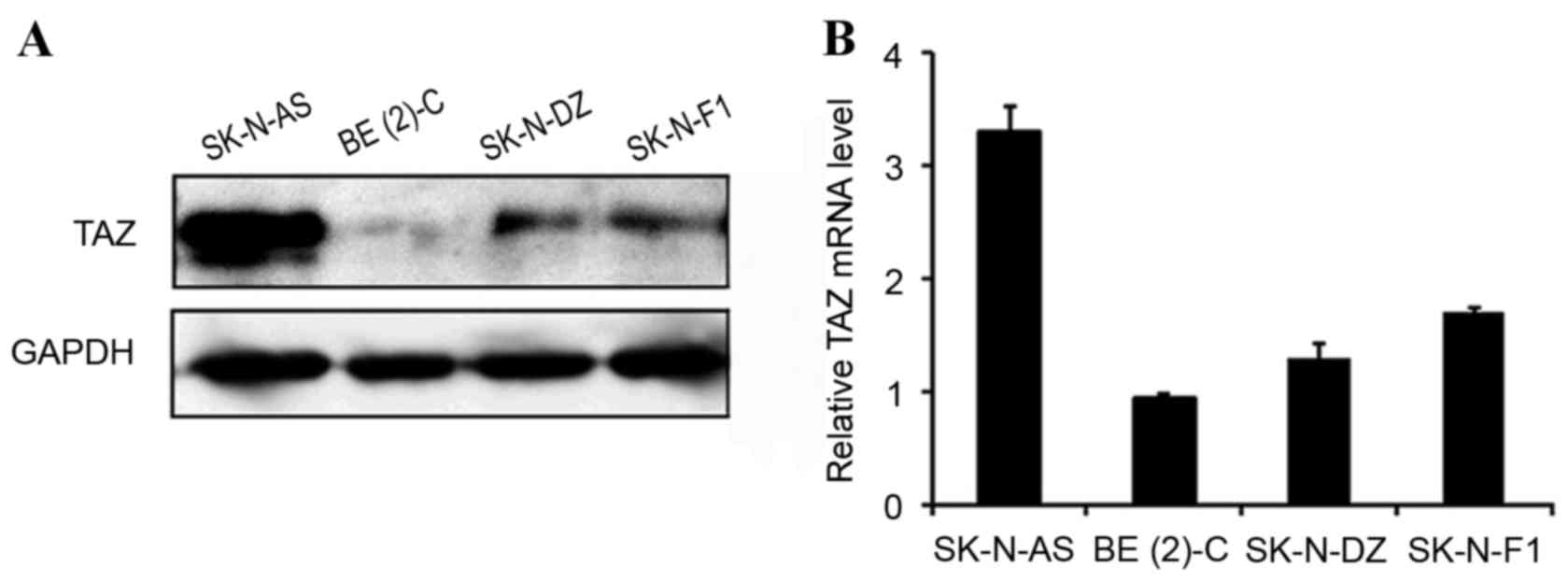
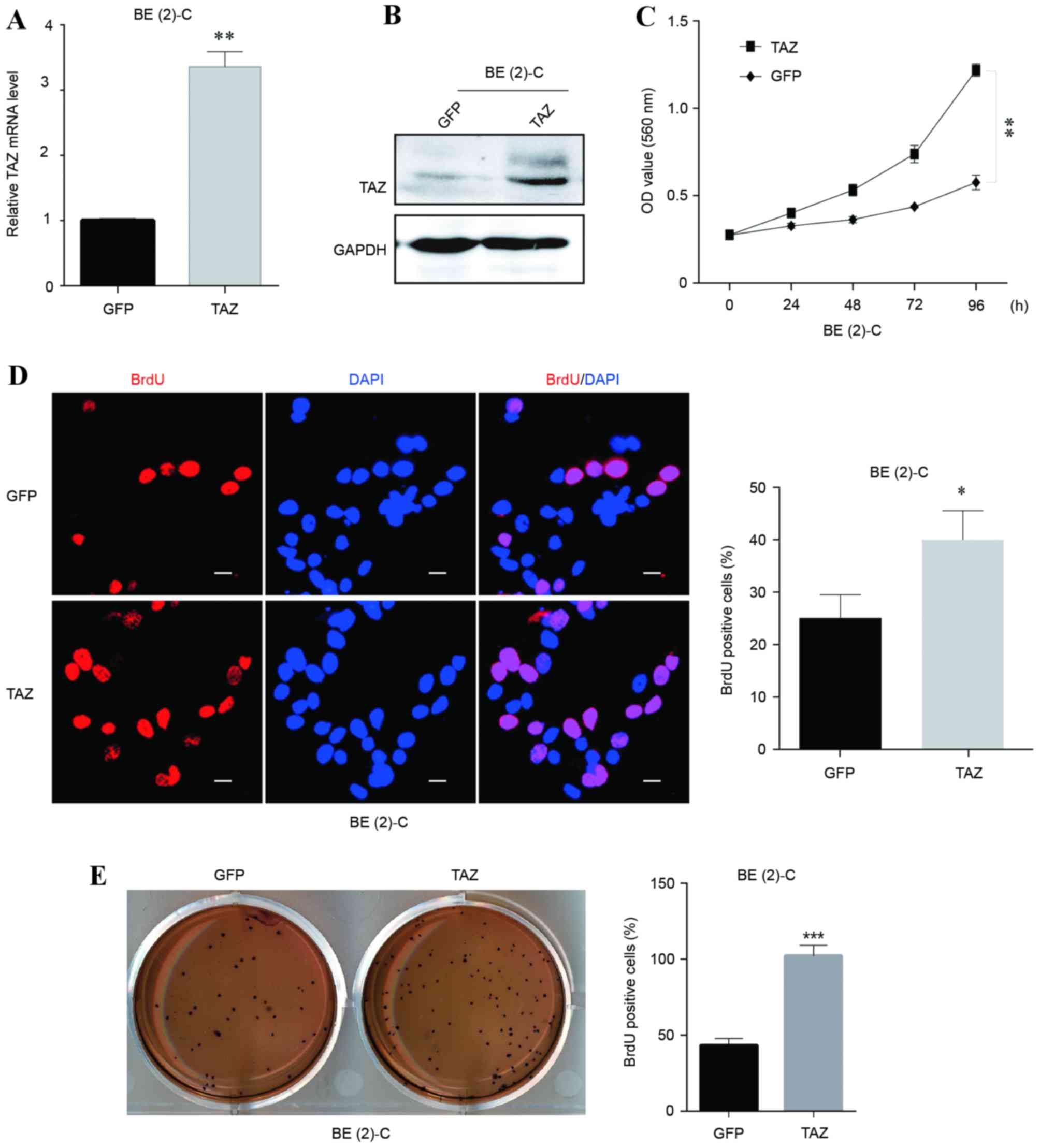
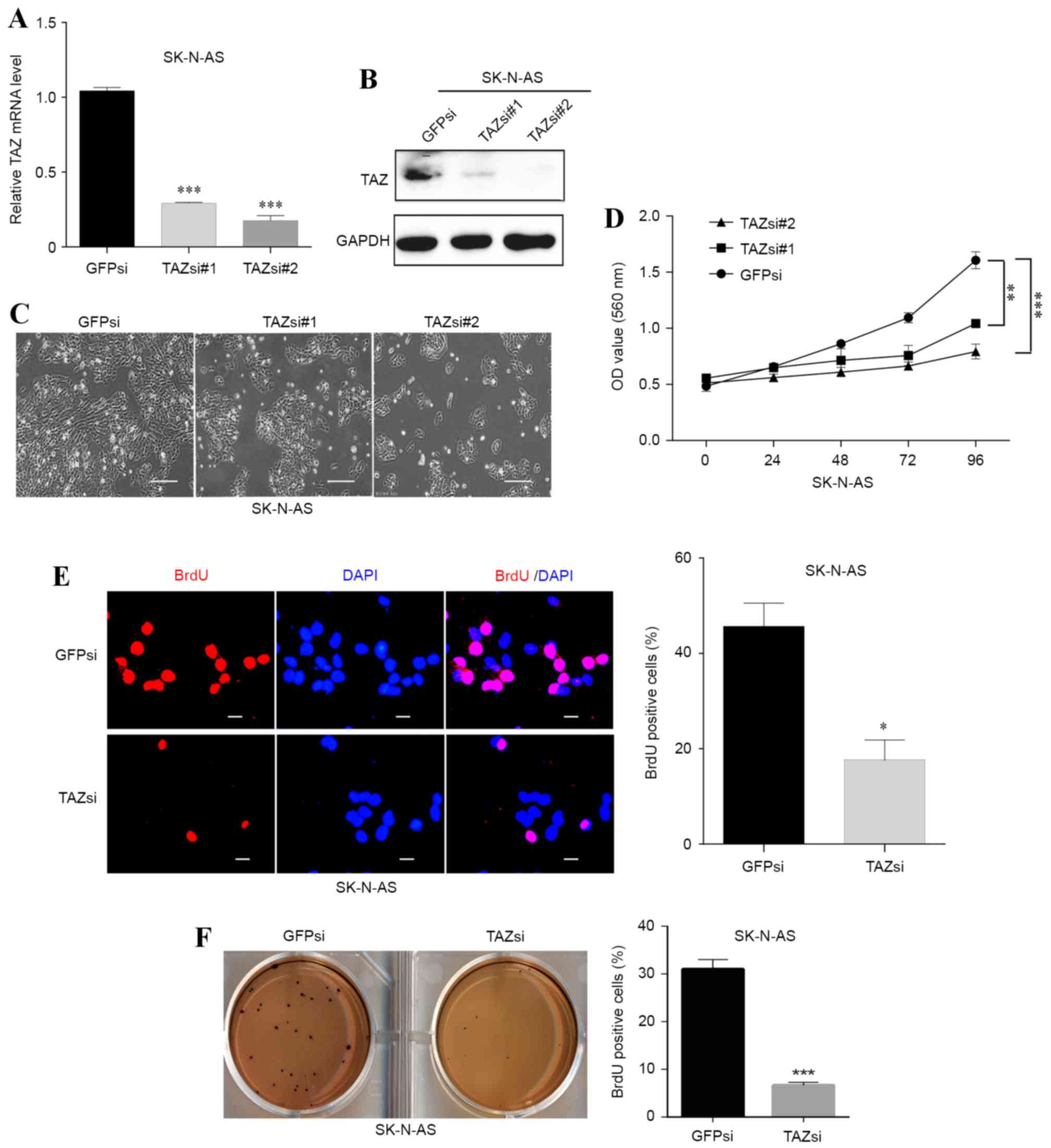
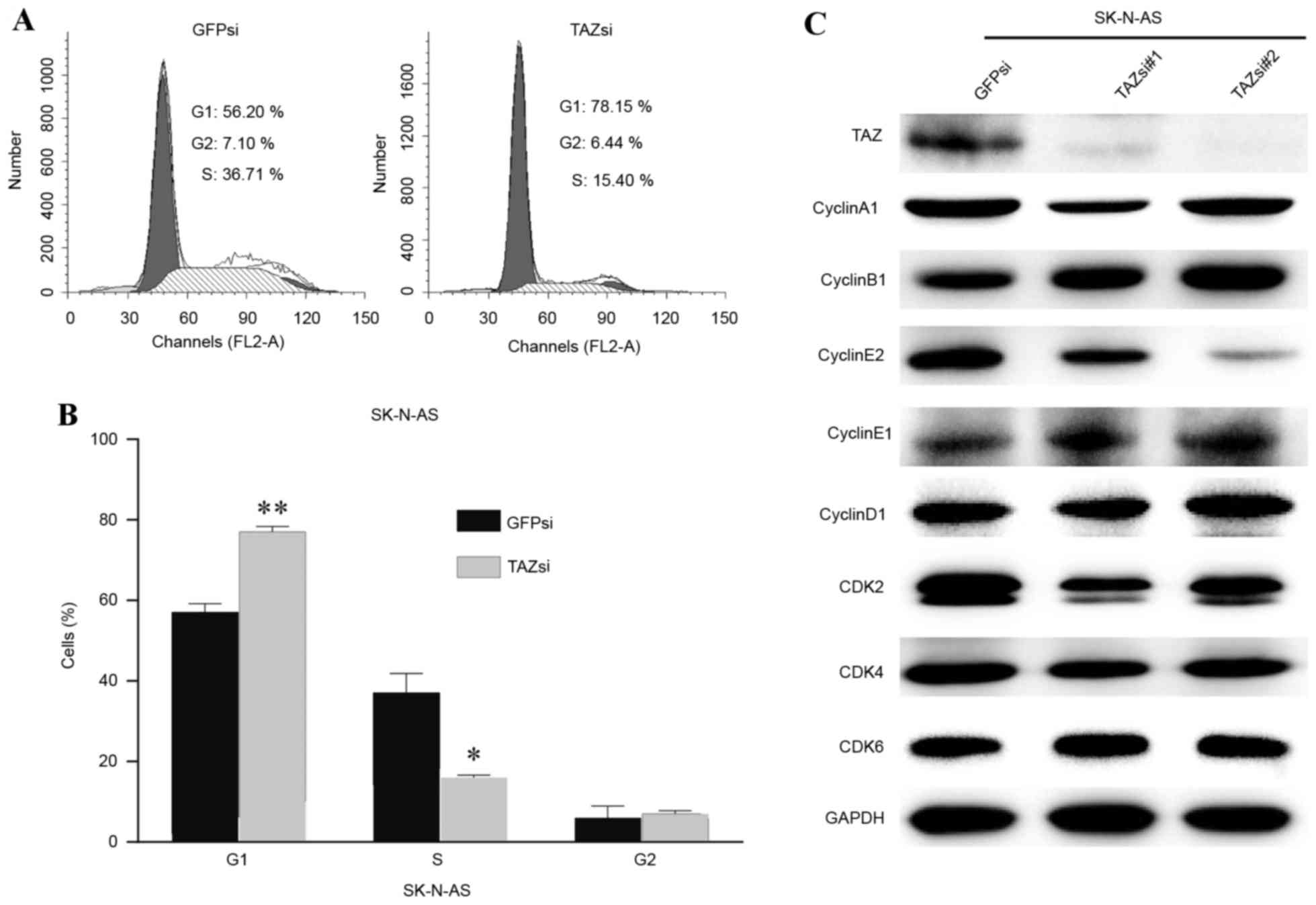
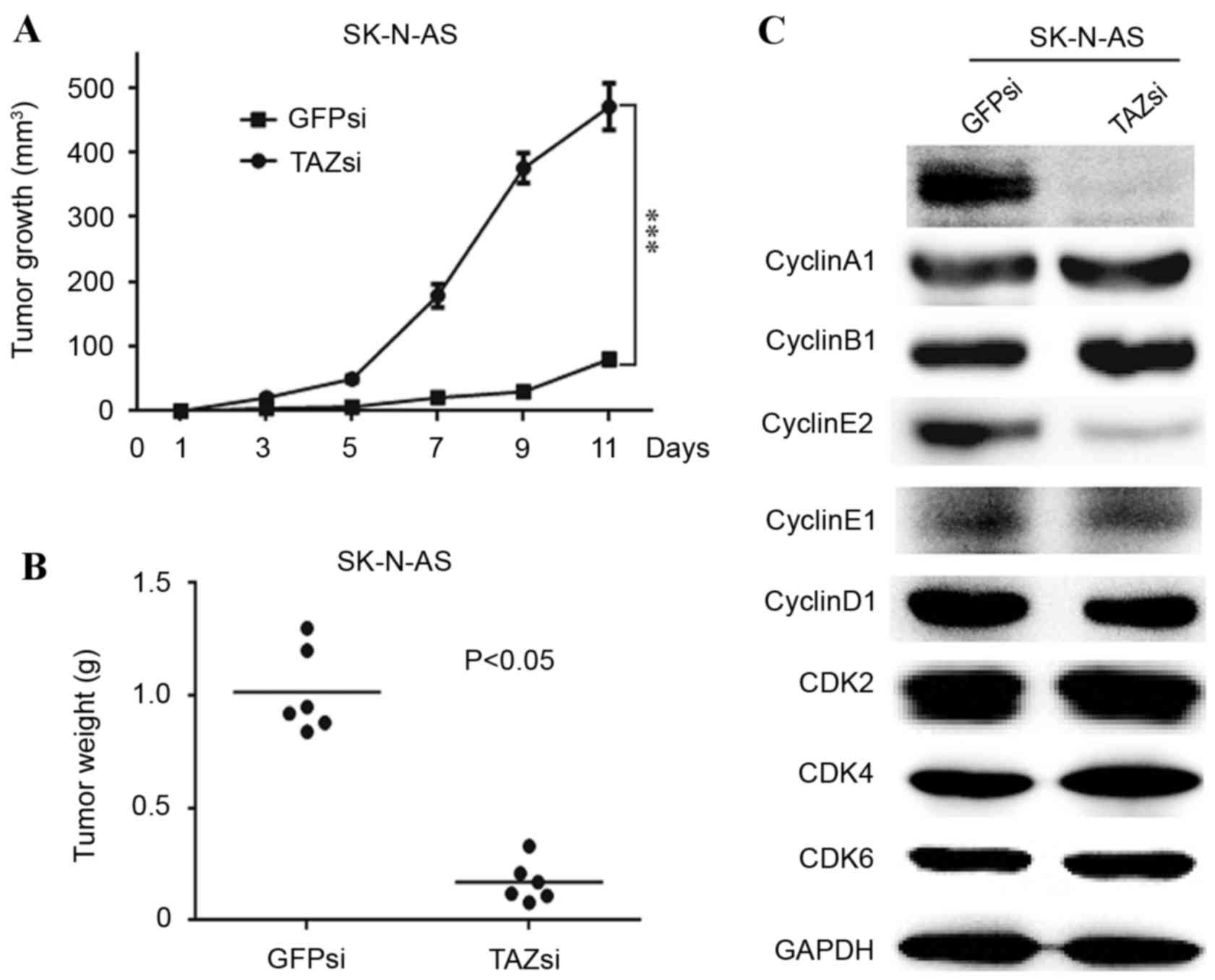
|
1
|
Brodeur GM: Neuroblastoma: Biological
insights into a clinical enigma. Nat Rev Cancer. 3:203–216. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Shimada H, Ambros IM, Dehner LP, Hata J,
Joshi VV, Roald B, Stram DO, Gerbing RB, Lukens JN, Matthay KK and
Castleberry RP: The international neuroblastoma pathology
classification (the Shimada system). Cancer. 86:364–372. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Cohn SL, Pearson AD, London WB, Monclair
T, Ambros PF, Brodeur GM, Faldum A, Hero B, Iehara T, Machin D, et
al: The International neuroblastoma risk group (INRG)
classification system: An INRG Task Force report. J Clin Oncol.
27:289–297. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Modak S and Cheung NK: Neuroblastoma:
Therapeutic strategies for a clinical enigma. Cancer Treat Rev.
36:307–317. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Maris JM: Recent advances in
neuroblastoma. N Engl J Med. 362:2202–2211. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cui H, Schroering A and Ding HF: p53
mediates DNA damaging drug-induced apoptosis through a
caspase-9-dependent pathway in SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells. Mol
Cancer Ther. 1:679–686. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Cui CB, Cooper LF, Yang X, Karsenty G and
Aukhil I: Transcriptional coactivation of bone-specific
transcription factor Cbfa1 by TAZ. Mol Cell Biol. 23:1004–1013.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Cordenonsi M, Zanconato F, Azzolin L,
Forcato M, Rosato A, Frasson C, Inui M, Montagner M, Parenti AR,
Poletti A, et al: The Hippo transducer TAZ confers cancer stem
cell-related traits on breast cancer cells. Cell. 147:759–772.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang M, Liu Y, Zou J, Yang R, Xuan F, Wang
Y, Gao N and Cui H: Transcriptional co-activator TAZ sustains
proliferation and tumorigenicity of neuroblastoma by targeting CTGF
and PDGF-β. Oncotarget. 6:9517–9530. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hiemer SE, Zhang L, Kartha VK, Packer TS,
Almershed M, Noonan V, Kukuruzinska M, Bais MV, Monti S and Varelas
X: A YAP/TAZ-regulated molecular signature is associated with oral
squamous cell carcinoma. Mol Cancer Res. 13:957–968. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hiemer SE, Szymaniak AD and Varelas X: The
transcriptional regulators TAZ and YAP direct transforming growth
factor β-induced tumorigenic phenotypes in breast cancer cells. J
Biol Chem. 289:13461–13474. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Xu W, Wei Y, Wu S, Wang Y, Wang Z, Sun Y,
Cheng SY and Wu J: Up-regulation of the Hippo pathway effector TAZ
renders lung adenocarcinoma cells harboring EGFR-T790M mutation
resistant to gefitinib. Cell Biosci. 5:72015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tan G, Cao X, Dai Q, Zhang B, Huang J,
Xiong S, Zhang Yy, Chen W, Yang J and Li H: A novel role for
microRNA-129-5p in inhibiting ovarian cancer cell proliferation and
survival via direct suppression of transcriptional co-activators
YAP and TAZ. Oncotarget. 6:8676–8686. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang L, Shi S, Guo Z, Zhang X, Han S, Yang
A, Wen W and Zhu Q: Overexpression of YAP and TAZ is an independent
predictor of prognosis in colorectal cancer and related to the
proliferation and metastasis of colon cancer cells. PLoS One.
8:e655392013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lei QY, Zhang H, Zhao B, Zha ZY, Bai F,
Pei XH, Zhao S, Xiong Y and Guan KL: TAZ promotes cell
proliferation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition and is
inhibited by the hippo pathway. Mol Cell Biol. 28:2426–2436. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lai D, Ho KC, Hao Y and Yang X: Taxol
resistance in breast cancer cells is mediated by the hippo pathway
component TAZ and its downstream transcriptional targets Cyr61 and
CTGF. Cancer Res. 71:2728–2738. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chan SW, Lim CJ, Loo LS, Chong YF, Huang C
and Hong W: TEADs mediate nuclear retention of TAZ to promote
oncogenic transformation. J Biol Chem. 284:14347–14358. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang H, Liu CY, Zha ZY, Zhao B, Yao J,
Zhao S, Xiong Y, Lei QY and Guan KL: TEAD transcription factors
mediate the function of TAZ in cell growth and
epithelial-mesenchymal transitio. J Biol Chem. 284:13355–13362.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhao D, Zhi X, Zhou Z and Chen C: TAZ
antagonizes the WWP1-mediated KLF5 degradation and promotes breast
cell proliferation and tumorigenesis. Carcinogenesis. 33:59–67.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yuen HF, McCrudden CM, Huang YH, Tham JM,
Zhang X, Zeng Q, Zhang SD and Hong W: TAZ expression as a
prognostic indicator in colorectal cancer. PLoS One. 8:e542112013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lin CW, Chang YL, Chang YC, Lin JC, Chen
CC, Pan SH, Wu CT, Chen HY, Yang SC, Hong TM and Yang PC:
MicroRNA-135b promotes lung cancer metastasis by regulating
multiple targets in the Hippo pathway and LZTS1. Nat Commun.
4:18772013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|