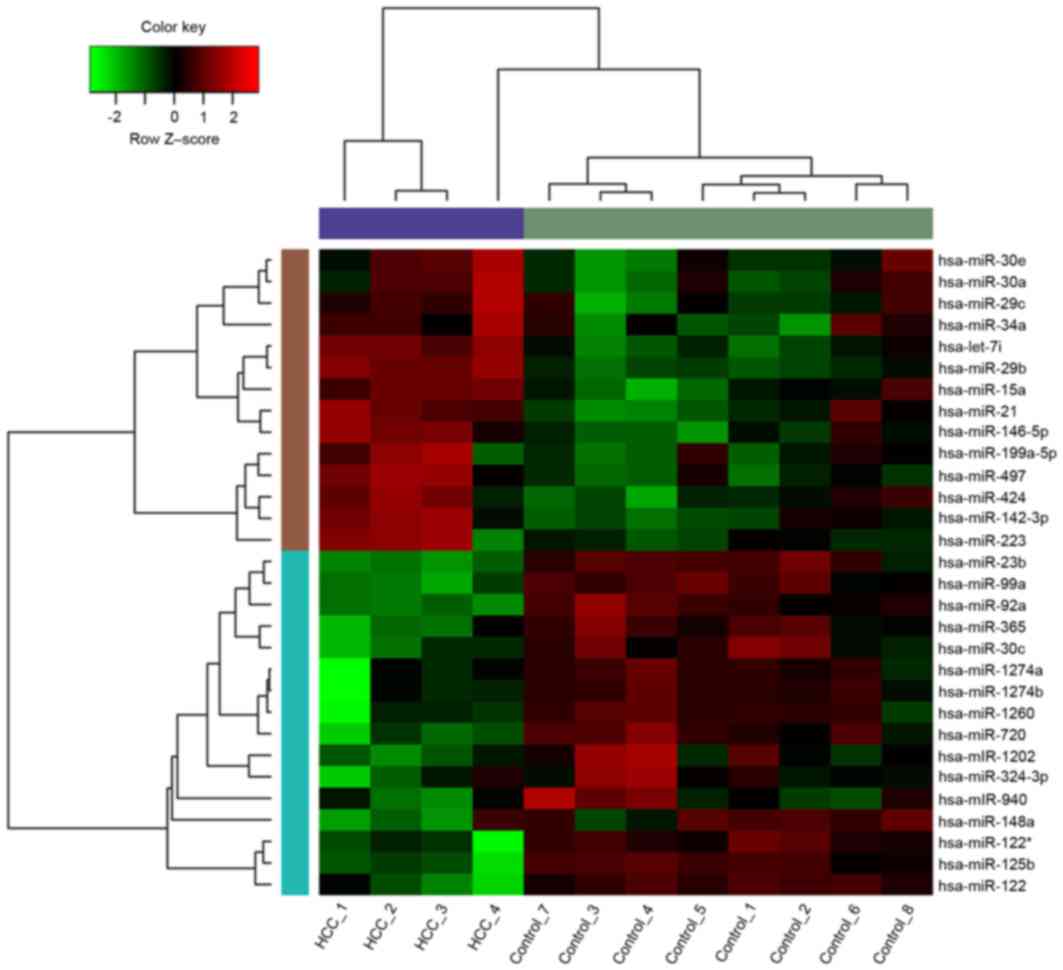
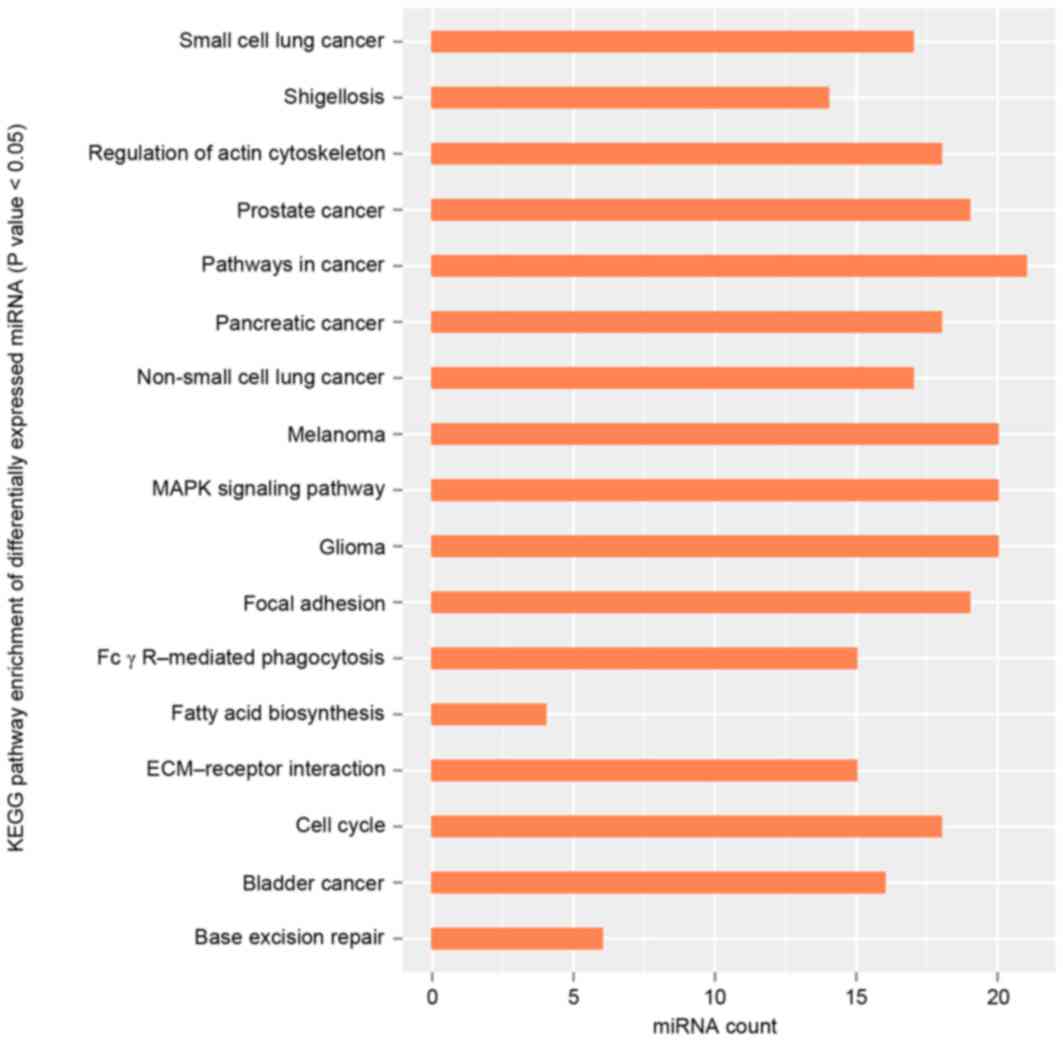
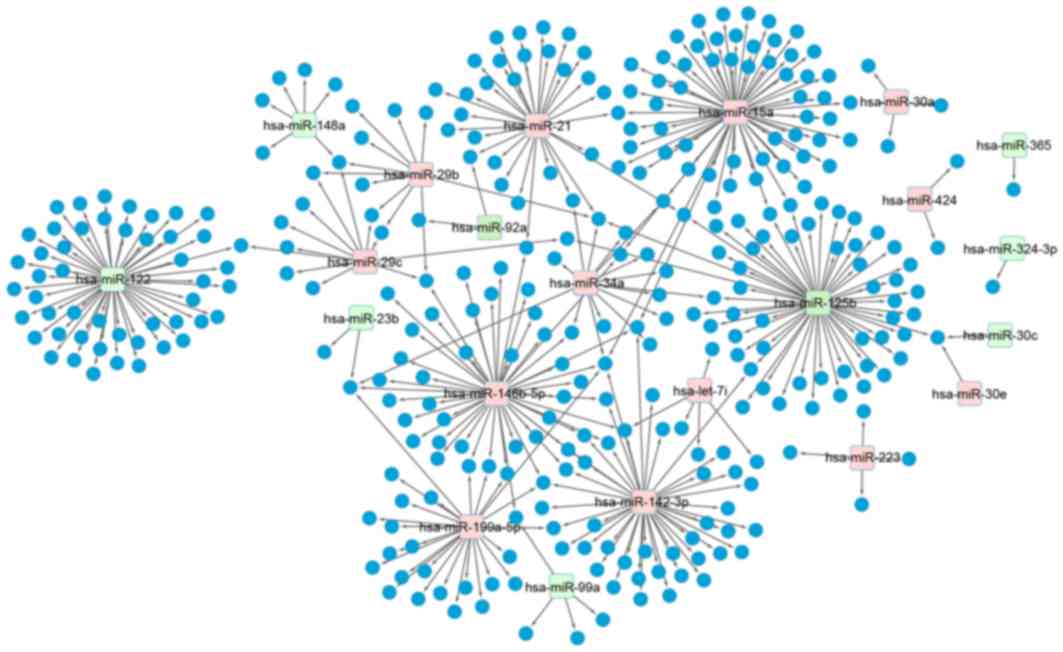
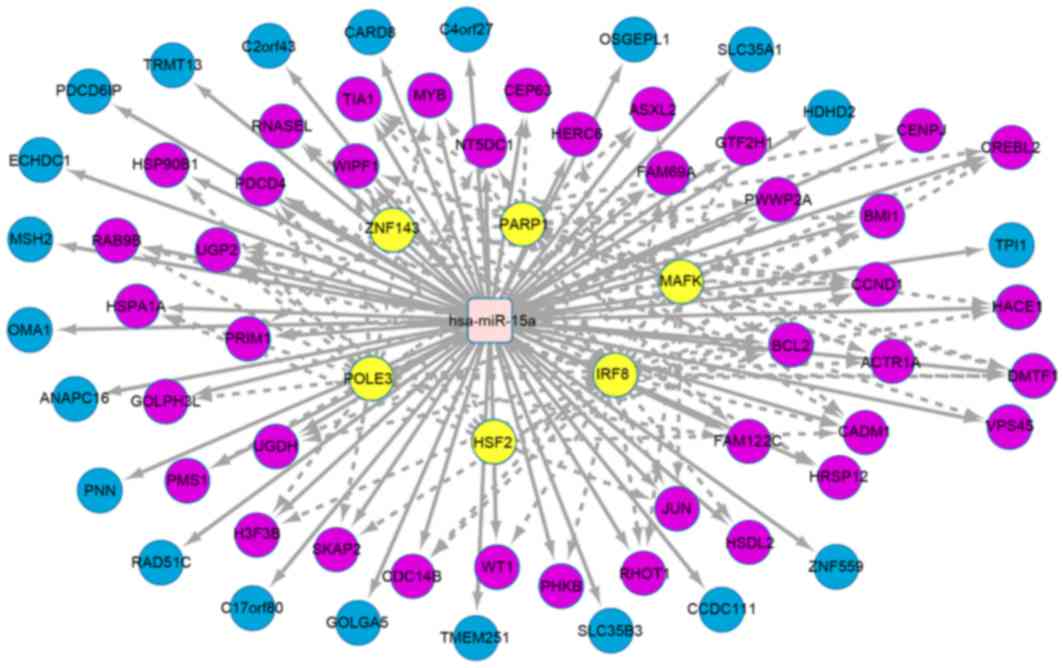
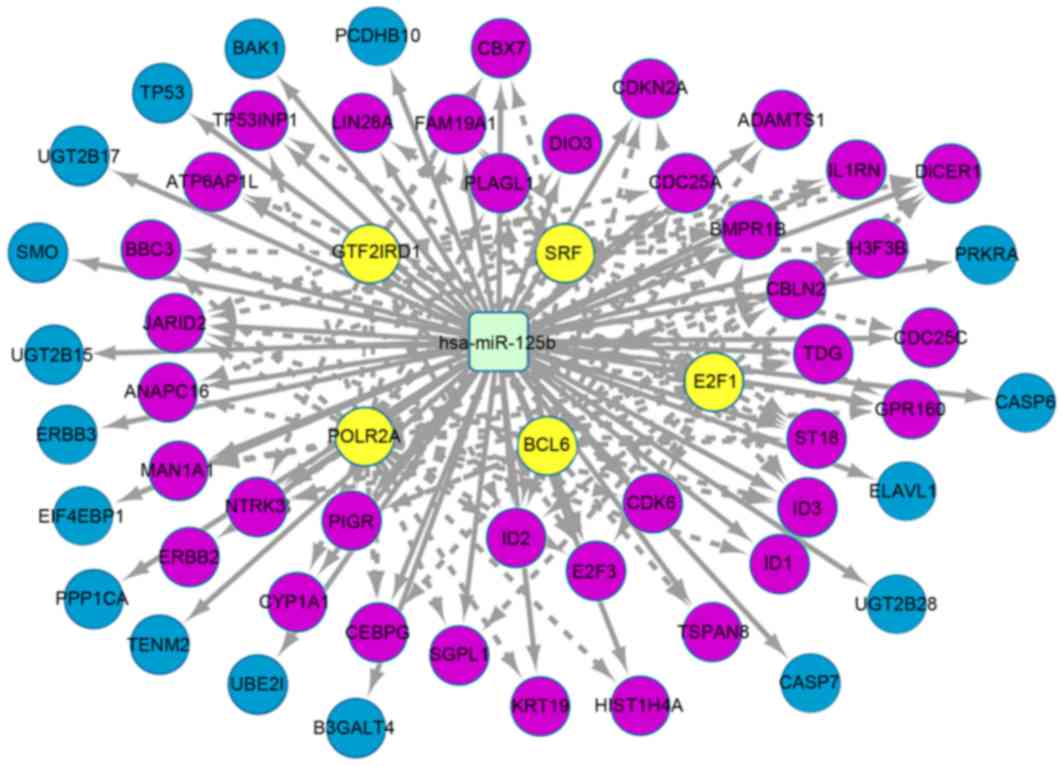
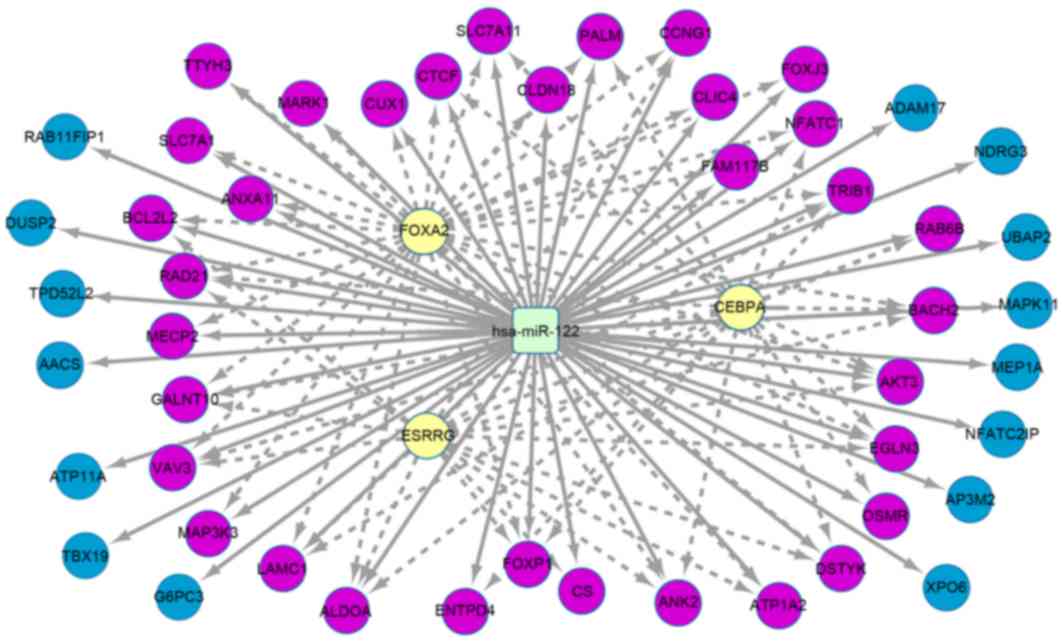
|
1
|
Chen KW, Ou TM, Hsu CW, Horng CT, Lee CC,
Tsai YY, Tsai CC, Liou YS, Yang CC, Hsueh CW, et al: Current
systemic treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: A review of the
literature. World J Hepatol. 7:1412–1420. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lin S, Hoffmann K and Schemmer P:
Treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review. Liver
Cancer. 1:144–158. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Cabrera R and Nelson DR: Review article:
The management of hepatocellular carcinoma. Aliment Pharmacol Ther.
31:461–476. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Liang HH, Wei PL, Hung CS, Wu CT, Wang W,
Huang MT and Chang YJ: MicroRNA-200a/b influenced the therapeutic
effects of curcumin in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells. Tumour
Biol. 34:3209–3218. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Cao W, Guo Q, Zhang T, Zhong D and Yu Q:
Prognostic value of microRNAs in acute myocardial infarction: A
systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Cardiol. 189:79–84.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Gao Y, He Y, Ding J, Wu K, Hu B, Liu Y, Wu
Y, Guo B, Shen Y, Landi D, et al: An insertion/deletion
polymorphism at miRNA-122-binding site in the interleukin-1alpha 3′
untranslated region confers risk for hepatocellular carcinoma.
Carcinogenesis. 30:2064–2069. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Liu J, Yan J, Zhou C, Ma Q, Jin Q and Yang
Z: miR-1285-3p acts as a potential tumor suppressor miRNA via
downregulating JUN expression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Tumour
Biol. 36:219–225. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yang Z, Zhang Y and Wang L: A feedback
inhibition between miRNA-127 and TGFβ/c-Jun cascade in HCC cell
migration via MMP13. PLoS One. 8:e652562013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ziari K, Zarea M, Gity M, Fayyaz AF,
Yahaghi E, Darian EK and Hashemian AM: Downregulation of miR-148b
as biomarker for early detection of hepatocellular carcinoma and
may serve as a prognostic marker. Tumour Biol. 37:5765–5768. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Huang X and Jia Z: Construction of
HCC-targeting artificial miRNAs using natural miRNA precursors. Exp
Ther Med. 6:209–215. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Borel F, Konstantinova P and Jansen PL:
Diagnostic and therapeutic potential of miRNA signatures in
patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 56:1371–1383.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yang N, Ekanem NR, Sakyi CA and Ray SD:
Hepatocellular carcinoma and microRNA: New perspectives on
therapeutics and diagnostics. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 81:62–74. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Murakami Y, Tanahashi T, Okada R, Toyoda
H, Kumada T, Enomoto M, Tamori A, Kawada N, Taguchi YH and Azuma T:
Comparison of hepatocellular carcinoma miRNA expression profiling
as evaluated by next generation sequencing and microarray. PLoS
One. 9:e1063142014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Xie Y, Yao Q, Butt AM, Guo J, Tian Z, Bao
X, Li H, Meng Q and Lu J: Expression profiling of serum
microRNA-101 in HBV-associated chronic hepatitis, liver cirrhosis,
and hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Biol Ther. 15:1248–1255. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang Y, Lee AT, Ma JZ, Wang J, Ren J, Yang
Y, Tantoso E, Li KB, Ooi LL, Tan P and Lee CG: Profiling microRNA
expression in hepatocellular carcinoma reveals microRNA-224
up-regulation and apoptosis inhibitor-5 as a microRNA-224-specific
target. J Biol Chem. 283:13205–13215. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wei L, Lian B, Zhang Y, Li W, Gu J, He X
and Xie L: Application of microRNA and mRNA expression profiling on
prognostic biomarker discovery for hepatocellular carcinoma. BMC
Genomics. 15:(Suppl 1). S132014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Edgar R, Domrachev M and Lash AE: Gene
expression omnibus: NCBI gene expression and hybridization array
data repository. Nucleic Acids Res. 30:207–210. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Huber W, Von Heydebreck A, Sültmann H,
Poustka A and Vingron M: Variance stabilization applied to
microarray data calibration and to the quantification of
differential expression. Bioinformatics. 18:(Suppl 1). S96–S104.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ritchie ME, Phipson B, Wu D, Hu Y, Law CW,
Shi W and Smyth GK: limma powers differential expression analyses
for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res.
43:e472015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Xiao F, Zuo Z, Cai G, Kang S, Gao X and Li
T: miRecords: An integrated resource for microRNA-target
interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 37:(Database Issue). D105–D110.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Dweep H, Sticht C, Pandey P and Gretz N:
miRWalk-database: Prediction of possible miRNA binding sites by
‘walking’ the genes of three genomes. J Biomed Inform. 44:839–847.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Dennis G Jr, Sherman BT, Hosack DA, Yang
J, Gao W, Lane HC and Lempicki RA: DAVID: Database for annotation,
visualization, and integrated discovery. Genome Biol. 4:P32003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kanehisa M and Goto S: KEGG: Kyoto
encyclopaedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 28:27–30.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Enright AJ, John B, Gaul U, Tuschl T,
Sander C and Marks DS: MicroRNA targets in Drosophila. Genome Biol.
5:R12003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Janky R, Verfaillie A, Imrichová H, Van de
Sande B, Standaert L, Christiaens V, Hulselmans G, Herten K,
Sanchez M Naval, Potier D, et al: iRegulon: From a gene list to a
gene regulatory network using large motif and track collections.
PLoS Comput Biol. 10:e10037312014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Davis AP, Grondin CJ, Lennon-Hopkins K,
Saraceni-Richards C, Sciaky D, King BL, Wiegers TC and Mattingly
CJ: The comparative toxicogenomics database's 10th year
anniversary: Update 2015. Nucleic Acids Res. 43:(Database Issue).
D914–D920. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kitamoto S, Yamada N, Yokoyama S, Houjou
I, Higashi M, Goto M, Batra SK and Yonezawa S: DNA methylation and
histone H3-K9 modifications contribute to MUC17 expression.
Glycobiology. 21:247–256. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sewalt RG, Lachner M, Vargas M, Hamer KM,
den Blaauwen JL, Hendrix T, Melcher M, Schweizer D, Jenuwein T and
Otte AP: Selective interactions between vertebrate polycomb
homologs and the SUV39H1 histone lysine methyltransferase suggest
that histone H3-K9 methylation contributes to chromosomal targeting
of Polycomb group proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 22:5539–5553. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Tu T, Shackel NA and McCaughan G: ‘Testing
your methyl’: DNA methylation profiling of serum DNA of HCC
patients. Hepatol Int. 7:785–787. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Peng JC and Karpen GH: Heterochromatic
genome stability requires regulators of histone H3 K9 methylation.
PLoS Genet. 5:e10004352009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Daroqui MC, Vazquez P, Bal de Kier Joffé
E, Bakin AV and Puricelli LI: TGF-β autocrine pathway and MAPK
signaling promote cell invasiveness and in vivo mammary
adenocarcinoma tumor progression. Oncol Rep. 28:567–575.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Gustin JA, Pincheira R, Mayo LD, Ozes ON,
Kessler KM, Baerwald MR, Korgaonkar CK and Donner DB: Tumor
necrosis factor activates CRE-binding protein through a p38
MAPK/MSK1 signaling pathway in endothelial cells. Am J Physiol Cell
Physiol. 286:C547–C555. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wang S, Li W, Lian B, Liu X, Zhang Y, Dai
E, Yu X, Meng F, Jiang W and Li X: TMREC: A database of
transcription factor and MiRNA regulatory cascades in human
diseases. PLoS One. 10:e01252222015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Peng C, Wang M, Shen Y, Feng H and Li A:
Reconstruction and analysis of transcription factor-miRNA
co-regulatory feed-forward loops in human cancers using
filter-wrapper feature selection. PLoS One. 8:e781972013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Katakowski M, Zheng X, Jiang F, Rogers T,
Szalad A and Chopp M: MiR-146b-5p suppresses EGFR expression and
reduces in vitro migration and invasion of glioma. Cancer Invest.
28:1024–1030. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Li Y, Wang Y, Yu L, Sun C, Cheng D, Yu S,
Wang Q, Yan Y, Kang C, Jin S, et al: miR-146b-5p inhibits glioma
migration and invasion by targeting MMP16. Cancer Lett.
339:260–269. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Halász T, Horváth G, Pár G, Werling K,
Kiss A, Schaff Z and Lendvai G: miR-122 negatively correlates with
liver fibrosis as detected by histology and FibroScan. World J
Gastroenterol. 21:7814–7823. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Park HK, Jo W, Choi HJ, Jang S, Ryu JE,
Lee HJ, Lee H, Kim H, Yu ES and Son WC: Time-course changes in the
expression levels of miR-122, −155 and −21 as markers of liver cell
damage, inflammation, and regeneration in acetaminophen-induced
liver injury in rats. J Vet Sci. 17:45–51. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|