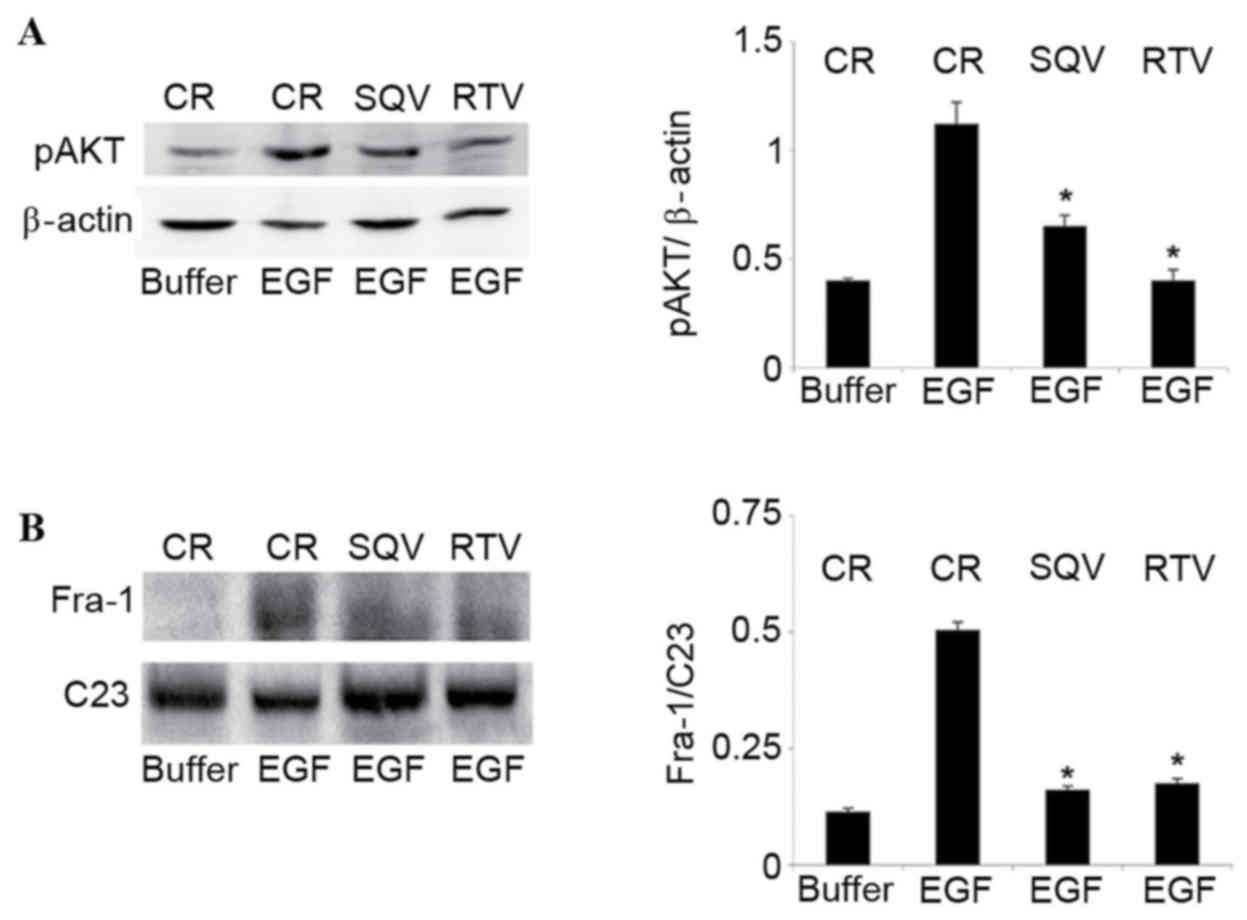
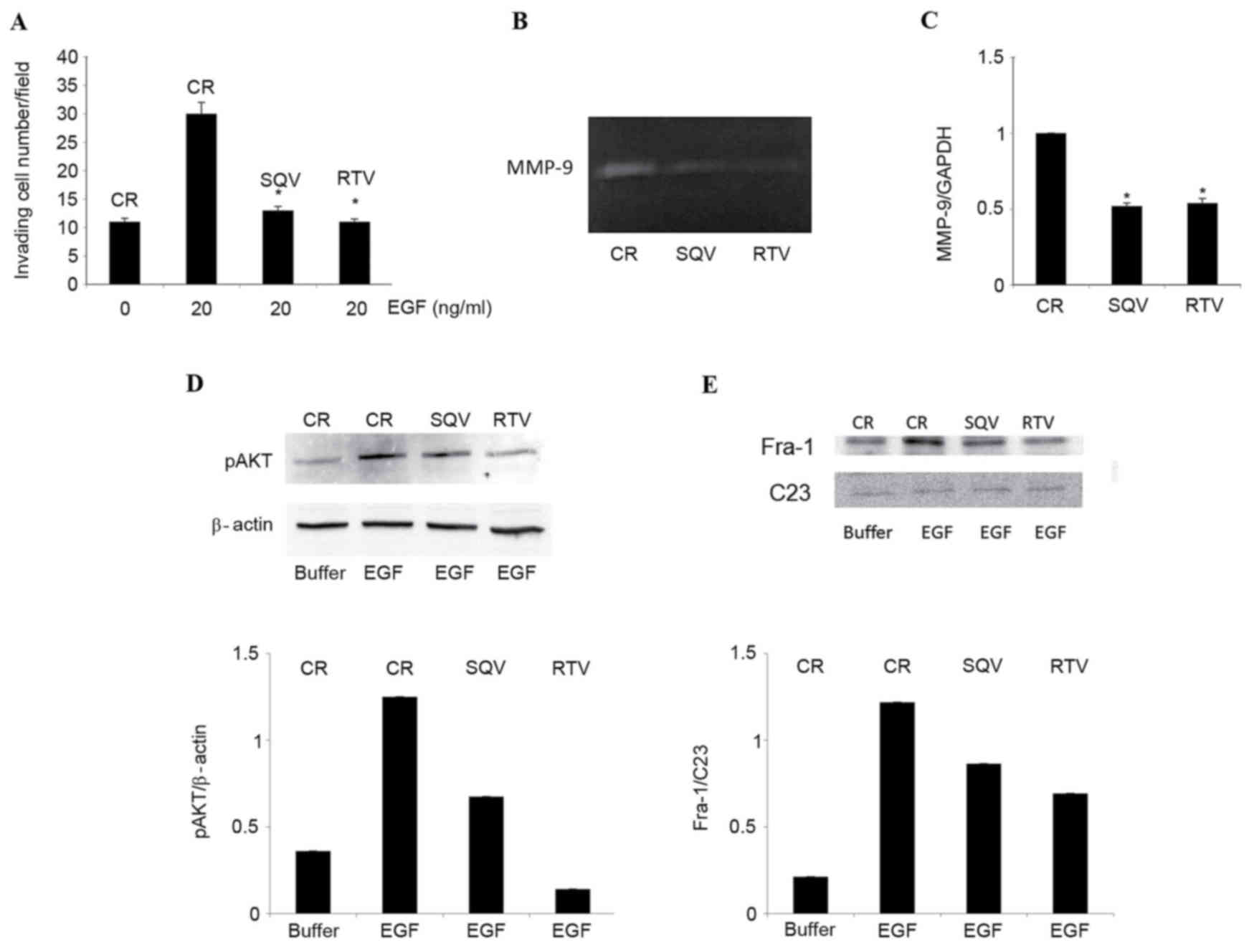
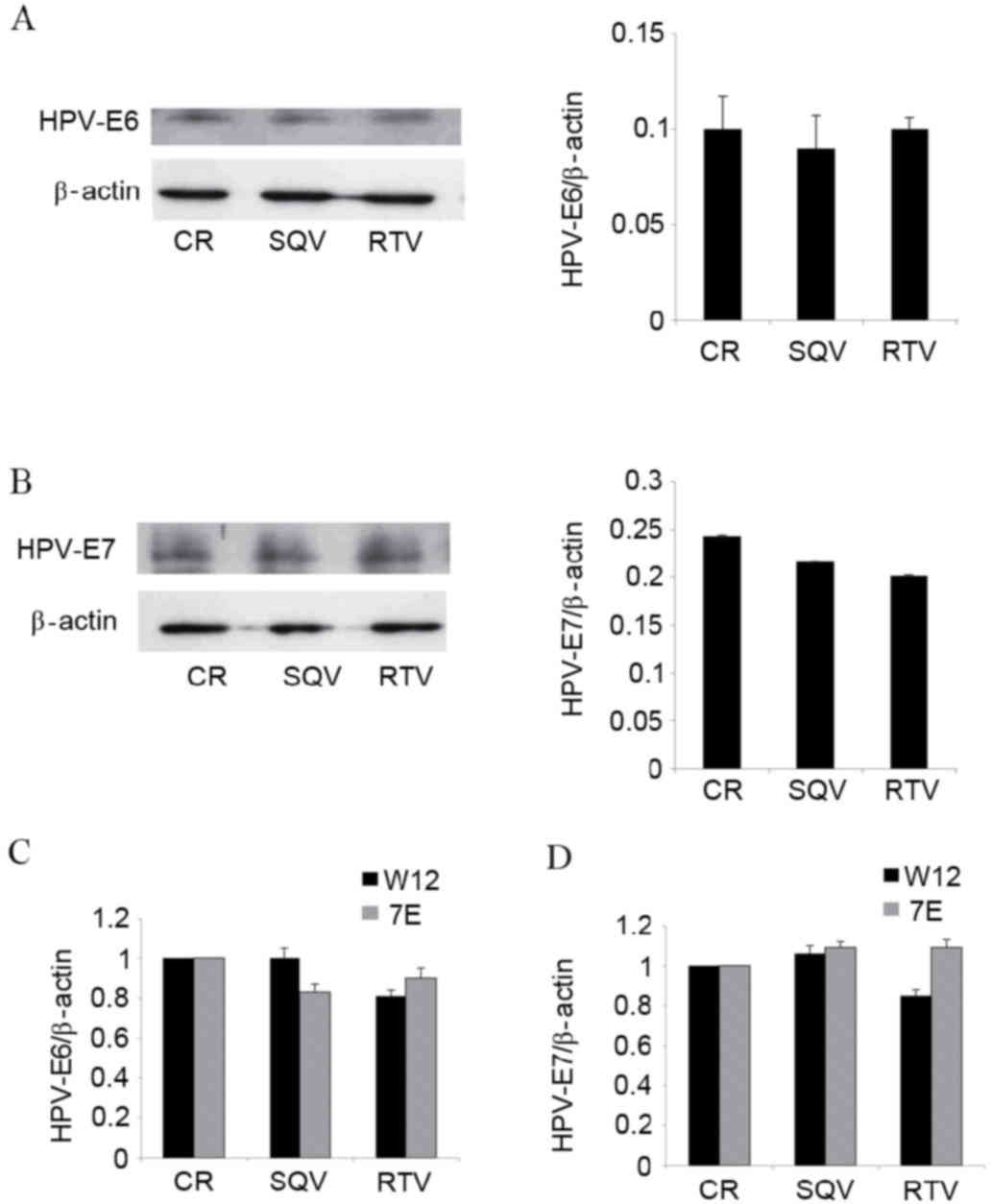
|
1
|
Denslow SA, Rositch AF, Firnhaber C, Ting
J and Smith JS: Incidence and progression of cervical lesions in
women with HIV: A systematic global review. Int J STD AIDS.
25:163–177. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Heard I, Schmitz V, Costagliola D, Orth G
and Kazatchkine MD: Early regression of cervical lesions in
HIV-seropositive women receiving highly active antiretroviral
therapy. AIDS. 12:1459–1464. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Omar T, Schwartz S, Hanrahan C,
Modisenyane T, Tshabangu N, Golub JE, McIntyre JA, Gray GE, Mohapi
L and Martinson NA: Progression and regression of premalignant
cervical lesions in HIV-infected women from Soweto: A prospective
cohort. AIDS. 25:87–94. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Blitz S, Baxter J, Raboud J, Walmsley S,
Rachlis A, Smaill F, Ferenczy A, Coutlée F, Hankins C and Money D:
Canadian Women's HIV Study Group: Evaluation of HIV and highly
active antiretroviral therapy on the natural history of human
papillomavirus infection and cervical cytopathologic findings in
HIV-positive and high-risk HIV-negative women. J Infect Dis.
208:454–462. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Barillari G, Iovane A, Bacigalupo I,
Palladino C, Bellino S, Leone P, Monini P and Ensoli B: Ritonavir
or saquinavir impairs the invasion of cervical intraepithelial
neoplasia cells via a reduction of MMP expression and activity.
AIDS. 26:909–919. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sgadari C, Barillari G, Toschi E, Carlei
D, Bacigalupo I, Baccarini S, Palladino C, Leone P, Bugarini R,
Malavasi L, et al: HIV protease inhibitors are potent
anti-angiogenic molecules and promote regression of Kaposi sarcoma.
Nat Med. 8:225–232. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Monini P, Sgadari C, Toschi E, Barillari G
and Ensoli B: Antitumour effects of antiretroviral therapy. Nat Rev
Cancer. 4:861–875. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Brunner TB, Geiger M, Grabenbauer GG,
Lang-Welzenbach M, Mantoni TS, Cavallaro A, Sauer R, Hohenberger W
and McKenna WG: Phase I trial of the human immunodeficiency virus
protease inhibitor nelfinavir and chemoradiation for locally
advanced pancreatic cancer. J Clin Oncol. 26:2699–2706. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Monini P, Sgadari C, Grosso MG, Bellino S,
Di Biagio A, Toschi E, Bacigalupo I, Sabbatucci M, Cencioni G,
Salvi E, et al: Clinical course of classic Kaposi's sarcoma in
HIV-negative patients treated with the HIV protease inhibitor
indinavir. AIDS. 23:534–538. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Rengan R, Mick R, Pryma D, Rosen MA, Lin
LL, Maity AM, Evans TL, Stevenson JP, Langer CJ, Kucharczuk J, et
al: A phase I trial of the HIV protease inhibitor nelfinavir with
concurrent chemoradiotherapy for unresectable stage IIIA/IIIB
non-small cell lung cancer: A report of toxicities and clinical
response. J Thorac Oncol. 7:709–715. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Barillari G, Iovane A, Bacigalupo I,
Labbaye C, Chiozzini C, Sernicola L, Quaranta MT, Falchi M, Sgadari
C and Ensoli B: The HIV protease inhibitor indinavir down-regulates
the expression of the pro-angiogenic MT1-MMP by human endothelial
cells. Angiogenesis. 7:831–838. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Batchu RB, Gruzdyn OV, Bryant CS, Qazi AM,
Kumar S, Chamala S, Kung ST, Sanka RS, Puttagunta US, Weaver DW and
Gruber SA: Ritonavir-mediated induction of apoptosis in pancreatic
cancer occurs via the RB/E2F-1 and AKT pathways. Pharmaceuticals
(Basel). 7:46–57. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kraus M, Müller-Ide H, Rückrich T, Bader
J, Overkleeft H and Driessen C: Ritonavir, nelfinavir, saquinavir
and lopinavir induce proteotoxic stress in acute myeloid leukemia
cells and sensitize them for proteasome inhibitor treatment at low
micromolar drug concentrations. Leuk Res. 38:383–392. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sato A: The human immunodeficiency virus
protease inhibitor ritonavir is potentially active against
urological malignancies. Onco Targets Ther. 8:761–768. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Libra M, Scalisi A, Vella N, Clementi S,
Sorio R, Stivala F, Spandidos DA and Mazzarino C: Uterine cervical
carcinoma: Role of matrix metalloproteinases (Review). Int J Oncol.
34:897–903. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Talvensaari-Mattila A and
Turpeenniemi-Hujanen T: Matrix metalloproteinase 9 in the uterine
cervix during tumor progression. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 92:83–84.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yang SF, Wang PH, Lin LY, Ko JL, Chen GD,
Yang JS, Lee HS and Hsieh YS: A significant elevation of plasma
level of matrix metalloproteinase-9 in patients with high-grade
intraepithelial neoplasia and early squamous cell carcinoma of the
uterine cervix. Reprod Sci. 14:710–718. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Matheus ER, Zonta MA, Discacciati MG,
Paruci P, Velame F, Cardeal LB, Barros SB, Pignatari AC and
Maria-Engler SS: MMP-9 expression increases according to the grade
of squamous intraepithelial lesion in cervical smears. Diagn
Cytopathol. 42:827–833. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Mathur SP, Mathur RS, Rust PF and Young
RC: Human papilloma virus (HPV)-E6/E7 and epidermal growth factor
receptor (EGF-R) protein levels in cervical cancer and cervical
intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN). Am J Reprod Immunol. 46:280–287.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hsieh CY, Tsai PC, Tseng CH, Chen YL,
Chang LS and Lin SR: Inhibition of EGF/EGFR activation with
naphtho[1,2-b]furan-4,5-dione blocks migration and invasion of
MDA-MB-231 cells. Toxicol In Vitro. 27:1–10. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Seitz O, Schürmann C, Pfeilschifter J,
Frank S and Sader R: Identification of the Fra-1 transcription
factor in healing skin flaps transplants: A potential role as a
negative regulator of VEGF release from keratinocytes. J
Craniomaxillofac Surg. 40:379–386. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Belguise K, Kersual N, Galtier F and
Chalbos D: FRA-1 expression level regulates proliferation and
invasiveness of breast cancer cells. Oncogene. 18:1434–1444. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Adiseshaiah P, Vaz M, Machireddy N,
Kalvakolanu DV and Reddy SP: A Fra-1-dependent, matrix
metalloproteinase driven EGFR activation promotes human lung
epithelial cell motility and invasion. J Cell Physiol. 216:405–412.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Das A, Li Q, Laws MJ, Kaya H, Bagchi MK
and Bagchi IC: Estrogen-induced expression of Fos-related antigen 1
(FRA-1) regulates uterine stromal differentiation and remodeling. J
Biol Chem. 287:19622–19630. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Menges CW, Baglia LA, Lapoint R and
McCance DJ: Human papillomavirus type 16 E7 up-regulates AKT
activity through the retinoblastoma protein. Cancer Res.
66:5555–5559. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Spangle JM and Münger K: The human
papillomavirus type 16 E6 oncoprotein activates mTORC1 signalling
and increases protein synthesis. J Virol. 84:9398–9407. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Cardeal LB, Boccardo E, Termini L,
Rabachini T, Andreoli MA, di Loreto C, Longatto Filho A, Villa LL
and Maria-Engler SS: HPV16 oncoproteins induce MMPs/RECK-TIMP-2
imbalance in primary keratinocytes: Possible implications in
cervical carcinogenesis. PLoS One. 7:e335852012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Shiau MY, Fan LC, Yang SC, Tsao CH, Lee H,
Cheng YW, Lai LC and Chang YH: Human papillomavirus up-regulates
MMP-2 and MMP-9 expression and activity by inducing interleukin-8
in lung adenocarcinomas. PLoS One. 8:e544232013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Stanley MA, Browne HM, Appleby M and
Minson AC: Properties of a non-tumorigenic cervical keratinocyte
cell line. Int J Cancer. 43:672–676. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Pray TR and Laimins LA:
Differentiation-dependent expression of E1-E4 proteins in cell
lines maintaining episomes of human papillomavirus type 31b.
Virology. 206:679–685. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Toschi E, Rota R, Antonini A, Melillo G
and Capogrossi MC: Wild-type p53 gene transfer inhibits invasion
and reduces matrix metalloproteinase-2 levels in p53-mutated human
melanoma cells. J Invest Dermatol. 114:1188–1194. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Barillari G, Iovane A, Bonuglia M,
Albonici L, Garofano P, Di Campli E, Falchi M, Condò I, Manzari V
and Ensoli B: Fibroblast growth factor-2 transiently activates the
p53 oncosuppressor protein in human primary vascular smooth muscle
cells: Implications for atherogenesis. Atherosclerosis.
210:400–406. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Bertelsen BI, Steine SJ, Sandvei R, Molven
A and Laerum OD: Molecular analysis of the PI3K-AKT pathway in
uterine cervical neoplasia: Frequent PIK3CA amplification and AKT
phosphorylation. Int J Cancer. 118:1877–1883. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Du CX and Wang Y: Expression of P-Akt,
NFkappa B and their correlation with human papillomavirus infection
in cervical carcinoma. Eur J Gynaecol Oncol. 33:274–277.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Xu F, Cao M, Shi Q, Chen H, Wang Y and Li
X: Integration of the full-length HPV16 genome in cervical cancer
and Caski and Siha cell lines and the possible ways of HPV
integration. Virus Genes. 50:210–220. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Rusan M, Li YY and Hammerman PS: Genomic
landscape of human papillomavirus-associated cancers. Clin Cancer
Res. 21:2009–2019. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Adler DH: The impact of HAART on
HPV-related cervical disease. Curr HIV Res. 8:493–497. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Justesen US: Protease inhibitor plasma
concentrations in HIV antiretroviral therapy. Dan Med Bull.
55:165–185. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|