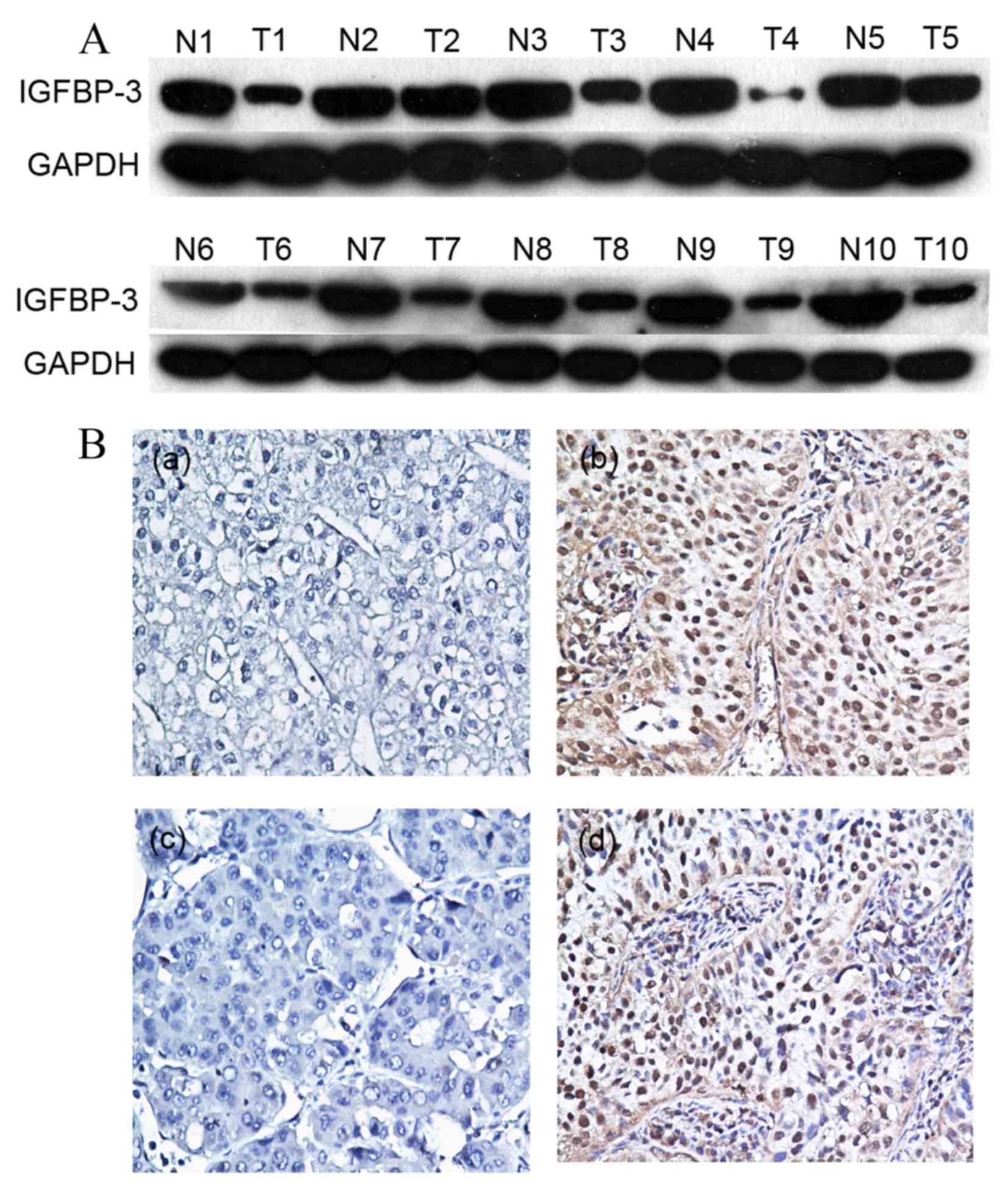
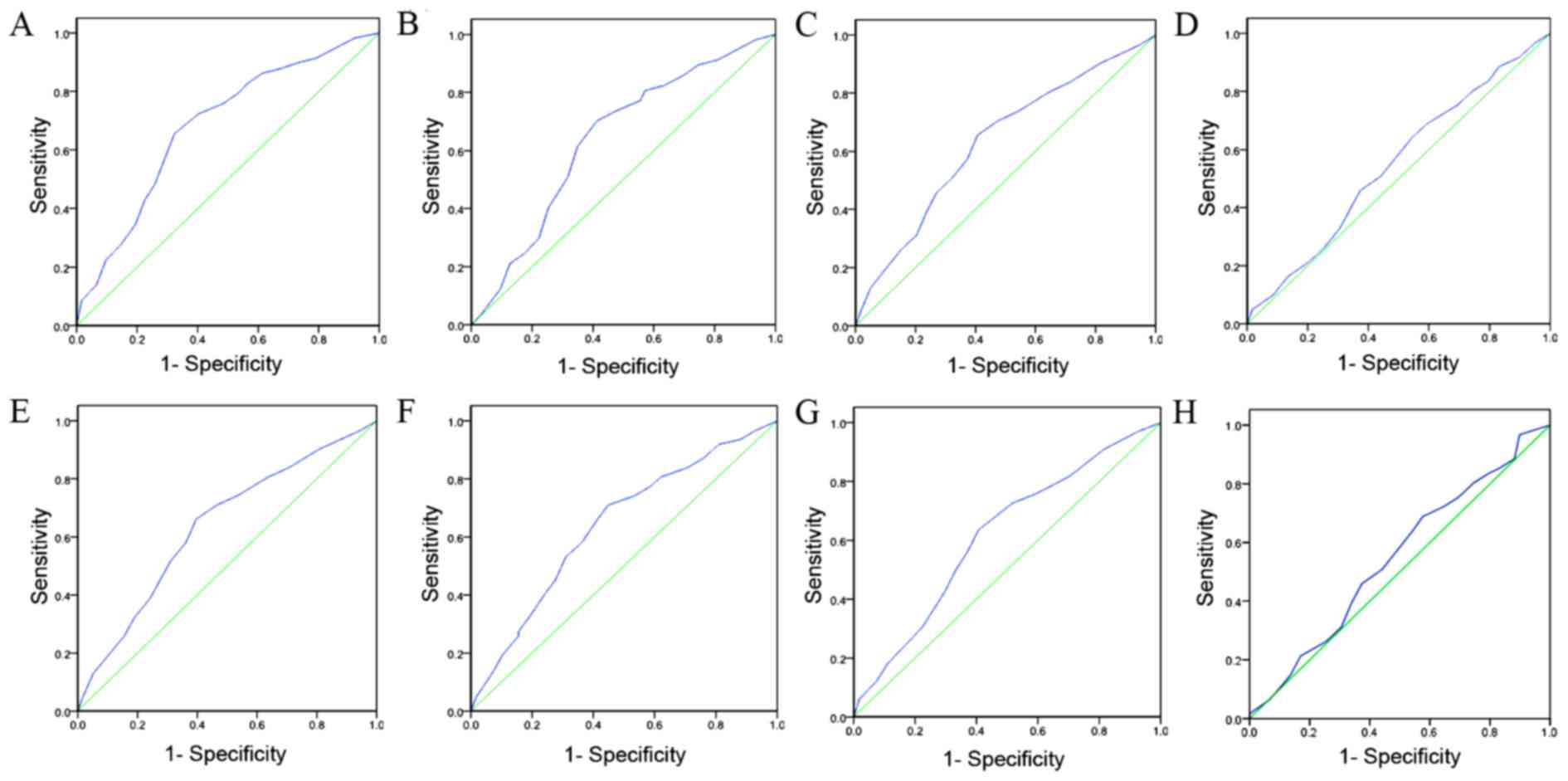
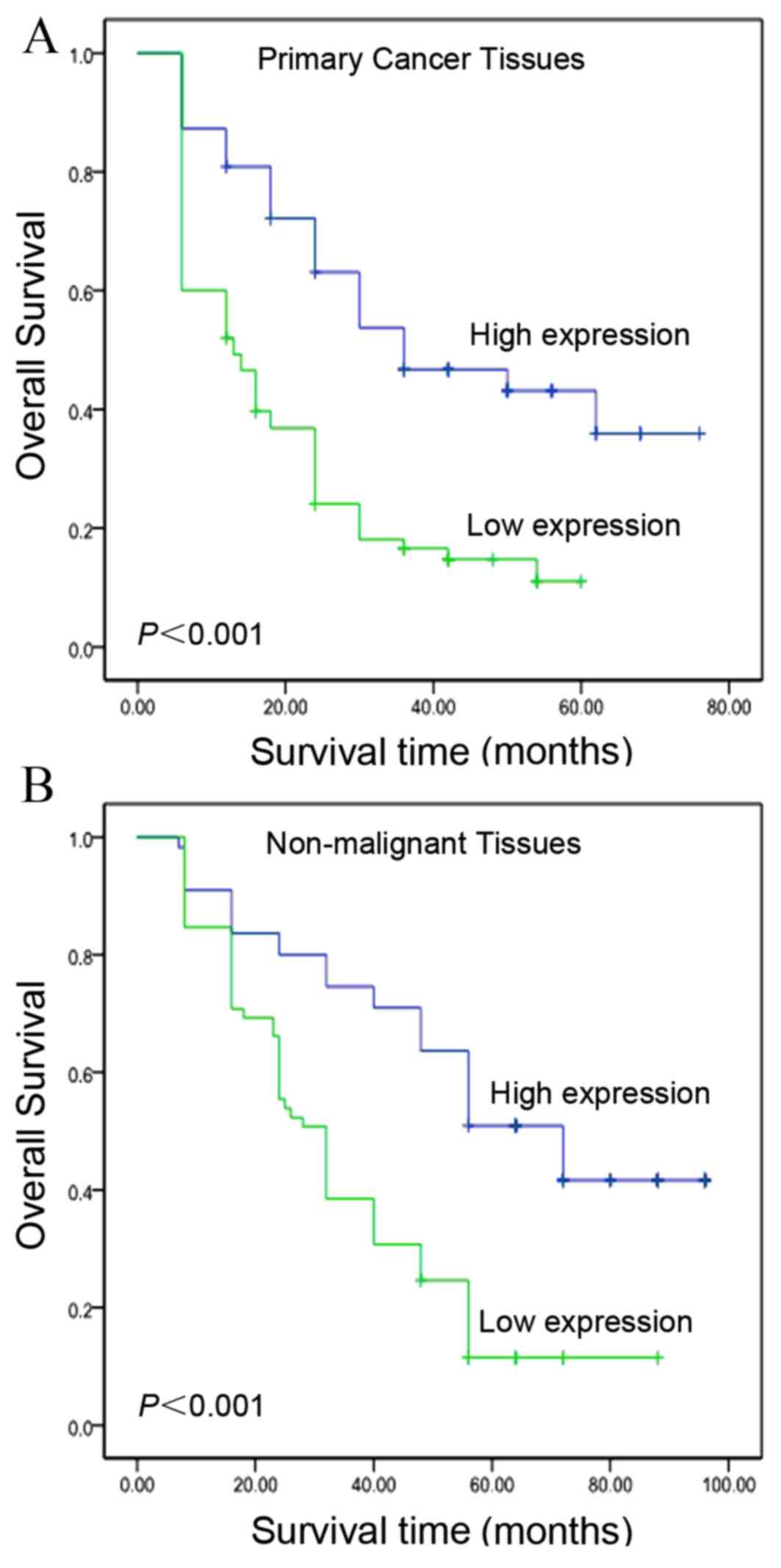
|
1
|
El-Serag HB: Epidemiology of viral
hepatitis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology.
142:1264–1273.e1. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bolondi L, Sofia S, Siringo S, Gaiani S,
Casali A, Zironi G, Piscaglia F, Gramantieri L, Zanetti M and
Sherman M: Surveillance programme of cirrhotic patients for early
diagnosis and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: A cost
effectiveness analysis. Gut. 48:251–259. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yuen MF, Cheng CC, Lauder IJ, Lam SK, Ooi
CG and Lai CL: Early detection of hepatocellular carcinoma
increases the chance of treatment: Hong Kong experience.
Hepatology. 31:330–335. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Mikami E, Kanno N, Ueno Y and Shimosegawa
T: Retrospective evaluation of tumor-mass-reduction therapy for the
prognosis of recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol Int.
1:460–468. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Cho EJ, Lee JH, Yoo JJ, Choi WM, Lee MJ,
Cho Y, Lee DH, Lee YB, Kwon JH, Yu SJ, et al: Serum insulin-like
growth factor-I level is an independent predictor of recurrence and
survival in early hepatocellular carcinoma: A prospective cohort
study. Clin Cancer Res. 19:4218–4227. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Gao L, Wang X, Wang X, Zhang L, Qiang C,
Chang S, Ren W, Li S, Yang Y, Tong D, et al: IGF-1R, a target of
let-7b, mediates crosstalk between IRS-2/Akt and MAPK pathways to
promote proliferation of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget.
5:2562–2574. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Jin C and Guo J, Qiu X, Ma K, Xiang M, Zhu
X and Guo J: IGF-1 induces iNOS expression via the p38 MAPK signal
pathway in the anti-apoptotic process in pulmonary artery smooth
muscle cells during PAH. J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 34:325–331.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yan XD, Yao M, Wang L, Zhang HJ, Yan MJ,
Gu X, Shi Y, Chen J, Dong ZZ and Yao DF: Overexpression of
insulin-like growth factor-I receptor as a pertinent biomarker for
hepatocytes malignant transformation. World J Gastroenterol.
19:6084–6092. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sedlaczek N, Hasilik A, Neuhaus P,
Schuppan D and Herbst H: Focal overexpression of insulin-like
growth factor 2 by hepatocytes and cholangiocytes in viral liver
cirrhosis. Br J Cancer. 88:733–739. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Jogie-Brahim S, Min HK and Oh Y: Potential
of proteomics towards the investigation of the IGF-independent
actions of IGFBP-3. Expert Rev Proteomics. 2:71–86. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Akturk M, Arslan M, Altinova A, Ozdemir A,
Ersoy R, Yetkin I, Ayvali E, Gonen S and Toruner F: Association of
serum levels of IGF-I and IGFBP-1 with renal function in patients
with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Growth Horm Igf Res. 17:186–193.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Jeschke MG, Barrow RE, Suzuki F, Rai J,
Benjamin D and Herndon DN: IGF-I/IGFBP-3 equilibrates ratios of
pro- to anti-inflammatory cytokines, which are predictors for organ
function in severely burned pediatric patients. Mol Med. 8:238–246.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhao Z, Liu Y, He H, Chen X, Chen J and Lu
YC: Candidate genes influencing sensitivity and resistance of human
glioblastoma to Semustine. Brain Res Bull. 86:189–194. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhao L, He LR, Zhang R, Cai MY, Liao YJ,
Qian D, Xi M, Zeng YX, Xie D and Liu MZ: Low expression of IGFBP-3
predicts poor prognosis in patients with esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma. Med Oncol. 29:2669–2676. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Varotti G, Ramacciato G, Ercolani G, Grazi
GL, Vetrone G, Cescon M, Del Gaudio M, Ravaioli M, Ziparo V, Lauro
A and Pinna A: Comparison between the fifth and sixth editions of
the AJCC/UICC TNM staging systems for hepatocellular carcinoma:
Multicentric study on 393 cirrhotic respected patients. Eur J Surg
Oncol. 31:760–767. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Xie D, Zeng YX, Wang HJ, Wen JM, Tao Y,
Sham JS and Guan XY: Expression of cytoplasmic and nuclear Survivin
in primary and secondary human glioblastoma. Br J Cancer.
94:108–114. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zlobec I, Steele R, Terracciano L, Jass JR
and Lugli A: Selecting immunohistochemical cut-off scores for novel
biomarkers of progression and survival in colorectal cancer. J Clin
Pathol. 60:1112–1116. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Cai MY, Zhang B, He WP, Yang GF, Rao HL,
Rao ZY, Wu QL, Guan XY, Kung HF, Zeng YX and Xie D: Decreased
expression of PinX1 protein is correlated with tumor development
and is a new independent poor prognostic factor in ovarian
carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 101:1543–1549. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Mesa MS, Marrodán MD, Lomaglio DB,
López-Ejeda N, Moreno-Romero S, Bejarano JI, Dipierri JE and
Pacheco JL: Anthropometric parameters in screening for excess of
adiposity in argentinian and spanish adolescents: Evaluation using
receiver operating characteristic (ROC) methodology. Ann Hum Biol.
40:396–405. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hanley JA: Receiver operating
characteristic (ROC) methodology: The state of the art. Crit Rev
Diagn Imaging. 29:307–335. 1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Taylor SC and Posch A: The design of a
quantitative western blot experiment. Biomed Res Int.
2014:3615902014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yoshino K, Motoyama S, Koyota S, Shibuya
K, Usami S, Maruyama K, Saito H, Minamiya Y, Sugiyama T and Ogawa
J: IGFBP3 and BAG1 enhance radiation-induced apoptosis in squamous
esophageal cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 404:1070–1075.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Tanaka H, Iijima H, Higashiura A, Yoh K,
Ishii A, Takashima T, Sakai Y, Aizawa N, Iwata K, Ikeda N, et al:
New malignant grading system for hepatocellular carcinoma using the
Sonazoid contrast agent for ultrasonography. J Gastroenterol.
49:755–763. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Han DH, Choi GH, Kim KS, Choi JS, Park YN,
Kim SU, Park JY, Ahn SH and Han KH: Prognostic significance of the
worst grade in hepatocellular carcinoma with heterogeneous
histologic grades of differentiation. J Gastroenterol Hepatol.
28:1384–1390. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Shahjee HM and Bhattacharyya N: Activation
of various downstream signaling molecules by IGFBP-3. J Cancer
Ther. 5:830–835. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Tas F, Karabulut S, Bilgin E, Tastekin D
and Duranyildiz D: Clinical significance of serum insulin-like
growth factor-1 (IGF-1) and insulin-like growth factor binding
protein-3 (IGFBP-3) in patients with breast cancer. Tumour Biol.
35:9303–9309. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ingermann AR, Yang YF, Han J, Mikami A,
Garza AE, Mohanraj L, Fan L, Idowu M, Ware JL, Kim HS, et al:
Identification of a novel cell death receptor mediating
IGFBP-3-induced anti-tumor effects in breast and prostate cancer. J
Biol Chem. 285:30233–30246. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Butt AJ and Williams AC: IGFBP-3 and
apoptosis-a license to kill? Apoptosis. 6:199–205. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Huang XP, Zhou WH and Zhang YF: Genetic
variations in the IGF-IGFR-IGFBP axis confer susceptibility to lung
and esophageal cancer. Genet Mol Res. 13:2107–2119. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Gill ZP, Perks CM, Newcomb PV and Holly
JM: Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein (IGFBP-3)
predisposes breast cancer cells to programmed cell death in a
non-IGF-dependent manner. J Biol Chem. 272:25602–25607. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Vijayababu MR, Kanagaraj P, Arunkumar A,
Ilangovan R, Dharmarajan A and Arunakaran J: Quercetin induces
p53-independent apoptosis in human prostate cancer cells by
modulating Bcl-2-related proteins: A possible mediation by IGFBP-3.
Oncol Res. 16:67–74. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Butt AJ, Firth SM, King MA and Baxter RC:
Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3 modulates expression
of Bax and Bcl-2 and potentiates p53-independent radiation-induced
apoptosis in human breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem.
275:39174–39181. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Takaoka M, Harada H, Andl CD, Oyama K,
Naomoto Y, Dempsey KL, Klein-Szanto AJ, El-Deiry WS, Grimberg A and
Nakagawa H: Epidermal growth factor receptor regulates aberrant
expression of insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 3. Cancer
Res. 64:7711–7723. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhao L, He LR, Xi M, Cai MY, Shen JX, Li
QQ, Liao YJ, Qian D, Feng ZZ, Zeng YX, et al: Nimotuzumab promotes
radiosensitivity of EGFR-overexpression esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma cells by upregulating IGFBP-3. J Transl Med. 10:2492012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Adamek A, Kasprzak A, Mikoś H,
Przybyszewska W, Seraszek-Jaros A, Czajka A, Sterzyńska K and
Mozer-Lisewska I: The insulin-like growth factor-1 and expression
of its binding protein-3 in chronic hepatitis C and hepatocellular
carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 30:1337–1345. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Aleem E, Elshayeb A, Elhabachi N, Mansour
AR, Gowily A and Hela A: Serum IGFBP-3 is a more effective
predictor than IGF-1 and IGF-2 for the development of
hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with chronic HCV infection.
Oncol Lett. 3:704–712. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|