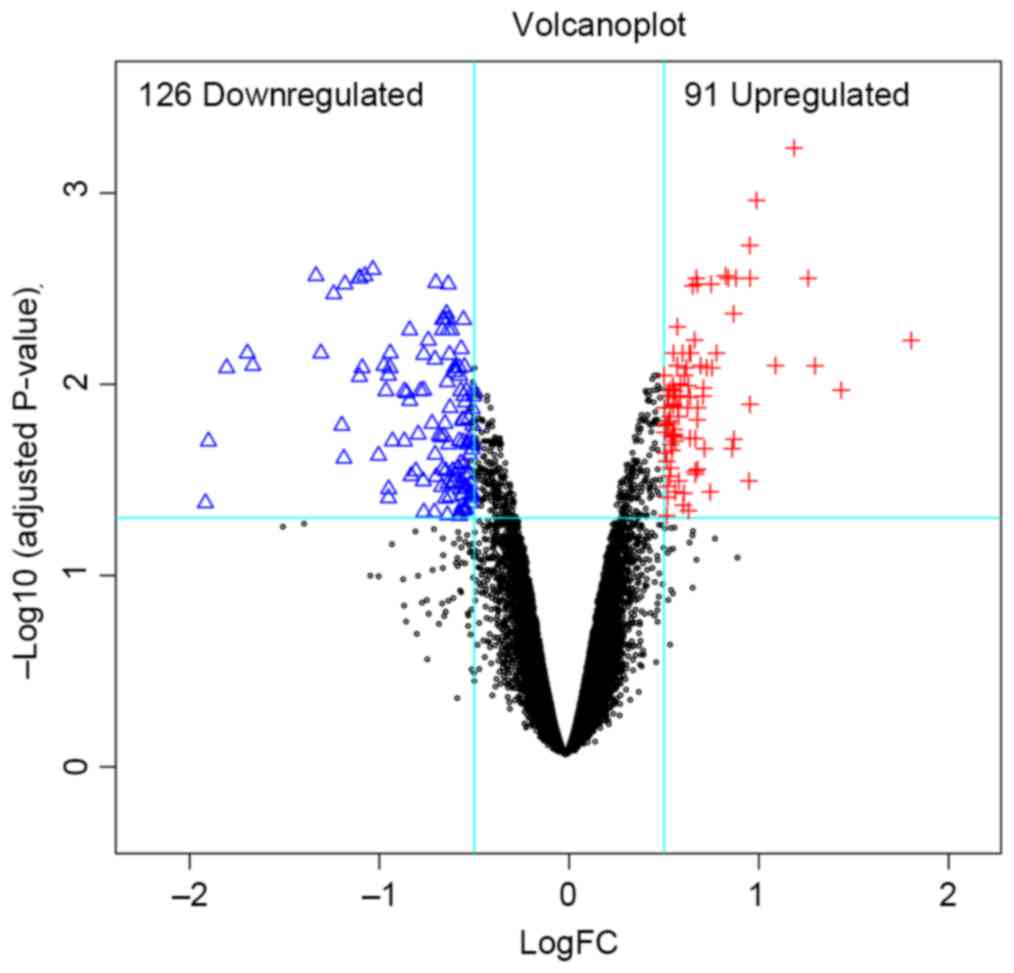
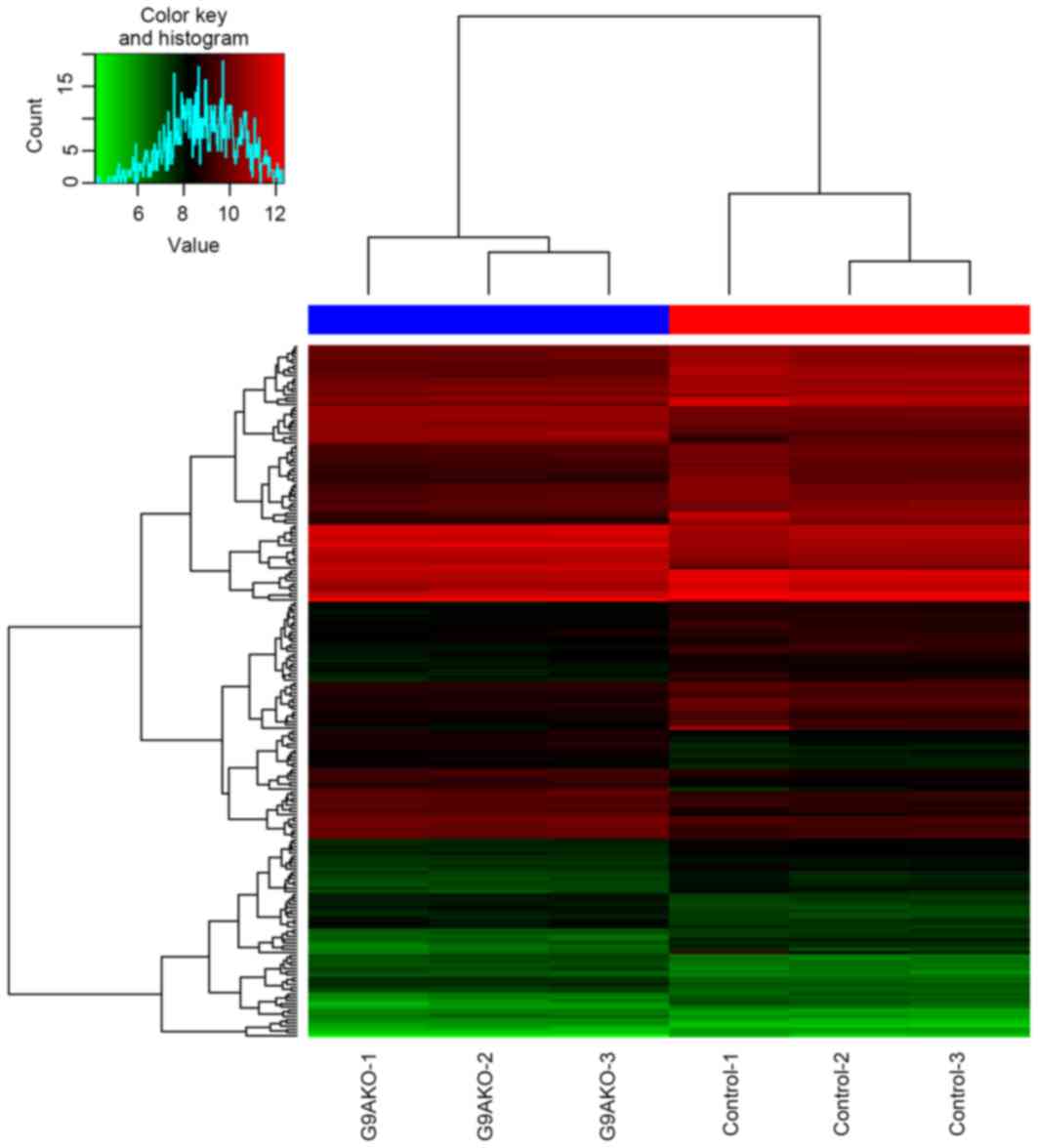
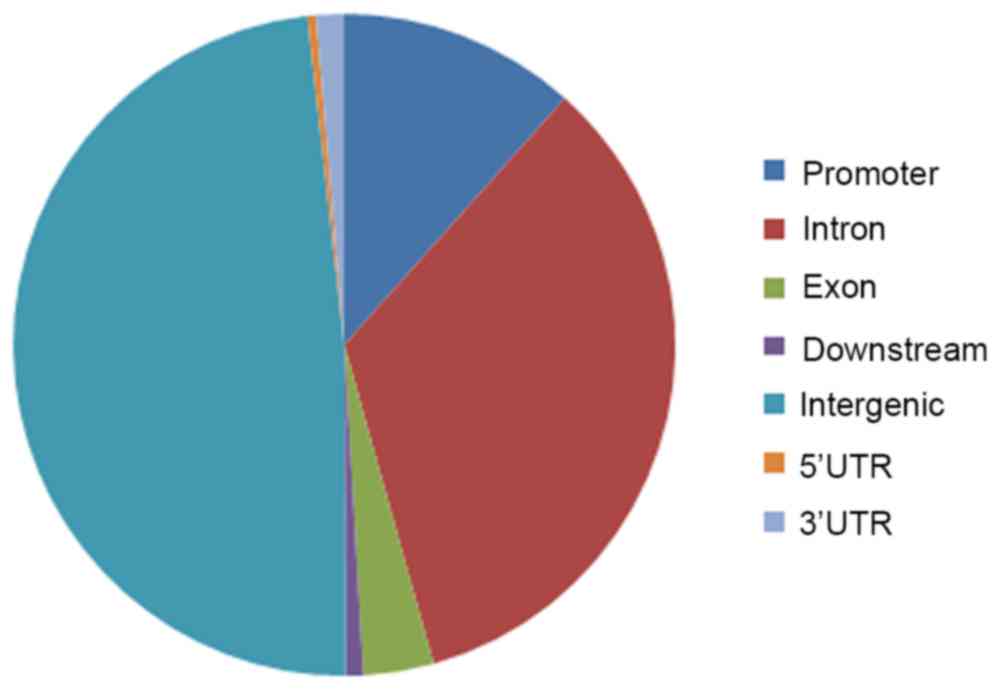
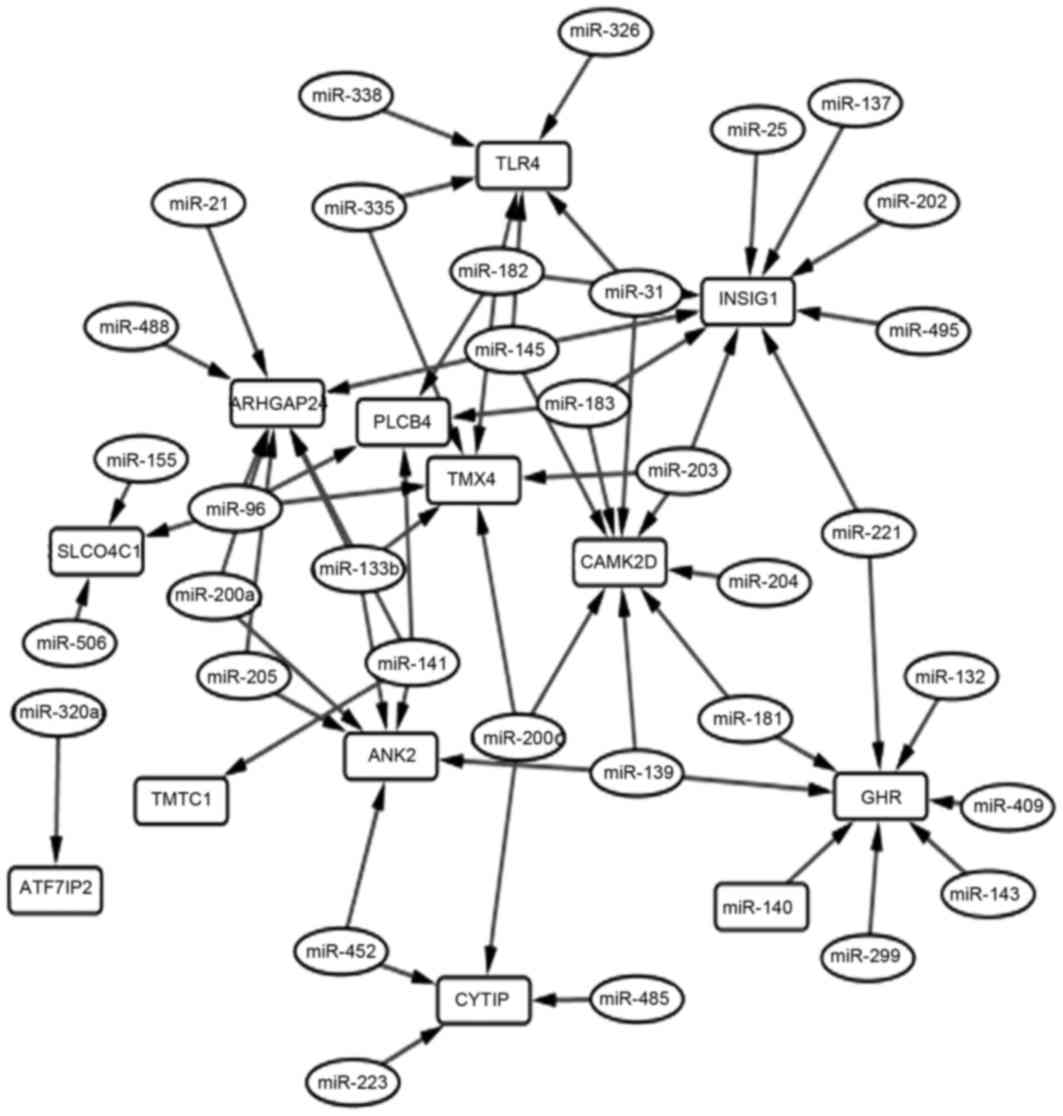
|
1
|
Zhu J, Chen JG, Chen YS, Zhang YH, Ding LL
and Chen TY: Female breast cancer survival in Qidong, China,
1972–2011: A population-based study. BMC Cancer. 14:3182014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Fan L, Goss PE and Strasser-Weippl K:
Current status and future projections of breast cancer in Asia.
Breast Care (Basel). 10:372–378. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Onega T, Tosteson AN, Weiss J,
Alford-Teaster J, Hubbard RA, Henderson LM, Kerlikowske K, Goodrich
ME, O'Donoghue C, Wernli KJ, et al: Costs of diagnostic and
preoperative workup with and without breast MRI in older women with
a breast cancer diagnosis. BMC Health Serv Res. 16:762016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Dare AJ, Anderson BO, Sullivan R, Pramesh
CS, Andre I, Adewole IF, Badwe RA and Gauvreau CL: Surgical
services for cancer care. 2015.
|
|
5
|
Daroudi R, Sari A Akbari, Nahvijou A,
Kalaghchi B, Najafi M and Zendehdel K: The economic burden of
breast cancer in Iran. Iran J Public Health. 44:1225–1233.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhang J, He P, Xi Y, Geng M, Chen Y and
Ding J: Down-regulation of G9a triggers DNA damage response and
inhibits colorectal cancer cells proliferation. Oncotarget.
6:2917–2927. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Liu S, Ye D, Guo W, Yu W, He Y, Hu J, Wang
Y, Zhang L, Liao Y, Song H, et al: G9a is essential for
EMT-mediated metastasis and maintenance of cancer stem cell-like
characters in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget.
6:6887–6901. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Laumet G, Garriga J, Chen SR, Zhang Y, Li
DP, Smith TM, Dong Y, Jelinek J, Cesaroni M, Issa JP and Pan HL:
G9a is essential for epigenetic silencing of K(+) channel genes in
acute-to-chronic pain transition. Nat Neurosci. 18:1746–1755. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lee JY, Lee SH, Heo SH, Kim KS, Kim C, Kim
DK, Ko JJ and Park KS: Novel function of lysine methyltransferase
G9a in the regulation of Sox2 protein stability. PLoS One.
10:e01411182015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Si W, Huang W, Zheng Y, Yang Y, Liu X,
Shan L, Zhou X, Wang Y, Su D, Gao J, et al: Dysfunction of the
reciprocal feedback loop between GATA3- and ZEB2-nucleated
repression programs contributes to breast cancer metastasis. Cancer
Cell. 27:822–836. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Liu X, Liao S, Xu Z, Zhu L, Yang F and Guo
W: Identification and analysis of the porcine MicroRNA in porcine
cytomegalovirus-infected macrophages using deep sequencing. PLoS
One. 11:e01509712016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hu JY, Yi W, Zhang MY, Xu R, Zeng LS, Long
XR, Zhou XM, Zheng XS, Kang Y and Wang HY: MicroRNA-711 is a
prognostic factor for poor overall survival and has an oncogenic
role in breast cancer. Oncol Lett. 11:2155–2163. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ali HO, Arroyo AB, González-Conejero R,
Stavik B, Iversen N, Sandset PM, Martínez C and Skretting G: The
role of microRNA −27a/b and microRNA-494 in oestrogen mediated
downregulation of tissue factor pathway inhibitor α. J Thromb
Haemost. 14:1226–1237. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Dong C, Wu Y, Yao J, Wang Y, Yu Y,
Rychahou PG, Evers BM and Zhou BP: G9a interacts with Snail and is
critical for Snail-mediated E-cadherin repression in human breast
cancer. J Clin Invest. 122:1469–1486. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Gautier L, Cope L, Bolstad BM and Irizarry
RA: affy-analysis of Affymetrix GeneChip data at the probe level.
Bioinformatics. 20:307–315. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Stuhlmüller B: A composition of nucleic
acid sequences, specific for inflammatory disease, in particular
rheumatoid arthritis. EP 1795610 A1. December 6. 2005 June
13–2007.
|
|
17
|
Dennis G Jr, Sherman BT, Hosack DA, Yang
J, Gao W, Lane HC and Lempicki RA: DAVID: Database for annotation,
visualization, and integrated discovery. Genome Biol. 4:P32003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Langmead B and Salzberg SL: Fast
gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat Methods. 9:357–359. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Feng J, Liu T, Qin B, Zhang Y and Liu XS:
Identifying ChIP-seq enrichment using MACS. Nat Protoc.
7:1728–1740. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yu G, Wang LG and He QY: ChIPseeker: An
R/Bioconductor package for ChIP peak annotation, comparison and
visualization. Bioinformatics. 31:2382–2383. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Song X, Cheng L, Zhou T, Guo X, Zhang X,
Chen YP, Han P and Sha J: Predicting miRNA-mediated gene silencing
mode based on miRNA-target duplex features. Comput Biol Med.
42:1–7. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Fenga C: Occupational exposure and risk of
breast cancer. Biomed Rep. 4:282–292. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Inoue K and Fry EA: Novel molecular
markers for breast cancer. Biomark Cancer. 8:25–42. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Rizk SM, Shahin NN and Shaker OG:
Association between SIRT1 gene polymorphisms and breast cancer in
Egyptians. PLoS One. 11:e01519012016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Shen Y and Cai T: Identifying predictive
markers for personalized treatment selection. Biometrics.
72:1017–1025. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Becht E, de Reyniès A, Giraldo NA, Pilati
C, Buttard B, Lacroix L, Selves J, Sautès-Fridman C, Laurent-Puig
Pa and Fridman WH: Immune and stromal classification of colorectal
cancer is associated with molecular subtypes and relevant for
precision immunotherapy. Clin Cancer Res. 22:4057–4066. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Abou-Shousha S, Moaz M, Sheta M and
Motawea MA: An approach to breast cancer immunotherapy: The
apoptotic activity of recombinant anti-interleukin-6 monoclonal
antibodies in intact tumor microenvironment of breast carcinoma.
Scand J Immunol. 83:427–437. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Biswas T, Efird JT, Prasad S, James SE,
Walker PR and Zagar TM: Inflammatory TNBC breast cancer: Demography
and clinical outcome in a large cohort of patients with TNBC. Clin
Breast Cancer. 16:212–216. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Suárez-Arroyo IJ, Rios-Fuller TJ,
Feliz-Mosquea YR, Lacourt-Ventura M, Leal-Alviarez DJ,
Maldonado-Martinez G, Cubano LA and Martínez-Montemayor MM:
Ganoderma lucidum combined with the EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor,
erlotinib synergize to reduce inflammatory breast cancer
progression. J Cancer. 7:500–511. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yang X, Jia M, Li Z, Lu S, Qi X, Zhao B,
Wang X, Rong Y, Shi J, Zhang Z, et al: Bioinformatics analysis of
aggressive behavior of breast cancer via an integrated gene
regulatory network. J Cancer Res Ther. 10:1013–1018. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sun Y, Yuan K, Zhang P, Ma R, Zhang QW and
Tian XS: Crosstalk analysis of pathways in breast cancer using a
network model based on overlapping differentially expressed genes.
Exp Ther Med. 10:743–748. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chen HF and Wu KJ: Epigenetics, TET
proteins, and hypoxia in epithelial-mesenchymal transition and
tumorigenesis. Biomedicine (Taipei). 6:12016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Tsai YP, Chen HF, Chen SY, Cheng WC, Wang
HW, Shen ZJ, Song C, Teng SC, He C and Wu KJ: TET1 regulates
hypoxia-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition by acting as a
co-activator. Genome Biol. 15:5132014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ghose A, Kundu R, Toumeh A, Hornbeck C and
Mohamed I: A review of obesity, insulin resistance, and the role of
exercise in breast cancer patients. Nutr Cancer. 67:197–202. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Hernández-Vargas H, Rodriguez-Pinilla SM,
Julián-Tendero M, Sánchez-Rovira P, Cuevas C, Antón A, Ríos MJ,
Palacios J and Moreno-Bueno G: Gene expression profiling of breast
cancer cells in response to gemcitabine: NF-kappaB pathway
activation as a potential mechanism of resistance. Breast Cancer
Res Treat. 102:157–172. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Einbond LS, Su T, Wu HA, Friedman R, Wang
X, Jiang B, Hagan T, Kennelly EJ, Kronenberg F and Weinstein IB:
Gene expression analysis of the mechanisms whereby black cohosh
inhibits human breast cancer cell growth. Anticancer Res.
27:697–712. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Shi Y, Tan YJ, Zeng DZ, Qian F and Yu PW:
miR-203 suppression in gastric carcinoma promotes Slug-mediated
cancer metastasis. Tumour Biol. Jul 21–2015.(Epub ahead of
print).
|
|
38
|
Taipaleenmäki H, Browne G, Akech J, Zustin
J, Van Wijnen AJ, Stein JL, Hesse E, Stein GS and Lian JB:
Targeting of Runx2 by miR-135 and miR-203 impairs progression of
breast cancer and metastatic bone disease. Cancer Res.
75:1433–1444. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zhou Y, Hu HY, Meng W, Jiang L, Zhang X,
Sha JJ, Lu Z and Yao Y: MEK inhibitor effective against
proliferation in breast cancer cell. Tumour Biol. 35:9269–9279.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Li P, Guo Y, Bledsoe G, Yang Z, Chao L and
Chao J: Kallistatin induces breast cancer cell apoptosis and
autophagy by modulating Wnt signaling and microRNA synthesis. Exp
Cell Res. 340:305–314. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|