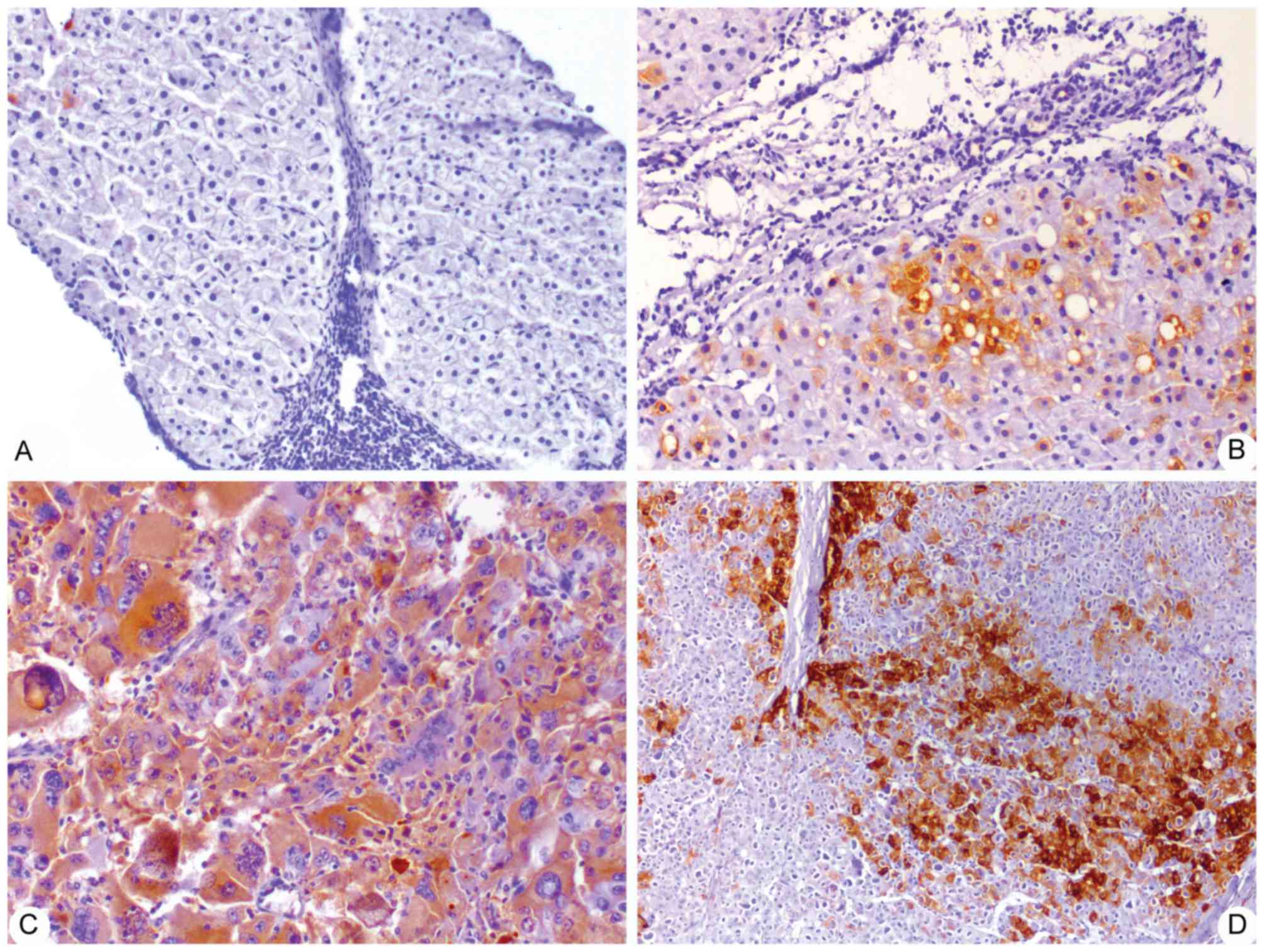
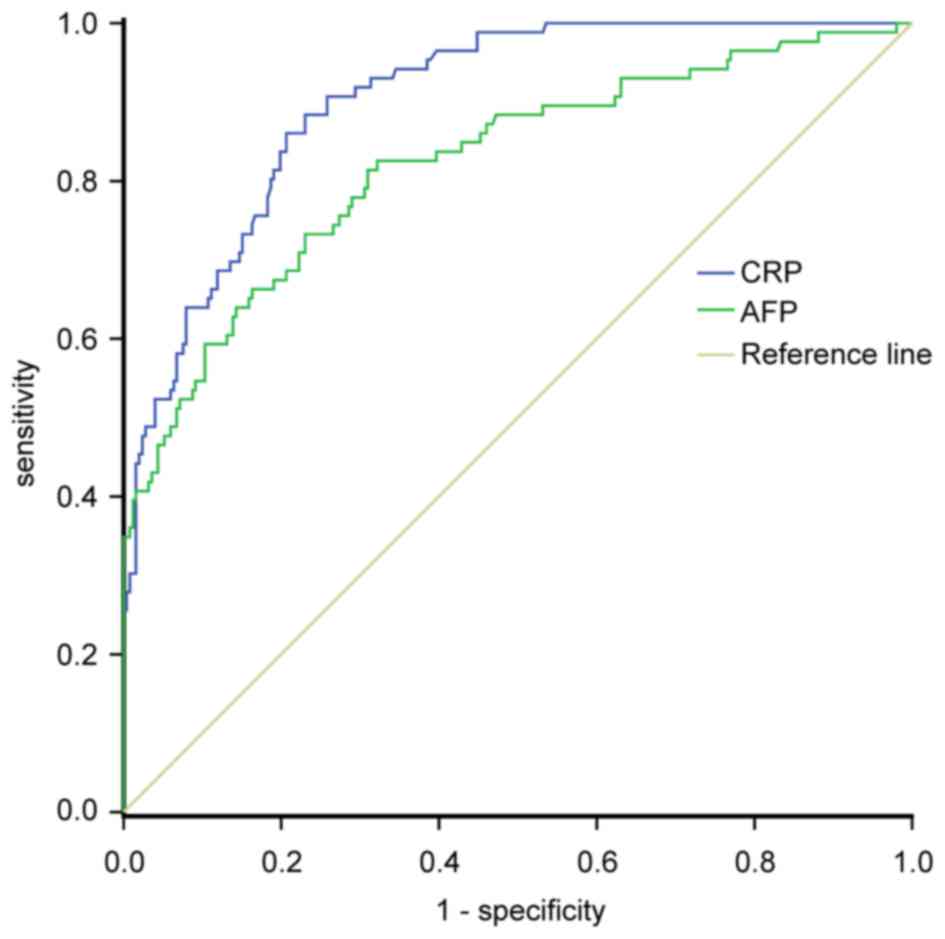
|
1
|
El-Serag HB: Epidemiology of viral
hepatitis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology.
142:1264–1273.e1. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Luk JM and Liu AM: Proteomics of
hepatocellular carcinoma in Chinese patients. OMICS. 15:261–266.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Tang ZY: Hepatocellular carcinoma-cause,
treatment and metastasis. World J Gastroenterol. 7:445–454. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lin CL and Kao JH: Risk stratification for
hepatitis B virus related hepatocellular carcinoma. J Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 28:10–17. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Gao Y, Jiang Q, Zhou X, Ding B, Wang R,
Zhao G and Chen Y: HBV infection and familial aggregation of liver
cancer: An analysis of case-control family study. Cancer Causes
Control. 15:845–850. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Fu WM, Zhang JF, Wang H, Xi ZC, Wang WM,
Zhuang P, Zhu X, Chen SC, Chan TM, Leung KS, et al: Heat shock
protein 27 mediates the effect of
1,3,5-trihydroxy-13,13-dimethyl-2H-pyran [7,6-b] xanthone on
mitochondrial apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Proteomics.
75:4833–4843. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Patel M, Shariff MI, Ladep NG,
Thillainayagam AV, Thomas HC, Khan SA and Taylor-Robinson SD:
Hepatocellular carcinoma: Diagnostics and screening. J Eval Clin
Pract. 18:335–342. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Shariff MI, Cox IJ, Gomaa AI, Khan SA,
Gedroyc W and Taylor-Robinson SD: Hepatocellular carcinoma: Current
trends in worldwide epidemiology, risk factors, diagnosis and
therapeutics. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 3:353–367. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Xu C, Lee SA and Chen X: RNA interference
as therapeutics for hepatocellular carcinoma. Recent Pat Anticancer
Drug Discov. 6:106–115. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Siegel R, Naishadham D and Jemal A: Cancer
Statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 63:11–30. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Shen Q, Fan J, Yang XR, Tan Y, Zhao W, Xu
Y, Wang N, Niu Y, Wu Z, Zhou J, et al: Serum DKK1 as a protein
biomarker for the diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma: A
large-scale, multicentre study. Lancet Oncol. 13:817–826. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Jelic S and Sotiropoulos GC: ESMO
Guidelines Working Group: Hepatocellular carcinoma: ESMO clinical
practice guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann
Oncol. 21:(Suppl 5). v59–v64. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Llovet JM, Di Bisceglie AM, Bruix J,
Kramer BS, Lencioni R, Zhu AX, Sherman M, Schwartz M, Lotze M,
Talwalkar J, et al: Design and endpoints of clinical trials in
hepatocellular carcinoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 100:698–711. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Shameem M, Bhargava R, Ahmad Z, Saad T,
Fatima N and Malik A: Association between serum C-reactive protein
levels and other important predictive markers of outcome in COPD.
Acta Med Iran. 49:18–20. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tanrıverdi H, Tor MM, Kart L, Altın R,
Atalay F and SumbSümbüloğlu V: Prognostic value of serum
procalcitonin and C-reactive protein levels in critically ill
patients who developed ventilator-associated pneumonia. Ann Thorac
Med. 10:137–142. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Garcia-Rio F, Miravitlles M, Soriano JB,
Muñoz L, Duran-Tauleria E, Sánchez G, Sobradillo V and Ancochea J:
EPI-SCAN Steering Committee: Systemic inflammation in chronic
obstructive pulmonary disease: A population-based study. Respir
Res. 11:632010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Abd TT, Eapen DJ, Bajpai A, Goyal A,
Dollar A and Sperling L: The role of C-reactive protein as a risk
predictor of coronary atherosclerosis: Implications from the
JUPITER trial. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 13:154–161. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Peisajovich A, Marnell L, Mold C and Du
Clos TW: C reactive protein at the interface between innate
immunity and inflammation. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 4:379–390.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lin ZY, Wang LY, Yu ML, Chen SC, Chuang
WL, Hsieh MY, Tsai JF and Chang WY: Role of serum C-reactive
protein as a marker of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with
cirrhosis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 15:417–421. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Fabris C, Pirisi M, Soardo G, Falleti E,
Pezzetta F, Vitulli D, Toniutto P, Bortolotti N, Gonano F and
Bartoli E: Value of serum C-reactive protein measurement in the
detection of hepatocellular carcinoma superimposed on liver
cirrhosis. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 120:229–232. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lee FY, Lee SD, Tsai YT, Wu JC, Lai KH and
Lo KJ: Serum C-reactive protein as a serum marker for the diagnosis
of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer. 63:1567–1571. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Andreozzi P, Viscogliosi G, Colella F,
Subic M, Cipriani E, Marigliano B, Verrusio W, Servello A, Ettorre
E and Marigliano V: Predictors of liver fibrosis in patients with
non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. The role of metabolic syndrome,
insulin-resistance and inflammation. Recenti Prog Med. 103:570–574.
2012.(In Italian). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Komoriya T, Inoue N, Yoshimune K, Ogawa M,
Moriyama M and Kohno H: Use of a highly sensitive latex reagent
with amino acid spacer for determination of C-reactive protein
concentration in a variety of liver diseases. J Biosci Bioeng.
114:560–563. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Atta M, Cabral M, Santos G, Paraná R and
Atta A: Inflammation biomarkers in chronic hepatitis C: Association
with liver histopathology, HCV genotype and cryoglobulinemia.
Inflamm Res. 61:1101–1106. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sjöwall C, Cardell K, Boström EA, Bokarewa
MI, Enocsson H, Ekstedt M, Lindvall L, Frydén A and Almer S: High
prevalence of autoantibodies to C-reactive protein in patients with
chronic hepatitis C infection: Association with liver fibrosis and
portal inflammation. Hum Immunol. 73:382–388. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Rocha P, Morgan CJ, Templeton AJ, Pond GR,
Naik G and Sonpavde G: Prognostic impact of C-reactive protein in
metastatic prostate cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis.
Oncol Res Treat. 37:772–776. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Shibutani M, Maeda K, Nagahara H, Ohtani
H, Sugano K, Ikeya T, Kimura K, Amano R, Kubo N, Tanaka H, et al:
Elevated preoperative serum C-reactive protein levels are
associated with poor survival in patients with colorectal cancer.
Hepatogastroenterology. 61:2236–2240. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chen W, Wang JB, Abnet CC, Dawsey SM, Fan
JH, Yin LY, Yin J, Taylor PR, Qiao YL and Freedman ND: Association
between C-reactive protein, incident liver cancer, and chronic
liver disease mortality in the Linxian nutrition intervention
trials: A nested case-control study. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers
Prev. 24:386–392. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hefler LA, Concin N, Hofstetter G, Marth
C, Mustea A, Sehouli J, Zeillinger R, Leipold H, Lass H, Grimm C,
et al: Serum C-reactive protein as independent prognostic variable
in patients with ovarian cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 14:710–714. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Xu M, Zhu M, Du Y, Yan B, Wang Q, Wang C
and Zhao J: Serum C-reactive protein and risk of lung cancer: A
case-control study. Med Oncol. 30:3192013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Nozoe T, Matsumata T, Kitamura M and
Sugimachi K: Significance of preoperative elevation of serum
C-reactive protein as an indicator for prognosis in colorectal
cancer. Am J Surg. 176:335–338. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Alberti A and Caporaso N: HBV therapy:
Guidelines and open issues. Dig Liv Dis. 43:(Suppl 1). S57–S63.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Balkwill F and Mantovani A: Inflammation
and cancer: Back to Virchow? Lancet. 357:539–545. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Okada F: Inflammation-related
carcinogenesis: Current findings in epidemiological trends, causes
and mechanisms. Yonago Acta Med. 57:65–72. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Feng JF, Huang Y and Chen QX: A new
inflammation index is useful for patients with esophageal squamous
cell carcinoma. Onco Targets Ther. 7:1811–1815. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Nishikawa H, Arimoto A, Wakasa T, Kita R,
Kimura T and Osaki Y: Pre-treatment C-reactive protein as a
prognostic factor for recurrence after surgical resection of
hepatocellular carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 33:1181–1188.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhao X, Luo J, Li B, Liu S and Li D: The
association between preoperative serum C-reactive protein and
hepatocellular carcinoma recurrence in patients with chronic
hepatitis B virus HBV infection-a retrospective study. PLoS One.
10:e01169092015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
He X, Wang Y, Zhang W, Li H, Luo R, Zhou
Y, Liao CL, Huang H, Lv X, Xie Z and He M: Screening differential
expression of serum proteins in AFP-negative HBV-related
hepatocellular carcinoma using iTRAQ-MALDI-MS/MS. Neoplasma.
61:17–26. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Imai N, Kinoshita A, Onoda H, Iwaku A,
Oishi M, Tanaka K, Fushiya N, Koike K, Nishino H and Tajiri H:
Persistent elevated C-reactive protein after treatment is an
independent marker of a poor prognosis in patients with
hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Transl Oncol. 15:575–581. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Sieghart W, Pinter M, Hucke F, Graziadei
I, Schöniger-Hekele M, Müller C, Vogel W, Trauner M and
Peck-Radosavljevic M: Single determination of C-reactive protein at
the time of diagnosis predicts long-term outcome of patients with
hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 57:2224–2234. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Liu C, Zhang Y, Zhan J, Zhao Y, Wan Q,
Peng H and Zhu W: Interleukin-23A is associated with tumor growth
in Helicobacter-pylori-related human gastric cancer. Cancer Cell
Int. 14:1042014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Szabo G and Lippai D: Molecular hepatic
carcinogenesis: Impact of inflammation. Dig Dis. 30:243–248. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Morales-Sánchez A and Fuentes-Pananá EM:
Human Viruses and Cancer. Viruses. 6:4047–4079. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Chen Y, Williams V, Filippova M, Filippov
V and Duerksen-Hughes P: Viral carcinogenesis: Factors inducing DNA
damage and virus integration. Cancers (Basel). 6:2155–2186. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Sherman M and Colombo M: Hepatocellular
carcinoma screening and diagnosis. Semin Liver Dis. 34:389–397.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Yang SW, Kim GH, Chung JW, Sohn HR, Lee
SS, Hong S, Chung SM, Jang ES, Jeong SH and Kim JW: Prediction of
risk for hepatocellular carcinoma by response of serum
α-fetoprotein to entecavir therapy. J Gastroenterol Hepatol.
30:1175–1182. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Triolo M, Corte C Della and Colombo M:
Impact of HBV therapy on the incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Liver Int. 34:(Suppl 1). S139–S145. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|