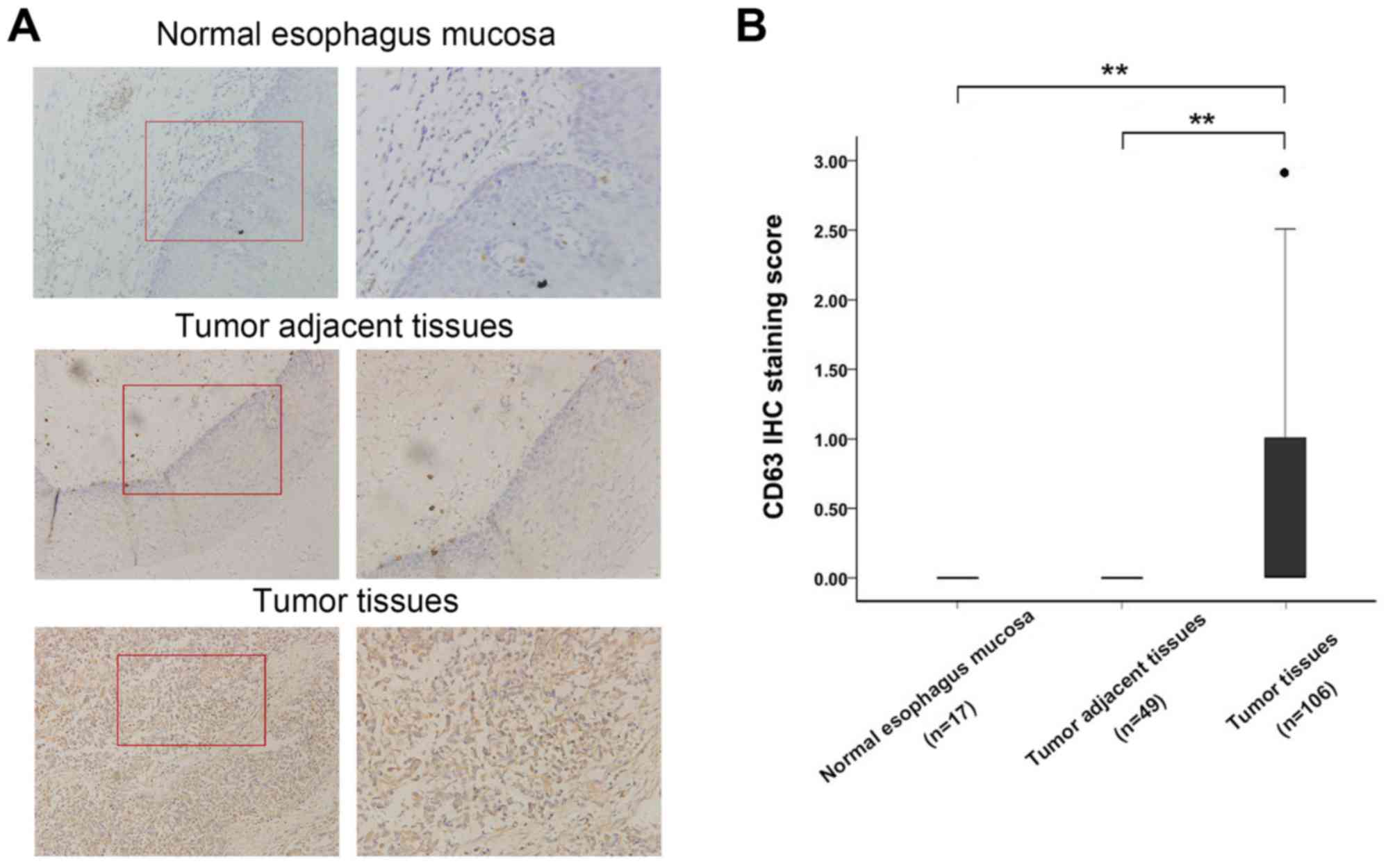
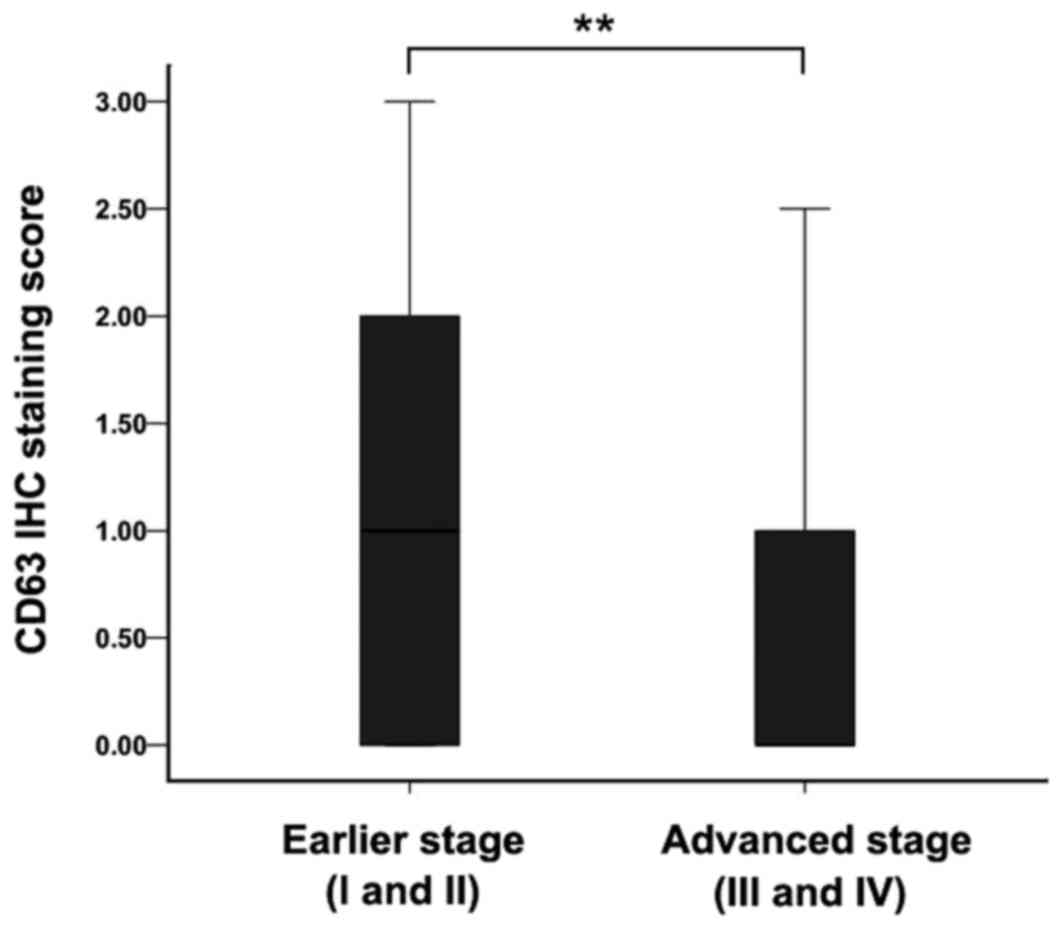
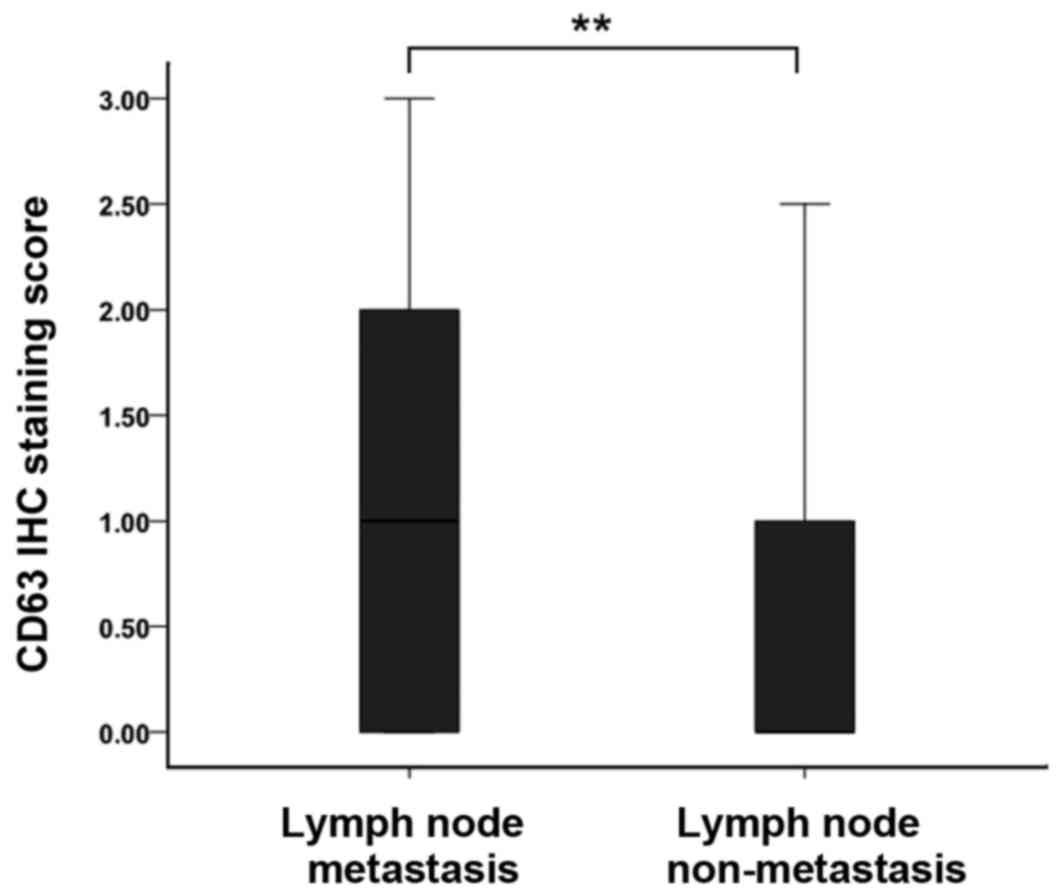
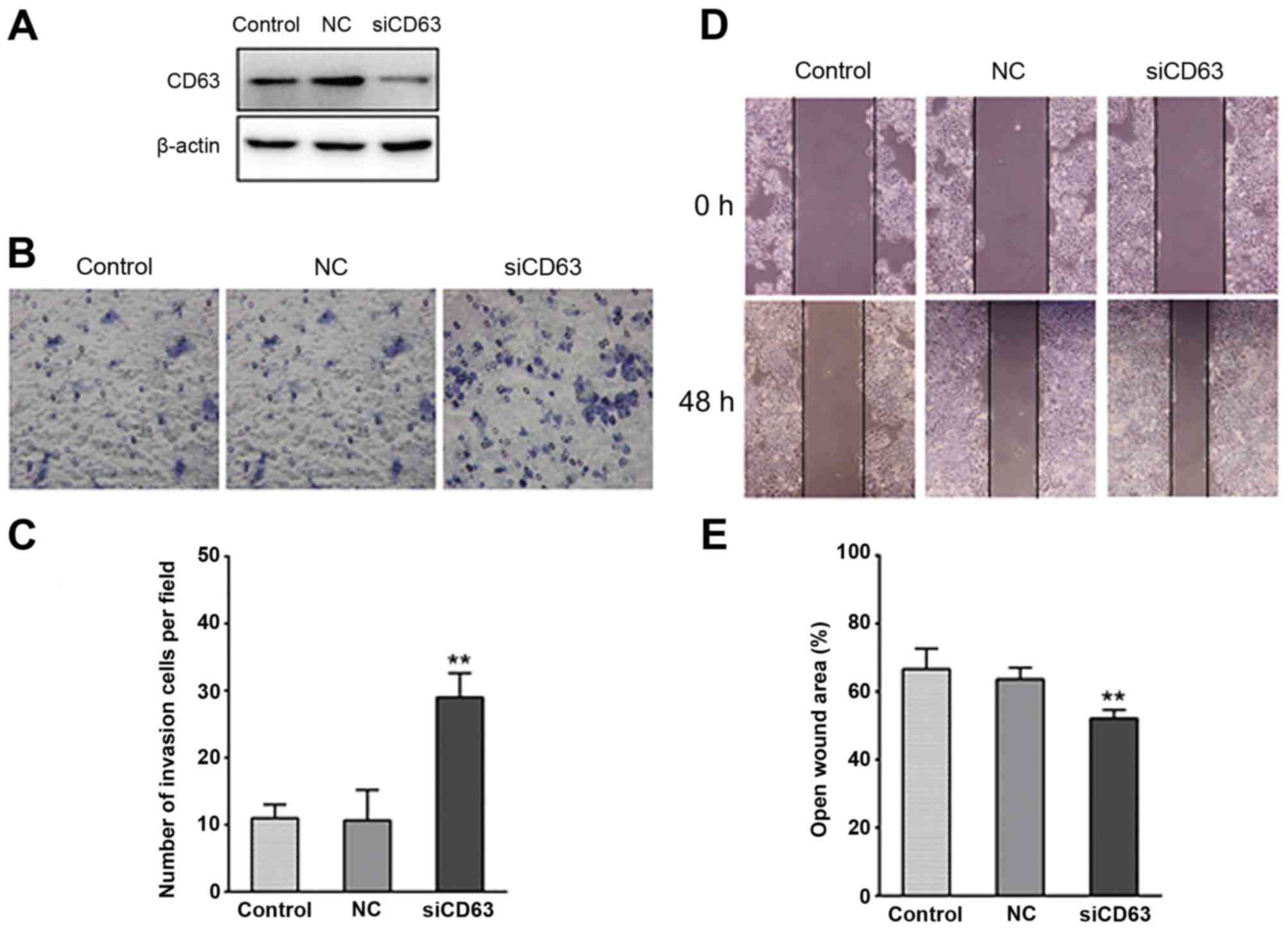
|
1
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Pennathur A, Gibson MK, Jobe BA and
Luketich JD: Oesophageal carcinoma. Lancet. 381:400–412. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Dipetrillo T, Suntharalingam M, Ng T,
Fontaine J, Horiba N, Oldenburg N, Perez K, Birnbaum A, Battafarano
R, Burrows W and Safran H: Neoadjuvant paclitaxel poliglumex,
cisplatin, and radiation for esophageal cancer: A phase 2 trial. Am
J Clin Oncol. 35:64–67. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
van Hagen P, Hulshof MC, van Lanschot JJ,
Steyerberg EW, van Berge Henegouwen MI, Wijnhoven BP, Richel DJ,
Nieuwenhuijzen GA, Hospers GA, Bonenkamp JJ, et al: Preoperative
chemoradiotherapy for esophageal or junctional cancer. N Engl J
Med. 366:2074–2084. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Eloubeidi MA, Desmond R, Arguedas MR, Reed
CE and Wilcox CM: Prognostic factors for the survival of patients
with esophageal carcinoma in the U.S.: The importance of tumor
length and lymph node status. Cancer. 95:1434–1443. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cho JW, Choi SC, Jang JY, Shin SK, Choi
KD, Lee JH, Kim SG, Sung JK, Jeon SW, Choi IJ, et al: Lymph node
metastases in esophageal carcinoma: An Endoscopist's view. Clin
Endosc. 47:523–529. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Maecker HT, Todd SC and Levy S: The
tetraspanin superfamily: Molecular facilitators. FASEB J.
11:428–442. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hunziker W and Geuze HJ: Intracellular
trafficking of lysosomal membrane proteins. Bioessays. 18:379–389.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Atkinson B, Ernst CS, Ghrist BF, Herlyn M,
Blaszczyk M, Ross AH, Herlyn D, Steplewski Z and Koprowski H:
Identification of melanoma-associated antigens using fixed tissue
screening of antibodies. Cancer Res. 44:2577–2581. 1984.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hemler ME: Tetraspanin proteins mediate
cellular penetration, invasion and fusion events and define a novel
type of membrane microdomain. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 19:397–422.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hemler ME, Mannion BA and Berditchevski F:
Association of TM4SF proteins with integrins: Relevance to cancer.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1287:67–71. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hölters S, Anacker J, Jansen L,
Beer-Grondke K, Dürst M and Rubio I: Tetraspanin 1 promotes
invasiveness of cervical cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 43:503–512.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kwon MS, Shin SH, Yim SH, Lee KY, Kang HM,
Kim TM and Chung YJ: CD63 as a biomarker for predicting the
clinical outcomes in adenocarcinoma of lung. Lung Cancer. 57:46–53.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kondoh M, Ueda M, Ichihashi M and Mishima
Y: Decreased expression of human melanoma-associated antigen ME491
along the progression of melanoma pre-canceroses to invasive and
metastatic melanomas. Melanoma Res. 3:241–245. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Radford KJ, Mallesch J and Hersey P:
Suppression of human melanoma cell growth and metastasis by the
melanoma-associated antigen CD63 (ME491). Int J Cancer. 62:631–635.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sordat I, Decraene C, Silvestre T,
Petermann O, Auffray C, Piétu G and Sordat B: Complementary DNA
arrays identify CD63 tetraspanin and alpha3 integrin chain as
differentially expressed in low and high metastatic human colon
carcinoma cells. Lab Invest. 82:1715–1724. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Seubert B, Cui H, Simonavicius N, Honert
K, Schäfer S, Reuning U, Heikenwalder M, Mari B and Kruger A:
Tetraspanin CD63 acts as a pro-metastatic factor via β-catenin
stabilization. Int J Cancer. 136:2304–2315. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kwon MS, Shin SH, Yim SH, Lee KY, Kang HM,
Kim TM and Chung YJ: CD63 as a biomarker for predicting the
clinical outcomes in adenocarcinoma of lung. Lung Cancer. 57:46–53.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jang HI and Lee H: A decrease in the
expression of CD63 tetraspanin protein elevates invasive potential
of human melanoma cells. Exp Mol Med. 35:317–323. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Toricelli M, Melo FH, Peres GB, Silva DC
and Jasiulionis MG: Timp1 interacts with beta-1 integrin and CD63
along melanoma genesis and confers anoikis resistance by activating
PI3-K signaling pathway independently of Akt phosphorylation. Mol
Cancer. 12:222013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhou Z, Ran YL, Hu H, Pan J, Li ZF, Chen
LZ, Sun LC, Peng L, Zhao XL, Yu L, et al: TM4SF3 promotes
esophageal carcinoma metastasis via upregulating ADAM12m
expression. Clin Exp Metastasis. 25:537–548. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kong KL, Kwong DL, Fu L, Chan TH, Chen L,
Liu H, Li Y, Zhu YH, Bi J, Qin YR, et al: Characterization of a
candidate tumor suppressor gene uroplakin 1A in esophageal squamous
cell carcinoma. Cancer Res. 70:8832–8841. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yamasaki M, Miyata H, Miyazaki Y,
Takahashi T, Kurokawa Y, Nakajima K, Takiguchi S, Mori M and Doki
Y: Evaluation of the nodal status in the 7th edition of the
UICC-TNM classification for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma:
Proposed modifications for improved survival stratification: Impact
of lymph node metastases on overall survival after esophagectomy.
Ann Surg Oncol. 21:2850–2856. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
D'Amico TA: Outcomes after surgery for
esophageal cancer. Gastrointest Cancer Res. 1:188–196.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Enzinger PC and Mayer RJ: Esophageal
cancer. N Engl J Med. 349:2241–2252. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hotta H, Ross AH, Huebner K, Isobe M,
Wendeborn S, Chao MV, Ricciardi RP, Tsujimoto Y, Croce CM and
Koprowski H: Molecular cloning and characterization of an antigen
associated with early stages of melanoma tumor progression. Cancer
Res. 48:2955–2962. 1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lin D, Kamsteeg EJ, Zhang Y, Jin Y,
Sterling H, Yue P, Roos M, Duffield A, Spencer J, Caplan M and Wang
WH: Expression of tetraspan protein CD63 activates protein-tyrosine
kinase (PTK) and enhances the PTK-induced inhibition of ROMK
channels. J Biol Chem. 283:7674–7681. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yoshida T, Ebina H and Koyanagi Y:
N-linked glycan-dependent interaction of CD63 with CXCR4 at the
Golgi apparatus induces downregulation of CXCR4. Microbiol Immunol.
53:629–635. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Sauer G, Kurzeder C, Grundmann R,
Kreienberg R, Zeillinger R and Deissler H: Expression of
tetraspanin adaptor proteins below defined threshold values is
associated with in vitro invasiveness of mammary carcinoma cells.
Oncol Rep. 10:405–410. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Radford KJ, Thorne RF and Hersey P:
Regulation of tumor cell motility and migration by CD63 in a human
melanoma cell line. J Immunol. 158:3353–3358. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Jung KK, Liu XW, Chirco R, Fridman R and
Kim HR: Identification of CD63 as a tissue inhibitor of
metalloproteinase-1 interacting cell surface protein. EMBO J.
25:3934–3942. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Tominaga N, Hagiwara K, Kosaka N, Honma K,
Nakagama H and Ochiya T: RPN2-mediated glycosylation of tetraspanin
CD63 regulates breast cancer cell malignancy. Mol Cancer.
13:1342014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Takino T, Miyamori H, Kawaguchi N, Uekita
T, Seiki M and Sato H: Tetraspanin CD63 promotes targeting and
lysosomal proteolysis of membrane-type 1 matrix metalloproteinase.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 304:160–166. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Rubinstein E, Le Naour F,
Lagaudrière-Gesbert C, Billard M, Conjeaud H and Boucheix C: CD9,
CD63, CD81, and CD82 are components of a surface tetraspan network
connected to HLA-DR and VLA integrins. Eur J Immunol. 26:2657–2665.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Berditchevski F, Zutter MM and Hemler ME:
Characterization of novel complexes on the cell surface between
integrins and proteins with 4 transmembrane domains (TM4 proteins).
Mol Biol Cell. 7:193–207. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Berditchevski F, Bazzoni G and Hemler ME:
Specific association of CD63 with the VLA-3 and VLA-6 integrins. J
Biol Chem. 270:17784–17790. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Skubitz KM, Campbell KD, Iida J and
Skubitz AP: CD63 associates with tyrosine kinase activity and
CD11/CD18 and transmits an activation signal in neutrophils. J
Immunol. 157:3617–3626. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Radford KJ, Thorne RF and Hersey P: CD63
associates with transmembrane 4 superfamily members, CD9 and CD81,
and with beta 1 integrins in human melanoma. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 222:13–18. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Si Z and Hersey P: Expression of the
neuroglandular antigen and analogues in melanoma. CD9 expression
appears inversely related to metastatic potential of melanoma. Int
J Cancer. 54:37–43. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zucker S and Vacirca J: Role of matrix
metalloproteinases (MMPs) in colorectal cancer. Cancer Metastasis
Rev. 23:101–117. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Tania M, Khan MA and Fu J: Epithelial to
mesenchymal transition inducing transcription factors and
metastatic cancer. Tumour Biol. 35:7335–7342. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|