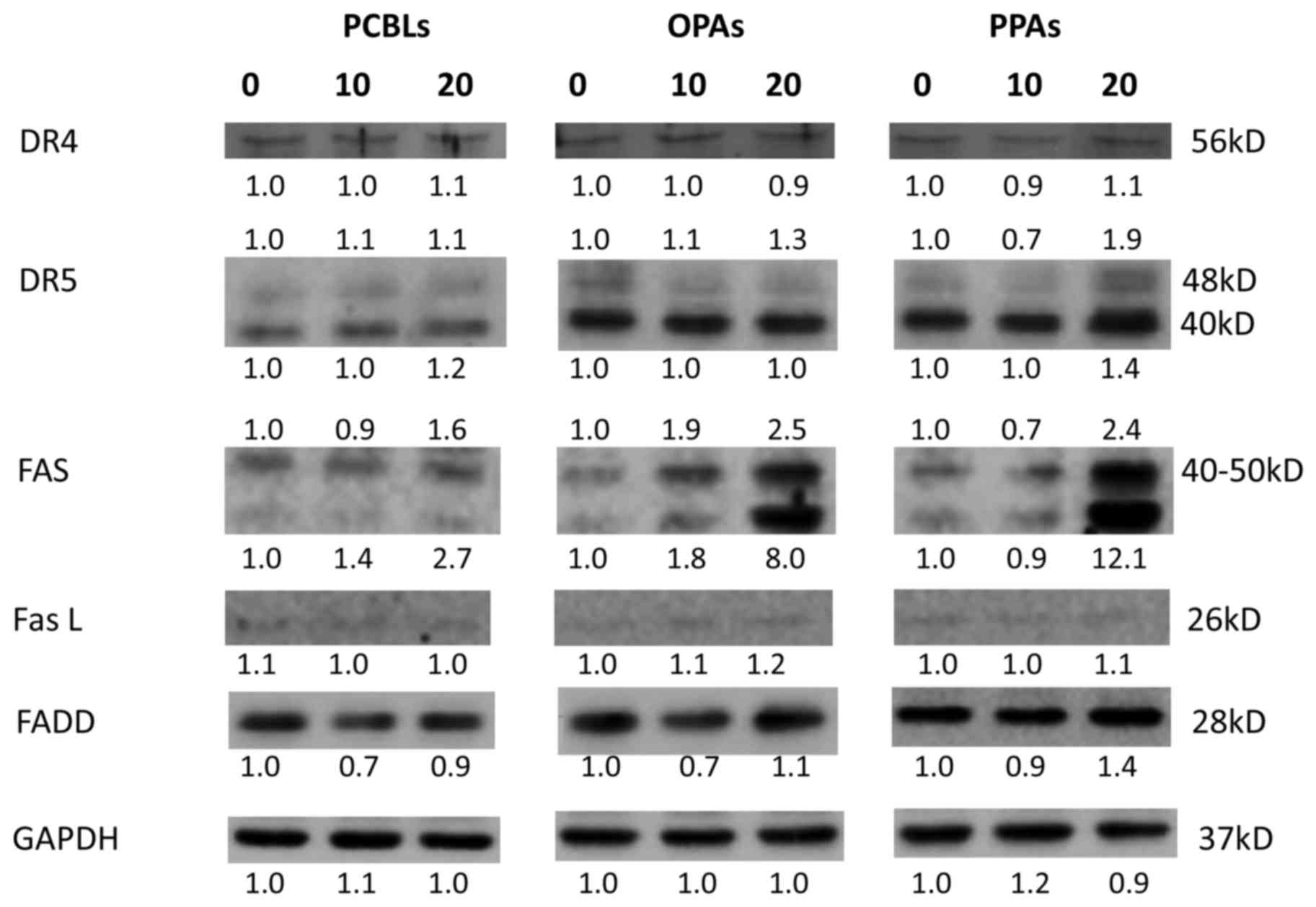
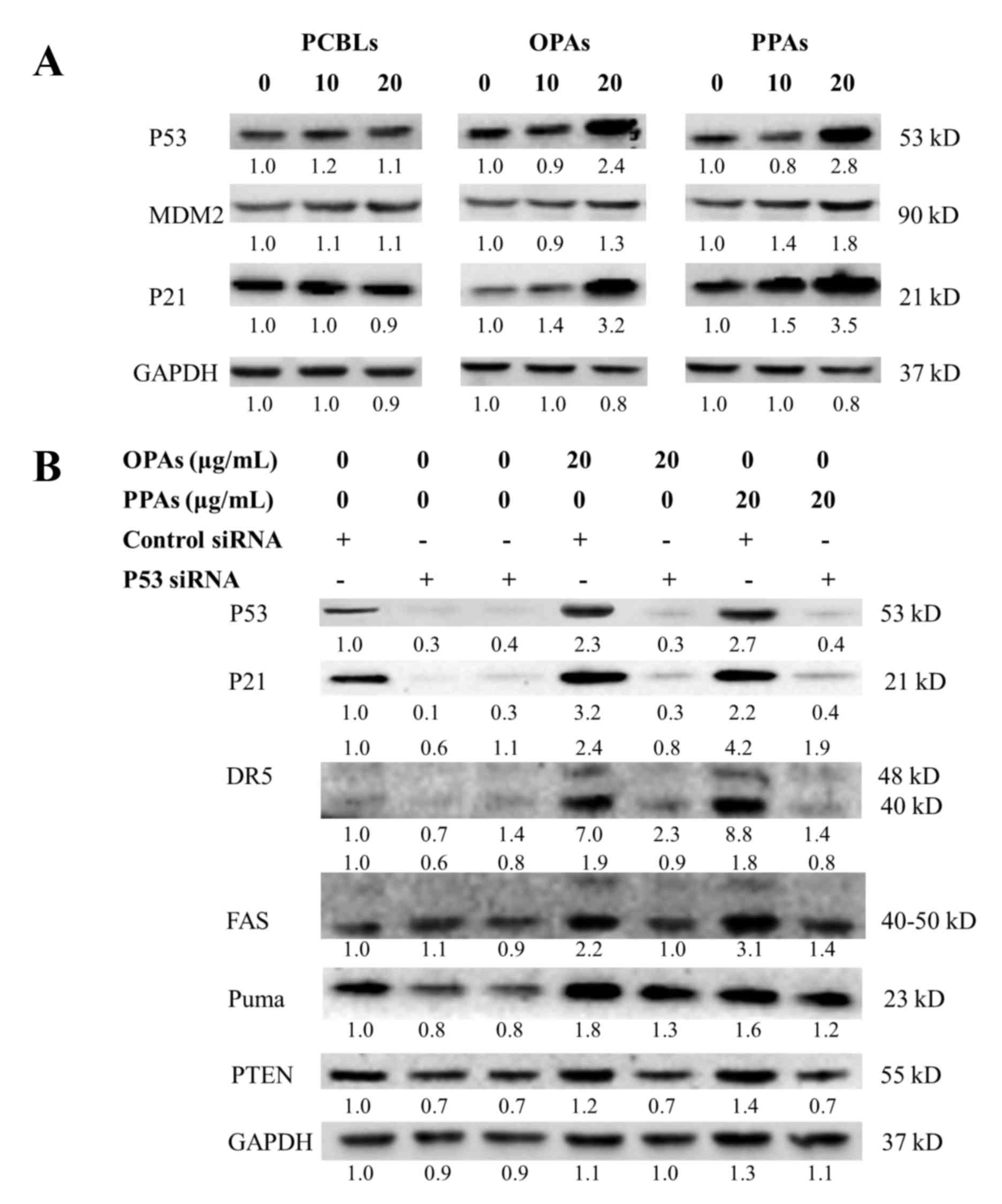
|
1
|
Nandakumar V, Singh T and Katiyar SK:
Multi-targeted prevention and therapy of cancer by
proanthocyanidins. Cancer Lett. 269:378–387. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Prior RL and Gu L: Occurrence and
biological significance of proanthocyanidins in the American diet.
Phytochemistry. 66:2264–2280. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
de la Iglesia R, Milagro FI, Campión J,
Boqué N and Martínez JA: Healthy properties of proanthocyanidins.
Biofactors. 36:159–168. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chen K, Xu C, Zhang B and Ferguson IB: Red
bayberry: Botany and horticulture. Horticultural Rev. 30:83–114.
2004.
|
|
5
|
Zhang SM, Gao ZS, Xu CJ and Chen KS:
Genetic diversity of Chinese bayberry (Myrica rubra Sieb. et
Zucc.) accessions revealed by amplified fragment length
polymorphism. Hort Sci. 44:487–491. 2009.
|
|
6
|
Fu Y, Qiao L, Cao Y, Zhou X, Liu Y and Ye
X: Structural elucidation and antioxidant activities of
proanthocyanidins from Chinese bayberry (Myrica rubra Sieb.
et Zucc.) leaves. PLoS One. 9:e961622014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yang H, Ye X, Liu D, Chen J, Zhang J, Shen
Y and Yu D: Characterization of unusual proanthocyanidins in leaves
of bayberry (Myrica rubra Sieb. et Zucc.). J Agric Food
Chem. 59:1622–1629. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Miura T, Chiba M, Kasai K, Nozaka H,
Nakamura T, Shoji T, Kanda T, Ohtake Y and Sato T: Apple
procyanidins induce tumor cell apoptosis through mitochondrial
pathway activation of caspase-3. Carcinogenesis. 29:585–593. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Han MH, Lee WS, Jung JH, Jeong JH, Park C,
Kim HJ, Kim G, Jung JM, Kwon TK, Kim GY, et al: Polyphenols
isolated from Allium cepa L. induces apoptosis by suppressing IAP-1
through inhibiting PI3K/Akt signaling pathways in human leukemic
cells. Food Chem Toxicol. 62:382–389. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Dai GH, Meng GM, Tong YL, Chen X, Ren ZM,
Wang K and Yang F: Growth-inhibiting and apoptosis-inducing
activities of Myricanol from the bark of Myrica rubra in
human lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells. Phytomedicine. 21:1490–1496.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kaur M, Mandair R, Agarwal R and Agarwal
C: Grape seed extract induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in
human colon carcinoma cells. Nutr Cancer. 60:(Suppl 1). S2–S11.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Kroemer G and Martin SJ:
Caspase-independent cell death. Nat Med. 11:725–730. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Huang C, Ma WY, Goranson A and Dong Z:
Resveratrol suppresses cell transformation and induces apoptosis
through a p53-dependent pathway. Carcinogenesis. 20:237–242. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Guan YQ, Li Z, Yang A, Huang Z, Zheng Z,
Zhang L, Li L and Liu JM: Cell cycle arrest and apoptosis of
OVCAR-3 and MCF-7 cells induced by co-immobilized TNF-α plus IFN-γ
on polystyrene and the role of p53 activation. Biomaterials.
33:6162–6171. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lin HY, Delmas D, Vang O, Hsieh TC, Lin S,
Cheng GY, Chiang HL, Chen CE, Tang HY, Crawford DR, et al:
Mechanisms of ceramide-induced COX-2-dependent apoptosis in human
ovarian cancer OVCAR-3 cells partially overlapped with resveratrol.
J Cell Biochem. 114:1940–1954. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Li B, Gao Y, Rankin GO, Rojanasakul Y,
Cutler SJ, Tu Y and Chen YC: Chaetoglobosin K induces apoptosis and
G2 cell cycle arrest through p53-dependent pathway in
cisplatin-resistant ovarian cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 356:418–433.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yang X, Fraser M, Moll UM, Basak A and
Tsang BK: Akt-mediated cisplatin resistance in ovarian cancer:
Modulation of p53 action on caspase-dependent mitochondrial death
pathway. Cancer Res. 66:3126–3136. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Xia M, Knezevic D and Vassilev LT: p21
does not protect cancer cells from apoptosis induced by
nongenotoxic p53 activation. Oncogene. 30:346–355. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hsu CP, Lin YH, Chou CC, Zhou SP, Hsu YC,
Liu CL, Ku FM and Chung YC: Mechanisms of grape seed
procyanidin-induced apoptosis in colorectal carcinoma cells.
Anticancer Res. 29:283–289. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Singh T, Sharma SD and Katiyar SK: Grape
proanthocyanidins induce apoptosis by loss of mitochondrial
membrane potential of human non-small cell lung cancer cells in
vitro and in vivo. PLoS One. 6:e274442011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Dinicola S, Cucina A, Antonacci D and
Bizzarri M: Anticancer effects of grape seed extract on human
cancers: A review. J Carcinogenesis Mutagenesis. 8:60–70. 2014.
|
|
22
|
Dinicola S, Cucina A, Pasqualato A,
D'Anselmi F, Proietti S, Lisi E, Pasqua G, Antonacci D and Bizzarri
M: Antiproliferative and apoptotic effects triggered by Grape Seed
Extract (GSE) versus epigallocatechin and procyanidins on colon
cancer cell lines. Int J Mol Sci. 13:651–664. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Prasad R and Katiyar SK: Bioactive
phytochemical proanthocyanidins inhibit growth of head and neck
squamous cell carcinoma cells by targeting multiple signaling
molecules. PLoS One. 7:e464042012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Deprez S, Mila I, Huneau JF, Tome D and
Scalbert A: Transport of proanthocyanidin dimer, trimer, and
polymer across monolayers of human intestinal epithelial Caco-2
cells. Antioxid Redox Signal. 3:957–967. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Faria A, Mateus N, de Freitas V and Calhau
C: Modulation of MPP+ uptake by procyanidins in Caco-2 cells:
Involvement of oxidation/reduction reactions. FEBS Lett.
580:155–160. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|