|
1
|
Thompson LD: Osteosarcoma. Ear Nose Throat
J. 92:288–290. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zhang J, Yu XH, Yan YG, Wang C and Wang
WJ: PI3K/Akt signaling in osteosarcoma. Clin Chim Acta.
444:182–192. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
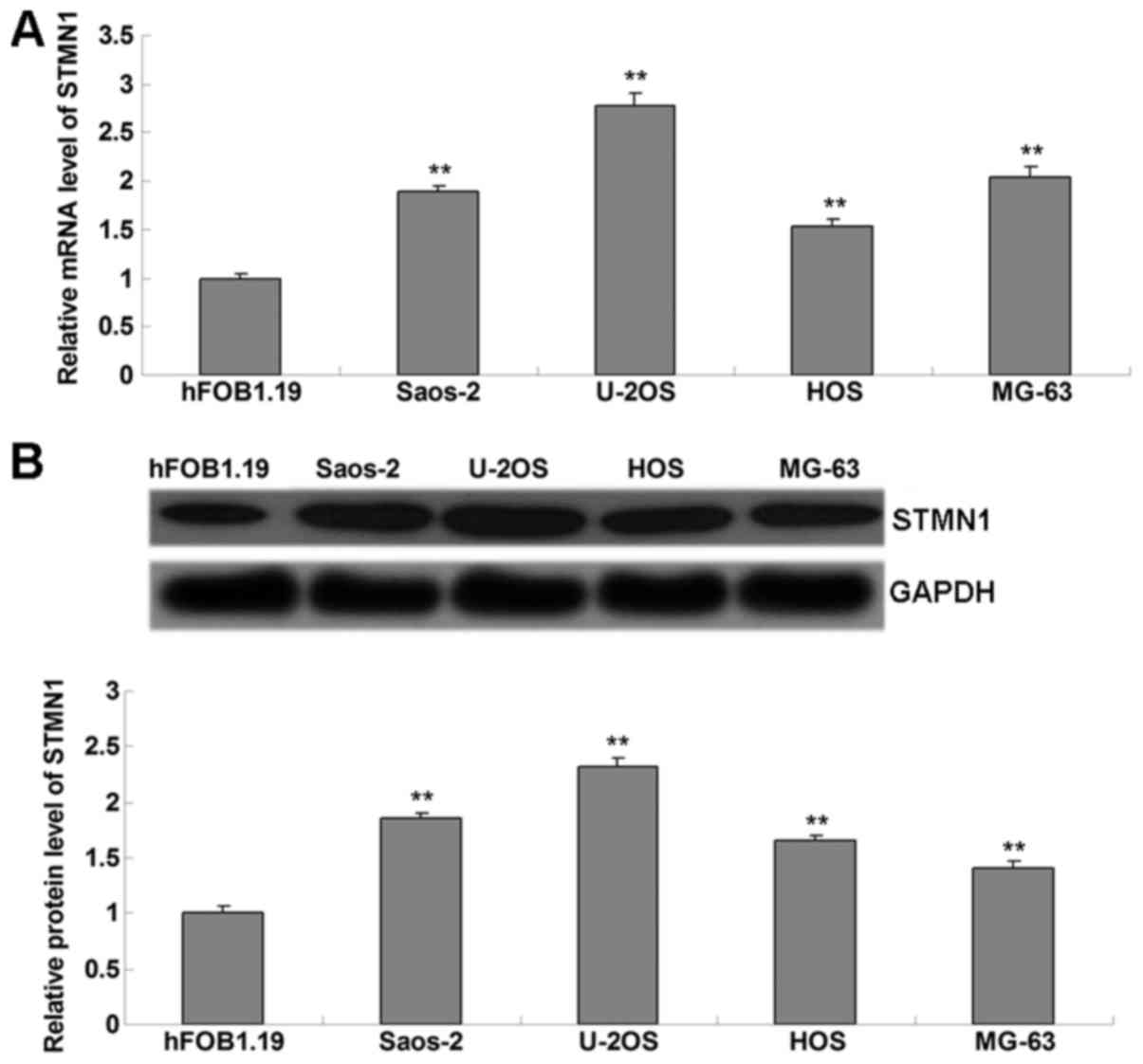
|
3
|
Chang Z, Huo L, Li K, Wu Y and Hu Z:
Blocked autophagy by miR-101 enhances osteosarcoma cell
chemosensitivity in vitro. ScientificWorldJournal. 2014:7947562014.
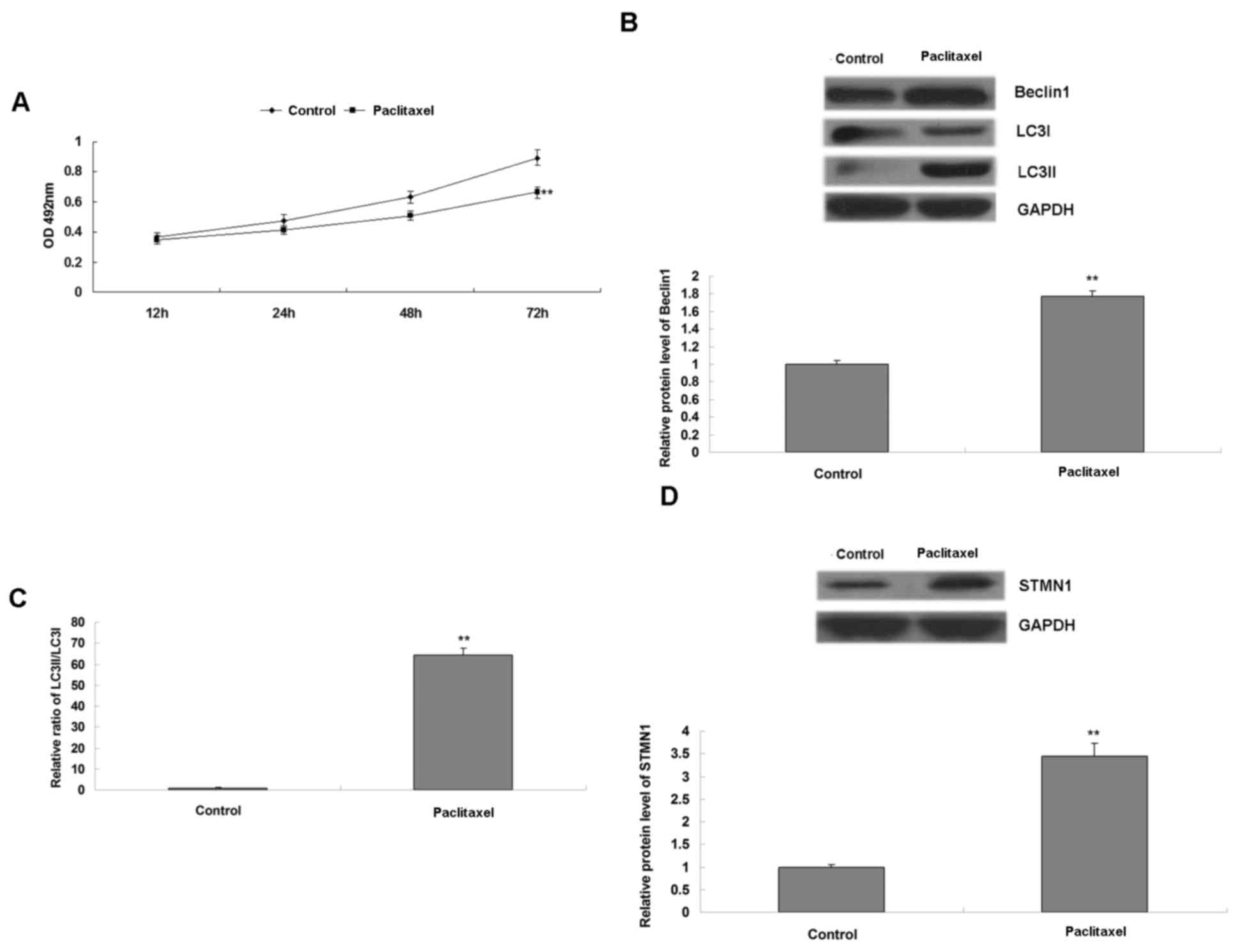
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
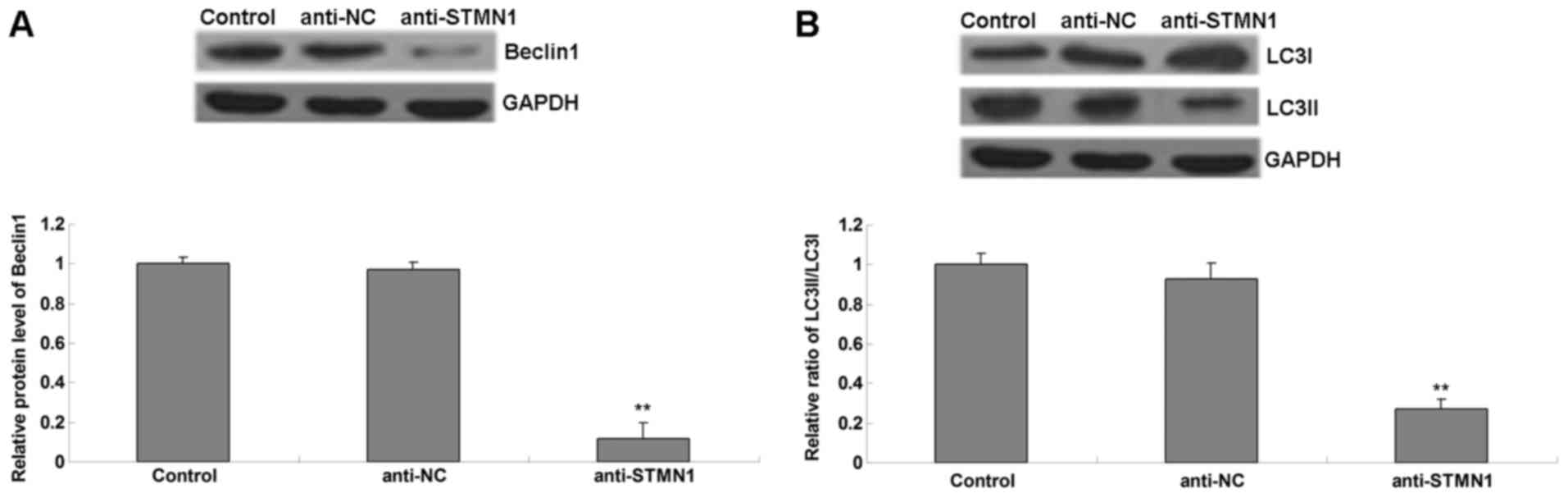
|
|
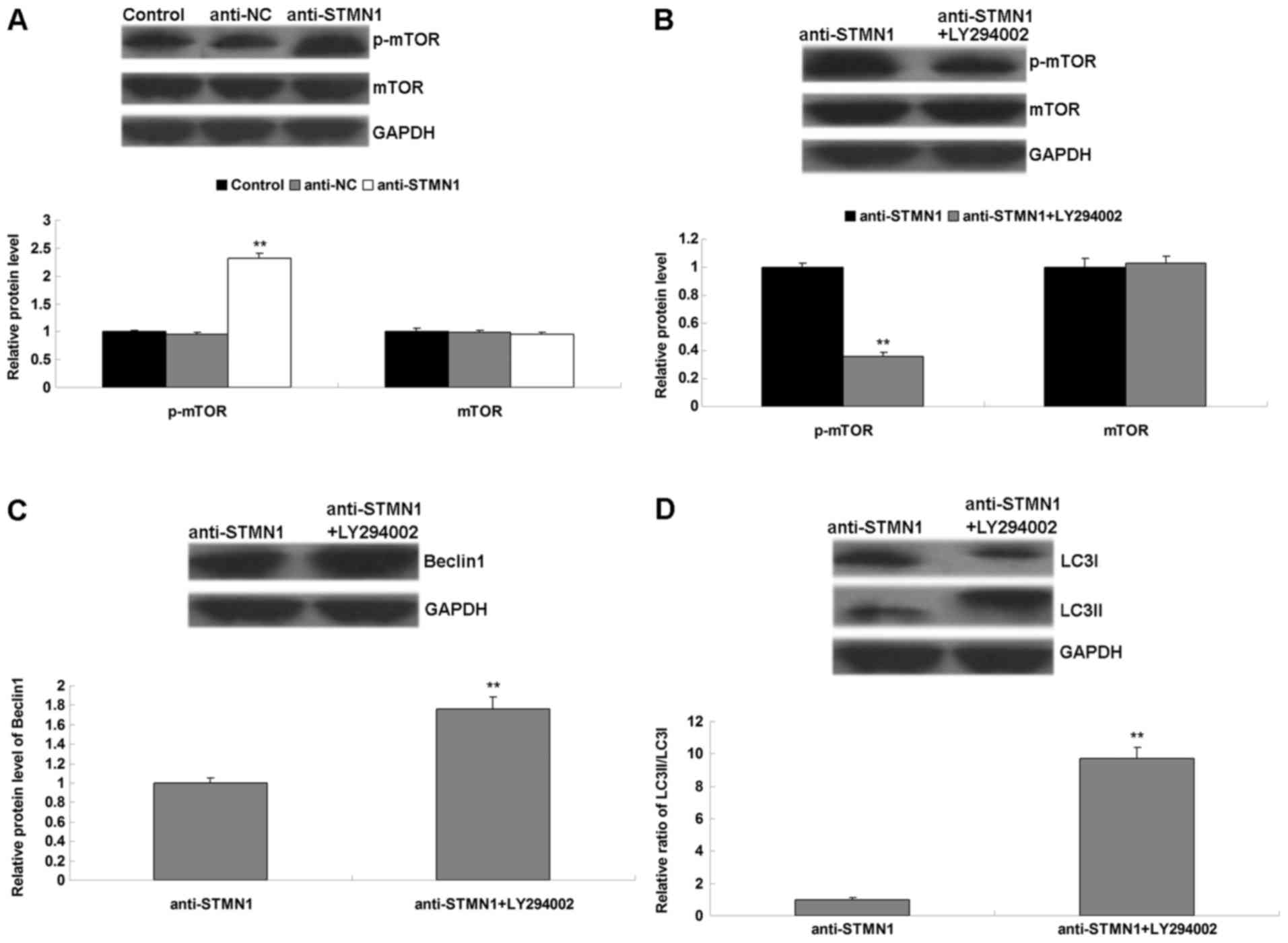
4
|
Zhou Y, Huang Z, Wu S, Zang X, Liu M and
Shi J: miR-33a is up-regulated in chemoresistant osteosarcoma and
promotes osteosarcoma cell resistance to cisplatin by
down-regulating TWIST. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 33:122014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hippert MM, O'Toole PS and Thorburn A:
Autophagy in cancer: Good, bad, or both? Cancer Res. 66:9349–9351.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Gonzalez CD, Alvarez S, Ropolo A,
Rosenzvit C, Gonzalez Bagnes MF and Vaccaro MI: Autophagy, Warburg
and Warburg reverse effects in human cancer. Biomed Res Int.
2014:9267292014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhang R, Wang R, Chen Q and Chang H:
Inhibition of autophagy using 3-methyladenine increases
cisplatin-induced apoptosis by increasing endoplasmic reticulum
stress in U251 human glioma cells. Mol Med Rep. 12:1727–1732.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zheng B, Zhu H, Gu D, Pan X, Qian L, Xue
B, Yang D, Zhou J and Shan Y: MiRNA-30a-mediated autophagy
inhibition sensitizes renal cell carcinoma cells to sorafenib.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 459:234–239. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Rebecca VW and Amaravadi RK: Emerging
strategies to effectively target autophagy in cancer. Oncogene.
35:1–11. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Rana S, Maples PB, Senzer N and Nemunaitis
J: Stathmin 1: A novel therapeutic target for anticancer activity.
Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 8:1461–1470. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Mistry SJ and Atweh GF: Role of stathmin
in the regulation of the mitotic spindle: Potential applications in
cancer therapy. Mt Sinai J Med. 69:299–304. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang S, Akhtar J and Wang Z: Anti-STMN1
therapy improves sensitivity to antimicrotubule drugs in esophageal
squamous cell carcinoma. Tumour Biol. 36:7797–7806. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhang HZ, Gao P, Yan L and Lin F:
Significance of stathmin gene overexpression in osteosarcoma cells.
Ai Zheng. 23:493–496. 2004.(In Chinies). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Phadke AP, Jay CM, Wang Z, Chen S, Liu S,
Haddock C, Kumar P, Pappen BO, Rao DD, Templeton NS, et al: In vivo
safety and antitumor efficacy of bifunctional small hairpin RNAs
specific for the human Stathmin 1 oncoprotein. DNA Cell Biol.
30:715–726. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Livak and Schmittgen: Analysis of relative
gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the
2-ΔΔCt method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chen X, Shen J, Li X, Wang X, Long M, Lin
F, Wei J, Yang L, Yang C, Dong K and Zhang H: Rlim, an E3 ubiquitin
ligase, influences the stability of Stathmin protein in human
osteosarcoma cells. Cell Signal. 26:1532–1538. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hemdan T, Lindén M, Lind SB, Namuduri AV,
Sjöstedt E, de Ståhl TD, Asplund A, Malmström PU and Segersten U:
The prognostic value and therapeutic target role of stathmin-1 in
urinary bladder cancer. Br J Cancer. 111:1180–1187. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang F, Xuan XY, Yang X, Cao L, Pang LN,
Zhou R, Fan QX and Wang LX: Stathmin is a marker of progression and
poor prognosis in esophageal carcinoma. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev.
15:3613–3618. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Guo Y, Huang C, Li G, Chen T, Li J and
Huang Z: Paxilitaxel induces apoptosis accompanied by protective
autophagy in osteosarcoma cells through hypoxiainducible factor-1α
pathway. Mol Med Rep. 12:3681–3687. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang W, Li Q, Song C and Lao L: Knockdown
of autophagy-related protein 6, Beclin-1, decreases cell growth,
invasion, and metastasis and has a positive effect on
chemotherapy-induced cytotoxicity in osteosarcoma cells. Tumour
Biol. 36:2531–2539. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wu W, Li W, Zhou Y and Zhang C: Inhibition
of beclin1 affects the chemotherapeutic sensitivity of
osteosarcoma. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 7:7114–7122. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Choi J, Jo M, Lee E, Lee DY and Choi D:
Dienogest enhances autophagy induction in endometriotic cells by
impairing activation of AKT, ERK1/2, and mTOR. Fertil Steril.
104:655–664. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Matsuzawa Y, Oshima S, Takahara M,
Maeyashiki C, Nemoto Y, Kobayashi M, Nibe Y, Nozaki K, Nagaishi T,
Okamoto R, et al: TNFAIP3 promotes survival of CD4 T cells by
restricting MTOR and promoting autophagy. Autophagy. 11:1052–1062.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chang Z, Shi G, Jin J, Guo H, Guo X, Luo
F, Song Y and Jia X: Dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitor NVP-BEZ235-induced
apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines is enhanced by
inhibitors of autophagy. Int J Mol Med. 31:1449–1456.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zheng F, Liao YJ, Cai MY, Liu TH, Chen SP,
Wu PH, Wu L, Bian XW, Guan XY, Zeng YX, et al: Systemic delivery of
microRNA-101 potently inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma in vivo by
repressing multiple targets. PLoS Genet. 11:e10048732015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wang R, Wang HB, Hao CJ, Cui Y, Han XC, Hu
Y, Li FF, Xia HF and Ma X: MiR-101 is involved in human breast
carcinogenesis by targeting Stathmin1. PLoS One. 7:e461732012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wang L, Zhang X, Jia LT, Hu SJ, Zhao J,
Yang JD, Wen WH, Wang Z, Wang T, Zhao J, et al: c-Myc-mediated
epigenetic silencing of MicroRNA-101 contributes to dysregulation
of multiple pathways in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology.
59:1850–1863. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Frankel LB, Wen J, Lees M, Høyer-Hansen M,
Farkas T, Krogh A, Jäättelä M and Lund AH: microRNA-101 is a potent
inhibitor of autophagy. EMBO J. 30:4628–4641. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Xu Y, An Y, Wang Y, Zhang C, Zhang H,
Huang C, Jiang H, Wang X and Li X: miR-101 inhibits autophagy and
enhances cisplatin-induced apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma
cells. Oncol Rep. 29:2019–2024. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sun Q, Liu T, Zhang T, Du S, Xie GX, Lin
X, Chen L and Yuan Y: MiR-101 sensitizes human nasopharyngeal
carcinoma cells to radiation by targeting stathmin 1. Mol Med Rep.
11:3330–3336. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|