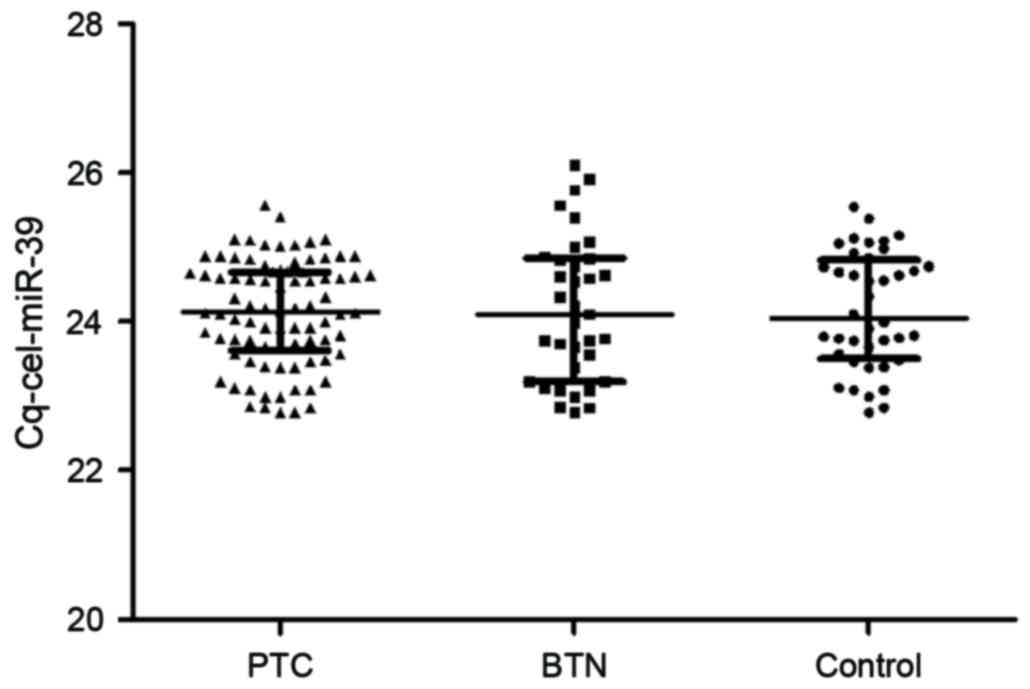
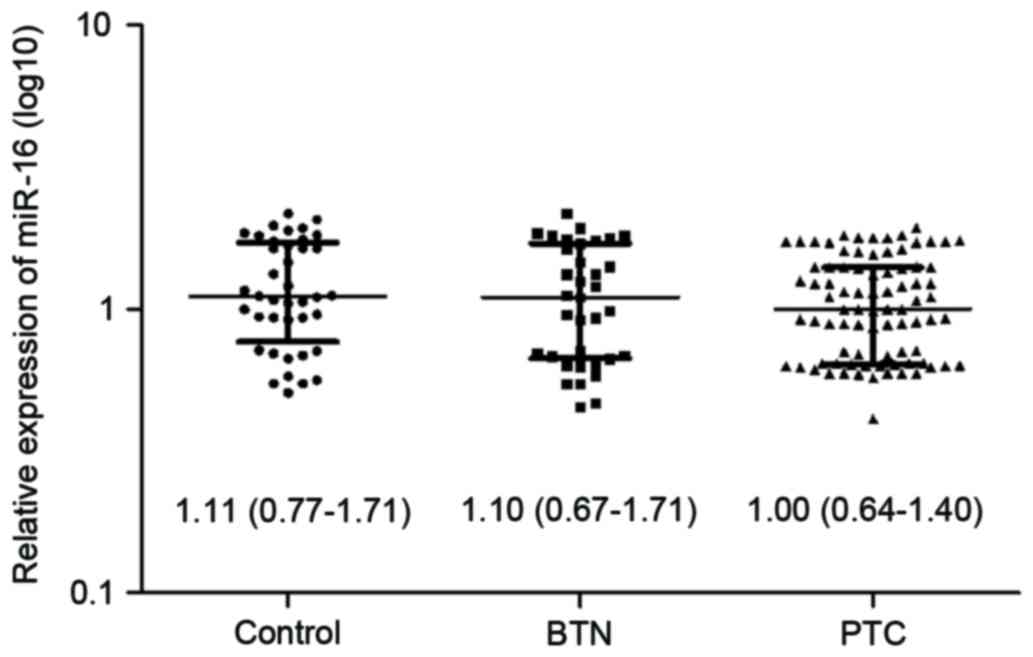
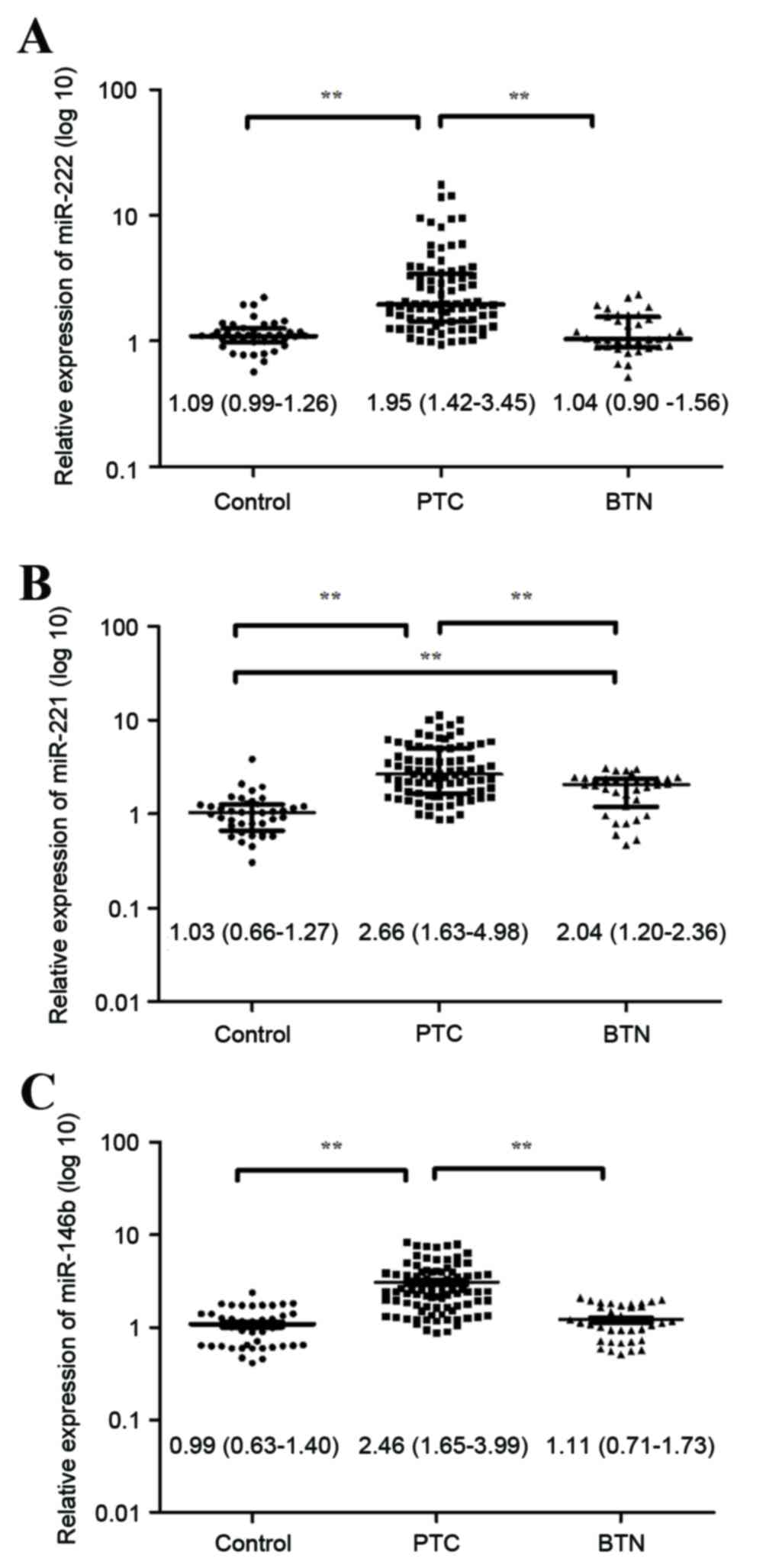
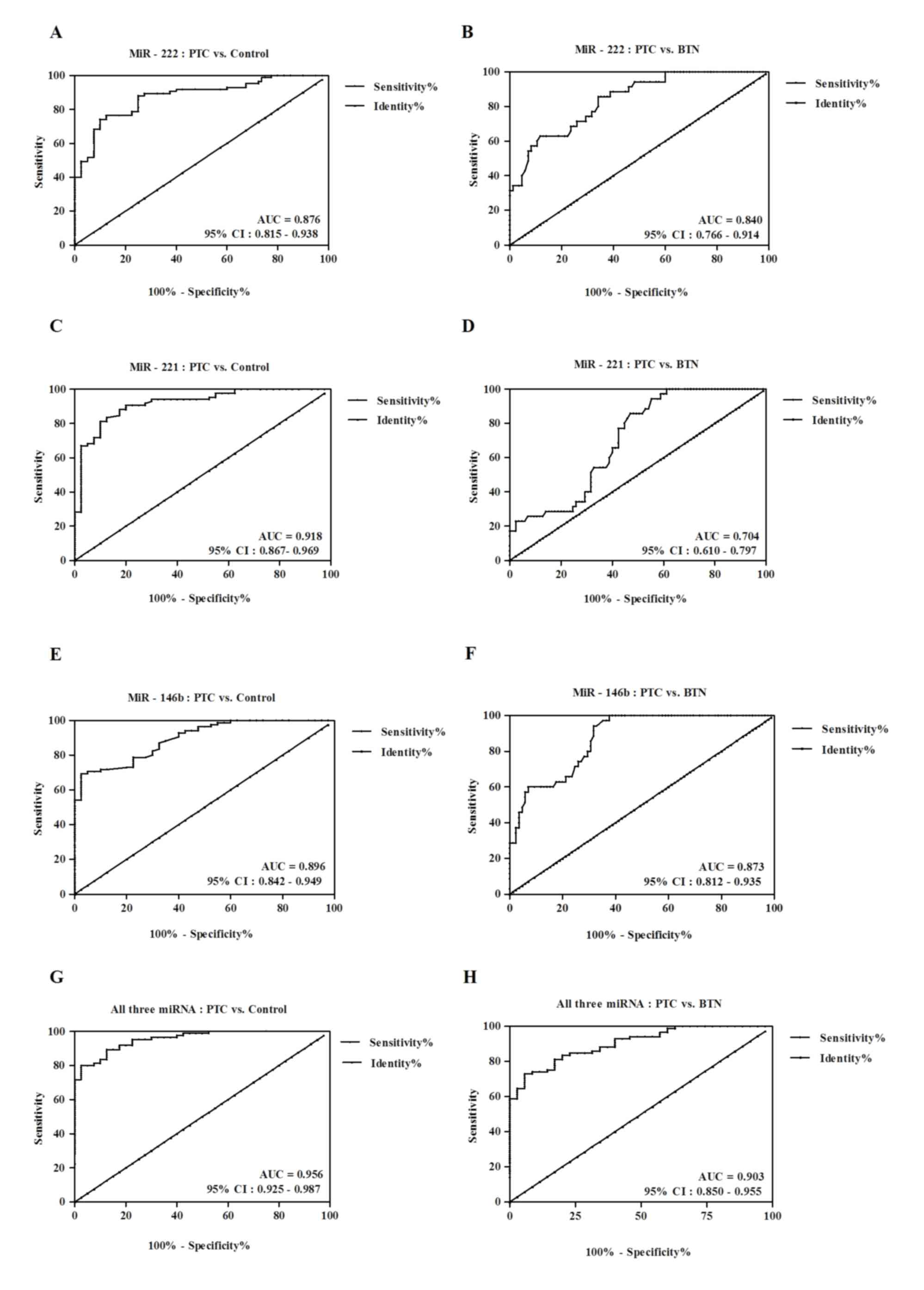
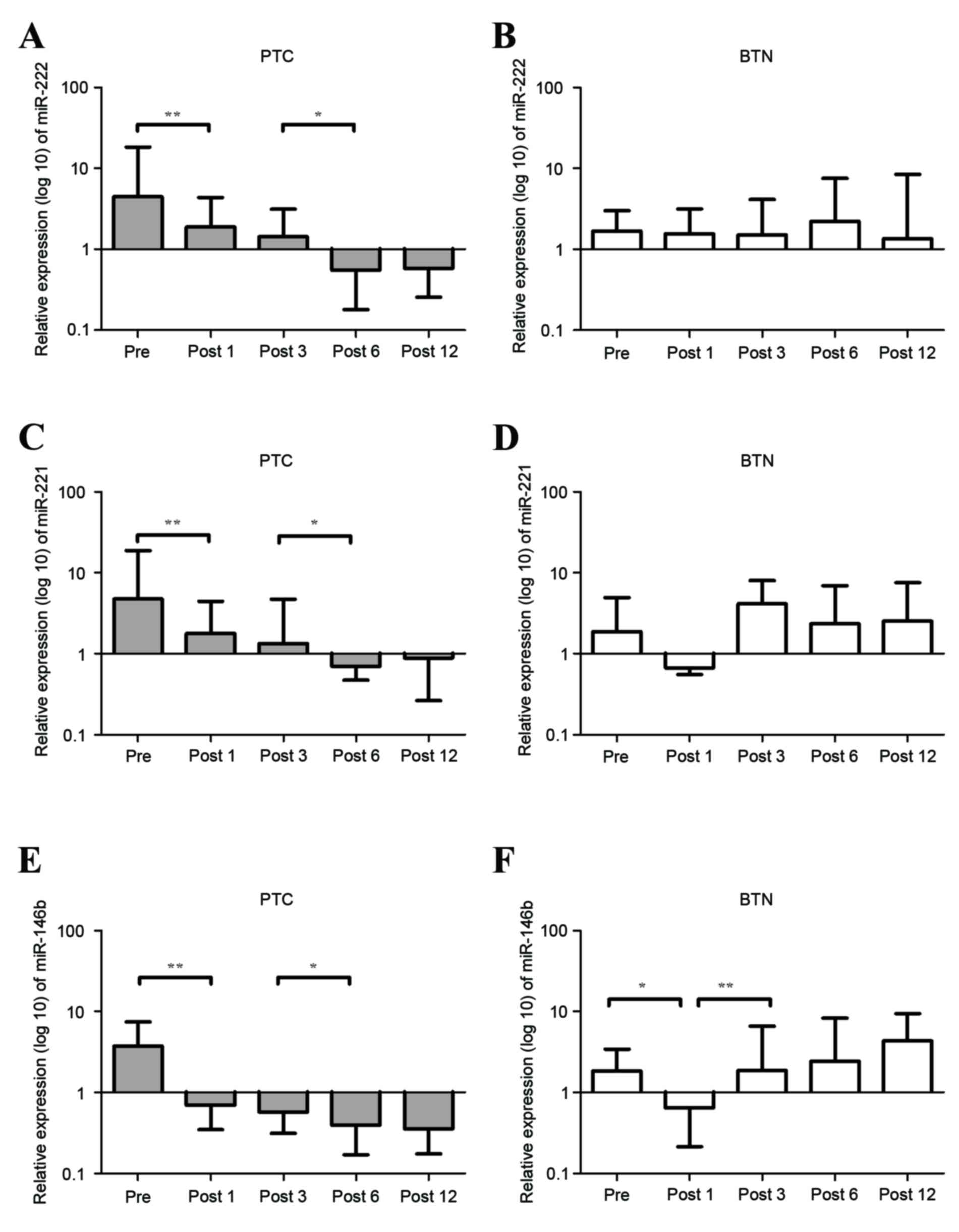
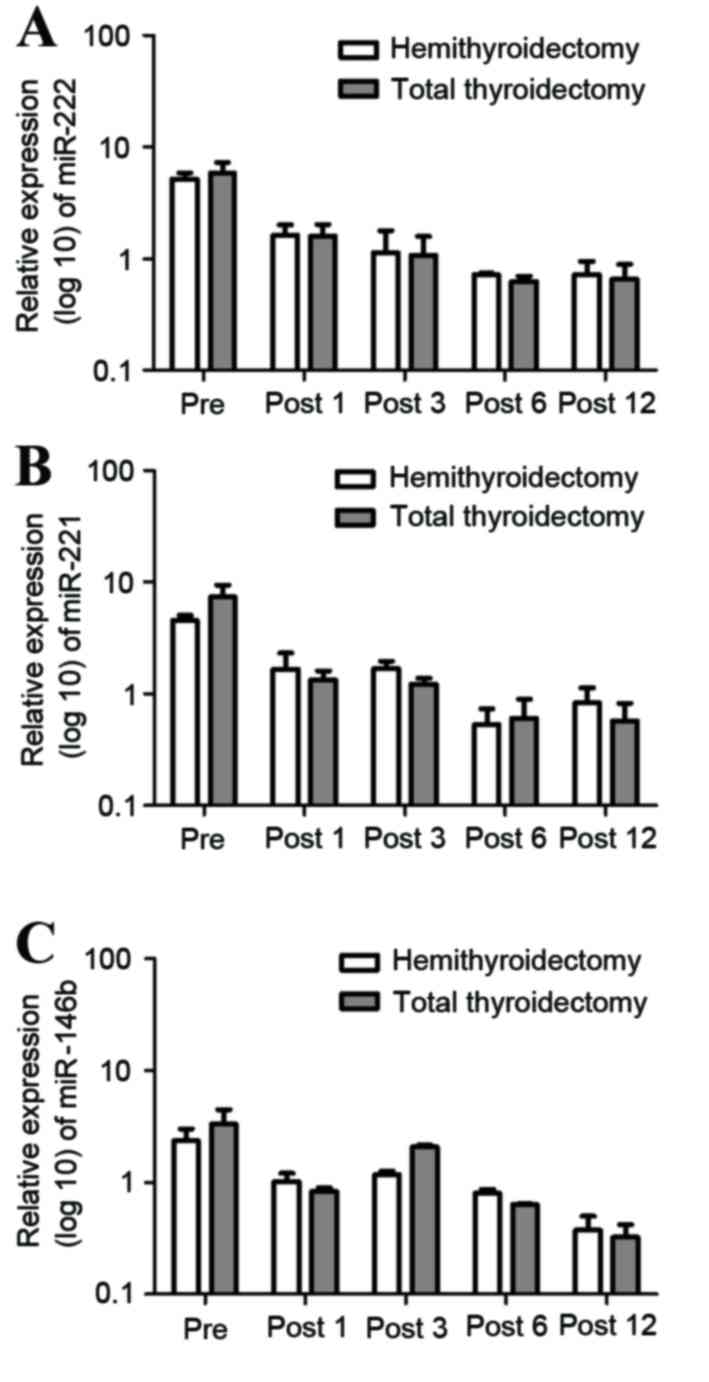
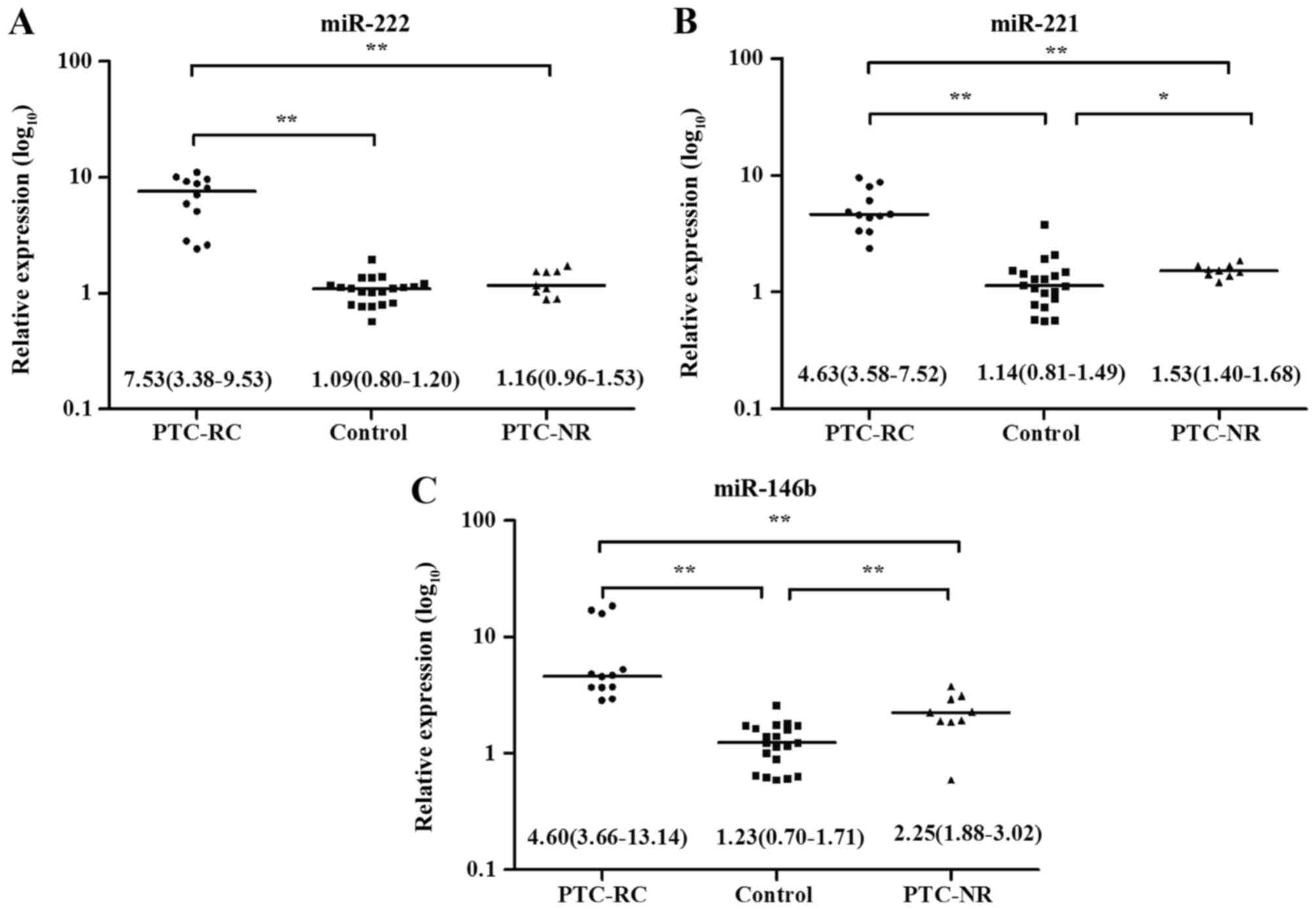
|
1
|
Bann DV, Goyal N, Camacho F and Goldenberg
D: Increasing incidence of thyroid cancer in the Commonwealth of
Pennsylvania. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 140:1149–1156. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
N Howlader AMN and M Krapcho JG: SEER
Cancer Statistics Review, 1975–2011. Bethesda, MD: National Cancer
Institute; 2014
|
|
3
|
Leenhardt L, Grosclaude P and
Chérié-Challine L; Thyroid Cancer Committee, : Increased incidence
of thyroid carcinoma in France: A true epidemic or thyroid nodule
management effects? Report from the French Thyroid Cancer
Committee. Thyroid. 14:1056–1060. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Pacini F, Schlumberger M, Dralle H, Elisei
R, Smit JW and Wiersinga W; European Thyroid Cancer, : European
consensus for the management of patients with differentiated
thyroid carcinoma of the follicular epithelium. Eur J Endocrinol.
154:787–803. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
American Thyroid Association (ATA)
Guidelines Taskforce on Thyroid Nodules and Differentiated Thyroid
Cancer, ; Cooper DS, Doherty GM, Haugen BR, Kloos RT, Lee SL,
Mandel SJ, Mazzaferri EL, McIver B, Pacini F, et al: Revised
American thyroid association management guidelines for patients
with thyroid nodules and differentiated thyroid cancer. Thyroid.
19:1167–1214. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cooper DS, Doherty GM, Haugen BR, Kloos
RT, Lee SL, Mandel SJ, Mazzaferri EL, McIver B, Sherman SI and
Tuttle RM: American Thyroid Association Guidelines Taskforce:
Management guidelines for patients with thyroid nodules and
differentiated thyroid cancer. Thyroid. 16:109–142. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Pusztaszeri MP, Bongiovanni M and Faquin
WC: Update on the cytologic and molecular features of medullary
thyroid carcinoma. Adv Anat Pathol. 21:26–35. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhao L, Gong Y, Wang J, Dawlett M, Huo L,
Caraway NP and Guo M: Ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration
biopsy of thyroid bed lesions from patients with thyroidectomy for
thyroid carcinomas. Cancer Cytopathol. 121:101–107. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lew JI, Snyder RA, Sanchez YM and
Solorzano CC: Fine needle aspiration of the thyroid: Correlation
with final histopathology in a surgical series of 797 patients. J
Am Coll Surg. 213:188–195. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Cibas ES and Ali SZ: The bethesda system
for reporting thyroid cytopathology. Thyroid. 19:1159–1165. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gharib H, Papini E, Paschke R, Duick DS,
Valcavi R, Hegedüs L and Vitti P: AACE/AME/ETA Task Force on
Thyroid Nodules: American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists,
Associazione Medici Endocrinologi and European Thyroid Association
Medical guidelines for clinical practice for the diagnosis and
management of thyroid nodules: Executive summary of
recommendations. Endocr Pract. 16:468–475. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Leboulleux S, Rubino C, Baudin E, Caillou
B, Hartl DM, Bidart JM, Travagli JP and Schlumberger M: Prognostic
factors for persistent or recurrent disease of papillary thyroid
carcinoma with neck lymph node metastases and/or tumor extension
beyond the thyroid capsule at initial diagnosis. J Clin Endocrinol
Metab. 90:5723–5729. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Suh YJ, Kwon H, Kim SJ, Choi JY, Lee KE,
Park YJ, do J Park and Youn YK: Factors affecting the locoregional
recurrence of conventional papillary thyroid carcinoma after
surgery: A retrospective analysis of 3381 patients. Ann Surg Oncol.
22:3543–3549. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Spencer CA: Challenges of serum
thyroglobulin (Tg) measurement in the presence of Tg
autoantibodies. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 89:3702–3704. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Woodmansee WW and Haugen BR: Uses for
recombinant human TSH in patients with thyroid cancer and nodular
goiter. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 61:163–173. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Castagna MG, Brilli L, Pilli T, Montanaro
A, Cipri C, Fioravanti C, Sestini F, Capezzone M and Pacini F:
Limited value of repeat recombinant human thyrotropin
(rhTSH)-stimulated thyroglobulin testing in differentiated thyroid
carcinoma patients with previous negative rhTSH-stimulated
thyroglobulin and undetectable basal serum thyroglobulin levels. J
Clin Endocrinol Metab. 93:76–81. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Snozek CL, Chambers EP, Reading CC, Sebo
TJ, Sistrunk JW, Singh RJ and Grebe SK: Serum thyroglobulin,
high-resolution ultrasound and lymph node thyroglobulin in
diagnosis of differentiated thyroid carcinoma nodal metastases. J
Clin Endocrinol Metab. 92:4278–4281. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Orlov S, Salari F, Kashat L, Freeman JL,
Vescan A, Witterick IJ and Walfish PG: Post-operative stimulated
thyroglobulin and neck ultrasound as personalized criteria for risk
stratification and radioactive iodine selection in low- and
intermediate-risk papillary thyroid cancer. Endocrine. 50:130–137.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Londero SC, Krogdahl A, Bastholt L,
Overgaard J, Pedersen HB, Hahn CH, Bentzen J, Schytte S,
Christiansen P, Gerke O, et al: Papillary thyroid carcinoma in
Denmark, 1996–2008: Outcome and evaluation of established
prognostic scoring systems in a prospective national cohort.
Thyroid. 25:78–84. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lu J, Getz G, Miska EA, Alvarez-Saavedra
E, Lamb J, Peck D, Sweet-Cordero A, Ebert BL, Mak RH, Ferrando AA,
et al: MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature.
435:834–838. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Volinia S, Calin GA, Liu CG, Ambs S,
Cimmino A, Petrocca F, Visone R, Iorio M, Roldo C, Ferracin M, et
al: A microRNA expression signature of human solid tumors defines
cancer gene targets. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:pp. 2257–2261.
2006; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lawrie CH, Gal S, Dunlop HM, Pushkaran B,
Liggins AP, Pulford K, Banham AH, Pezzella F, Boultwood J,
Wainscoat JS, et al: Detection of elevated levels of
tumour-associated microRNAs in serum of patients with diffuse large
B-cell lymphoma. Br J Haematol. 141:672–675. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kou CH, Zhou T, Han XL, Zhuang HJ and Qian
HX: Downregulation of mir-23b in plasma is associated with poor
prognosis in patients with colorectal cancer. Oncol Lett.
12:4838–4844. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hanke M, Hoefig K, Merz H, Feller AC,
Kausch I, Jocham D, Warnecke JM and Sczakiel G: A robust
methodology to study urine microRNA as tumor marker: microRNA-126
and microRNA-182 are related to urinary bladder cancer. Urol Oncol.
28:655–661. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Park NJ, Zhou H, Elashoff D, Henson BS,
Kastratovic DA, Abemayor E and Wong DT: Salivary microRNA:
Discovery, characterization, and clinical utility for oral cancer
detection. Clin Cancer Res. 15:5473–5477. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Faam B, Ghaffari MA, Ghadiri A and Azizi
F: Epigenetic modifications in human thyroid cancer. Biomed Rep.
3:3–8. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yang Z, Yuan Z, Fan Y, Deng X and Zheng Q:
Integrated analyses of microRNA and mRNA expression profiles in
aggressive papillary thyroid carcinoma. Mol Med Rep. 8:1353–1358.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Peng Y, Li C, Luo DC, Ding JW, Zhang W and
Pan G: Expression profile and clinical significance of microRNAs in
papillary thyroid carcinoma. Molecules. 19:11586–11599. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lee JC, Zhao JT, Clifton-Bligh RJ, Gill A,
Gundara JS, Ip JC, Glover A, Sywak MS, Delbridge LW, Robinson BG
and Sidhu SB: MicroRNA-222 and microRNA-146b are tissue and
circulating biomarkers of recurrent papillary thyroid cancer.
Cancer. 119:4358–4365. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wang Z, Zhang H, He L, Dong W, Li J, Shan
Z and Teng W: Association between the expression of four
upregulated miRNAs and extrathyroidal invasion in papillary thyroid
carcinoma. Onco Targets Ther. 6:281–287. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Dettmer M, Perren A, Moch H, Komminoth P,
Nikiforov YE and Nikiforova MN: Comprehensive MicroRNA expression
profiling identifies novel markers in follicular variant of
papillary thyroid carcinoma. Thyroid. 23:1383–1389. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
He H, Jazdzewski K, Li W, Liyanarachchi S,
Nagy R, Volinia S, Calin GA, Liu CG, Franssila K, Suster S, et al:
The role of microRNA genes in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 102:pp. 19075–19080. 2005; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yu S, Liu Y, Wang J, Guo Z, Zhang Q, Yu F,
Zhang Y, Huang K, Li Y, Song E, et al: Circulating microRNA
profiles as potential biomarkers for diagnosis of papillary thyroid
carcinoma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 97:2084–2092. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Cantara S, Pilli T, Sebastiani G, Cevenini
G, Busonero G, Cardinale S, Dotta F and Pacini F: Circulating
miRNA95 and miRNA190 are sensitive markers for the differential
diagnosis of thyroid nodules in a Caucasian population. J Clin
Endocrinol Metab. 99:4190–4198. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lee YS, Lim YS, Lee JC, Wang SG, Park HY,
Kim SY and Lee BJ: Differential expression levels of plasma-derived
miR-146b and miR-155 in papillary thyroid cancer. Oral Oncol.
51:77–83. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Vrachimis A, Gerss J, Stoyke M, Wittekind
C, Maier T, Wenning C, Rahbar K, Schober O and Riemann B: No
significant difference in the prognostic value of the 5th and 7th
editions of AJCC staging for differentiated thyroid cancer. Clin
Endocrinol (Oxf). 80:911–917. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Cady B and Rossi R: An expanded view of
risk-group definition in differentiated thyroid carcinoma. Surgery.
104:947–953. 1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Sun Y, Yu S, Liu Y, Wang F, Liu Y and Xiao
H: Expression of miRNAs in papillary thyroid carcinomas is
associated with BRAF mutation and clinicopathological features in
Chinese patients. Int J Endocrinol. 2013:1287352013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Chou CK, Chen RF, Chou FF, Chang HW, Chen
YJ, Lee YF, Yang KD, Cheng JT, Huang CC and Liu RT: miR-146b is
highly expressed in adult papillary thyroid carcinomas with high
risk features including extrathyroidal invasion and the BRAF
(V600E) mutation. Thyroid. 20:489–494. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Kroh EM, Parkin RK, Mitchell PS and Tewari
M: Analysis of circulating microRNA biomarkers in plasma and serum
using quantitative reverse transcription-PCR (qRT-PCR). Methods.
50:298–301. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Toiyama Y, Tanaka K, Inoue Y, Mohri Y and
Kusunoki M: Circulating cell-free microRNAs as biomarkers for
colorectal cancer. Surg Today. 46:13–24. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Xiang M, Zeng Y, Yang R, Xu H, Chen Z,
Zhong J, Xie H, Xu Y and Zeng X: U6 is not a suitable endogenous
control for the quantification of circulating microRNAs. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 454:210–214. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
McDermott AM, Kerin MJ and Miller N:
Identification and validation of miRNAs as endogenous controls for
RQ-PCR in blood specimens for breast cancer studies. PLoS One.
8:e837182013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Alegre E, Sanmamed MF, Rodriguez C,
Carranza O, Martin-Algarra S and Gonzalez A: Study of circulating
microRNA-125b levels in serum exosomes in advanced melanoma. Arch
Pathol Lab Med. 138:828–832. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Lee RC, Feinbaum RL and Ambros V: The C.
elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense
complementarity to lin-14. Cell. 75:843–854. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Griffiths-Jones S, Saini HK, van Dongen S
and Enright AJ: miRBase: Tools for microRNA genomics. Nucleic Acids
Res. 36(Database issue): D154–D158. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Wang C, Lu S, Jiang J, Jia X, Dong X and
Bu P: Hsa-microRNA-101 suppresses migration and invasion by
targeting Rac1 in thyroid cancer cells. Oncol Lett. 8:1815–1821.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Nikiforova MN, Tseng GC, Steward D, Diorio
D and Nikiforov YE: MicroRNA expression profiling of thyroid
tumors: Biological significance and diagnostic utility. J Clin
Endocrinol Metab. 93:1600–1608. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Zhu YZ, Zheng K, Zhang HH, Chen L, Wu KL,
Ren CH, Wang ZC, Kong LJ, Ruan WH and Chen XJ: Expression of
microRNA-155 in papillary thyroid carcinoma and its clinical
significance. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 36:1364–1368. 2016.(In
Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Xu J, Zhang D, Niu Q, Nan Y, Shi C, Zhao H
and Liang X: Value of distinguishing differentiated thyroid
carcinoma by miRNA. Oncol Lett. 12:79–82. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Engelhardt S: Small RNA biomarkers come of
age. J Am Coll Cardiol. 60:300–303. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Markou A, Sourvinou I, Vorkas PA, Yousef
GM and Lianidou E: Clinical evaluation of microRNA expression
profiling in non small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 81:388–396.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Eichelser C, Flesch-Janys D, Chang-Claude
J, Pantel K and Schwarzenbach H: Deregulated serum concentrations
of circulating cell-free microRNAs miR-17, miR-34a, miR-155, and
miR-373 in human breast cancer development and progression. Clin
Chem. 59:1489–1496. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Menendez P, Villarejo P, Padilla D,
Menéndez JM and Montes JA: Diagnostic and prognostic significance
of serum microRNAs in colorectal cancer. J Surg Oncol. 107:217–220.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Ng EK, Chong WW, Jin H, Lam EK, Shin VY,
Yu J, Poon TC, Ng SS and Sung JJ: Differential expression of
microRNAs in plasma of patients with colorectal cancer: A potential
marker for colorectal cancer screening. Gut. 58:1375–1381. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Yip L, Kelly L, Shuai Y, Armstrong MJ,
Nikiforov YE, Carty SE and Nikiforova MN: MicroRNA signature
distinguishes the degree of aggressiveness of papillary thyroid
carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol. 18:2035–2041. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Chou CK, Yang KD, Chou FF, Huang CC, Lan
YW, Lee YF, Kang HY and Liu RT: Prognostic implications of miR-146b
expression and its functional role in papillary thyroid carcinoma.
J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 98:E196–E205. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Sun M, Fang S, Li W, Li C, Wang L, Wang F
and Wang Y: Associations of miR-146a and miR-146b expression and
clinical characteristics in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Cancer
Biomark. 15:33–40. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Geraldo MV, Yamashita AS and Kimura ET:
MicroRNA miR-146b-5p regulates signal transduction of TGF-β by
repressing SMAD4 in thyroid cancer. Oncogene. 31:1910–1922. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Lima CR, Geraldo MV, Fuziwara CS, Kimura
ET and Santos MF: MiRNA-146b-5p upregulates migration and invasion
of different papillary thyroid carcinoma cells. BMC Cancer.
16:1082016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Cong D, He M, Chen S, Liu X, Liu X and Sun
H: Expression profiles of pivotal microRNAs and targets in thyroid
papillary carcinoma: an analysis of The Cancer Genome Atlas. Onco
Targets Ther. 8:2271–2277. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Lee JC, Zhao JT, Gundara J, Serpell J,
Bach LA and Sidhu S: Papillary thyroid cancer-derived exosomes
contain miRNA-146b and miRNA-222. J Surg Res. 196:39–48. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Chen YT, Kitabayashi N, Zhou XK, Fahey TJ
III and Scognamiglio T: MicroRNA analysis as a potential diagnostic
tool for papillary thyroid carcinoma. Mod Pathol. 21:1139–1146.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Diao Y, Fu H and Wang Q: MiR-221
exacerbate cell proliferation and invasion by targeting TIMP3 in
papillary thyroid carcinoma. Am J Ther. Apr 12–2016.(Epub ahead of
print).
|
|
66
|
Zhang L, Wang T, Wright AF, Suri M,
Schwartz CE, Stevenson RE and Valle D: A microdeletion in Xp11.3
accounts for co-segregation of retinitis pigmentosa and mental
retardation in a large kindred. Am J Med Genet A. 140:349–357.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Yang QE, Racicot KE, Kaucher AV, Oatley MJ
and Oatley JM: MicroRNAs 221 and 222 regulate the undifferentiated
state in mammalian male germ cells. Development. 140:280–290. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Martins CS, Camargo RC, Saggioro FP, Neder
L, Machado HR, Moreira AC and de Castro M: P27/CDKN1B translational
regulators in pituitary tumorigenesis. Horm Metab Res. 48:840–846.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Castagnino P, Kothapalli D, Hawthorne EA,
Liu SL, Xu T, Rao S, Yung Y and Assoian RK: miR-221/222 compensates
for Skp2-mediated p27 degradation and is a primary target of cell
cycle regulation by prostacyclin and cAMP. PLoS One. 8:e561402013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Kothapalli D, Castagnino P, Rader DJ,
Phillips MC, Lund-Katz S and Assoian RK: Apolipoprotein E-mediated
cell cycle arrest linked to p27 and the Cox2-dependent repression
of miR221/222. Atherosclerosis. 227:65–71. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Sun K, Wang W, Lei ST, Wu CT and Li GX:
MicroRNA-221 promotes colon carcinoma cell proliferation in vitro
by inhibiting CDKN1C/p57 expression. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao.
31:1885–1889. 2011.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Visone R, Russo L, Pallante P, de Martino
I, Ferraro A, Leone V, Borbone E, Petrocca F, Alder H, Croce CM and
Fusco A: MicroRNAs (miR)-221 and miR-222, both overexpressed in
human thyroid papillary carcinomas, regulate p27Kip1 protein levels
and cell cycle. Endocr Relat Cancer. 14:791–798. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|