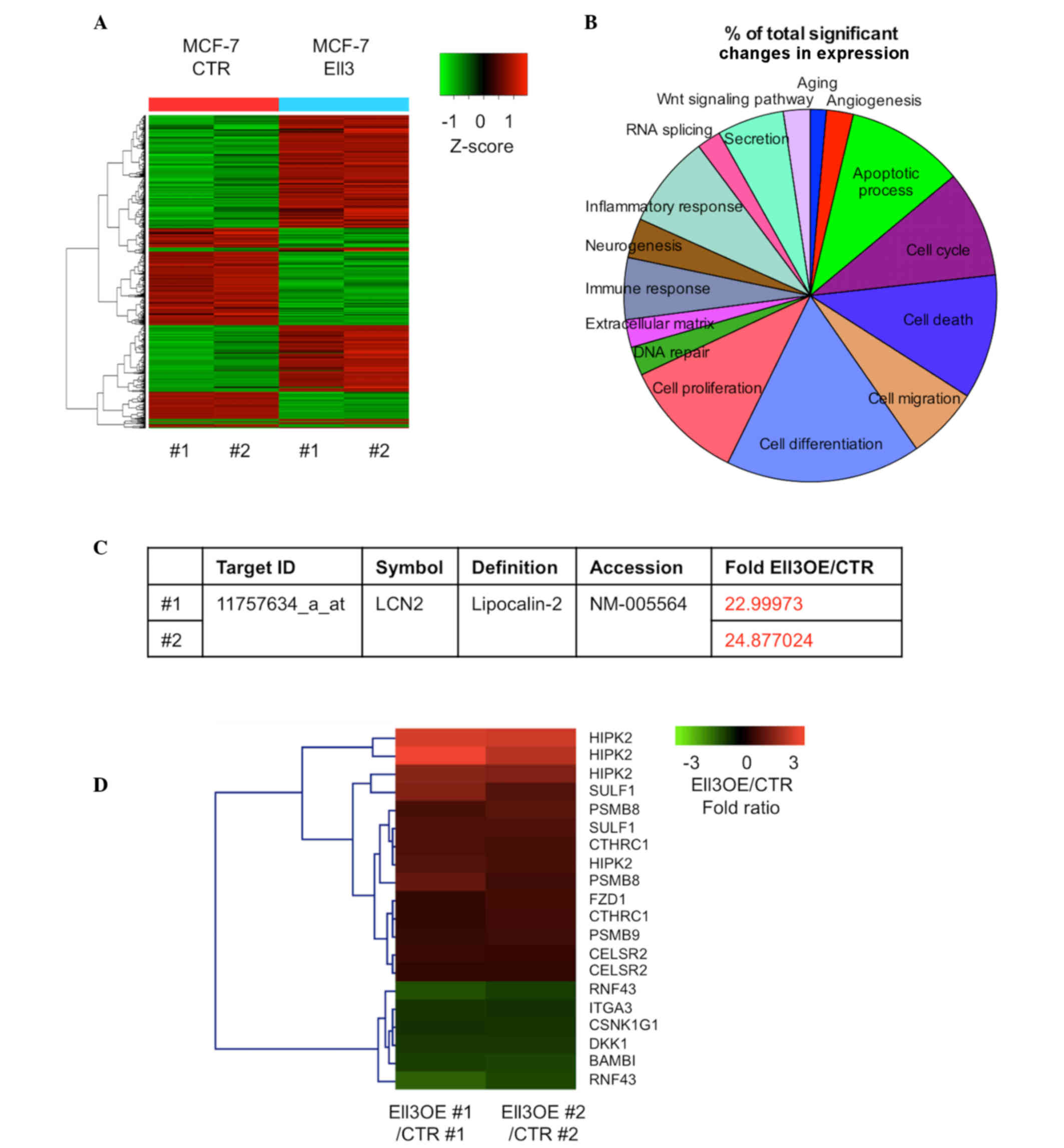
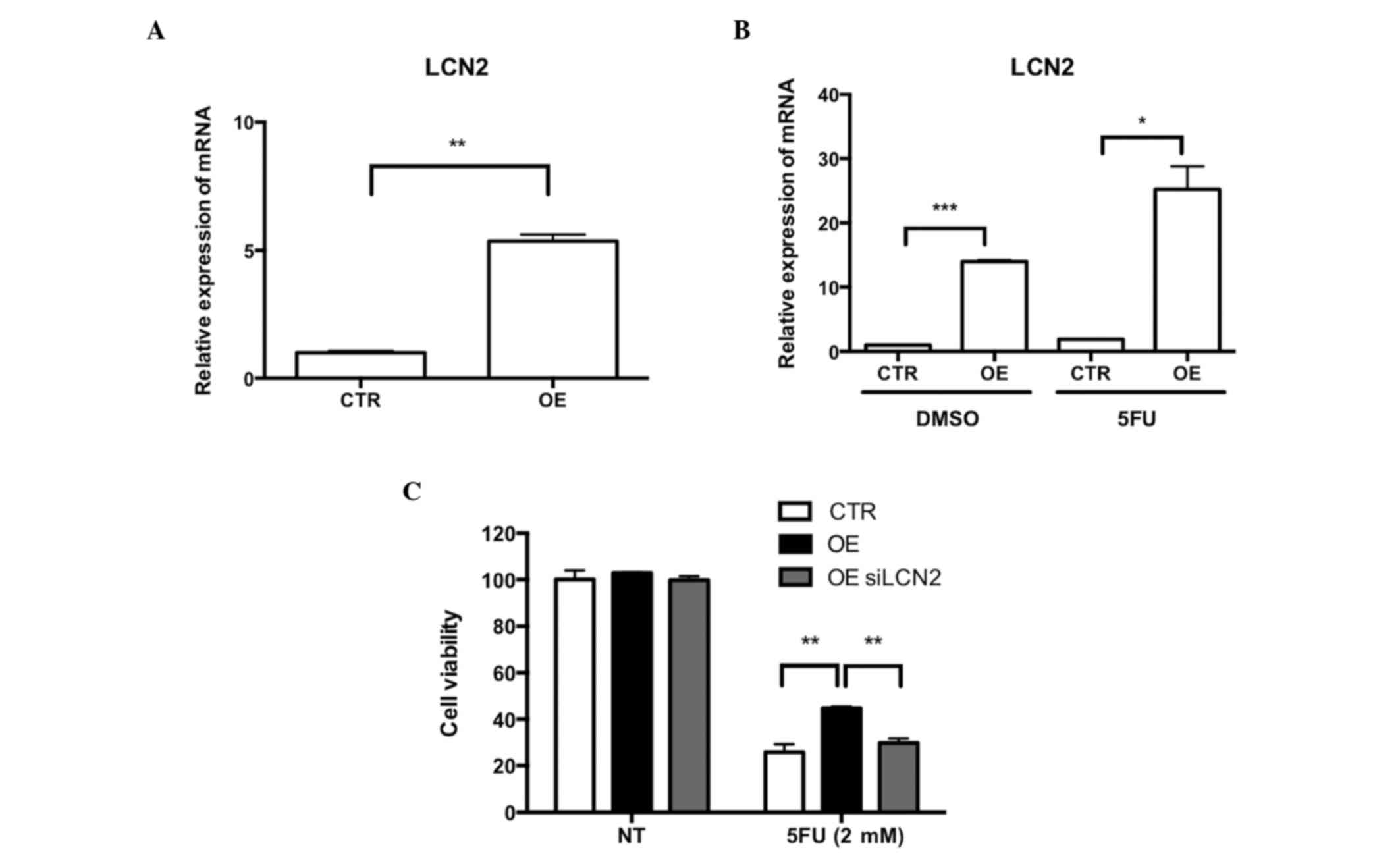
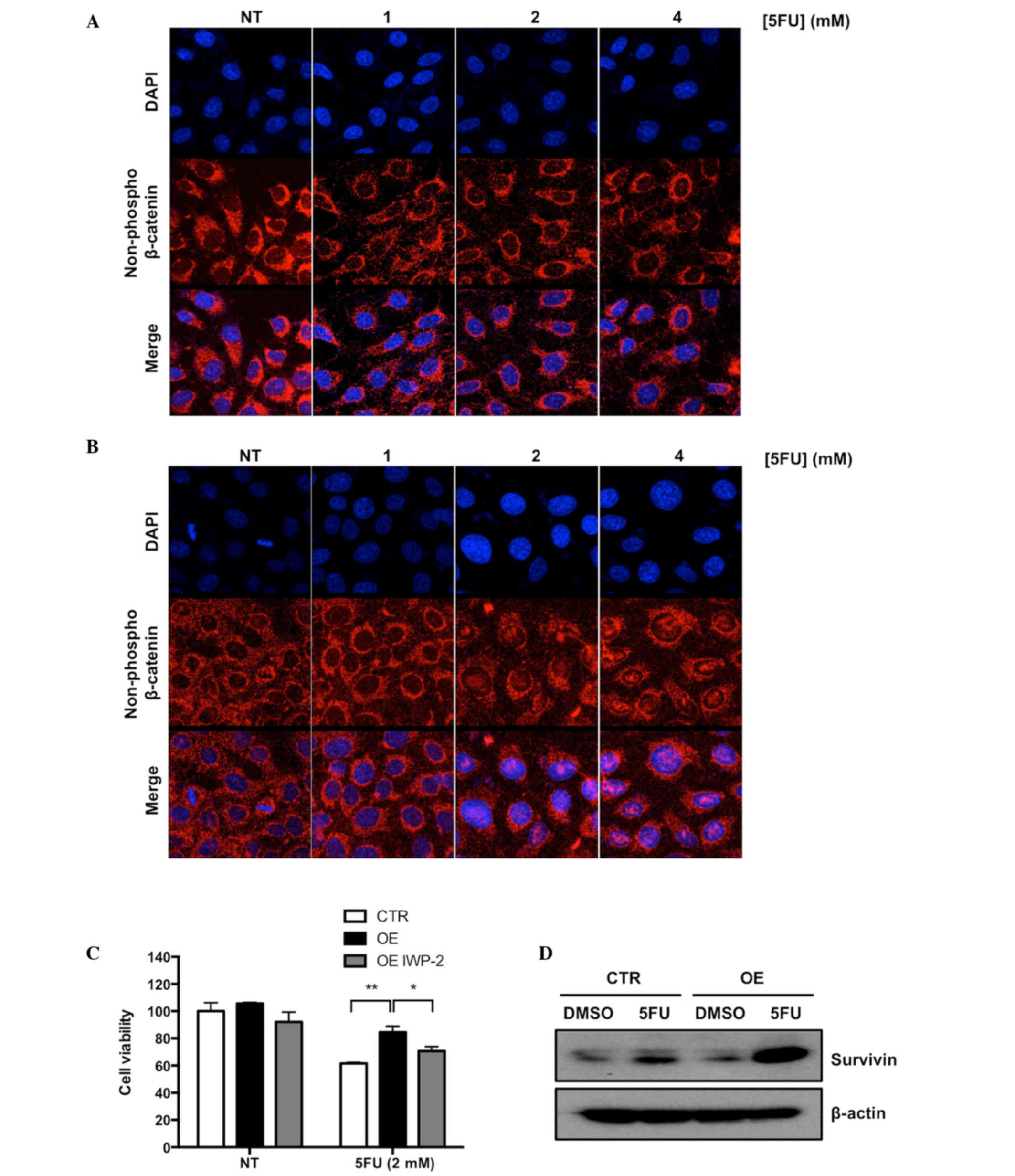
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:7–30. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ahn HJ, Kim G and Park KS: Ell3 stimulates
proliferation, drug resistance, and cancer stem cell properties of
breast cancer cells via a MEK/ERK-dependent signaling pathway.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 437:557–564. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Miller T, Williams K, Johnstone RW and
Shilatifard A: Identification, cloning, expression, and biochemical
characterization of the testis-specific RNA polymerase II
elongation factor ELL3. J Biol Chem. 275:32052–32056. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Maki K, Mitani K, Yamagata T, Kurokawa M,
Kanda Y, Yazaki Y and Hirai H: Transcriptional inhibition of p53 by
the MLL/MEN chimeric protein found in myeloid leukemia. Blood.
93:3216–3224. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Johnstone RW, Gerber MA, Landewe T,
Tollefson A, Wold WS and Shilatifard A: Functional analysis of the
leukemia protein ELL: Evidence for a role in the regulation of cell
growth and survival. Mol Cell Biol. 21:1672–1681. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lin C, Garruss AS, Luo Z, Guo F and
Shilatifard A: The RNA Pol II elongation factor Ell3 marks
enhancers in ES cells and primes future gene activation. Cell.
152:144–156. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Iannetti A, Pacifico F, Acquaviva R,
Lavorgna A, Crescenzi E, Vascotto C, Tell G, Salzano AM, Scaloni A,
Vuttariello E, et al: The neutrophil gelatinase-associated
lipocalin (NGAL), a NF-kappaB-regulated gene, is a survival factor
for thyroid neoplastic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
105:14058–14063. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhang H, Xu L, Xiao D, Xie J, Zeng H, Wang
Z, Zhang X, Niu Y, Shen Z, Shen J, et al: Upregulation of
neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin in oesophageal squamous
cell carcinoma: Significant correlation with cell differentiation
and tumour invasion. J Clin Pathol. 60:555–561. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Leng X, Ding T, Lin H, Wang Y, Hu L, Hu J,
Feig B, Zhang W, Pusztai L, Symmans WF, et al: Inhibition of
lipocalin 2 impairs breast tumorigenesis and metastasis. Cancer
Res. 69:8579–8584. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yang J, McNeish B, Butterfield C and Moses
MA: Lipocalin 2 is a novel regulator of angiogenesis in human
breast cancer. FASEB J. 27:45–50. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gruvberger S, Ringnér M, Chen Y, Panavally
S, Saal LH, Borg A, Fernö M, Peterson C and Meltzer PS: Estrogen
receptor status in breast cancer is associated with remarkably
distinct gene expression patterns. Cancer Res. 61:5979–5984.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bauer M, Eickhoff JC, Gould MN, Mundhenke
C, Maass N and Friedl A: Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin
(NGAL) is a predictor of poor prognosis in human primary breast
cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 108:389–397. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Tong Z, Wu X, Ovcharenko D, Zhu J, Chen CS
and Kehrer JP: Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin as a
survival factor. Biochem J. 391:441–448. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Giles RH, van Es JH and Clevers H: Caught
up in a Wnt storm: Wnt signaling in cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1653:1–24. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
van Noort M, Meeldijk J, van Der Zee R,
Destree O and Clevers H: Wnt signaling controls the phosphorylation
status of beta-catenin. J Biol Chem. 277:17901–17905. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Matsuda Y, Schlange T, Oakeley EJ, Boulay
A and Hynes NE: WNT signaling enhances breast cancer cell motility
and blockade of the WNT pathway by sFRP1 suppresses MDA-MB-231
xenograft growth. Breast Cancer Res. 11:R322009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Many AM and Brown AM: Both canonical and
non-canonical Wnt signaling independently promote stem cell growth
in mammospheres. PLoS One. 9:e1018002014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhang Y, Zhang X, Huang J and Dong Q: Wnt
signaling regulation of stem-like properties in human lung
adenocarcinoma cell lines. Med Oncol. 32:1572015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Cui J, Jiang W, Wang S, Wang L and Xie K:
Role of Wnt/β-catenin signaling in drug resistance of pancreatic
cancer. Curr Pharm Des. 18:2464–2471. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chikazawa N, Tanaka H, Tasaka T, Nakamura
M, Tanaka M, Onishi H and Katano M: Inhibition of Wnt signaling
pathway decreases chemotherapy-resistant side-population colon
cancer cells. Anticancer Res. 30:2041–2048. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Pećina-Slaus N: Wnt signal transduction
pathway and apoptosis: A review. Cancer Cell Int. 10:222010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
You L, He B, Xu Z, Uematsu K, Mazieres J,
Fujii N, Mikami I, Reguart N, McIntosh JK, Kashani-Sabet M, et al:
An anti-Wnt-2 monoclonal antibody induces apoptosis in malignant
melanoma cells and inhibits tumor growth. Cancer Res. 64:5385–5389.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Mita AC, Mita MM, Nawrocki ST and Giles
FJ: Survivin: Key regulator of mitosis and apoptosis and novel
target for cancer therapeutics. Clin Cancer Res. 14:5000–5005.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Fodde R and Brabletz T: Wnt/beta-catenin
signaling in cancer stemness and malignant behavior. Curr Opin Cell
Biol. 19:150–158. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kim PJ, Plescia J, Clevers H, Fearon ER
and Altieri DC: Survivin and molecular pathogenesis of colorectal
cancer. Lancet. 362:205–209. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Holohan C, Van Schaeybroeck S, Longley DB
and Johnston PG: Cancer drug resistance: An evolving paradigm. Nat
Rev Cancer. 13:714–726. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Livak KJ and Schimittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PDCR and
the 2 delta delta method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chappell WH, Abrams SL, Franklin RA,
LaHair MM, Montalto G, Cervello M, Martelli AM, Nicoletti F,
Candido S, Libra M, et al: Ectopic NGAL expression can alter
sensitivity of breast cancer cells to EGFR, Bcl-2, CaM-K inhibitors
and the natural plant product berberine. Cell Cycle. 11:4447–4461.
2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ogata H, Goto S, Sato K, Fujibuchi W, Bono
H and Kanehisa M: KEGG: Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes.
Nucleic Acids Res. 27:29–34. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yu DS, Wu CL, Ping SY, Huang YL and Shen
KH: NGAL can alternately mediate sunitinib resistance in renal cell
carcinoma. J Urol. 192:559–566. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Leung L, Radulovich N, Zhu CQ, Organ S,
Bandarchi B, Pintilie M, To C, Panchal D and Tsao MS: Lipocalin2
promotes invasion, tumorigenicity and gemcitabine resistance in
pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. PLoS One. 7:e466772012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|