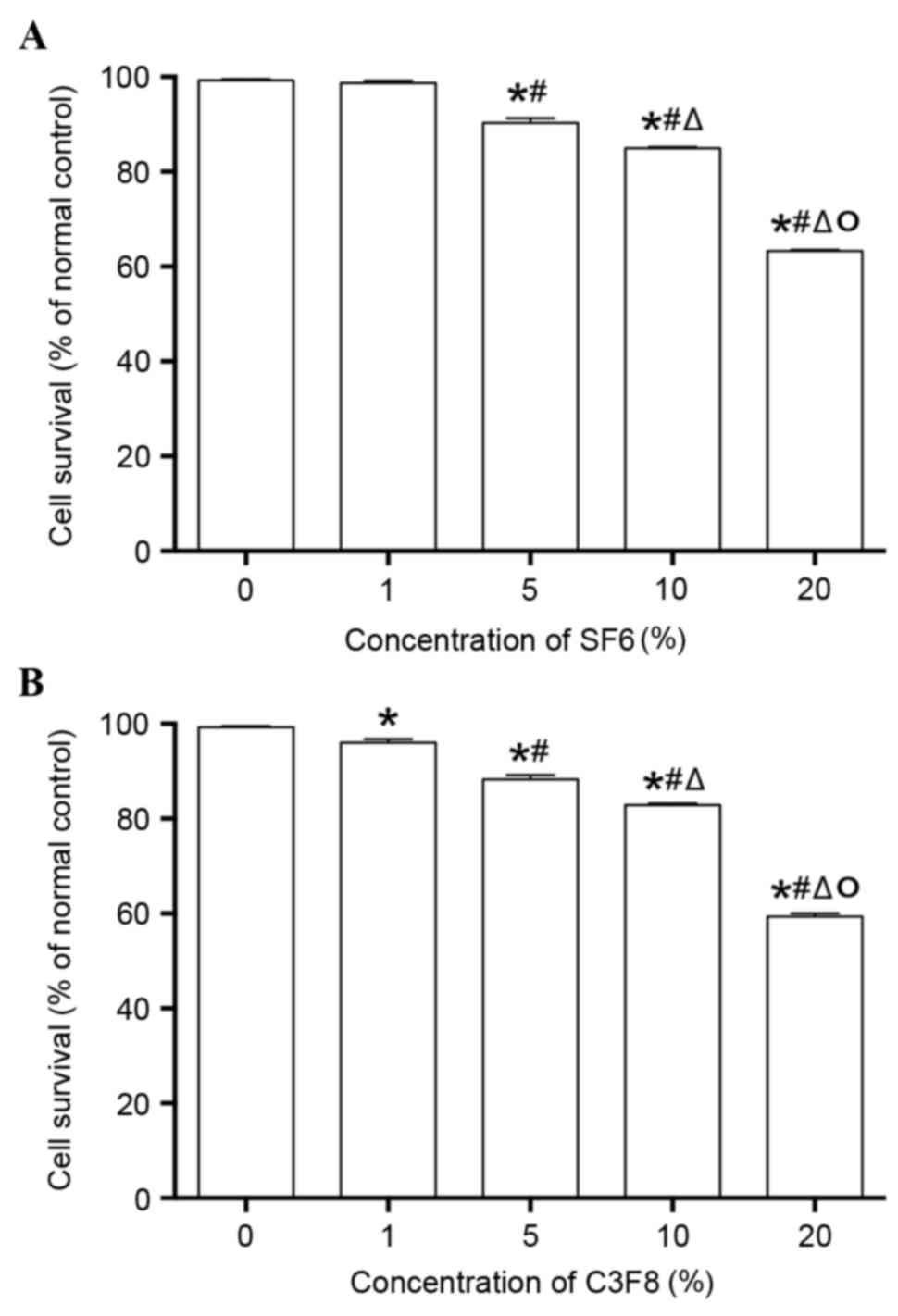
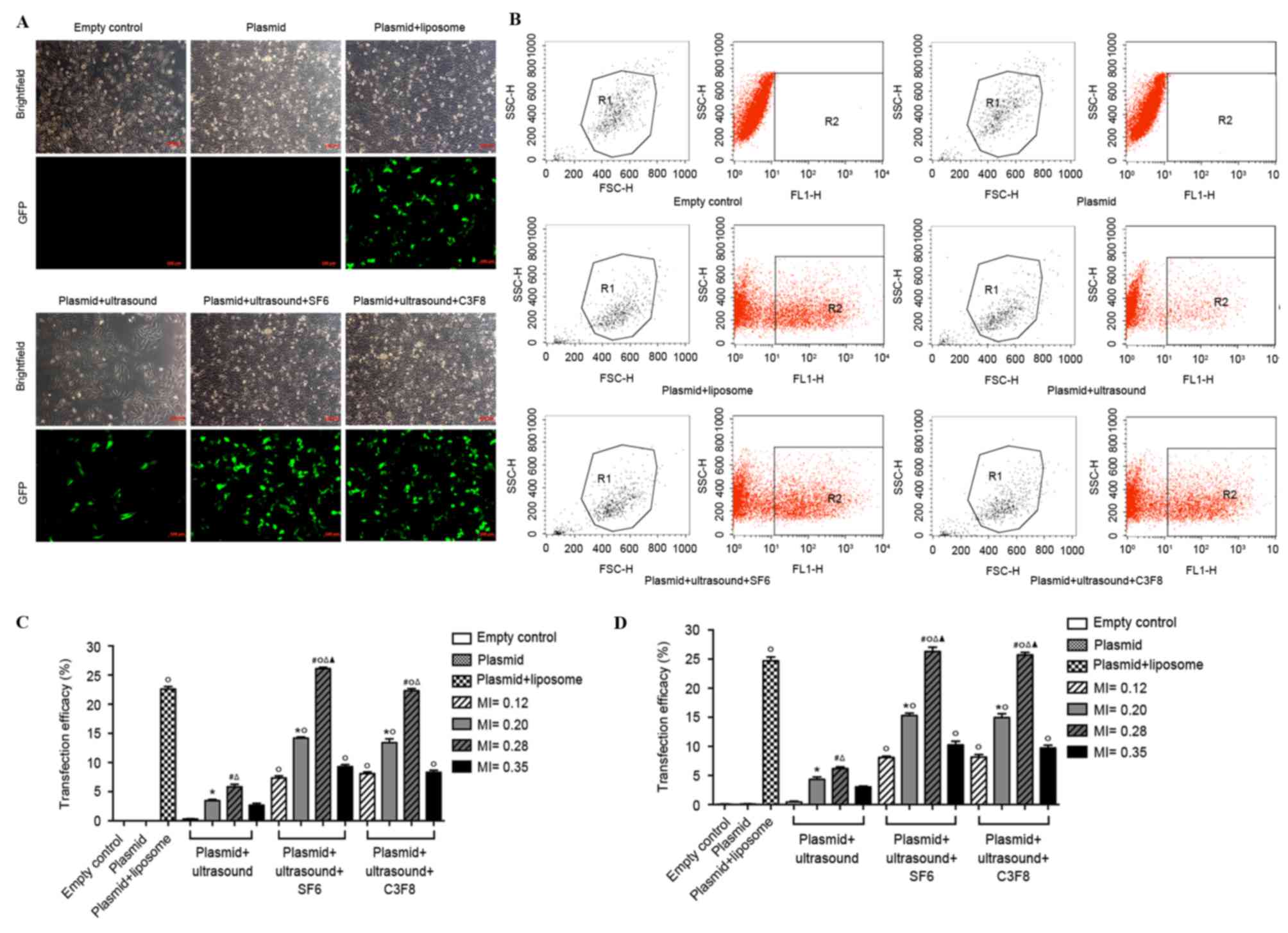
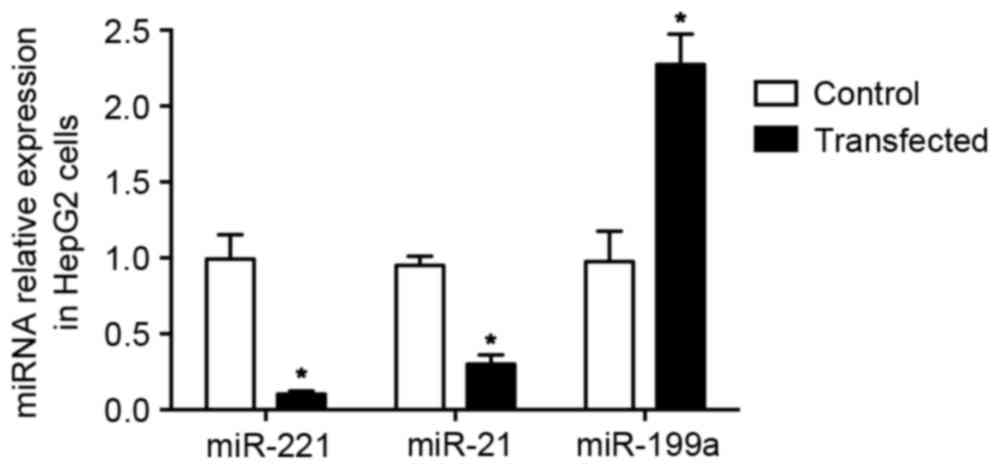
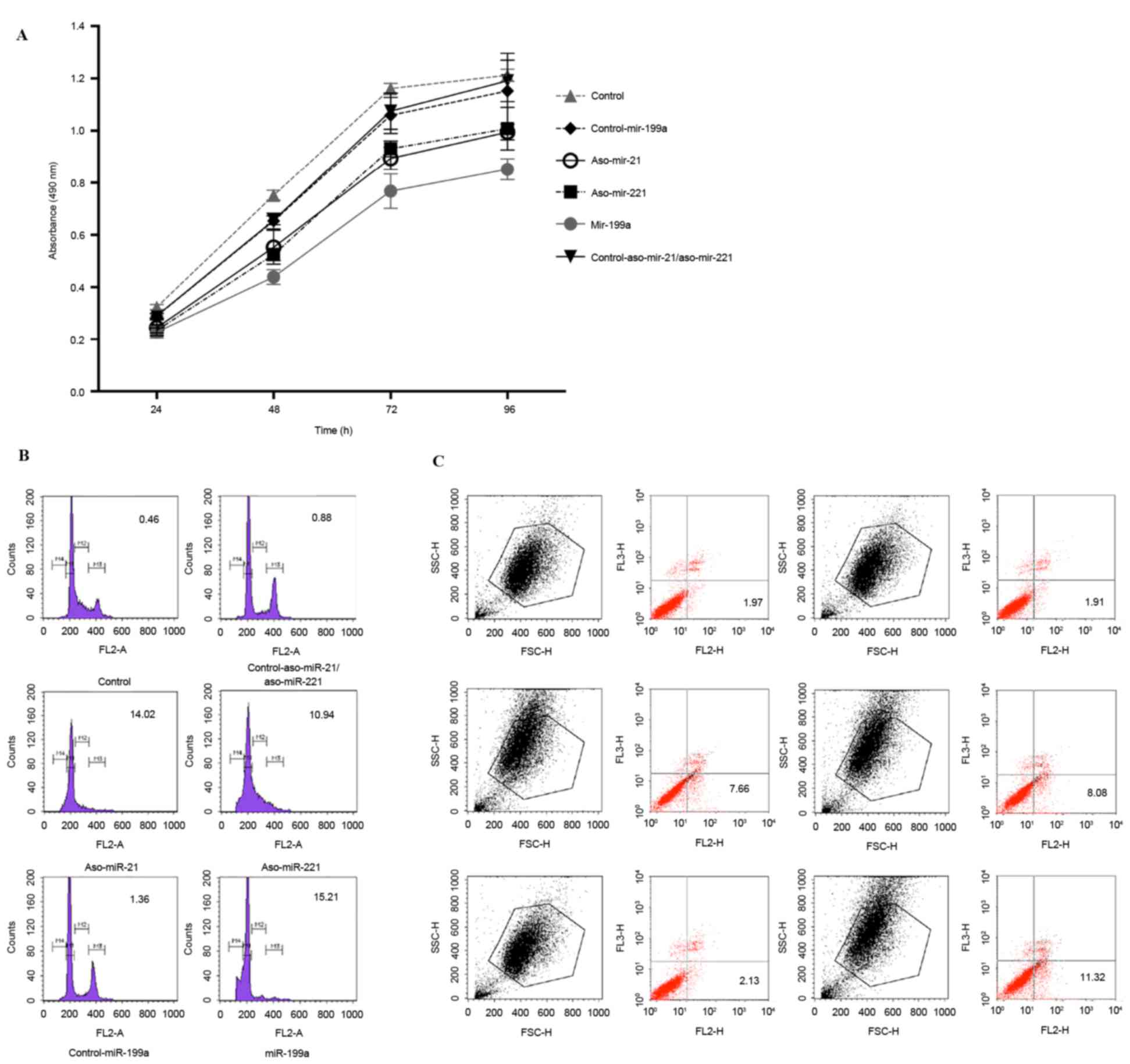
|
1
|
Stewart BW and Wild CP: World Cancer
Report 2014. World Health Organization. (In Press). 2014.
|
|
2
|
Sun J, Lu H, Wang X and Jin H: MicroRNAs
in hepatocellular carcinoma: Regulation, function, and clinical
implications. ScientificWorldJournal. 2013:9242062013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yang N, Ekanem NR, Sakyi CA and Ray SD:
Hepatocellular carcinoma and microRNA: New perspectives on
therapeutics and diagnostics. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 81:62–74. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hung CH, Chiu YC, Chen CH and Hu TH:
MicroRNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma: Carcinogenesis, progression,
and therapeutic target. Biomed Res Int. 2014:4864072014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bellissimo F, Pinzone MR, Cacopardo B and
Nunnari G: Diagnostic and therapeutic management of hepatocellular
carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol. 21:12003–12021. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Gomaa AI and Waked I: Recent advances in
multidisciplinary management of hepatocellular carcinoma. World J
Hepatol. 7:673–687. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yang XD, Pan LH, Wang L, Ke Y, Cao J, Yang
C, Zhong JH, Luo W, Guo J and Li LQ: Systematic review of single
large and/or multinodular hepatocellular carcinoma: Surgical
resection improves survival. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 16:5541–5547.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kudo M: Surveillance, diagnosis,
treatment, and outcome of liver cancer in Japan. Liver Cancer.
4:39–50. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lim KC, Chow PK, Allen JC, Siddiqui FJ,
Chan ES and Tan SB: Systematic review of outcomes of liver
resection for early hepatocellular carcinoma within the Milan
criteria. Br J Surg. 99:1622–1629. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wiggins JF, Ruffino L, Kelnar K, Omotola
M, Patrawala L, Brown D and Bader AG: Development of a lung cancer
therapeutic based on the tumor suppressor microRNA-34. Cancer Res.
70:5923–5930. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Raisch J, Darfeuille-Michaud A and Nguyen
HT: Role of microRNAs in the immune system, inflammation and
cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 19:2985–2996. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Calin GA and Croce CM: MicroRNA signatures
in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:857–866. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Vettori S, Gay S and Distler O: Role of
MicroRNAs in Fibrosis. Open Rheumatol J. 6:130–139. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Murakami Y, Yasuda T, Saigo K, Urashima T,
Toyoda H, Okanoue T and Shimotohno K: Comprehensive analysis of
microRNA expression patterns in hepatocellular carcinoma and
non-tumorous tissues. Oncogene. 25:2537–2545. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Jiang J, Gusev Y, Aderca I, Mettler TA,
Nagorney DM, Brackett DJ, Roberts LR and Schmittgen TD: Association
of MicroRNA expression in hepatocellular carcinomas with hepatitis
infection, cirrhosis, and patient survival. Clin Cancer Res.
14:419–427. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Huang XH, Wang Q, Chen JS, Fu XH, Chen XL,
Chen LZ, Li W, Bi J, Zhang LJ, Fu Q, et al: Bead-based microarray
analysis of microRNA expression in hepatocellular carcinoma:
miR-338 is downregulated. Hepatol Res. 39:786–794. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Connolly E, Melegari M, Landgraf P,
Tchaikovskaya T, Tennant BC, Slagle BL, Rogler LE, Zavolan M,
Tuschl T and Rogler CE: Elevated expression of the miR-17-92
polycistron and miR-21 in hepadnavirus-associated hepatocellular
carcinoma contributes to the malignant phenotype. Am J Pathol.
173:856–864. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ladeiro Y, Couchy G, Balabaud C,
Bioulac-Sage P, Pelletier L, Rebouissou S and Zucman-Rossi J:
MicroRNA profiling in hepatocellular tumors is associated with
clinical features and oncogene/tumor suppressor gene mutations.
Hepatology. 47:1955–1963. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Suzuki R, Oda Y, Utoguchi N and Maruyama
K: Progress in the development of ultrasound-mediated gene delivery
systems utilizing nano- and microbubbles. J Control Release.
149:36–41. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yan C, Zhu D, Huang D and Xia G: Role of
ultrasound and microbubble-mediated heat shock protein 72 siRNA on
ischemia-reperfusion liver injury in rat. Int J Clin Exp Med.
8:5746–5752. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chen Z, Liang K, Xie M, Wang X, Lu Q and
Zhang J: Novel ultrasound-targeted microbubble destruction mediated
short hairpin RNA plasmid transfection targeting survivin inhibits
gene expression and induces apoptosis of HeLa cells. Mol Biol Rep.
36:2059–2067. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kimura S, Egashira K, Chen L, Nakano K,
Iwata E, Miyagawa M, Tsujimoto H, Hara K, Morishita R, Sueishi K,
et al: Nanoparticle-mediated delivery of nuclear factor kappaB
decoy into lungs ameliorates monocrotaline-induced pulmonary
arterial hypertension. Hypertension. 53:877–883. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Fattal E and Barratt G: Nanotechnologies
and controlled release systems for the delivery of antisense
oligonucleotides and small interfering RNA. Br J Pharmacol.
157:179–194. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Shen ZP, Brayman AA, Chen L and Miao CH:
Ultrasound with microbubbles enhances gene expression of plasmid
DNA in the liver via intraportal delivery. Gene Ther. 15:1147–1155.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Jia XQ, Cheng HQ, Qian X, Bian CX, Shi ZM,
Zhang JP, Jiang BH and Feng ZQ: Lentivirus-mediated overexpression
of microRNA-199a inhibits cell proliferation of human
hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Biochem Biophys. 62:237–244. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Verma IM and Somia N: Gene
therapy-promises, problems and prospects. Nature. 389:239–242.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Tomanin R and Scarpa M: Why do we need new
gene therapy viral vectors? Characteristics, limitations and future
perspectives of viral vector transduction. Curr Gene Ther.
4:357–372. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Sonoda S, Tachibana K, Uchino E, Okubo A,
Yamamoto M, Sakoda K, Hisatomi T, Sonoda KH, Negishi Y, Izumi Y, et
al: Gene transfer to corneal epithelium and keratocytes mediated by
ultrasound with microbubbles. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci.
47:558–564. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Bekeredjian R, Bohris C, Hansen A, Katus
HA, Kuecherer HF and Hardt SE: Impact of microbubbles on shock
wave-mediated DNA uptake in cells in vitro. Ultrasound Med Biol.
33:743–750. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Iorio MV, Ferracin M, Liu CG, Veronese A,
Spizzo R, Sabbioni S, Magri E, Pedriali M, Fabbri M, Campiglio M,
et al: MicroRNA gene expression deregulation in human breast
cancer. Cancer Res. 65:7065–7070. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhu S, Wu H, Wu F, Nie D, Sheng S and Mo
YY: MicroRNA-21 targets tumor suppressor genes in invasion and
metastasis. Cell Res. 18:350–359. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Huang Y, Yang YB, Zhang XH, Yu XL, Wang ZB
and Cheng XC: MicroRNA-21 gene and cancer. Med Oncol. 30:3762013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Meng F, Henson R, Wehbe-Janek H, Ghoshal
K, Jacob ST and Patel T: MicroRNA-21 regulates expression of the
PTEN tumor suppressor gene in human hepatocellular cancer.
Gastroenterology. 133:647–658. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Gramantieri L, Fornari F, Ferracin M,
Veronese A, Sabbioni S, Calin GA, Grazi GL, Croce CM, Bolondi L and
Negrini M: MicroRNA-221 targets Bmf in hepatocellular carcinoma and
correlates with tumor multifocality. Clin Cancer Res. 15:5073–5081.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Turato C, Simonato D, Quarta S, Gatta A
and Pontisso P: MicroRNAs and SerpinB3 in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Life Sci. 100:9–17. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Fu X, Wang Q, Chen J, Huang X, Chen X, Cao
L, Tan H, Li W, Zhang L, Bi J, et al: Clinical significance of
miR-221 and its inverse correlation with p27Kip¹ in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Mol Biol Rep. 38:3029–3035. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Fornari F, Gramantieri L, Ferracin M,
Veronese A, Sabbioni S, Calin GA, Grazi GL, Giovannini C, Croce CM,
Bolondi L and Negrini M: MiR-221 controls CDKN1C/p57 and CDKN1B/p27
expression in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene.
27:5651–5661. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Hou J, Lin L, Zhou W, Wang Z, Ding G, Dong
Q, Qin L, Wu X, Zheng Y, Yang Y, et al: Identification of miRNomes
in human liver and hepatocellular carcinoma reveals miR-199a/b-3p
as therapeutic target for hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Cell.
19:232–243. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Fornari F, Milazzo M, Chieco P, Negrini M,
Calin GA, Grazi GL, Pollutri D, Croce CM, Bolondi L and Gramantieri
L: MiR-199a-3p regulates mTOR and c-Met to influence the
doxorubicin sensitivity of human hepatocarcinoma cells. Cancer Res.
70:5184–5193. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|