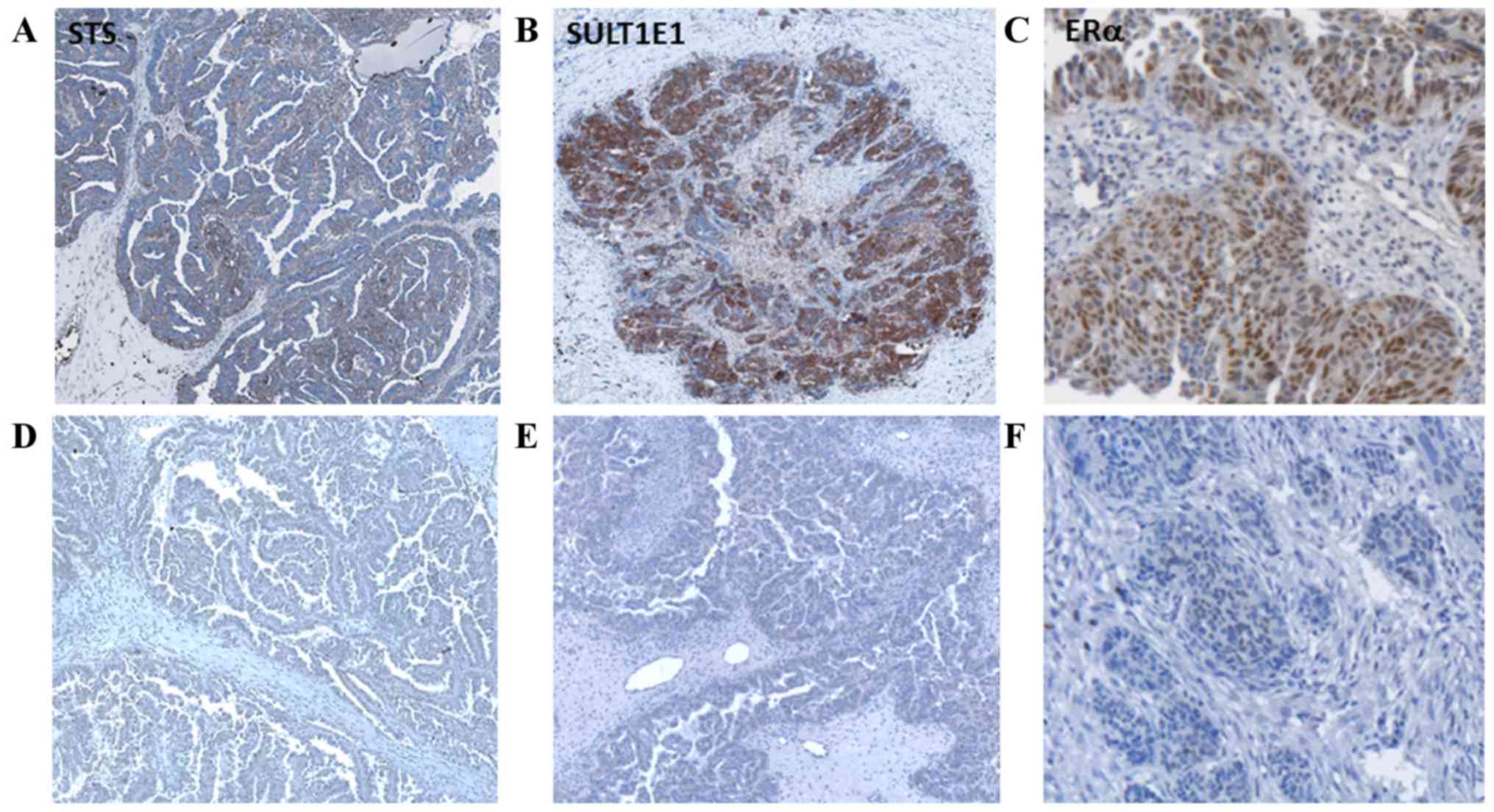
|
1
|
American Cancer Society, American Cancer
Society, . 2016 Ovarian epithelial, fallopian tube and primary
peritoneal cancer treatment (PDQ®). https://www.cancer.gov/types/ovarian/hp/ovarian-epithelial-treatment-pdqJanuary
17–2017.
|
|
2
|
Kessler M, Fotopoulou C and Meyer T: The
molecular fingerprint of high grade serous ovarian cancer reflects
its fallopian tube origin. Int J Mol Sci. 14:6571–6596. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Brown J and Frumovitz M: Mucinous tumors
of the ovary: Current thoughts on diagnosis and management. Curr
Oncol Rep. 16:3892014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sapiezynski J, Taratula O,
Rodriguez-Rodriguez L and Minko T: Precision targeted therapy of
ovarian cancer. J Control Release. 243:250–268. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chuffa LG, Lupi-Junior LA, Costa AB,
Amorim JP and Seiva FR: The role of sex hormones and steroid
receptors on female reproductive cancers. Steroids. 118:93–108.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Beral V; Million Women Study
Collaborators, ; Bull D, Green J and Reeves G: Ovarian cancer and
hormone replacement therapy in the Million Women Study. Lancet.
369:1703–1710. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kurian AW, Balise RR, McGuire V and
Whittemore AS: Histologic types of epithelial ovarian cancer: Have
they different risk factors? Gynecol Oncol. 96:520–530. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Rice LW: Hormone prevention strategies for
breast, endometrial and ovarian cancers. Gynecol Oncol.
118:202–207. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Schock H, Surcel HM, Zeleniuch-Jacquotte
A, Grankvist K, Lakso HÅ, Fortner RT, Kaaks R, Pukkala E, Lehtinen
M, Toniolo P and Lundin E: Early pregnancy sex steroids and
maternal risk of epithelial ovarian cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer.
21:831–844. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Trabert B, Brinton LA, Anderson GL,
Pfeiffer RM, Falk RT, Strickler HD, Sliesoraitis S, Kuller LH, Gass
ML, Fuhrman BJ, et al: Circulating estrogens and postmenopausal
ovarian cancer risk in the Women's Health initiative observational
study. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 25:648–656. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Svoboda M, Wlcek K, Taferner B, Hering S,
Stieger B, Tong D, Zeillinger R, Thalhammer T and Jäger W:
Expression of organic anion-transporting polypeptides 1B1 and 1B3
in ovarian cancer cells: Relevance for paclitaxel transport. Biomed
Pharmacother. 65:417–426. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sasano H, Miki Y, Nagasaki S and Suzuki T:
In situ estrogen production and its regulation in human breast
carcinoma: From endocrinology to intracrinology. Pathol Int.
59:777–789. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Suzuki T, Miki Y, Nakamura Y, Ito K and
Sasano H: Steroid sulfatase and estrogen sulfotransferase in human
carcinomas. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 340:148–153. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ren X, Wu X, Hillier SG, Fegan KS,
Critchley HO, Mason JI, Sarvi S and Harlow CR: Local estrogen
metabolism in epithelial ovarian cancer suggests novel targets for
therapy. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 150:54–63. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Rizner TL: Estrogen biosynthesis, phase I
and phase II metabolism, and action in endometrial cancer. Mol Cell
Endocrinol. 381:124–139. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
McNamara KM and Sasano H: The
intracrinology of breast cancer. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol.
145:172–178. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Müller P, Rothschild SI, Arnold W,
Hirschmann P, Horvath L, Bubendorf L, Savic S and Zippelius A:
Metastatic spread in patients with non-small cell lung cancer is
associated with a reduced density of tumor-infiltrating T cells.
Cancer Immunol Immunother. 65:1–11. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hanamura T, Niwa T, Gohno T, Kurosumi M,
Takei H, Yamaguchi Y, Ito K and Hayashi S: Possible role of the
aromatase-independent steroid metabolism pathways in hormone
responsive primary breast cancers. Breast Cancer Res Treat.
143:69–80. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chura JC, Blomquist CH, Ryu HS and Argenta
PA: Estrone sulfatase activity in patients with advanced ovarian
cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 112:205–209. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hevir N, Ribič-Pucelj M and Lanišnik
Rižner T: Disturbed balance between phase I and II metabolizing
enzymes in ovarian endometriosis: A source of excessive
hydroxy-estrogens and ROS? Mol Cell Endocrinol. 367:74–84. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Xu Y, Liu X, Guo F, Ning Y, Zhi X, Wang X,
Chen S, Yin L and Li X: Effect of estrogen sulfation by SULT1E1 and
PAPSS on the development of estrogen-dependent cancers. Cancer Sci.
103:1000–1009. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Utsunomiya H, Ito K, Suzuki T, Kitamura T,
Kaneko C, Nakata T, Niikura H, Okamura K, Yaegashi N and Sasano H:
Steroid sulfatase and estrogen sulfotransferase in human
endometrial carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 10:5850–5856. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Purohit A, Woo LW and Potter BV: Steroid
sulfatase: A pivotal player in estrogen synthesis and metabolism.
Mol Cell Endocrinol. 340:154–160. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Mungenast F and Thalhammer T: Estrogen
biosynthesis and action in ovarian cancer. Front Endocrinol
(Lausanne). 5:1922014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Park SH, Cheung LW, Wong AS and Leung PC:
Estrogen regulates Snail and Slug in the down-regulation of
E-cadherin and induces metastatic potential of ovarian cancer cells
through estrogen receptor alpha. Mol Endocrinol. 22:2085–2098.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Haring J, Schuler S, Lattrich C, Ortmann O
and Treeck O: Role of estrogen receptor β in gynecological cancer.
Gynecol Oncol. 127:673–676. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Voutsadakis IA: Hormone receptors in
serous ovarian carcinoma: Prognosis, pathogenesis, and treatment
considerations. Clin Med Insights Oncol. 10:17–25. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Silverberg SG: Histopathologic grading of
ovarian carcinoma: A review and proposal. Int J Gynecol Pathol.
19:7–15. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Aust S, Bachmayr-Heyda A, Pateisky P, Tong
D, Darb-Esfahani S, Denkert C, Chekerov R, Sehouli J, Mahner S, van
Gorp T, et al: Role of TRAP1 and estrogen receptor alpha in
patients with ovarian cancer-a study of the OVCAD consortium. Mol
Cancer. 11:692012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kounnis V, Ioachim E, Svoboda M, Tzakos A,
Sainis I, Thalhammer T, Steiner G and Briasoulis E: Expression of
organic anion-transporting polypeptides 1B3, 1B1, and 1A2 in human
pancreatic cancer reveals a new class of potential therapeutic
targets. Onco Targets Ther. 4:27–32. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Remmele W and Stegner HE: Recommendation
for uniform definition of an immunoreactive score (IRS) for
immunohistochemical estrogen receptor detection (ER-ICA) in breast
cancer tissue. Pathologe. 8:138–140. 1987.(In German). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chekerov R, Braicu I, Castillo-Tong DC,
Richter R, Cadron I, Mahner S, Woelber L, Marth C, van Gorp T,
Speiser P, et al: Outcome and clinical management of 275 patients
with advanced ovarian cancer International Federation of Obstetrics
and Gynecology II to IV inside the European Ovarian Cancer
Translational Research Consortium-OVCAD. Int J Gynecol Cancer.
23:268–275. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kobel M, Kalloger SE, Boyd N, McKinney S,
Mehl E, Palmer C, Leung S, Bowen NJ, Ionescu DN, Rajput A, et al:
Ovarian carcinoma subtypes are different diseases: Implications for
biomarker studies. PLoS Med. 5:e2322008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Rizner TL: The important roles of steroid
sulfatase and sulfotransferases in gynecological diseases. Front
Pharmacol. 7:302016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Smuc T and Rizner TL: Aberrant
pre-receptor regulation of estrogen and progesterone action in
endometrial cancer. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 301:74–82. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Li L, He D, Wilborn TW, Falany JL and
Falany CN: Increased SULT1E1 activity in HepG2 hepatocytes
decreases growth hormone stimulation of STAT5b phosphorylation.
Steroids. 74:20–29. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Falany CN, Comer KA, Dooley TP and Glatt
H: Human dehydroepiandrosterone sulfotransferase. Purification,
molecular cloning, and characterization. Ann N Y Acad Sci.
774:59–72. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Adjei AA and Weinshilboum RM:
Catecholestrogen sulfation: Possible role in carcinogenesis.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 292:402–408. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Abulafia O, Lee YC, Wagreich A, Economos
K, Serur E and Nacharaju VL: Sulfatase activity in normal and
neoplastic endometrium. Gynecol Obstet Invest. 67:57–60. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Tanaka K, Kubushiro K, Iwamori Y, Okairi
Y, Kiguchi K, Ishiwata I, Tsukazaki K, Nozawa S and Iwamori M:
Estrogen sulfotransferase and sulfatase: Roles in the regulation of
estrogen activity in human uterine endometrial carcinomas. Cancer
Sci. 94:871–876. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Purohit A, Fusi L, Brosens J, Woo LW,
Potter BV and Reed MJ: Inhibition of steroid sulphatase activity in
endometriotic implants by 667 COUMATE: A potential new therapy. Hum
Reprod. 23:290–297. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Reed MJ, Purohit A, Woo LW, Newman SP and
Potter BV: Steroid sulfatase: Molecular biology, regulation, and
inhibition. Endocr Rev. 26:171–202. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Zaichuk T, Ivancic D, Scholtens D,
Schiller C and Khan SA: Tissue-specific transcripts of human
steroid sulfatase are under control of estrogen signaling pathways
in breast carcinoma. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 105:76–84. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Jonsson JM, Arildsen N Skovbjerg, Malander
S, Måsbäck A, Hartman L, Nilbert M and Hedenfalk I: Sex steroid
hormone receptor expression affects ovarian cancer survival. Transl
Oncol. 8:424–433. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Lin SX, Chen J, Mazumdar M, Poirier D,
Wang C, Azzi A and Zhou M: Molecular therapy of breast cancer:
Progress and future directions. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 6:485–493.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Foster PA, Woo LW, Potter BV, Reed MJ and
Purohit A: The use of steroid sulfatase inhibitors as a novel
therapeutic strategy against hormone-dependent endometrial cancer.
Endocrinology. 149:4035–4042. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Chanplakorn N, Chanplakorn P, Suzuki T,
Ono K, Chan MS, Miki Y, Saji S, Ueno T, Toi M and Sasano H:
Increased estrogen sulfatase (STS) and 17beta-hydroxysteroid
dehydrogenase type 1 (17beta-HSD1) following neoadjuvant aromatase
inhibitor therapy in breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res
Treat. 120:639–648. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Day JM, Purohit A, Tutill HJ, Foster PA,
Woo LW, Potter BV and Reed MJ: The development of steroid sulfatase
inhibitors for hormone-dependent cancer therapy. Ann N Y Acad Sci.
1155:80–87. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Falany JL and Falany CN: Regulation of
SULT1E1 expression in Ishikawa adenocarcinoma cells by tibolone.
Steroids. 71:880–885. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Hormone Health Network: Menopause, .
http://www.hormone.org/diseases-and-conditions/womens-health/menopauseJanuary
17–2017.
|