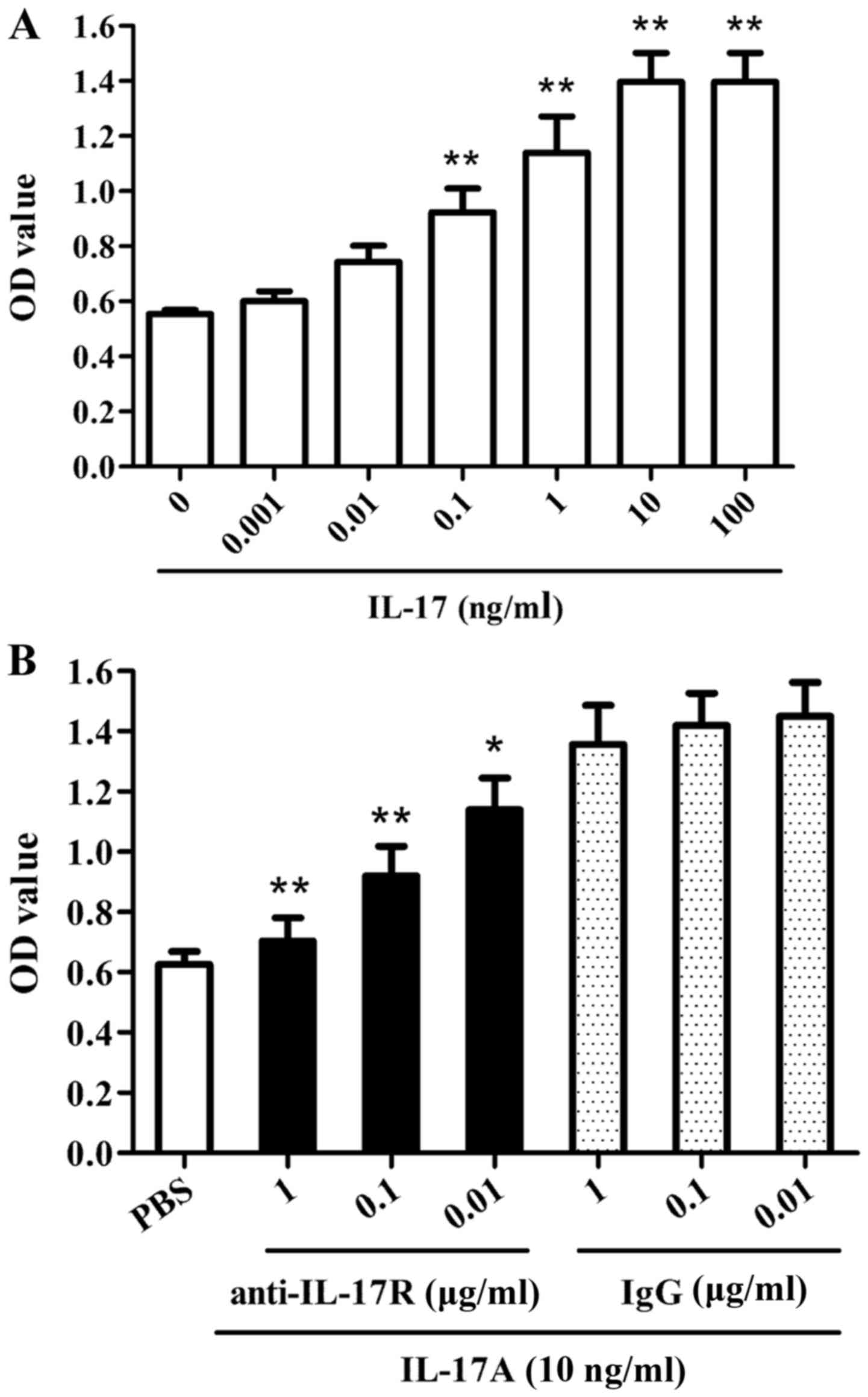
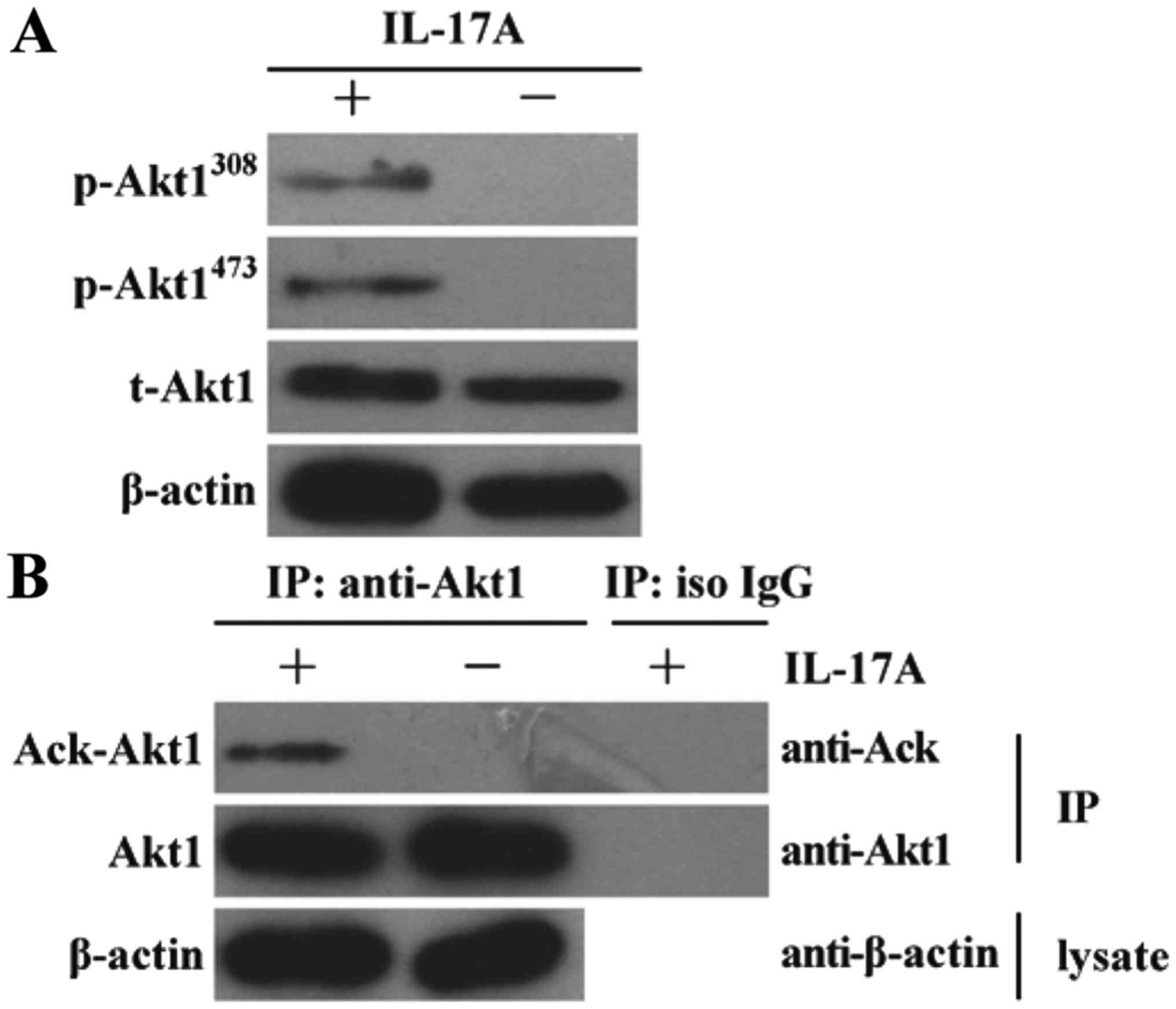
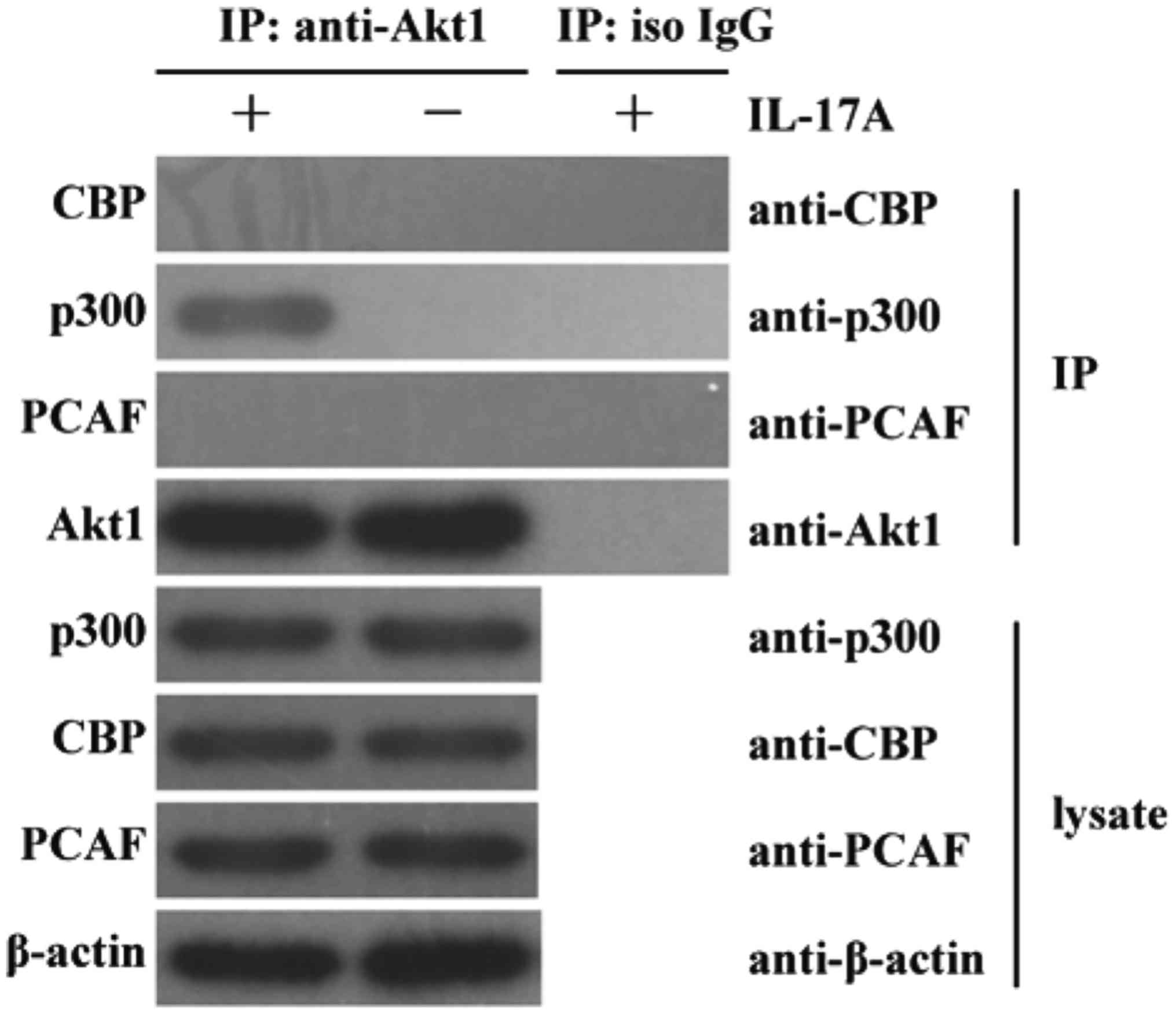
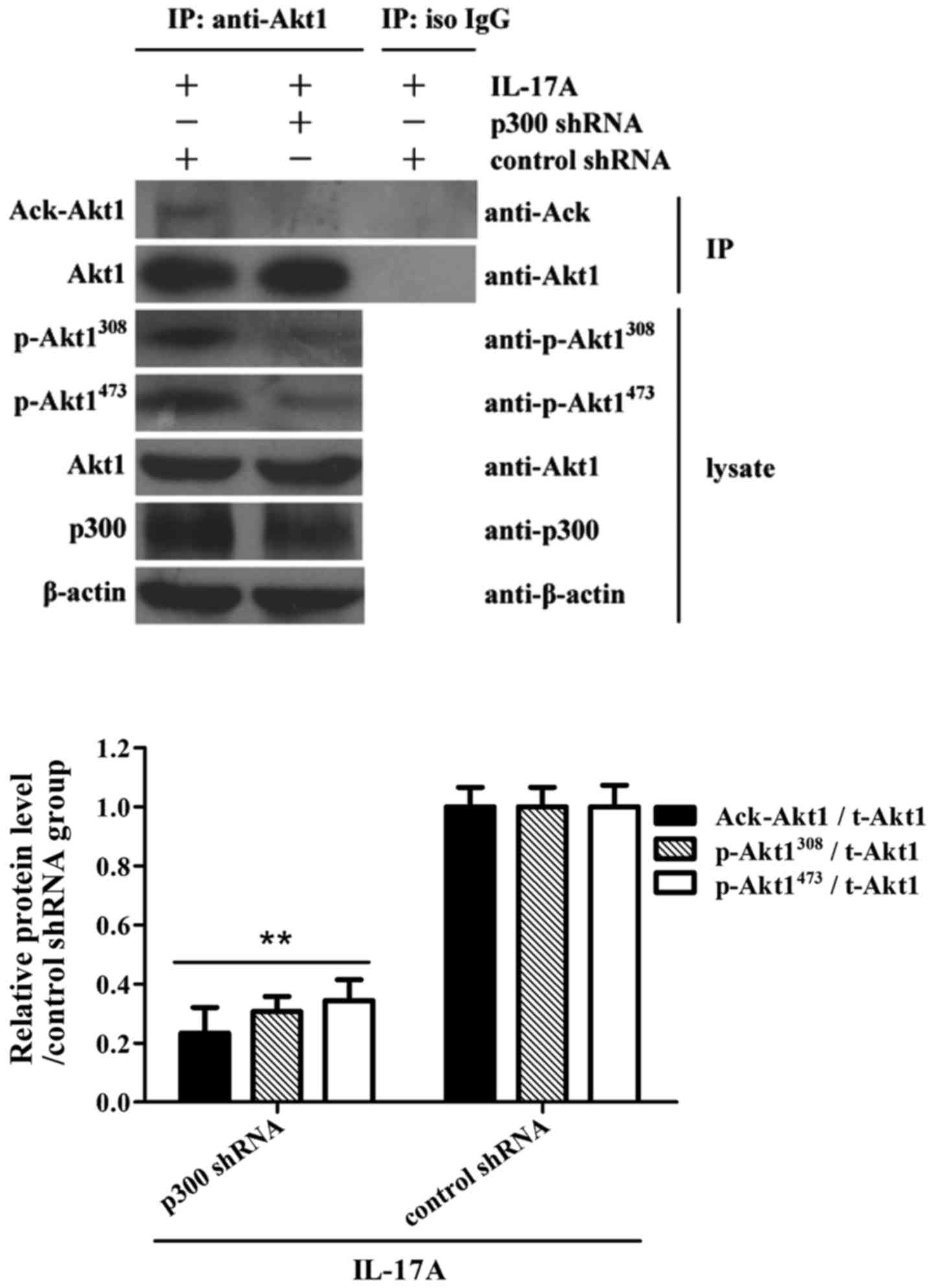
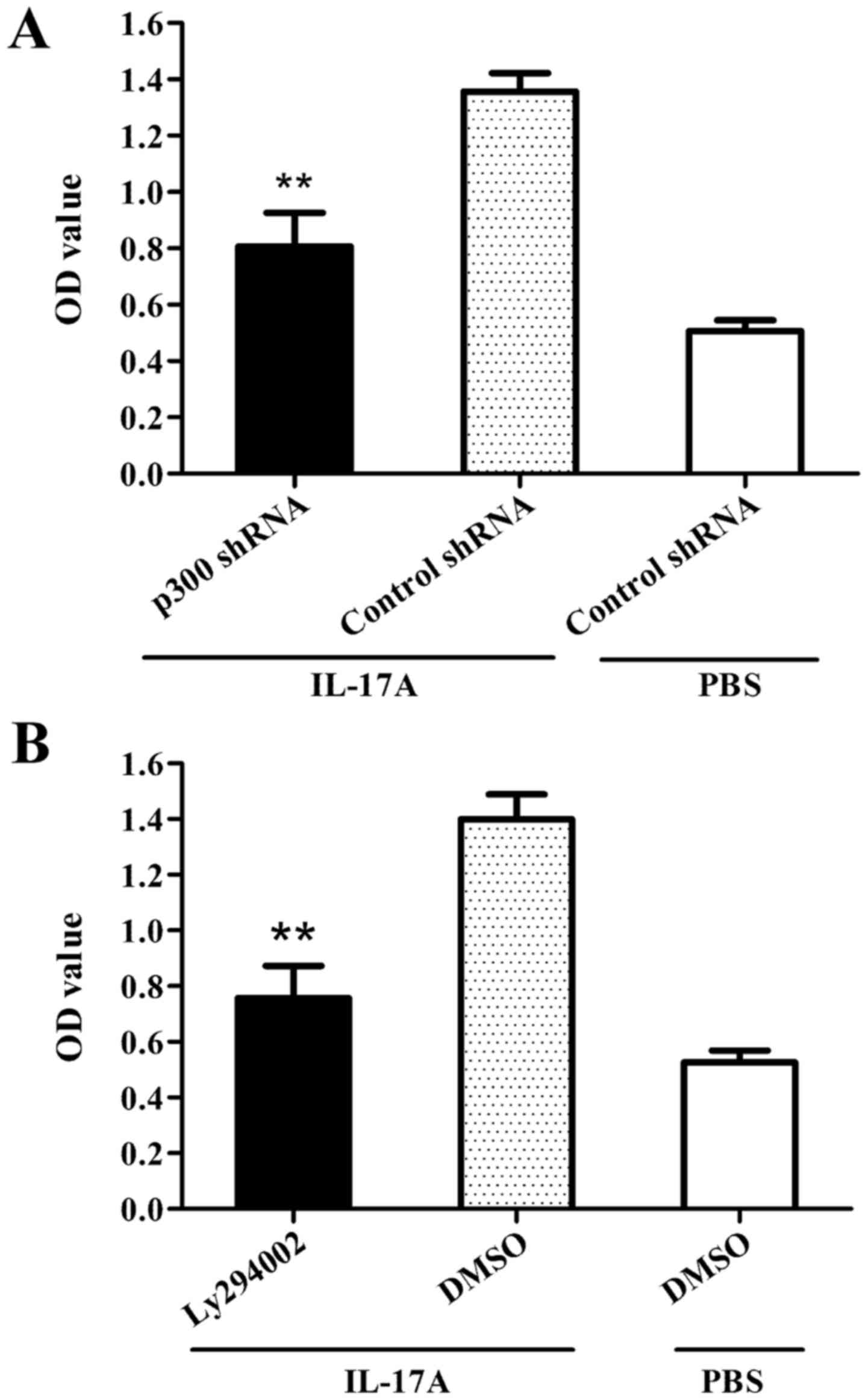
|
1
|
Yan M, Zhang Y, He B, Xiang J, Wang ZF,
Zheng FM, Xu J, Chen MY, Zhu YL, Wen HJ, et al: IKKα restoration
via EZH2 suppression induces nasopharyngeal carcinoma
differentiation. Nat Commun. 5:36612014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Du XJ, Tang LL, Mao YP, Sun Y, Zeng MS,
Kang TB, Jia WH, Lin AH and Ma J: The pretreatment albumin to
globulin ratio has predictive value for long-term mortality in
nasopharyngeal carcinoma. PLoS One. 9:e944732014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Xu T, Fan B, Lv C and Xiao D: Slug
mediates nasopharyngeal carcinoma radioresistance via
downregulation of PUMA in a p53-dependent and -independent manner.
Oncol Rep. 33:2631–2638. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zuo Y, Liao S, Xu Z, Xie J, Huang W and Yu
Z: A new version of targeted minicircle producer system for
EBV-positive human nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Oncol Rep.
32:2564–2570. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Edefonti V, Nicolussi F, Polesel J, Bravi
F, Bosetti C, Garavello W, La Vecchia C, Bidoli E, Decarli A,
Serraino D, et al: Nutrient-based dietary patterns and
nasopharyngeal cancer: Evidence from an exploratory factor
analysis. Br J Cancer. 112:446–454. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Punkenburg E, Vogler T, Büttner M, Amann
K, Waldner M, Atreya R, Abendroth B, Mudter J, Merkel S, Gallmeier
E, et al: Batf-dependent Th17 cells critically regulate IL-23
driven colitis-associated colon cancer. Gut. 65:1139–1150. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Prado-Garcia H, Romero-Garcia S,
Rumbo-Nava U and Lopez-Gonzalez JS: Predominance of th17 over
regulatory T-cells in pleural effusions of patients with lung
cancer implicates a proinflammatory profile. Anticancer Res.
35:1529–1535. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Paladugu M, Thakur A, Lum LG, Mittal S and
Parajuli P: Generation and immunologic functions of Th17 cells in
malignant gliomas. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 62:75–86. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang L, Ma R, Kang Z, Zhang Y, Ding H, Guo
W, Gao Q and Xu M: Effect of IL-17A on the migration and invasion
of NPC cells and related mechanisms. PLoS One. 9:e1080602014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
House CD, Wang BD, Ceniccola K, Williams
R, Simaan M, Olender J, Patel V, Baptista-Hon DT, Annunziata CM,
Gutkind JS, et al: Voltage-gated Na+ channel activity increases
colon cancer transcriptional activity and invasion via persistent
MAPK signaling. Sci Rep. 5:115412015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yuan J, Liu M, Yang L, Tu G, Zhu Q, Chen
M, Cheng H, Luo H, Fu W, Li Z and Yang G: Acquisition of
epithelial-mesenchymal transition phenotype in the
tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer cell: A new role for G
protein-coupled estrogen receptor in mediating tamoxifen resistance
through cancer-associated fibroblast-derived fibronectin and
β1-integrin signaling pathway in tumor cells. Breast Cancer Res.
17:692015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wen W, Wu J, Liu L, Tian Y, Buettner R,
Hsieh MY, Horne D, Dellinger TH, Han ES, Jove R and Yim JH:
Synergistic anti-tumor effect of combined inhibition of EGFR and
JAK/STAT3 pathways in human ovarian cancer. Mol Cancer. 14:1002015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhang P, Guo X, Li J, Yu S, Wang L, Jiang
G, Yang D, Wei Z, Zhang N, Liu J and Sun Y: Immunoglobulin-like
transcript 4 promotes tumor progression and metastasis and
up-regulates VEGF-C expression via ERK signaling pathway in
non-small cell lung cancer. Oncotarget. 6:13550–13563. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Huang W, Liu J, Feng X, Chen H, Zeng L,
Huang G, Liu W, Wang L, Jia W, Chen J and Ren C: DLC-1 induces
mitochondrial apoptosis and epithelial mesenchymal transition
arrest in nasopharyngeal carcinoma by targeting EGFR/Akt/NF-κB
pathway. Med Oncol. 32:1152015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Qin J, Ji J, Deng R, Tang J, Yang F, Feng
GK, Chen WD, Wu XQ, Qian XJ, Ding K and Zhu XF: DC120, a novel AKT
inhibitor, preferentially suppresses nasopharyngeal carcinoma
cancer stem-like cells by downregulating Sox2. Oncotarget.
6:6944–6958. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Xu T, Su B, Wang C, Wang S, Huang H, Pan
Y, Wang D, Wei W, Claret FX and Yang H: Molecular markers to assess
short-term disease local recurrence in nasopharyngeal carcinoma.
Oncol Rep. 33:1418–1426. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhang M, Zhou X and Zhou K: Resveratrol
inhibits human nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell growth via blocking
pAkt/p70S6K signaling pathways. Int J Mol Med. 31:621–627.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Joglekar M, Elbazanti WO, Weitzman MD,
Lehman HL and van Golen KL: Caveolin-1 mediates inflammatory breast
cancer cell invasion via the Akt1 pathway and RhoC GTPase. J Cell
Biochem. 16:923–933. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Zhou H, Wei J, Dai Q, Wang L, Luo J,
Cheang T and Wang S: CaCO3/CaIP6 composite nanoparticles
effectively deliver AKT1 small interfering RNA to inhibit human
breast cancer growth. Int J Nanomedicine. 10:4255–4266.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chiu CT, Chen JH, Chou FP and Lin HH:
Hibiscus sabdariffa leaf extract inhibits human prostate cancer
cell invasion via down-regulation of Akt/NF-kB/MMP-9 pathway.
Nutrients. 7:5065–5087. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Qian D, Chen K, Deng H, Rao H, Huang H,
Liao Y, Sun X, Lu S, Yuan Z, Xie D and Cai Q: MicroRNA-374b
suppresses proliferation and promotes apoptosis in T-cell
lymphoblastic lymphoma by repressing AKT1 and Wnt-16. Clin Cancer
Res. 21:4881–4891. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Webster BR, Scott I, Han K, Li JH, Lu Z,
Stevens MV, Malide D, Chen Y, Samsel L, Connelly PS, et al:
Restricted mitochondrial protein acetylation initiates
mitochondrial autophagy. J Cell Sci. 126:4843–4849. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Karthik S, Sankar R, Varunkumar K, Anusha
C and Ravikumar V: Blocking NF-κB sensitizes non-small cell lung
cancer cells to histone deacetylase inhibitor induced extrinsic
apoptosis through generation of reactive oxygen species. Biomed
Pharmacother. 69:337–344. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kim HJ, Joe Y, Yu JK, Chen Y, Jeong SO,
Mani N, Cho GJ, Pae HO, Ryter SW and Chung HT: Carbon monoxide
protects against hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury by modulating
the miR-34a/SIRT1 pathway. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1852:1550–1559.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ansari MA, Dutta S, Veettil MV, Dutta D,
Iqbal J, Kumar B, Roy A, Chikoti L, Singh VV and Chandran B:
Herpesvirus genome recognition induced acetylation of nuclear IFI16
is essential for its cytoplasmic translocation, inflammasome and
IFN-β responses. PLoS Pathog. 11:e10050192015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yang H, Zhou L, Shi Q, Zhao Y, Lin H,
Zhang M, Zhao S, Yang Y, Ling ZQ, Guan KL, et al: SIRT3-dependent
GOT2 acetylation status affects the malate-aspartate NADH shuttle
activity and pancreatic tumor growth. EMBO J. 34:1110–1125. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhang S, Sun G, Wang Z, Wan Y, Guo J and
Shi L: PCAF-mediated Akt1 acetylation enhances the proliferation of
human glioblastoma cells. Tumour Biol. 36:1455–1462. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Cai K, Wan Y, Wang Z, Wang Y, Zhao X and
Bao X: C5a promotes the proliferation of human nasopharyngeal
carcinoma cells through PCAF-mediated STAT3 acetylation. Oncol Rep.
32:2260–2266. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Liu Y, Li Z, Wu L, Wang X, Yu Y, Zhao Q
and Luo F: MiRNA-125a-5p: A regulator and predictor of gefitinib's
effect on nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Cell Int. 14:242014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhu LH, Sun LH, Hu YL, Jiang Y, Liu HY,
Shen XY, Jin XY, Zhen X, Sun HX and Yan GJ: PCAF impairs
endometrial receptivity and embryo implantation by down-regulating
β3-integrin expression via HOXA10 acetylation. J Clin Endocrinol
Metab. 98:4417–4428. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Qiu W, Zhou J, Zhu G, Zhao D, He F, Zhang
J, Lu Y, Yu T, Liu L and Wang Y: Sublytic C5b-9 triggers glomerular
mesangial cell apoptosis via XAF1 gene activation mediated by
p300-dependent IRF-1 acetylation. Cell Death Dis. 5:e11762014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ma B, Fey M and Hottiger MO: WNT/β-catenin
signaling inhibits CBP-mediated RelA acetylation and expression of
proinflammatory NF-κB target genes. J Cell Sci. 128:2430–2436.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Sun Y, Zhu D, Wang G, Wang D, Zhou H, Liu
X, Jiang M, Liao L, Zhou Z and Hu J: Pro-inflammatory cytokine
IL-1β Up-regulates CXC chemokine receptor 4 via Notch and ERK
signaling pathways in tongue squamous cell carcinoma. PLoS One.
10:e01326772015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Mishra A, Sullivan L and Caligiuri MA:
Molecular pathways: Interleukin-15 signaling in health and in
cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 20:2044–2050. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Koh SJ, Kim JM, Kim IK, Ko SH and Kim JS:
Anti-inflammatory mechanism of metformin and its effects in
intestinal inflammation and colitis-associated colon cancer. J
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 29:502–510. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Li Z, Duan Y, Cheng S, Chen Y, Hu Y, Zhang
L, He J, Liao Q, Yang L and Sun LQ: EBV-encoded RNA via TLR3
induces inflammation in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Oncotarget.
6:24291–25303. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Sjökvist Ottsjö L, Flach CF, Nilsson S,
Rde W Malefyt, Walduck AK and Raghavan S: Defining the roles of
IFN-γ and IL-17A in inflammation and protection against
helicobacter pylori infection. PLoS One. 10:e01314442015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Dai H, Xu L, Tang Y, Liu Z and Sun T:
Treatment with a neutralising anti-rat interleukin-17 antibody
after multiple-trauma reduces lung inflammation. Injury.
46:1465–1470. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Gu K, Li MM, Shen J, Liu F, Cao JY, Jin S
and Yu Y: Interleukin-17-induced EMT promotes lung cancer cell
migration and invasion via NF-κB/ZEB1 signal pathway. Am J Cancer
Res. 5:1169–1179. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Mombelli S, Cochaud S, Merrouche Y, Garbar
C, Antonicelli F, Laprevotte E, Alberici G, Bonnefoy N, Eliaou JF,
Bastid J, et al: IL-17A and its homologs IL-25/IL-17E recruit the
c-RAF/S6 kinase pathway and the generation of pro-oncogenic LMW-E
in breast cancer cells. Sci Rep. 5:118742015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Li J, Mo HY, Xiong G, Zhang L, He J, Huang
ZF, Liu ZW, Chen QY, Du ZM, Zheng LM, et al: Tumor microenvironment
macrophage inhibitory factor directs the accumulation of
interleukin-17-producing tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and
predicts favorable survival in nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients. J
Biol Chem. 287:35484–35495. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Xiao W, Chen X and He M: Inhibition of the
Jagged/Notch pathway inhibits retinoblastoma cell proliferation via
suppressing the PI3K/Akt, Src, p38MAPK and Wnt/β-catenin signaling
pathways. Mol Med Rep. 10:453–458. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Hsu FT, Liu YC, Chiang IT, Liu RS, Wang
HE, Lin WJ and Hwang JJ: Sorafenib increases efficacy of vorinostat
against human hepatocellular carcinoma through transduction
inhibition of vorinostat-induced ERK/NF-κB signaling. Int J Oncol.
45:177–188. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Zheng D, Zhu G, Liao S, Yi W, Luo G, He J,
Pei Z, Li G and Zhou Y: Dysregulation of the PI3K/Akt signaling
pathway affects cell cycle and apoptosis of side population cells
in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Oncol Lett. 10:182–188.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Cheung AK, Ip JC, Chu AC, Cheng Y, Leong
MM, Ko JM, Shuen WH, Lung HL and Lung ML: PTPRG suppresses tumor
growth and invasion via inhibition of Akt signaling in
nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Oncotarget. 6:13434–13447. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Li R, Wei J, Jiang C, Liu D, Deng L, Zhang
K and Wang P: Akt SUMOylation regulates cell proliferation and
tumorigenesis. Cancer Res. 73:5742–5753. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Chan CH, Li CF, Yang WL, Gao Y, Lee SW,
Feng Z, Huang HY, Tsai KK, Flores LG, Shao Y, et al: The Skp2-SCF
E3 ligase regulates Akt ubiquitination, glycolysis, herceptin
sensitivity, and tumorigenesis. Cell. 149:1098–1111. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|