of AP-1 transcription factors and facilitates
invasion of oral squamous cell carcinoma. PLoS One. 9:e867772014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Chou CK, Wu CY, Chen JY, Ng MC, Wang HM,
Chen JH, Yuan SS, Tsai EM, Chang JG and Chiu CC: BubR1 acts as a
promoter in cellular motility of human oral squamous cancer cells
through regulating MMP-2 and MMP-9. Int J Mol Sci. 16:15104–15117.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lee AY, Fan CC, Chen YA, Cheng CW, Sung
YJ, Hsu CP and Kao TY: Curcumin inhibits invasiveness and
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in oral squamous cell carcinoma
through reducing matrix metalloproteinase 2, 9 and modulating
p53-E-cadherin pathway. Integr Cancer Ther. 14:484–490. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Liu FY, Safdar J, Li ZN, Fang QG, Zhang X,
Xu ZF and Sun CF: CCR7 regulates cell migration and invasion
through MAPKs in metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of head and
neck. Int J Oncol. 45:2502–2510. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chen PN, Hsieh YS, Chiang CL, Chiou HL,
Yang SF and Chu SC: Silibinin inhibits invasion of oral cancer
cells by suppressing the MAPK pathway. J Dent Res. 85:220–225.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|