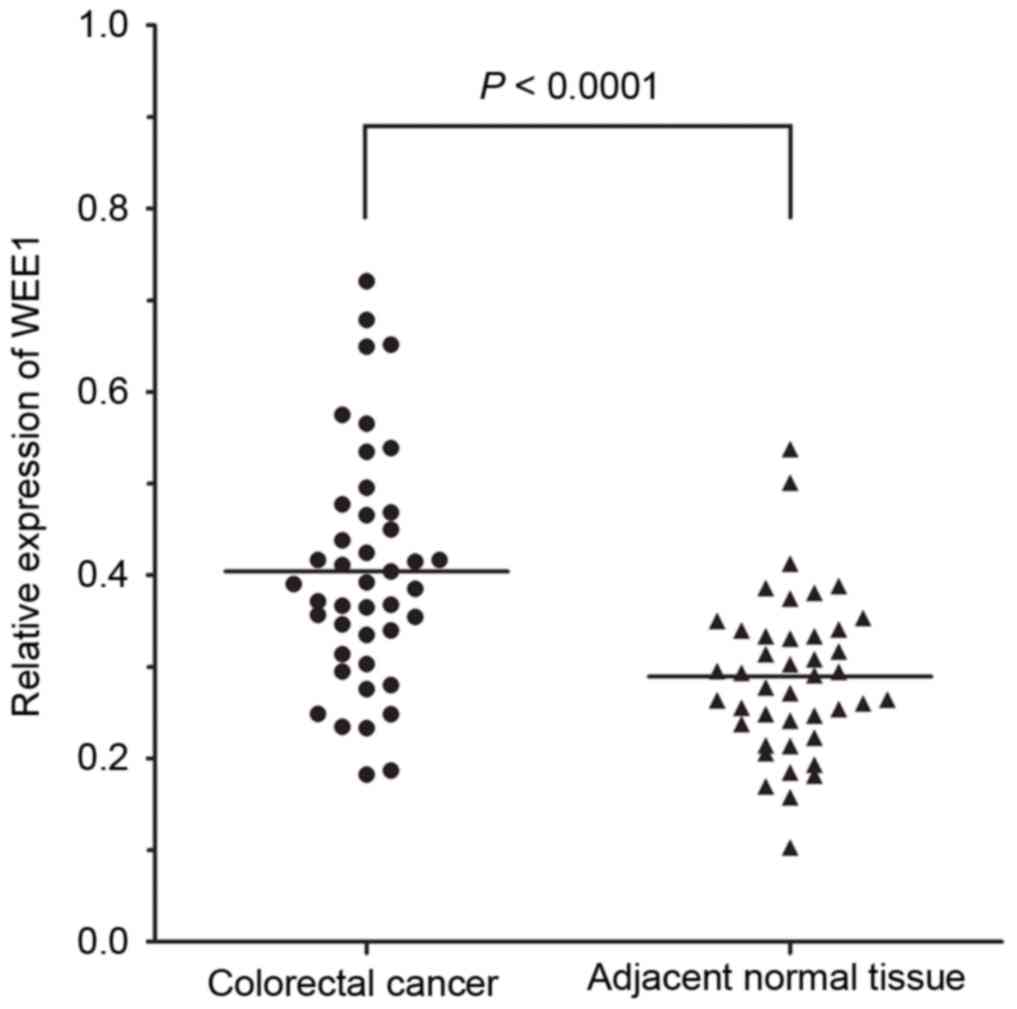
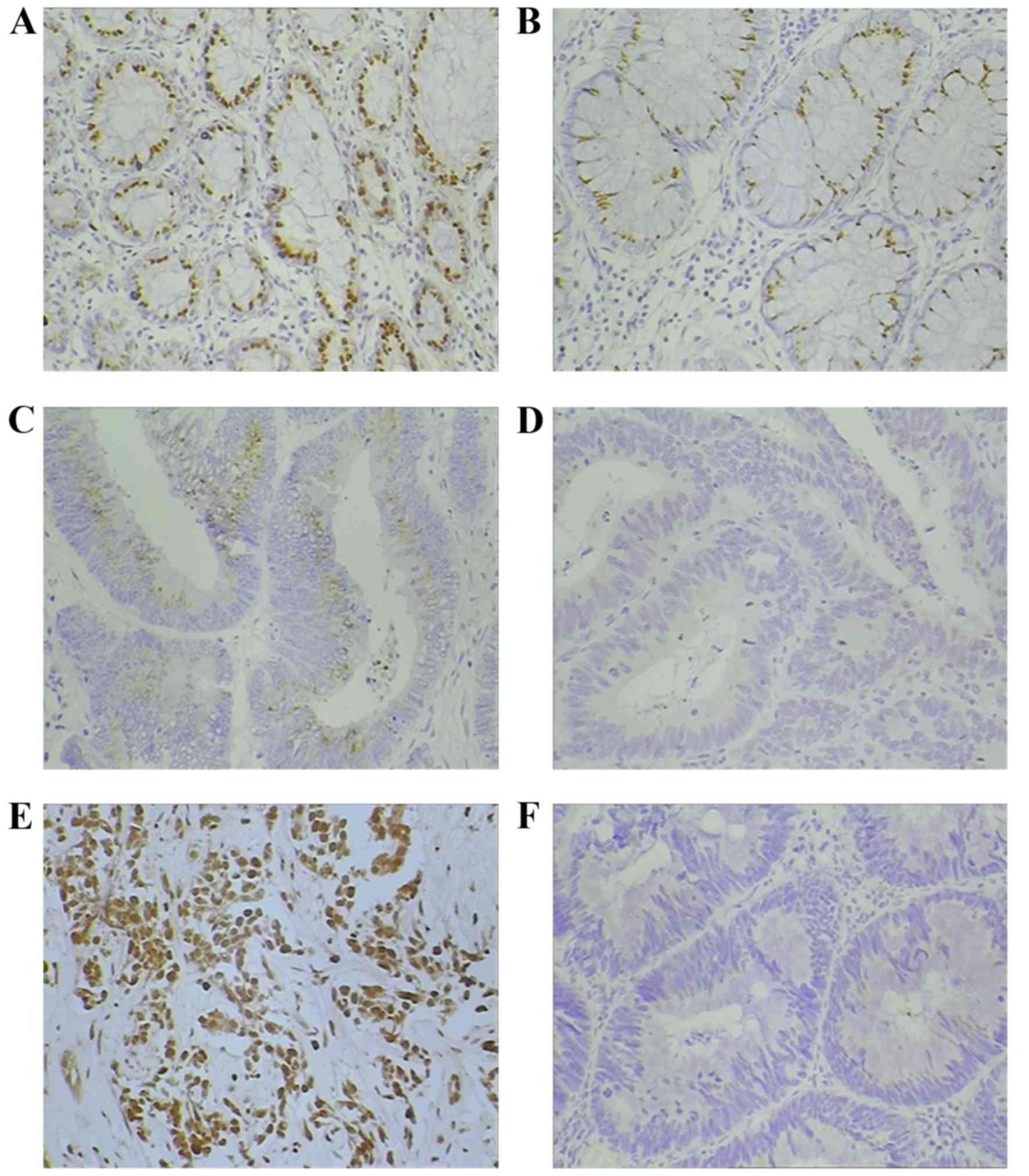
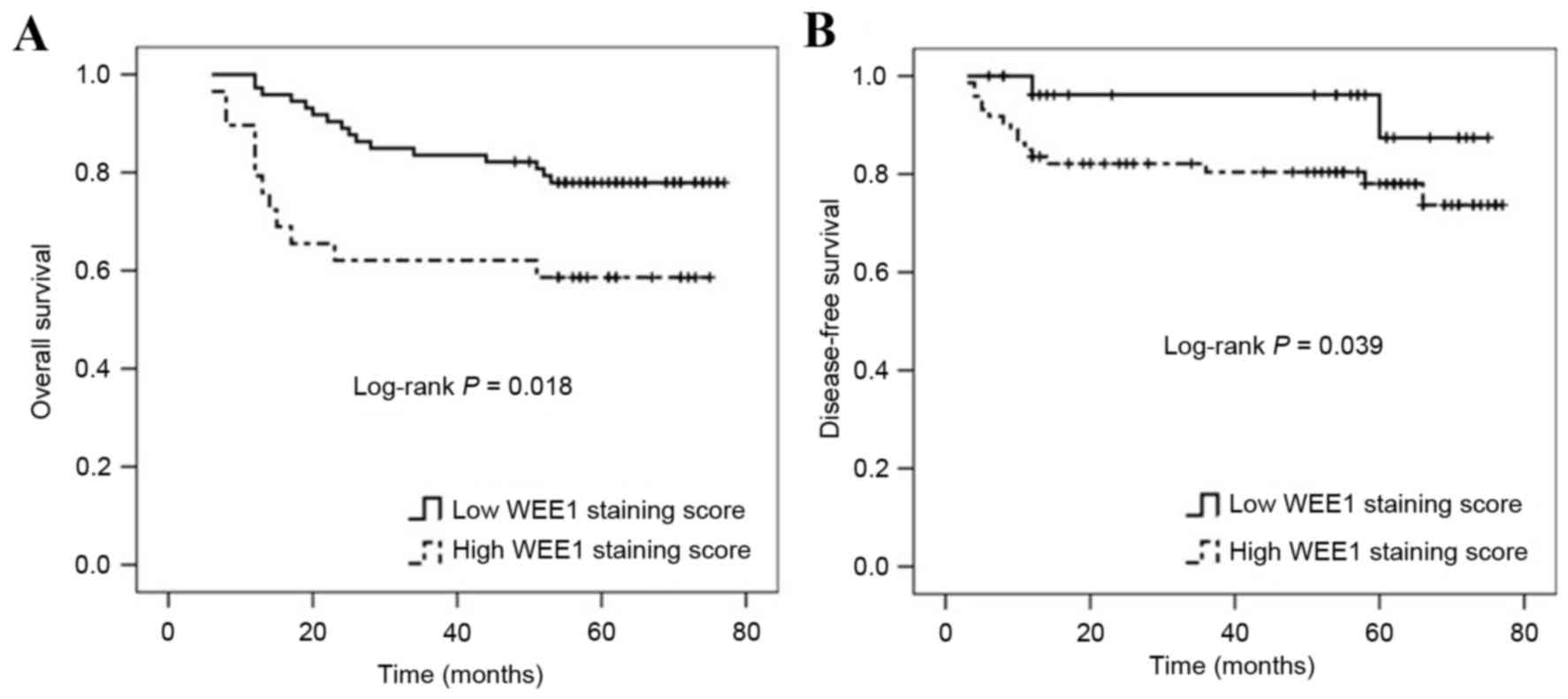
|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sung JJ, Lau JY, Young GP, Sano Y, Chiu
HM, Byeon JS, Yeoh KG, Goh KL, Sollano J, Rerknimitr R, et al: Asia
Pacific consensus recommendations for colorectal cancer screening.
Gut. 57:1166–1176. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Matsuda T, Marugame T, Kamo K, Katanoda K,
Ajiki W and Sobue T; Japan Cancer Surveillance Research Group, :
Cancer incidence and incidence rates in Japan in 2006: Based on
data from 15 population-based cancer registries in the monitoring
of cancer incidence in Japan (MCIJ) project. Jpn J Clin Oncol.
42:139–147. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bos JL, Fearon ER, Hamilton SR, Verlaan-de
Vries M, Van Boom JH, van der Eb AJ and Vogelstein B: Prevalence of
ras gene mutations in human colorectal cancers. Nature.
327:293–297. 1987. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Baker SJ, Markowitz S, Fearon ER, Willson
JK and Vogelstein B: Suppression of human colorectal carcinoma cell
growth by wild-type p53. Science. 249:912–925. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Nishisho I, Nakamura Y, Miyoshi Y, Miki Y,
Ando H, Horii A, Koyama K, Utsunomiya J, Baba S and Hedge P:
Mutations of chromosome 5q21 genes in FAP and colorectal cancer
patients. Science. 253:665–669. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wu F, Shirahata A, Sakuraba K, Kitamura Y,
Goto T, Saito M, Ishibashi K, Kigawa G, Nemoto H, Sanada Y and Hibi
K: Downregulation of Mus81 as a novel prognostic biomarker for
patients with colorectal carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 102:472–477. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wu F, Shirahata A, Sakuraba K, Kitamura Y,
Goto T, Saito M, Ishibashi K, Kigawa G, Nemoto H, Sanada Y and Hibi
K: Down-regulation of EGFL8: A novel biomarker for advanced gastric
cancer. Anticancer Res. 31:3377–3380. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Walther A, Johnstone E, Swanton C, Midgley
R, Tomlinson I and Kerr D: Genetic prognostic and predictive
markers in colorectal cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 9:489–499. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Thuriaux P, Nurse P and Carter B: Mutants
altered in the control co-ordinating cell division with cell growth
in the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Mol Gen Genet.
161:215–220. 1978.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Perry JA and Kornbluth S: Cdc25 and Wee1:
Analogous opposites? Cell Div. 2:122007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Mueller PR, Coleman TR, Kumagai A and
Dunphy WG: Myt1: A membrane-associated inhibitory kinase that
phosphorylates Cdc2 on both threonine-14 and tyrosine-15. Science.
270:86–90. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Parker LL and Piwnica-Worms H:
Inactivation of the p34cdc2-cyclin B complex by the human WEE1
tyrosine kinase. Science. 257:1955–1957. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Watanabe N, Broome M and Hunter T:
Regulation of the human WEE1Hu CDK tyrosine 15-kinase during the
cell cycle. EBMO J. 14:1878–1891. 1995.
|
|
15
|
Kawabe T: G2 checkpoint abrogators as
anticancer drugs. Mol Cancer Ther. 3:513–519. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Masaki T, Shiratori Y, Rengifo W, Igarashi
K, Yamagata M, Kurokohchi K, Uchida N, Miyauchi Y, Yoshiji H,
Watanabe S, et al: Cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases:
Comparative study of hepatocellular carcinoma versus cirrhosis.
Hepatology. 37:534–543. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Magnussen GI, Holm R, Emilsen E, Rosnes
AK, Slipicevic A and Flørenes VA: High expression of Wee1 is
associated with poor disease-free survival in malignant melanoma:
Potential for targeted therapy. PLoS One. 7:e382542012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Magnussen GI, Hellesylt E, Nesland JM,
Trope CG, Flørenes VA and Holm R: High expression of wee1 is
associated with malignancy in vulvar squamous cell carcinoma
patients. BMC Cancer. 13:2882013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Slipicevic A, Holth A, Hellesylt E, Tropé
CG, Davidson B and Flørenes VA: Wee1 is a novel independent
prognostic marker of poor survival in post-chemotherapy ovarian
carcinoma effusions. Gynecol Oncol. 135:118–124. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Mir SE, De Witt Hamer PC, Krawczyk PM,
Balaj L, Claes A, Niers JM, Van Tilborg AA, Zwinderman AH, Geerts
D, Kaspers GJ, et al: In silico analysis of kinase expression
identifies WEE1 as a gatekeeper against mitotic catastrophe in
glioblastoma. Cancer Cell. 18:244–257. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Iorns E, Lord CJ, Grigoriadis A, McDonald
S, Fenwick K, Mackay A, Mein CA, Natrajan R, Savage K, Tamber N, et
al: Integrated functional, gene expression and genomic analysis for
the identification of cancer targets. PLoS One. 4:e51202009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Murrow LM, Garimella SV, Jones TL, Caplen
NJ and Lipkowitz S: Identification of WEE1 as a potential molecular
target in cancer cells by RNAi screening of the human tyrosine
kinome. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 122:347–357. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ford JB, Baturin D, Burleson TM, Van
Linden AA, Kim YM and Porter CC: AZD1775 sensitizes T cell acute
lymphoblastic leukemia cells to cytarabine by promoting apoptosis
over DNA repair. Oncotarget. 6:28001–28010. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hirai H, Arai T, Okada M, Nishibata T,
Kobayashi M, Sakai N, Imagaki K, Ohtani J, Sakai T, Yoshizumi T, et
al: MK-1775, a small molecule Wee1 inhibitor, enhances anti-tumor
efficacy of various DNA-damaging agents, including 5-fluorouracil.
Cancer Biol Ther. 9:514–522. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Weisberg E, Nonami A, Chen Z, Liu F, Zhang
J, Sattler M, Nelson E, Cowens K, Christie AL, Mitsiades C, Wong
KK, et al: Identification of Wee1 as a novel therapeutic target for
mutant RAS-driven acute leukemia and other malignancies. Leukemia.
29:27–37. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Backert S, Gelos M, Kobalz U, Hanski ML,
Böhm C, Mann B, Lövin N, Gratchev A, Mansmann U, Moyer MP, et al:
Differential gene expression in colon carcinoma cells and tissues
detected with a cDNA array. Int J Cancer. 82:868–874. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wu F, Liu SY, Tao YM, Ou DP, Fang F and
Yang LY: Decreased expression of methyl methansulfonate and
ultraviolet-sensitive gene clone 81 (Mus81) is correlated with a
poor prognosis in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer.
112:2002–2010. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Huisman SA, Oklejewicz M, Ahmadi AR,
Tamanini F, Ijzermans JN, van der Horst GT and de Bruin RW:
Colorectal liver metastases with a disrupted circadian rhythm phase
shift the peripheral clock in liver and kidney. Int J Cancer.
136:1024–1032. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Karantanos T, Theodoropoulos G, Pektasides
D and Gazouli M: Clock genes: Their role in colorectal cancer.
World J Gastroenterol. 20:1986–1992. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zlobec I and Lugli A: Prognostic and
predictive factors in colorectal cancer. J Clin Pathol. 61:561–569.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|