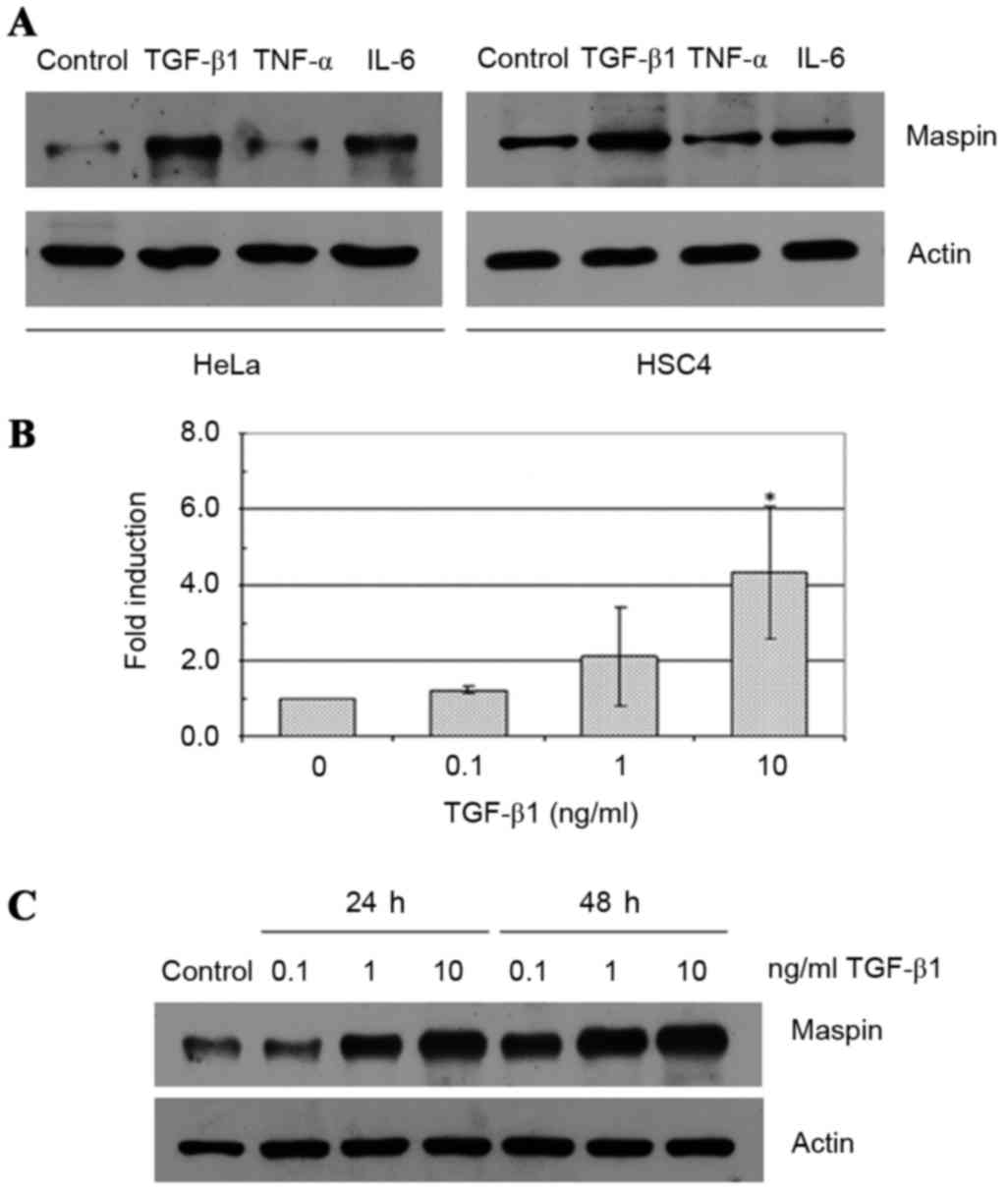
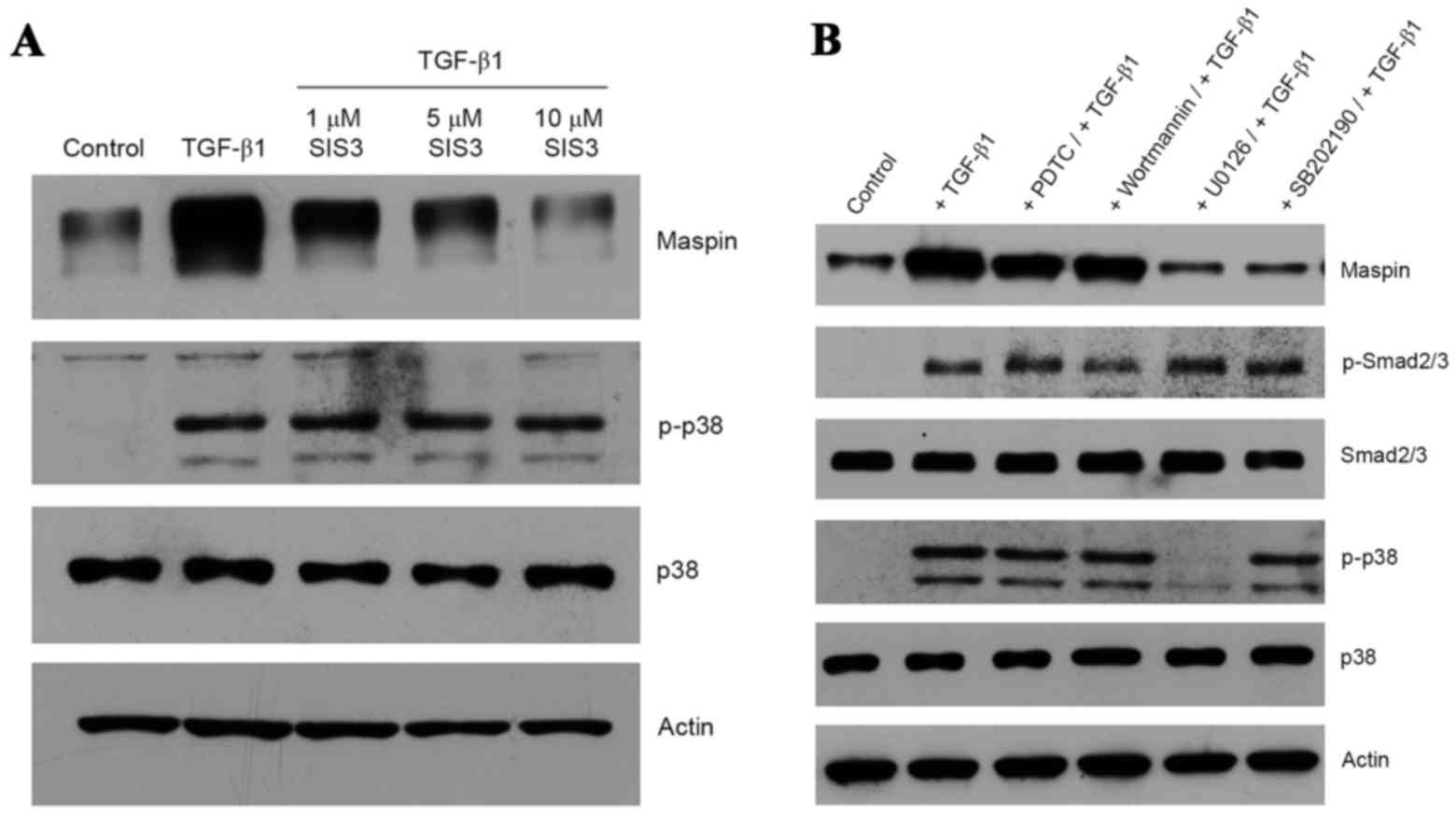
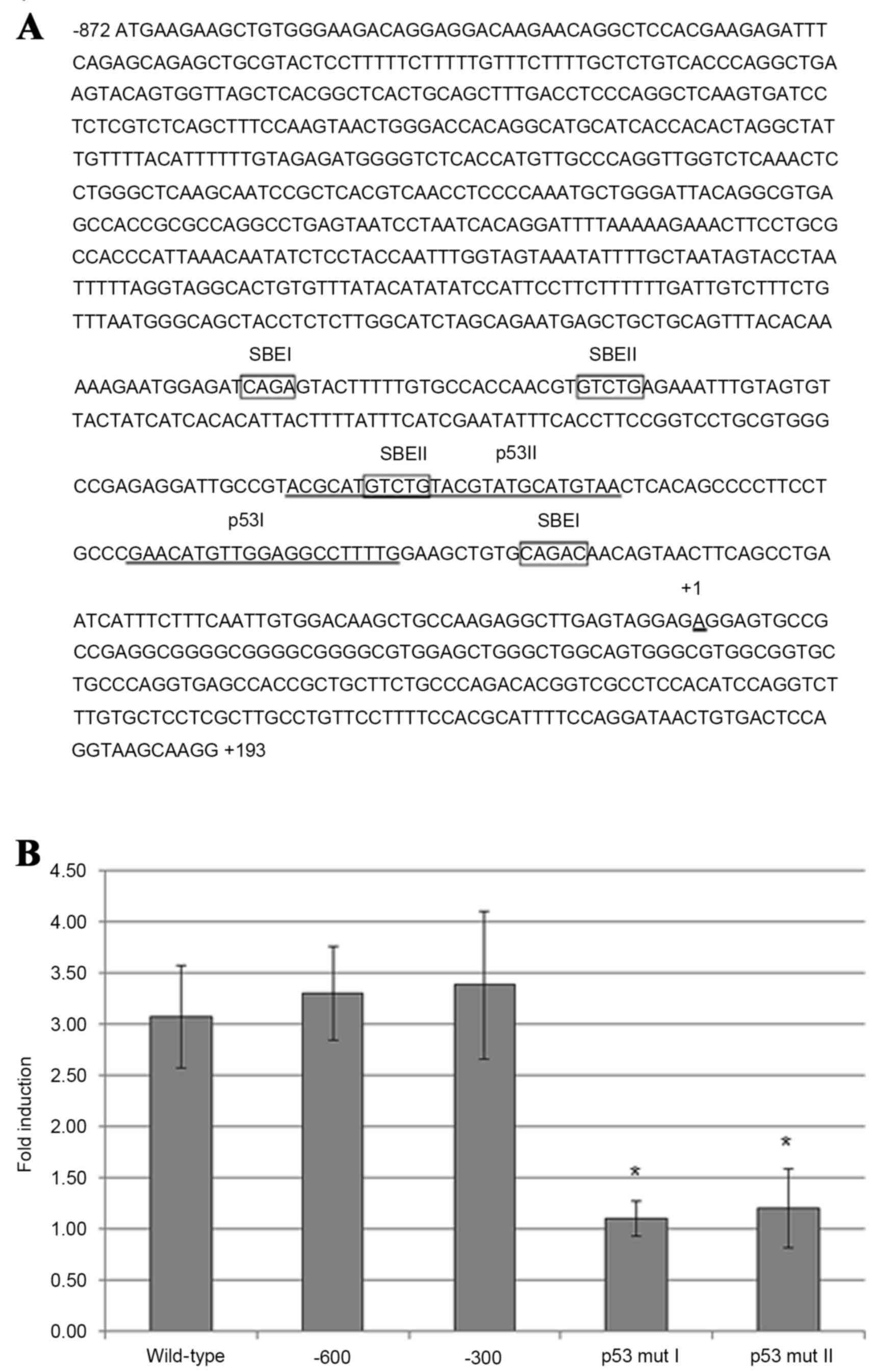
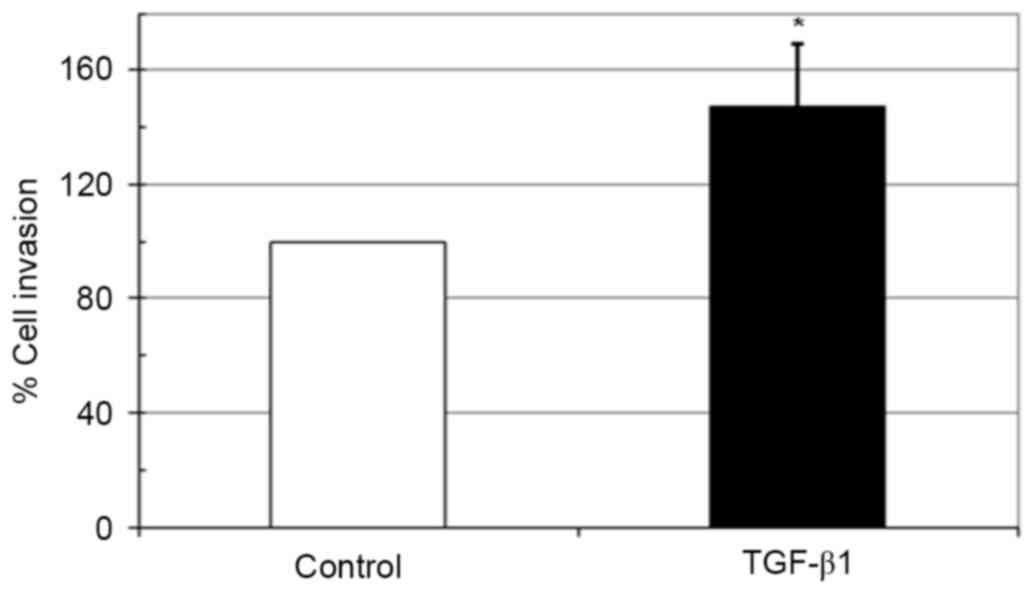
|
1
|
Silverman GA, Bird PI, Carrell RW, Church
FC, Coughlin PB, Gettins PG, Irving JA, Lomas DA, Luke CJ, Moyer
RW, et al: The serpins are an expanding superfamily of structurally
similar but functionally diverse proteins. Evolution, mechanism of
inhibition, novel functions, and a revised nomenclature. J Biol
Chem. 276:33293–33296. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bodenstine TM, Seftor RE, Khalkhali-Ellis
Z, Seftor EA, Pemberton PA and Hendrix MJ: Maspin: Molecular
mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Cancer Metastasis Rev.
31:529–551. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zou Z, Anisowicz A, Hendrix MJ, Thor A,
Neveu M, Sheng S, Rafidi K, Seftor E and Sager R: Maspin, a serpin
with tumor-suppressing activity in human mammary epithelial cells.
Science. 263:526–529. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Beltran A, Parikh S, Liu Y, Cuevas BD,
Johnson GL, Futscher BW and Blancafort P: Re-activation of a
dormant tumor suppressor gene maspin by designed transcription
factors. Oncogene. 26:2791–2798. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Maass N, Nagasaki K, Ziebart M, Mundhenke
C and Jonat W: Expression and regulation of tumor suppressor gene
maspin in breast cancer. Clin Breast Cancer. 3:281–287. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zou Z, Zhang W, Young D, Gleave MG, Rennie
P, Connell T, Connelly R, Moul J, Srivastava S and Sesterhenn I:
Maspin expression profile in human prostate cancer (CaP) and in
vitro induction of Maspin expression by androgen ablation. Clin
Cancer Res. 8:1172–1177. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bauerschlag DO, Habermann M, Weimer J,
Meinhold-Heerlein I, Hilpert F, Weigel M, Bauer M, Mundhenke C,
Jonat W, Maass N and Schem C: Heterogeneous expression of serine
protease inhibitor maspin in ovarian cancer. Anticancer Res.
30:2739–2744. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Frey A, Soubani AO, Adam AK, Sheng S, Pass
HI and Lonardo F: Nuclear, compared with combined nuclear and
cytoplasmic expression of maspin, is linked in lung adenocarcinoma
to reduced VEGF-A levels and in Stage I, improved survival.
Histopathology. 54:590–597. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Liu H, Shi J, Anandan V, Wang HL, Diehl D,
Blansfield J, Gerhard G and Lin F: Reevaluation and identification
of the best immunohistochemical panel (pVHL, Maspin, S100P, IMP-3)
for ductal adenocarcinoma of the pancreas. Arch Pathol Lab Med.
136:601–609. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Cao D, Wilentz RE, Abbruzzese JL, Ho L and
Maitra A: Aberrant expression of maspin in idiopathic inflammatory
bowel disease is associated with disease activity and neoplastic
transformation. Int J Gastrointest Cancer. 36:39–46. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kim J, Jang KT, Kim KH, Park JW, Chang BJ,
Lee KH, Lee JK, Heo JS, Choi SH, Choi DW, et al: Aberrant maspin
expression is involved in early carcinogenesis of gallbladder
cancer. Tumour Biol. 31:471–476. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Dinarello CA: The paradox of
pro-inflammatory cytokines in cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev.
25:307–313. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Gohji K, Nomi M, Hara I, Arakawa S and
Kamidono S: Influence of cytokines and growth factors on matrix
metalloproteinase-2 production and invasion of human renal cancer.
Urol Res. 26:33–37. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Heldin CH and Moustakas A: Role of Smads
in TGFb signaling. Cell Tissue Res. 347:21–36. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Mu Y, Gudey SK and Landström M: Non-Smad
signaling pathways. Cell Tissue Res. 347:11–20. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Arteaga CL, Dugger TC and Hurd SD: The
multifunctional role of transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta s on
mammary epithelial cell biology. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 38:49–56.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Drabsch Y and ten Dijke P: TGF-b signaling
in breast cancer cell invasion and bone metastasis. J Mammary Gland
Biol Neoplasia. 16:97–108. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang SE, Narasanna A, Whitell CW, Wu FY,
Friedman DB and Arteaga CL: Convergence of p53 and transforming
growth factor beta (TGFbeta) signaling on activating expression of
the tumor suppressor gene maspin in mammary epithelial cells. J
Biol Chem. 282:5661–5669. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Jung V, Pestka SB and Pestka S: Cloning of
polymerase chain reaction-generated DNA containing terminal
restriction endonuclease recognition sites. Methods Enzymol.
218:357–362. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Jinnin M, Ihn H and Tamaki K:
Characterization of SIS3, a novel specific inhibitor of Smad3, and
its effect on transforming growth factor-beta1-induced
extracellular matrix expression. Mol Pharmacol. 69:597–607. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kumar S, Jiang MS, Adams JL and Lee JC:
Pyridinylimidazole compound SB 203580 inhibits the activity but not
the activation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 263:825–831. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bailey CM, Khalkhali-Ellis Z, Seftor EA
and Hendrix MJ: Biological functions of maspin. J Cell Physiol.
209:617–624. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Elston R and Inman GJ: Crosstalk between
p53 and TGF-beta Signalling. J Signal Transduct. 2012:2940972012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Cordenonsi M, Dupont S, Maretto S, Insinga
A, Imbriano C and Piccolo S: Links between tumor suppressors: p53
is required for TGF-beta gene responses by cooperating with Smads.
Cell. 113:301–314. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Poddar R and Paul S: Novel crosstalk
between ERK MAPK and p38 MAPK leads to homocysteine-NMDA
receptor-mediated neuronal cell death. J Neurochem. 124:558–570.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Huang C, Ma WY, Maxiner A, Sun Y and Dong
Z: p38 kinase mediates UV-induced phosphorylation of p53 protein at
serine 389. J Biol Chem. 274:12229–12235. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Cordenonsi M, Montagner M, Adorno M,
Zacchigna L, Martello G, Mamidi A, Soligo S, Dupont S and Piccolo
S: Integration of TGF-beta and Ras/MAPK signaling through p53
phosphorylation. Science. 315:840–843. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yu L, Hebert MC and Zhang YE: TGF-beta
receptor-activated p38 MAP kinase mediates Smad-independent
TGF-beta responses. EMBO J. 21:3749–3759. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Oshiro MM, Watts GS, Wozniak RJ, Junk DJ,
Munoz-Rodriguez JL, Domann FE and Futscher BW: Mutant p53 and
aberrant cytosine methylation cooperate to silence gene expression.
Oncogene. 22:3624–3634. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Horswill MA, Narayan M, Warejcka DJ,
Cirillo LA and Twining SS: Epigenetic silencing of maspin
expression occurs early in the conversion of keratocytes to
fibroblasts. Exp Eye Res. 86:586–600. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Vo BT, Morton D Jr, Komaragiri S, Millena
AC, Leath C and Khan SA: TGF-b effects on prostate cancer cell
migration and invasion are mediated by PGE2 through activation of
PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Endocrinology. 154:1768–1779. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ngamkitidechakul C, Warejcka DJ, Burke JM,
O'Brien WJ and Twining SS: Sufficiency of the reactive site loop of
maspin for induction of cell-matrix adhesion and inhibition of cell
invasion. Conversion of ovalbumin to a maspin-like molecule. J Biol
Chem. 278:31796–31806. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yatabe Y, Mitsudomi T and Takahashi T:
Maspin expression in normal lung and non-small-cell lung cancers:
Cellular property-associated expression under the control of
promoter DNA methylation. Oncogene. 23:4041–4049. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Friedrich MG, Toma MI, Petri S, Cheng JC,
Hammerer P, Erbersdobler A and Huland H: Expression of Maspin in
non-muscle invasive bladder carcinoma: Correlation with tumor
angiogenesis and prognosis. Eur Urol. 45:737–743. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Rose SL, Fitzgerald MP, White NO, Hitchler
MJ, Futscher BW, De Geest K and Domann FE: Epigenetic regulation of
maspin expression in human ovarian carcinoma cells. Gynecol Oncol.
102:319–324. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Nosaka K, Horie Y, Shiomi T, Itamochi H,
Oishi T, Shimada M, Sato S, Sakabe T, Harada T and Umekita Y:
Cytoplasmic maspin expression correlates with poor prognosis of
patients with adenocarcinoma of the uterine cervix. Yonago Acta
Med. 58:151–156. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Torres A, Torres K, Paszkowski T, Radej S,
Staśkiewicz GJ, Ceccaroni M, Pesci A and Maciejewski R: Highly
increased maspin expression corresponds with up-regulation of
miR-21 in endometrial cancer: A preliminary report. Int J Gynecol
Cancer. 21:8–14. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Goulet B, Kennette W, Ablack A, Postenka
CO, Hague MN, Mymryk JS, Tuck AB, Giguère V, Chambers AF and Lewis
JD: Nuclear localization of maspin is essential for its inhibition
of tumor growth and metastasis. Lab Invest. 91:1181–1187. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|