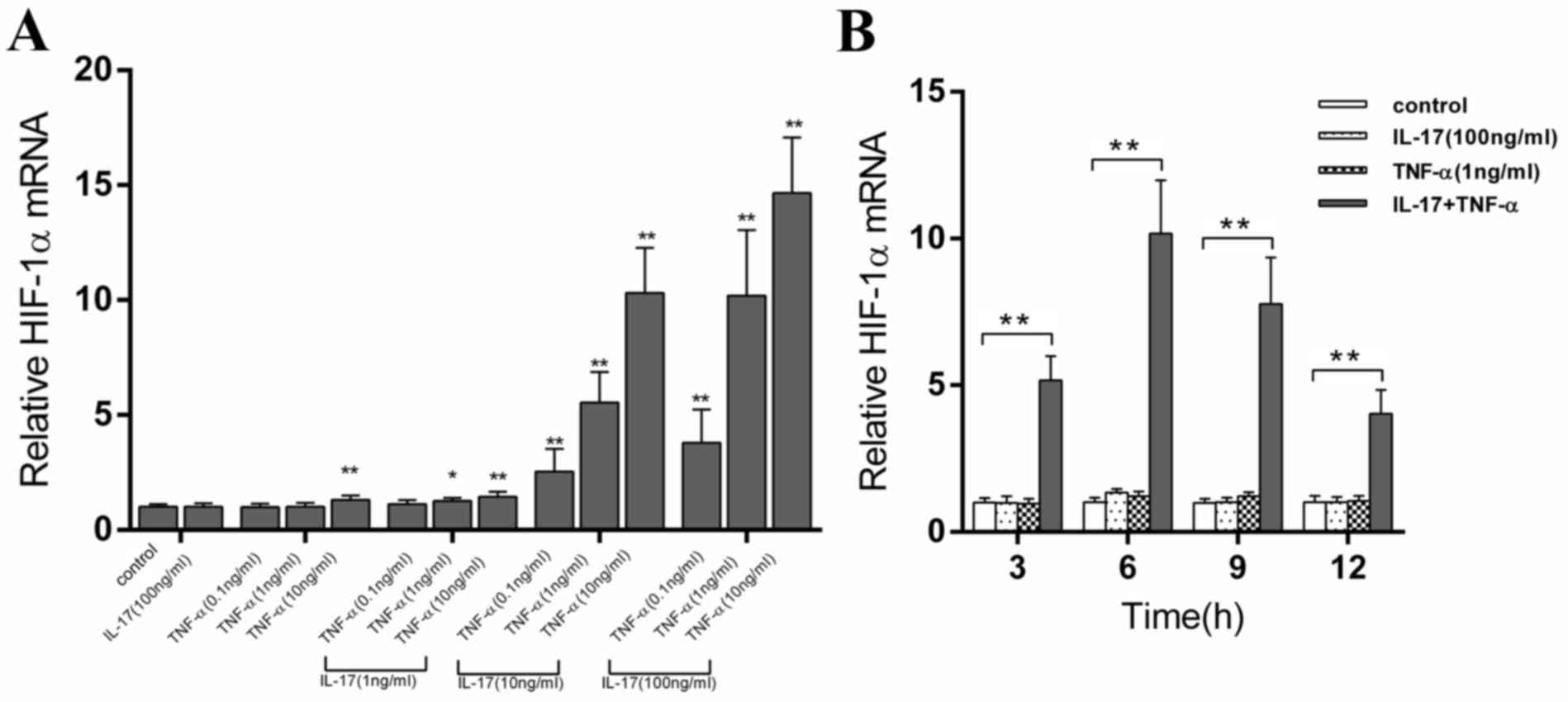
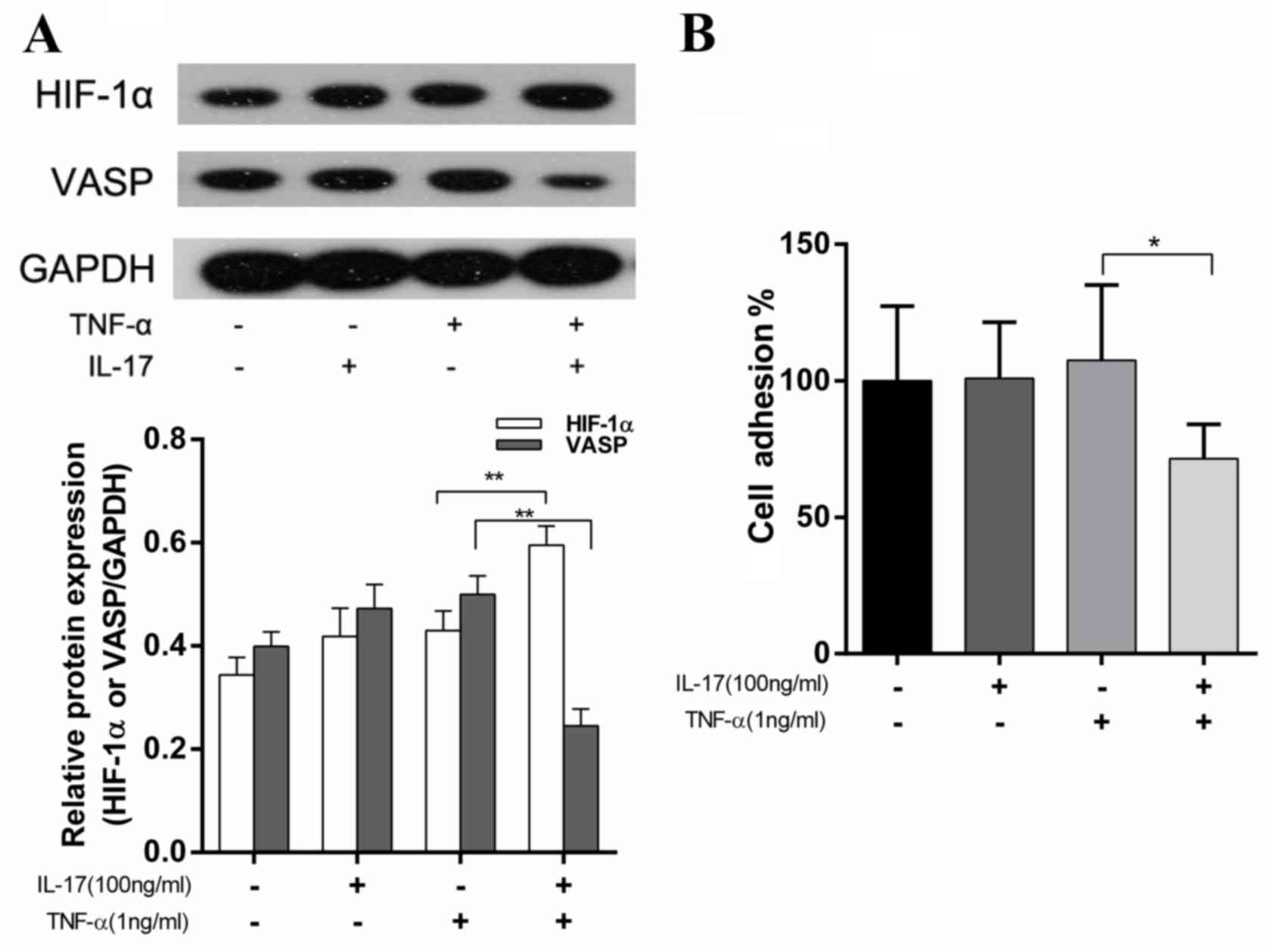
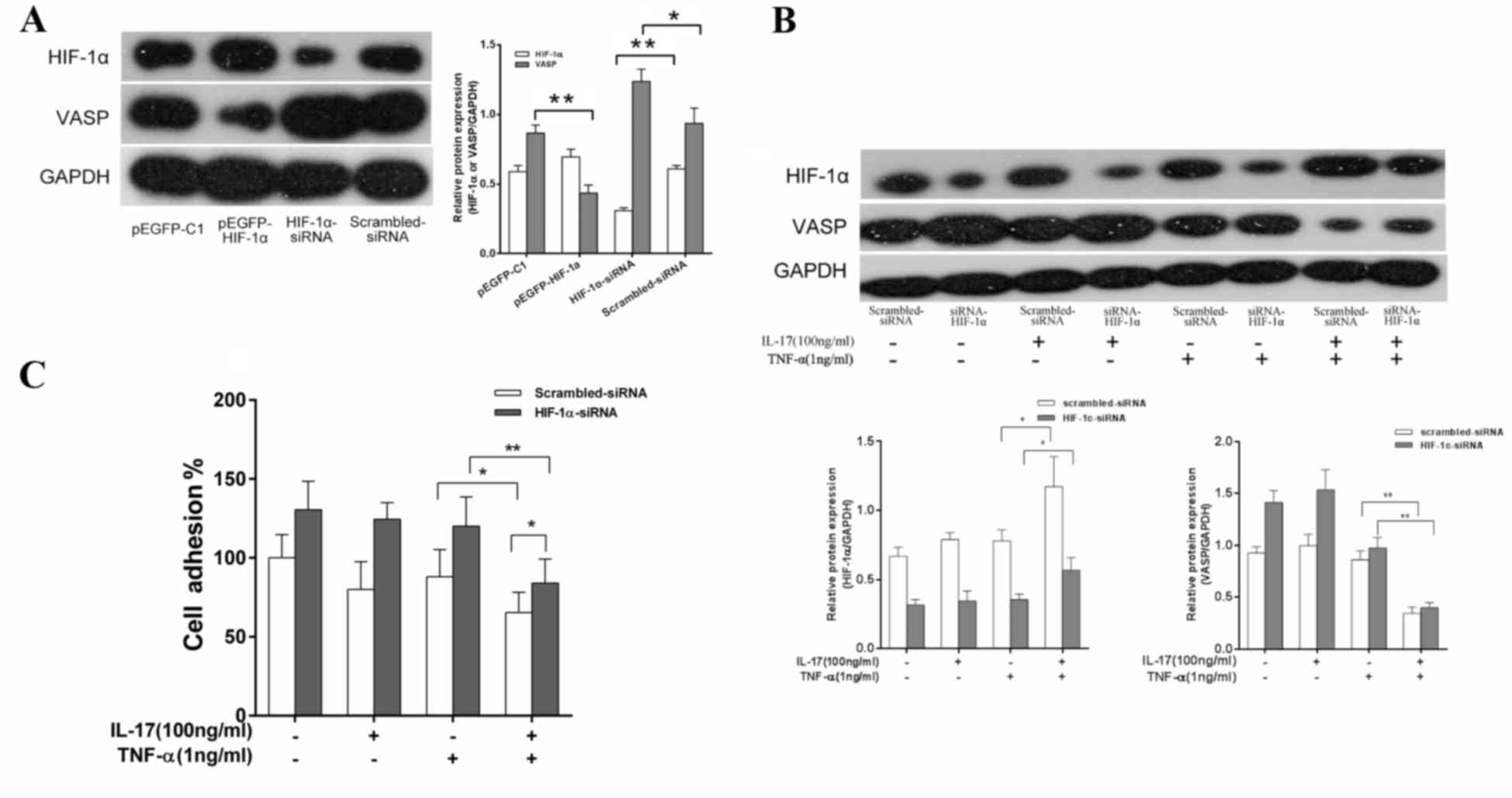
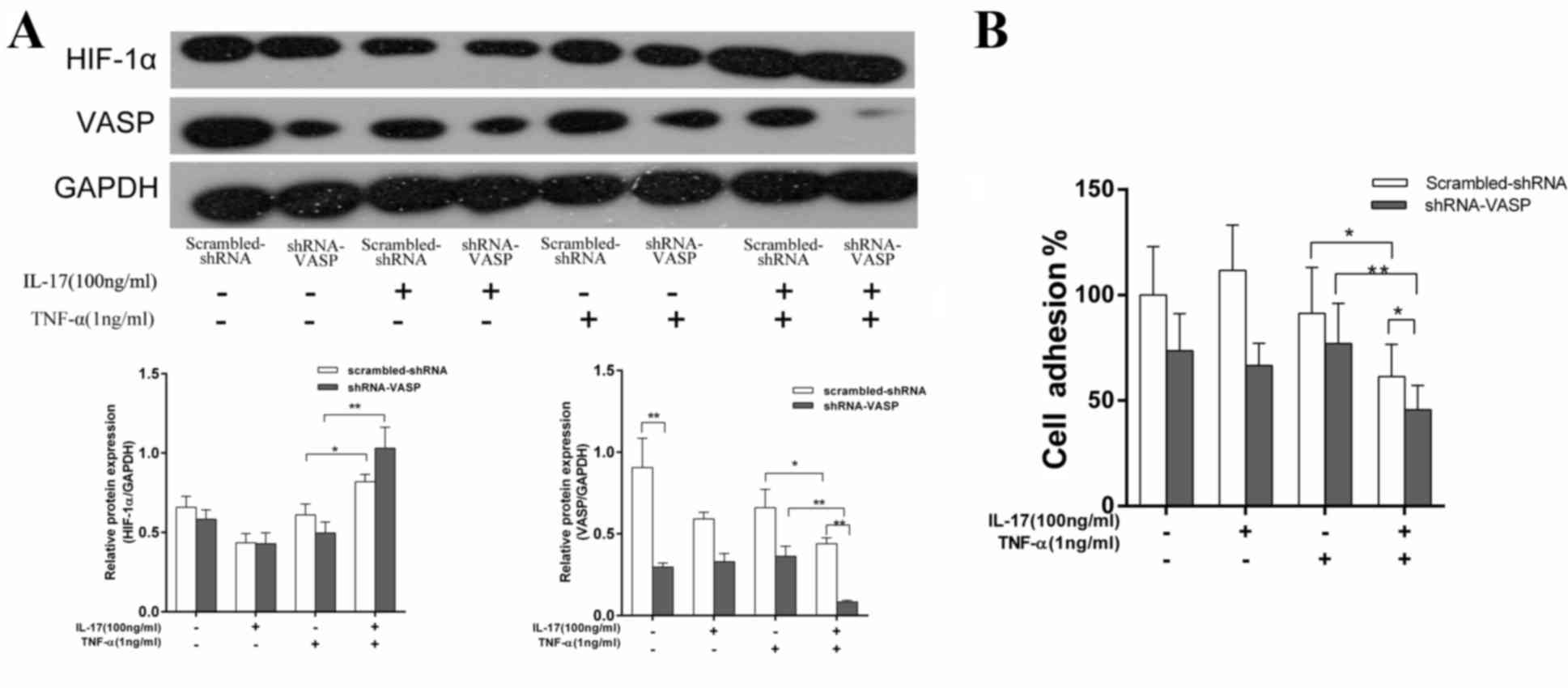
|
1
|
van Horssen R, Ten Hagen TL and Eggermont
AM: TNF-alpha in cancer treatment: Molecular insights, antitumor
effects, and clinical utility. Oncologist. 11:397–408. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wilt SG, Milward E, Zhou JM, Nagasato K,
Patton H, Rusten R, Griffin DE, O'Connor M and Dubois-Dalcq M: In
vitro evidence for a dual role of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in
human immunodeficiency virus type 1 encephalopathy. Ann Neurol.
37:381–394. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Han YP, Nien YD and Garner WL: Tumor
necrosis factor-alpha-induced proteolytic activation of pro-matrix
metalloproteinase-9 by human skin is controlled by down-regulating
tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 and mediated by
tissue-associated chymotrypsin-like proteinase. J Biol Chem.
277:27319–27327. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Jammal MP, DA Silva AA, Filho AM, DE
Castro Côbo E, Adad SJ, Murta EF and Nomelini RS:
Immunohistochemical staining of tumor necrosis factor-α and
interleukin-10 in benign and malignant ovarian neoplasms. Oncol
Lett. 9:979–983. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zhu N, Lalla R, Eves P, Brown TL, King A,
Kemp EH, Haycock JW and MacNeil S: Melanoma cell migration is
upregulated by tumour necrosis factor-alpha and suppressed by
alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone. Br J Cancer. 90:1457–1463.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chen M and Geng JG: P-selectin mediates
adhesion of leukocytes, platelets, and cancer cells in
inflammation, thrombosis, and cancer growth and metastasis. Arch
Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 54:75–84. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Fujino S, Andoh A, Bamba S, Ogawa A, Hata
K, Araki Y, Bamba T and Fujiyama Y: Increased expression of
interleukin 17 in inflammatory bowel disease. Gut. 52:65–70. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tzartos JS, Friese MA, Craner MJ, Palace
J, Newcombe J, Esiri MM and Fugger L: Interleukin-17 production in
central nervous system-infiltrating T cells and glial cells is
associated with active disease in multiple sclerosis. Am J Pathol.
172:146–155. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chabaud M, Garnero P, Dayer JM, Guerne PA,
Fossiez F and Miossec P: Contribution of interleukin 17 to synovium
matrix destruction in rheumatoid arthritis. Cytokine. 12:1092–1099.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wilke CM, Kryczek I, Wei S, Zhao E, Wu K,
Wang G and Zou W: Th17 cells in cancer: Help or hindrance?
Carcinogenesis. 32:643–649. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wilke CM, Bishop K, Fox D and Zou W:
Deciphering the role of Th17 cells in human disease. Trends
Immunol. 32:603–611. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hu J, Ye H, Zhang D, Liu W, Li M, Mao Y
and Lu Y: U87MG glioma cells overexpressing IL-17 acclerate
early-stage growth and cause a higher level of CD31 mRNA expression
in tumor tissues. Oncol Lett. 6:993–999. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hot A, Zrioual S, Lenief V and Miossec P:
IL-17 and tumour necrosis factor alpha combination induces a
HIF-1α-dependent invasive phenotype in synoviocytes. Ann Rheum Dis.
71:1393–1401. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Karlsen JR, Borregaard N and Cowland JB:
Induction of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin expression
by co-stimulation with interleukin-17 and tumor necrosis
factor-alpha is controlled by IkappaB-zeta but neither by
C/EBP-beta nor C/EBP-delta. J Biol Chem. 285:14088–14100. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Andoh A, Yasui H, Inatomi O, Zhang Z,
Deguchi Y, Hata K, Araki Y, Tsujikawa T, Kitoh K, Kim-Mitsuyama S,
et al: Interleukin-17 augments tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced
granulocyte and granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor
release from human colonic myofibroblasts. J Gastroenterol.
40:802–810. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Numasaki M, Lotze MT and Sasaki H:
Interleukin-17 augments tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced
elaboration of proangiogenic factors from fibroblasts. Immunol
Lett. 93:39–43. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hamilton T, Li X, Novotny M, Pavicic PG
Jr, Datta S, Zhao C, Hartupee J and Sun D: Cell type- and
stimulus-specific mechanisms for post-transcriptional control of
neutrophil chemokine gene expression. J Leukoc Biol. 91:377–383.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Koenders MI, Marijnissen RJ, Devesa I,
Lubberts E, Joosten LA, Roth J, van Lent PL, van de Loo FA and van
den Berg WB: Tumor necrosis factor-interleukin-17 interplay induces
S100A8, interleukin-1β, and matrix metalloproteinases, and drives
irreversible cartilage destruction in murine arthritis: Rationale
for combination treatment during arthritis. Arthritis Rheum.
63:2329–2339. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chiricozzi A, Guttman-Yassky E,
Suárez-Fariñas M, Nograles KE, Tian S, Cardinale I, Chimenti S and
Krueger JG: Integrative responses to IL-17 and TNF-alpha in human
keratinocytes account for key inflammatory pathogenic circuits in
psoriasis. The Journal of investigative dermatology. 131:677–687.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Barzik M, Kotova TI, Higgs HN, Hazelwood
L, Hanein D, Gertler FB and Schafer DA: Ena/VASP proteins enhance
actin polymerization in the presence of barbed end capping
proteins. J Biol Chem. 280:28653–28662. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Schirenbeck A, Arasada R, Bretschneider T,
Stradal TE, Schleicher M and Faix J: The bundling activity of
vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein is required for filopodium
formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:7694–7699. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Krause M, Dent EW, Bear JE, Loureiro JJ
and Gertler FB: Ena/VASP proteins: Regulators of the actin
cytoskeleton and cell migration. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol.
19:541–564. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Dertsiz L, Ozbilim G, Kayisli Y, Gokhan
GA, Demircan A and Kayisli UA: Differential expression of VASP in
normal lung tissue and lung adenocarcinomas. Thorax. 60:576–581.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Su K, Tian Y, Wang J, Shi W, Luo D, Liu J,
Tong Z, Wu J, Zhang J and Wei L: HIF-1alpha acts downstream of
TNF-α to inhibit vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein expression
and modulates the adhesion and proliferation of breast cancer
cells. DNA Cell Biol. 31:1078–1087. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Tang M, Tian Y, Li D, Lv J, Li Q, Kuang C,
Hu P, Wang Y, Wang J, Su K and Wei L: TNF-α mediated increase of
HIF-1α inhibits VASP expression, which reduces alveolar-capillary
barrier function during acute lung injury (ALI). PloS One.
9:e1029672014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wang J, Zhang J, Wu J, Luo D, Su K, Shi W,
Liu J, Tian Y and Wei L: MicroRNA-610 inhibits the migration and
invasion of gastric cancer cells by suppressing the expression of
vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein. Eur J Cancer. 48:1904–1913.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kato R, Ishikawa T, Kamiya S, Oguma F,
Ueki M, Goto S, Nakamura H, Katayama T and Fukai F: A new type of
antimetastatic peptide derived from fibronectin. Clin Cancer Res.
8:2455–2462. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Galler AB, Arguinzonis Garcia MI,
Baumgartner W, Kuhn M, Smolenski A, Simm A and Reinhard M:
VASP-dependent regulation of actin cytoskeleton rigidity, cell
adhesion, and detachment. Histochem Cell Biol. 125:457–474. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Straus DS: TNFα and IL-17 cooperatively
stimulate glucose metabolism and growth factor production in human
colorectal cancer cells. Mol Cancer. 12:782013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Stroka KM and Konstantopoulos K: Physical
biology in cancer. 4. Physical cues guide tumor cell adhesion and
migration. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 306:C98–C109. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Mareel M and Leroy A: Clinical, cellular,
and molecular aspects of cancer invasion. Physiol Rev. 83:337–376.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Bhatt T, Rizvi A, Batta SP, Kataria S and
Jamora C: Signaling and mechanical roles of E-cadherin. Cell Commun
Adhes. 20:189–199. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Le Clainche C and Carlier MF: Regulation
of actin assembly associated with protrusion and adhesion in cell
migration. Physiol Rev. 88:489–513. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Pula G and Krause M: Role of Ena/VASP
proteins in homeostasis and disease. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 39–65.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Lebrand C, Dent EW, Strasser GA, Lanier
LM, Krause M, Svitkina TM, Borisy GG and Gertler FB: Critical role
of Ena/VASP proteins for filopodia formation in neurons and in
function downstream of netrin-1. Neuron. 42:37–49. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Doppler H and Storz P: Regulation of VASP
by phosphorylation: consequences for cell migration. Cell Adh Migr.
7:482–486. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Bear JE and Gertler FB: Ena/VASP: Towards
resolving a pointed controversy at the barbed end. J Cell Sci.
122:1947–1953. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Trichet L, Sykes C and Plastino J:
Relaxing the actin cytoskeleton for adhesion and movement with
Ena/VASP. J Cell Biol. 181:19–25. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|