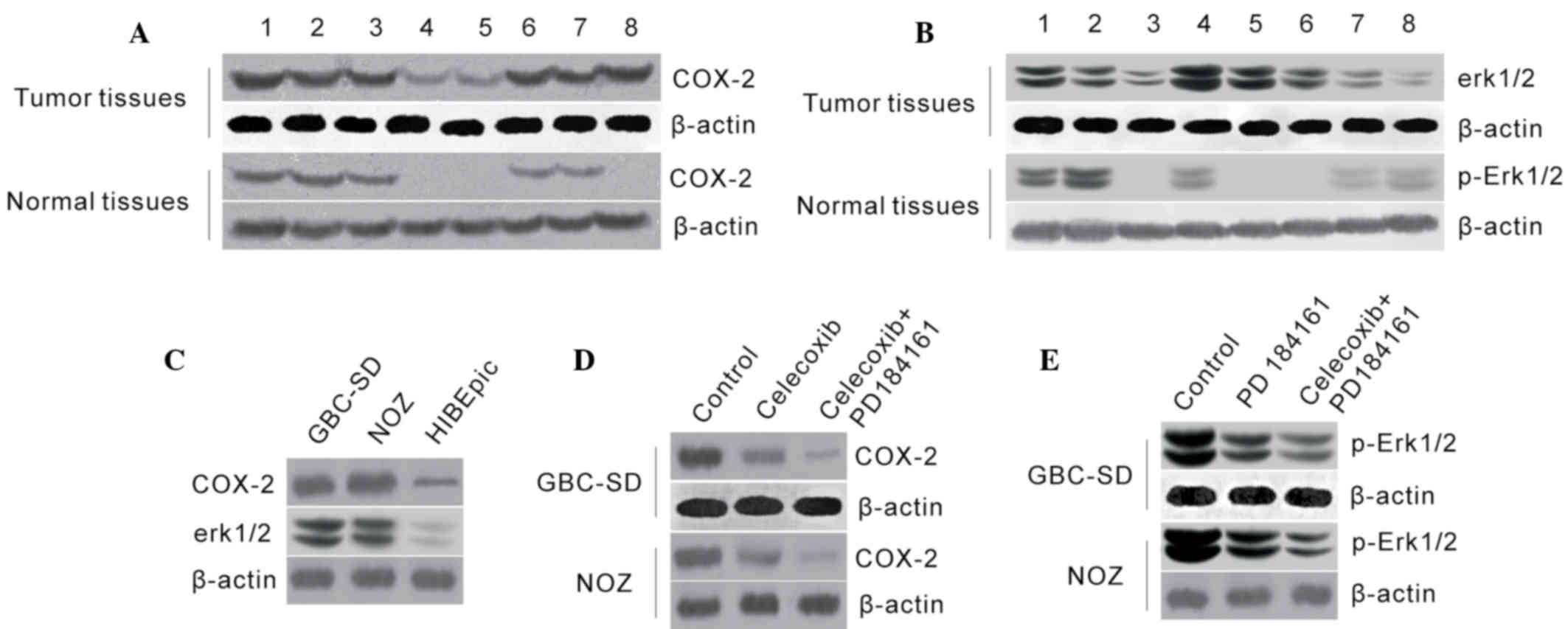
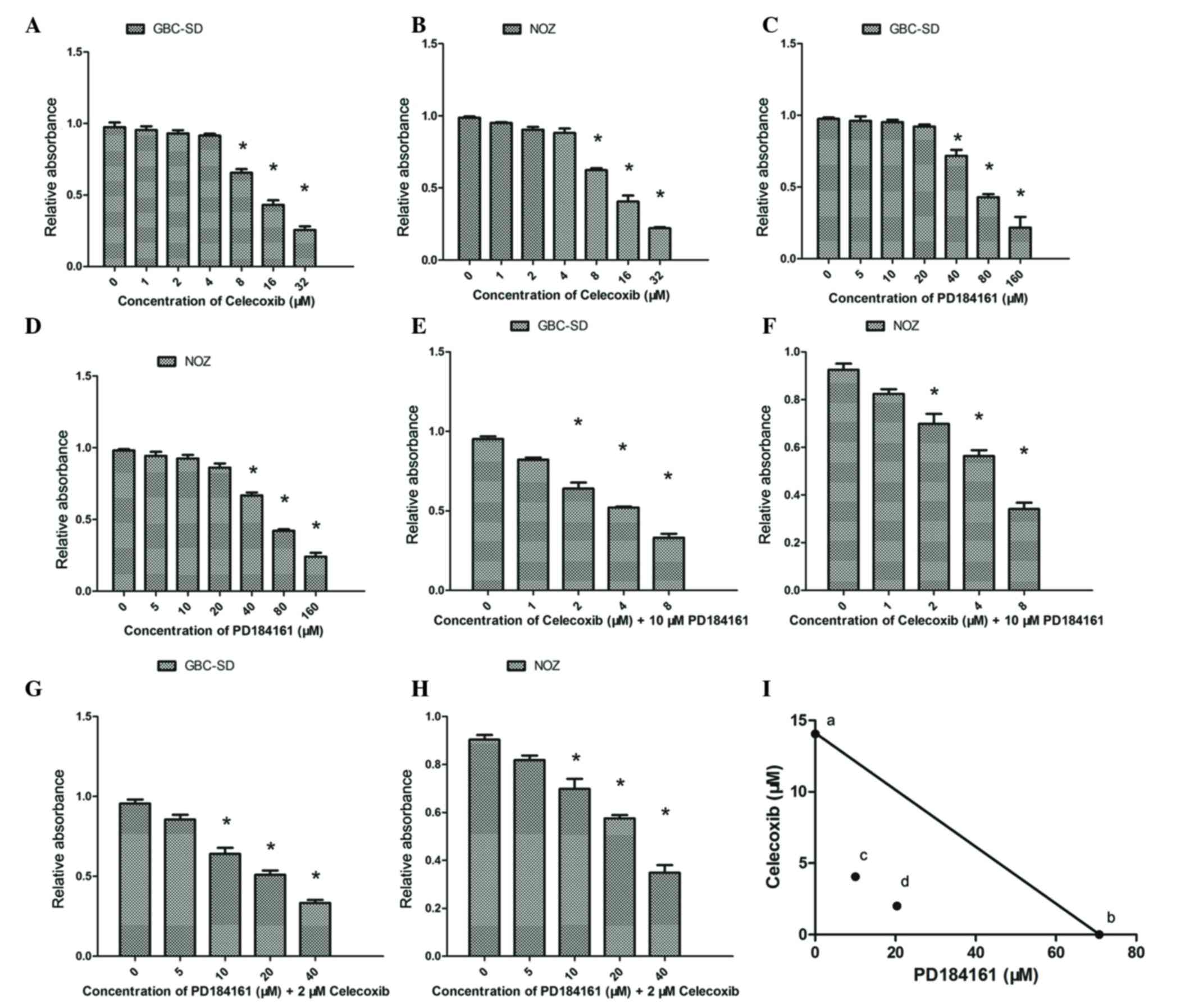
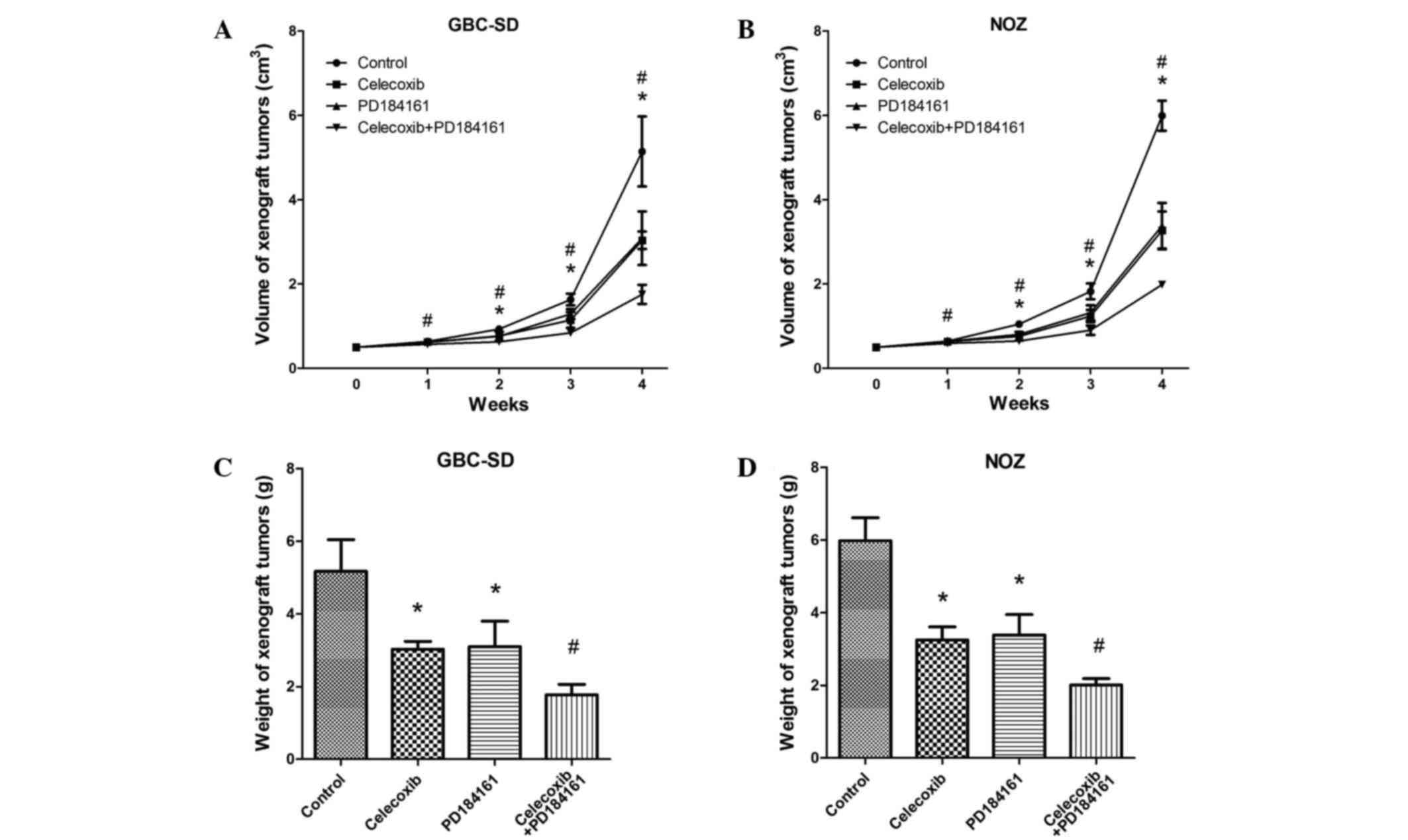
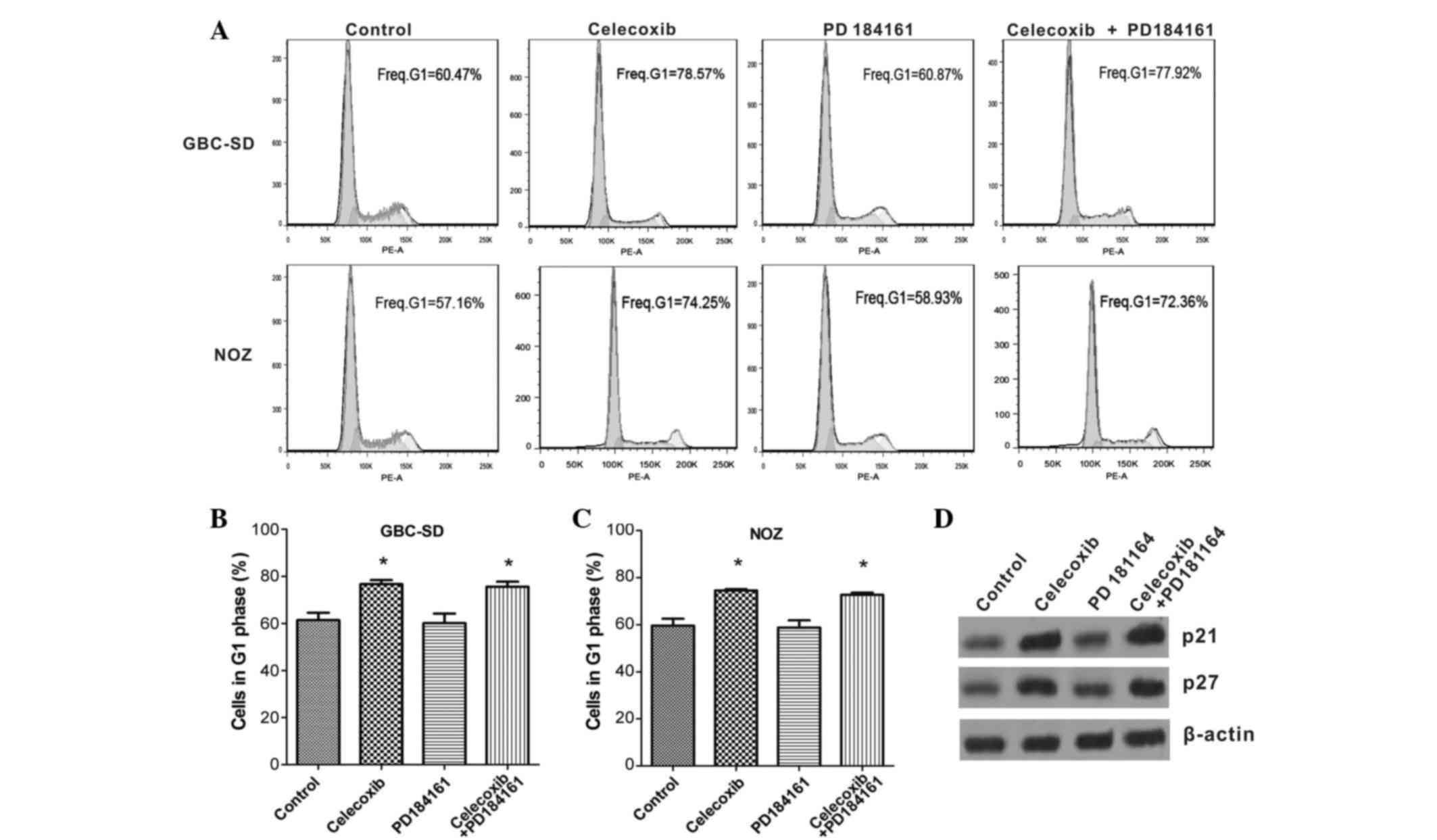
|
1
|
Stinton LM and Shaffer EA: Epidemiology of
gallbladder disease: Cholelithiasis and cancer. Gut Liver.
6:172–187. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Eslick GD: Epidemiology of gallbladder
cancer. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 39:307–330, ix. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hundal R and Shaffer EA: Gallbladder
cancer: Epidemiology and outcome. Clin Epidemiol. 6:99–109.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Levy AD, Murakata LA and Rohrmann CA Jr:
Gallbladder carcinoma: Radiologic-pathologic correlation.
Radiographics. 21:295–314. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bonet B, eltrán M, Allal AS, Gich I, Solé
JM and Carrió I: Is adjuvant radiotherapy needed after curative
resection of extrahepatic biliary tract cancers? A systematic
review with a meta-analysis of observational studies. Cancer Treat
Rev. 38:111–119. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhu AX and Hezel AF: Development of
molecularly targeted therapies in biliary tract cancers:
Reassessing the challenges and opportunities. Hepatology.
53:695–704. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bottegoni G, Favia AD, Recanatini M and
Cavalli A: The role of fragment-based and computational methods in
polypharmacology. Drug Discov Today. 17:23–34. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Greenhough A, Smartt HJ, Moore AE, Roberts
HR, Williams AC, Paraskeva C and Kaidi A: The COX-2/PGE2 pathway:
Key roles in the hallmarks of cancer and adaptation to the tumour
microenvironment. Carcinogenesis. 30:377–386. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Doval DC, Azam S, Sinha R, Batra U and
Mehta A: Expression of epidermal growth factor receptor, p53, Bcl2,
vascular endothelial growth factor, cyclooxygenase-2, cyclin D1,
human epidermal receptor-2 and Ki-67: Association with
clinicopathological profiles and outcomes in gallbladder carcinoma.
J Carcinog. 13:102014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li Q and Yang Z: Expression of
phospho-ERK1/2 and PI3-K in benign and malignant gallbladder
lesions and its clinical and pathological correlations. J Exp Clin
Cancer Res. 28:652009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Jinawath A, Akiyama Y, Yuasa Y and
Pairojkul C: Expression of phosphorylated ERK1/2 and homeodomain
protein CDX2 in cholangiocarcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol.
132:805–810. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Vicent S, López-Picazo JM, Toledo G,
Lozano MD, Torre W, Garcia-Corchón C, Quero C, Soria JC,
Martín-Algarra S, Manzano RG and Montuenga LM: ERK1/2 is activated
in non-small-cell lung cancer and associated with advanced tumours.
Br J Cancer. 90:1047–1052. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yeh JJ, Routh ED, Rubinas T, Peacock J,
Martin TD, Shen XJ, Sandler RS, Kim HJ, Keku TO and Der CJ:
KRAS/BRAF mutation status and ERK1/2 activation as biomarkers for
MEK1/2 inhibitor therapy in colorectal cancer. Mol Cancer Ther.
8:834–843. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wong DJL, Robert L, Atefi MS, Lassen A,
Avarappatt G, Cerniglia M, Avramis E, Tsoi J, Foulad D, Graeber TG,
et al: Antitumor activity of the ERK inhibitor SCH772984
[corrected] against BRAF mutant, NRAS mutant and wild-type
melanoma. Mol Cancer. 13:1942014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Reckamp KL, Koczywas M, Cristea MC, Dowell
JE, Wang HJ, Gardner BK, Milne GL, Figlin RA, Fishbein MC, Elashoff
RM and Dubinett SM: Randomized phase 2 trial of erlotinib in
combination with high-dose celecoxib or placebo in patients with
advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer. 121:3298–3306. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Steel GG and Peckham MJ: Exploitable
mechanisms in combined radiotherapy-chemotherapy: The concept of
additivity. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 5:85–91. 1979. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Smaili SS, Hsu YT, Carvalho AC, Rosenstoc
TR, Sharpe JC and Youle RJ: Mitochondria, calcium and pro-apoptotic
proteins as mediators in cell death signaling. Braz J Med Biol Res.
36:183–190. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wijesinghe P and Bollig-Fischer A: Lung
Cancer Genomics in the Era of Accelerated Targeted Drug
Development. Adv Exp Med Biol. 890:1–23. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Bae SH, Jung ES, Park YM, Kim BS, Kim BK,
Kim DG and Ryu WS: Expression of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) in
hepatocellular carcinoma and growth inhibition of hepatoma cell
lines by a COX-2 inhibitor, NS-398. Clin Cancer Res. 7:1410–1418.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
He XP, Shao Y, Li XL, Xu W, Chen GS, Sun
HH, Xu HC, Xu X, Tang D, Zheng XF, et al: Downregulation of miR-101
in gastric cancer correlates with cyclooxygenase-2 overexpression
and tumor growth. FEBS J. 279:4201–4212. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wendum D, Masliah J, Trugnan G and Fléjou
JF: Cyclooxygenase-2 and its role in colorectal cancer development.
Virchows Arch. 445:327–333. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Pomianowska E, Schjølberg AR, Clausen OP
and Gladhaug IP: COX-2 overexpression in resected pancreatic head
adenocarcinomas correlates with favourable prognosis. BMC Cancer.
14:4582014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lev-Ari S, Strier L, Kazanov D,
Madar-Shapiro L, Dvory-Sobol H, Pinchuk I, Marian B, Lichtenberg D
and Arber N: Celecoxib and curcumin synergistically inhibit the
growth of colorectal cancer cells. Clin Cancer Res. 11:6738–6744.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Klein PJ, Schmidt CM, Wiesenauer CA, Choi
JN, Gage EA, Yip-Schneider MT, Wiebke EA, Wang Y, Omer C and
Sebolt-Leopold JS: The effects of a novel MEK inhibitor PD184161 on
MEK-ERK signaling and growth in human liver cancer. Neoplasia.
8:1–8. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chen WS, Wei SJ, Liu JM, Hsiao M, Kou-Lin
J and Yang WK: Tumor invasiveness and liver metastasis of colon
cancer cells correlated with cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) expression
and inhibited by a COX-2-selective inhibitor, etodolac. Int J
Cancer. 91:894–899. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Huang ZF, Massey JB and Via DP:
Differential regulation of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) mRNA stability
by interleukin-1 beta (IL-1 beta) and tumor necrosis factor-alpha
(TNF-alpha) in human in vitro differentiated macrophages. Biochem
Pharmacol. 59:187–194. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Manna SK and Ramesh GT: Interleukin-8
induces nuclear transcription factor-kappaB through a
TRAF6-dependent pathway. J Biol Chem. 280:7010–7021. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Choi YH, Jin GY, Li GZ and Yan GH:
Cornuside suppresses lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory
mediators by inhibiting nuclear factor-kappaB activation in RAW
264.7 macrophages. Biol Pharm Bull. 34:959–966. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
He J, Wang M, Jiang Y, Chen Q, Xu S, Xu Q,
Jiang BH and Liu LZ: Chronic arsenic exposure and angiogenesis in
human bronchial epithelial cells via the
ROS/miR-199a-5p/HIF-1α/COX-2 pathway. Environ Health Perspect.
122:255–261. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kohno M and Pouyssegur J: Targeting the
ERK signaling pathway in cancer therapy. Ann Med. 38:200–211. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ferrandina G, Ranelletti FO, Legge F,
Lauriola L, Salutari V, Gessi M, Testa AC, Werner U, Navarra P,
Tringali G, et al: Celecoxib modulates the expression of
cyclooxygenase-2, ki67, apoptosis-related marker, and microvessel
density in human cervical cancer: A pilot study. Clin Cancer Res.
9:4324–4331. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Li F, Liu S, Ouyang Y, Fan C, Wang T,
Zhang C, Zeng B, Chai Y and Wang X: Effect of celecoxib on
proliferation, collagen expression, ERK1/2 and SMAD2/3
phosphorylation in NIH/3T3 fibroblasts. Eur J Pharmacol. 678:1–5.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Li F, Fan C, Zeng B, Zhang C, Chai Y, Liu
S and Ouyang Y: Celecoxib suppresses fibroblast proliferation and
collagen expression by inhibiting ERK1/2 and SMAD2/3
phosphorylation. Mol Med Rep. 5:827–831. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Liu H, Huang P, Xu X, Liu J and Guo C:
Anticancer effect of celecoxib via COX-2 dependent and independent
mechanisms in human gastric cancers cells. Dig Dis Sci.
54:1418–1424. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|