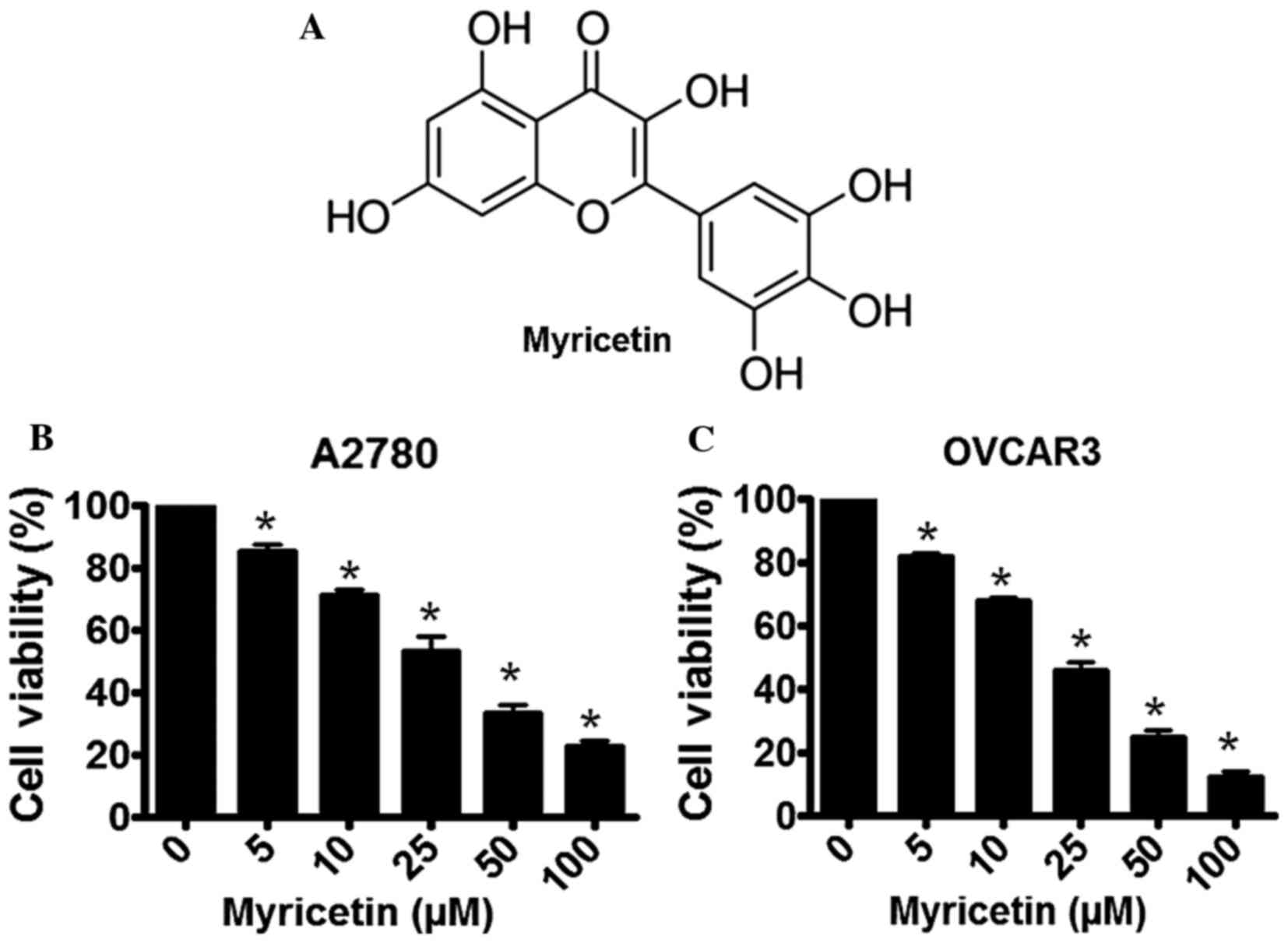
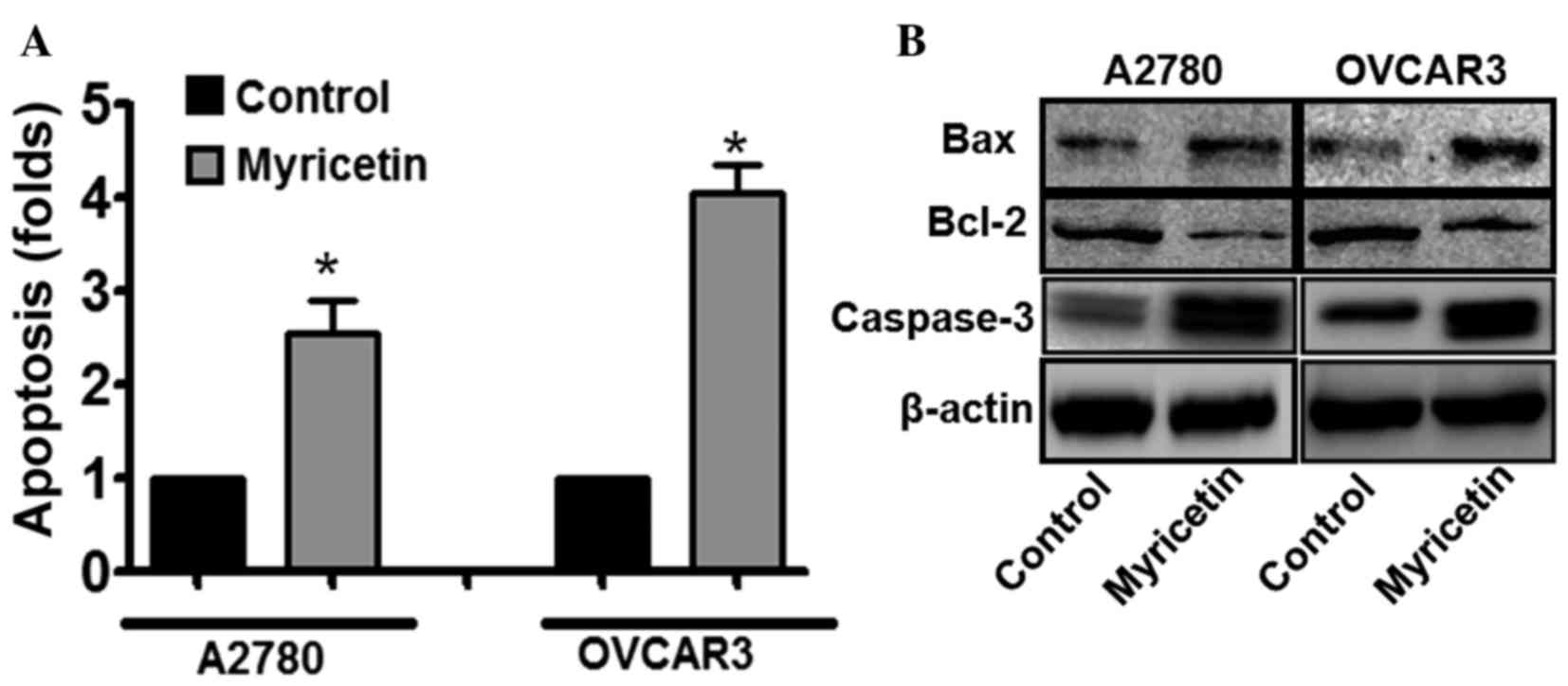
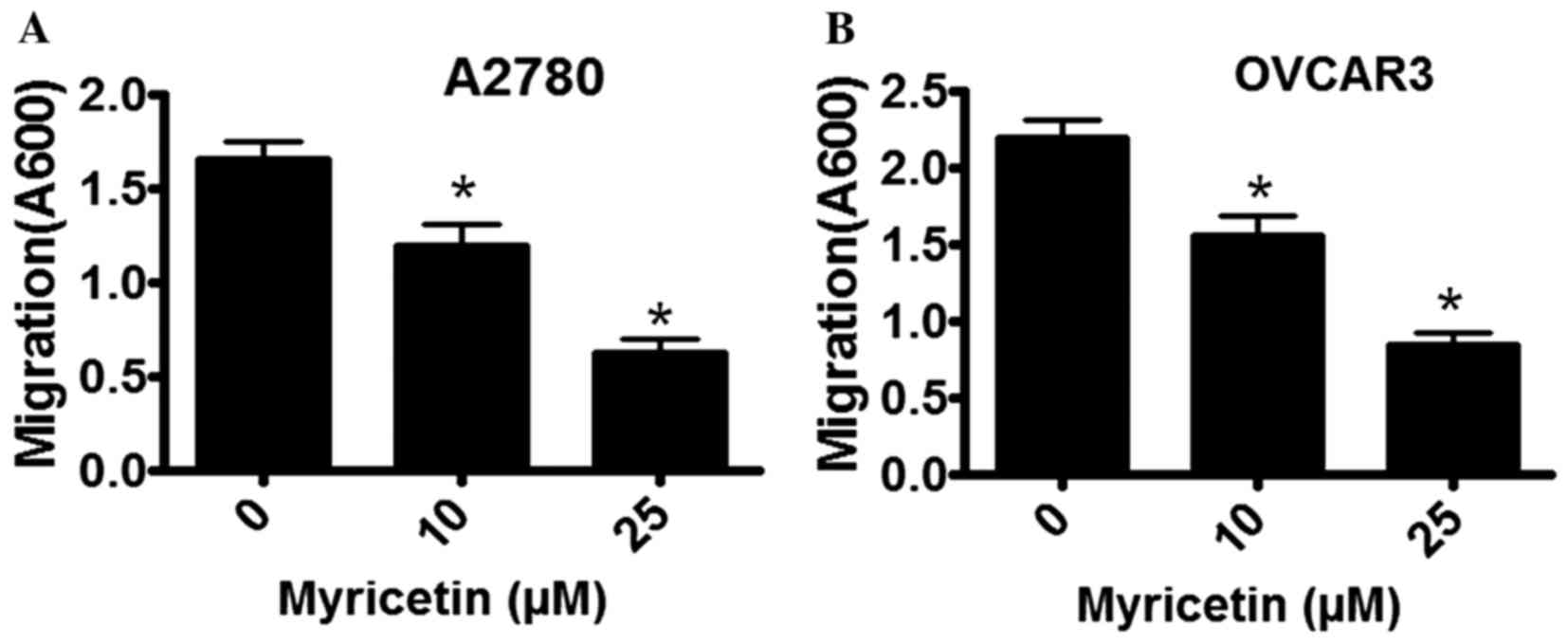
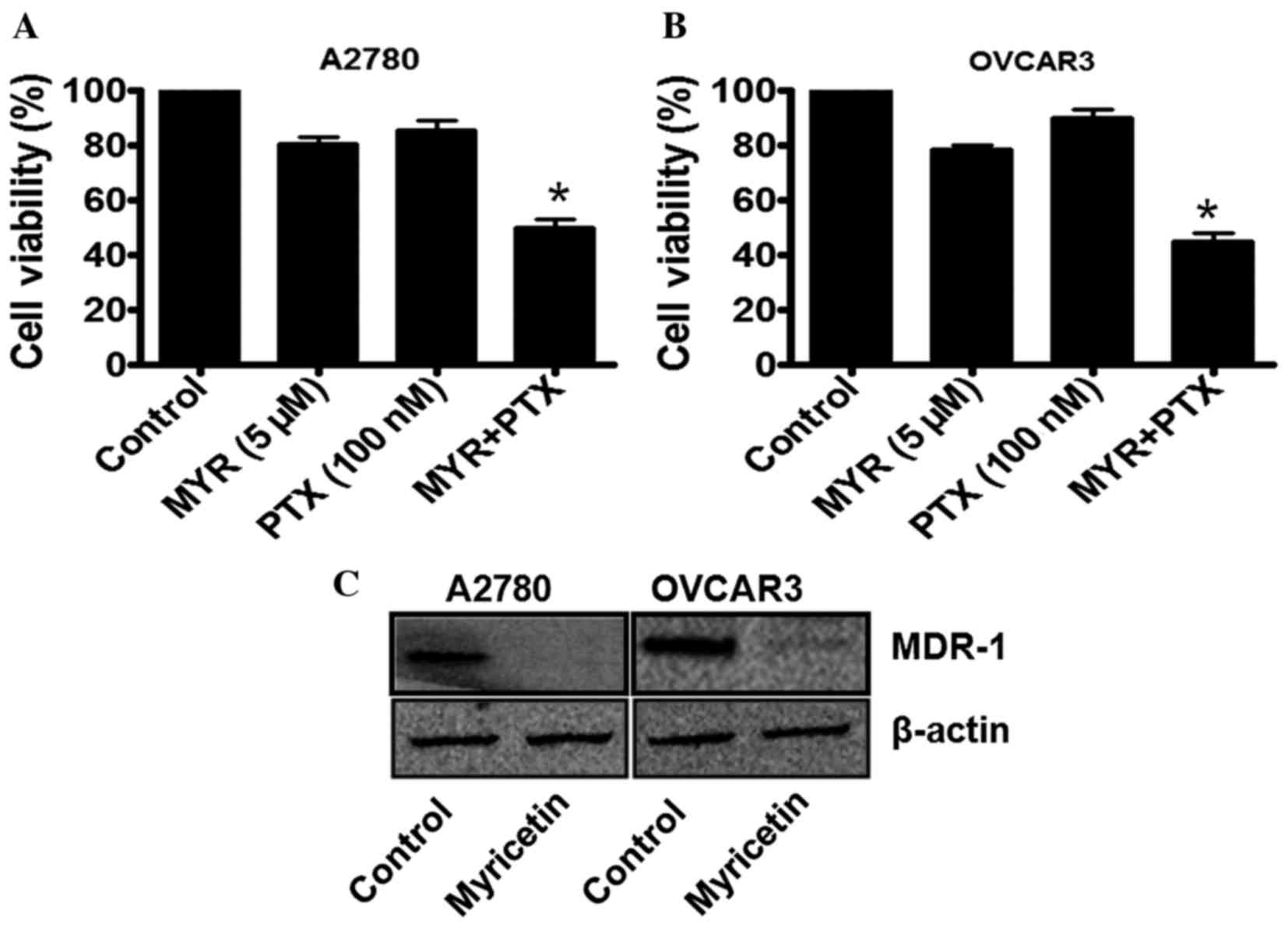
|
1
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J,
Murray T and Thun MJ: Cancer statistics, 2008. CA Cancer J Clin.
58:71–96. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Vecchione A, Belletti B, Lovat F, Volinia
S, Chiappetta G, Giglio S, Sonego M, Cirombella R, Onesti EC,
Pellegrini P, et al: A microRNA signature defines chemoresistance
in ovarian cancer through modulation of angiogenesis. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 110:pp. 9845–9850. 2013; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Jayson GC, Kohn EC, Kitchener HC and
Ledermann JA: Ovarian cancer. Lancet. 384:1376–1388. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Nam MS, Jung DB, Seo KH, Kim BI, Kim JH,
Kim JH, Kim B, Baek NI and Kim SH: Apoptotic effect of sanggenol L
via caspase activation and inhibition of NF-kB signaling in ovarian
cancer cells. Phytother Res. 30:90–96. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ivanov S, Ivanov S and Khadzhiolov N:
Ovarian tumours-accuracy of frozen section diagnosis. Akush Ginekol
(Sofiia). 44:11–13. 2005.(In Bulgarian).
|
|
6
|
Saika K and Sobue T: Cancer statistics in
the world. Gan To Kagaku Ryoho. 40:2475–2480. 2013.(In Japanese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Edwards SJ, Barton S, Thurgar E and Trevor
N: Topotecan, pegylated liposomal doxorubicin hydrochloride,
paclitaxel, trabectedin and gemcitabine for advanced recurrent or
refractory ovarian cancer: A systematic review and economic
evaluation. Health Technol Assess. 19:1–480. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Bookman MA, Brady MF, McGuire WP, Harper
PG, Alberts DS, Friedlander M, Colombo N, Fowler JM, Argenta PA, de
Geest K, et al: Evaluation of new platinum-based treatment regimens
in advanced-stage ovarian cancer: A Phase III Trial of the
gynecologic cancer intergroup. J Clin Oncol. 27:1419–1425. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sak K: Site-specific anticancer effects of
dietary flavonoid quercetin. Nutr Cancer. 66:177–193. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sak K: Cytotoxicity of dietary flavonoids
on different human cancer types. Pharmacogn Rev. 8:122–146. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gupta S, Afaq F and Mukhtar H: Selective
growth-inhibitory, cell-cycle deregulatory and apoptotic response
of apigenin in normal versus human prostate carcinoma cells.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 287:914–920. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Devi KP, Rajavel T, Habtemariam S, Nabavi
SF and Nabavi SM: Molecular mechanisms underlying anticancer
effects of myricetin. Life Sci. 142:19–25. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Harnly JM, Doherty RF, Beecher GR, Holden
JM, Haytowitz DB, Bhagwat S and Gebhardt S: Flavonoid content of
U.S. fruits, vegetables, and nuts. J Agric Food Chem. 54:9966–9977.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ong CK, Nee S, Rambaut A, Bernard HU and
Harvey PH: Elucidating the population histories and transmission
dynamics of papillomaviruses using phylogenetic trees. J Mol Evol.
44:199–206. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Boam T: Anti-androgenic effects of
flavonols in prostate cancer. Ecancermedicalscience.
9:5852015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Feng J, Chen X, Wang Y, Du Y, Sun Q, Zang
W and Zhao G: Myricetin inhibits proliferation and induces
apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in gastric cancer cells. Mol Cell
Biochem. 408:163–170. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Iyer SC, Gopal A and Halagowder D:
Myricetin induces apoptosis by inhibiting P21 activated kinase 1
(PAK1) signaling cascade in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Cell
Biochem. 407:223–237. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Maggioni D, Nicolini G, Rigolio R, Biffi
L, Pignataro L, Gaini R and Garavello W: Myricetin and naringenin
inhibit human squamous cell carcinoma proliferation and migration
in vitro. Nutr Cancer. 66:1257–1267. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Huang H, Chen AY, Ye X, Li B, Rojanasakul
Y, Rankin GO and Chen YC: Myricetin inhibits proliferation of
cisplatin-resistant cancer cells through a p53-dependent apoptotic
pathway. Int J Oncol. 47:1494–1502. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yi JL, Shi S, Shen YL, Wang L, Chen HY,
Zhu J and Ding Y: Myricetin and methyl eugenol combination enhances
the anticancer activity, cell cycle arrest and apoptosis induction
of cis-platin against HeLa cervical cancer cell lines. Int J Clin
Exp Pathol. 8:1116–1127. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Balint K, Xiao M, Pinnix CC, Soma A, Veres
I, Juhasz I, Brown EJ, Capobianco AJ, Herlyn M and Liu ZJ:
Activation of Notch1 signaling is required for
beta-catenin-mediated human primary melanoma progression. J Clin
Invest. 115:3166–3176. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tavassoli FA and Norris HJ: Sertoli tumors
of the ovary. A clinicopathologic study of 28 cases with
ultrastructural observations. Cancer. 46:2281–2297. 1980.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Burton ER, Brady M, Homesley HD, Rose PG,
Nakamura T, Kesterson JP, Rotmensch J, Thigpen J Tate and Van Le L:
A phase II study of paclitaxel for the treatment of ovarian stromal
tumors: An NRG oncology/gynecologic oncology group study. Gynecol
Oncol. 140:48–52. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
McGuire WP, Hoskins WJ, Brady MF, Kucera
PR, Partridge EE, Look KY, Clarke-Pearson DL and Davidson M:
Cyclophosphamide and cisplatin compared with paclitaxel and
cisplatin in patients with stage III and stage IV ovarian cancer. N
Engl J Med. 334:1–6. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Szakács G, Paterson JK, Ludwig JA,
Booth-Genthe C and Gottesman MM: Targeting multidrug resistance in
cancer. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 5:219–234. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Alvarez M, Paull K, Monks A, Hose C, Lee
JS, Weinstein J, Grever M, Bates S and Fojo T: Generation of a drug
resistance profile by quantitation of mdr-1/P-glycoprotein in the
cell lines of the national cancer institute anticancer drug screen.
J Clin Invest. 95:2205–2214. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chen H, Hao J, Wang L and Li Y:
Coexpression of invasive markers (uPA, CD44) and multiple
drug-resistance proteins (MDR1, MRP2) is correlated with epithelial
ovarian cancer progression. Br J Cancer. 101:432–440. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang B, Li S, Meng X, Shang H and Guan Y:
Inhibition of mdr1 by G-quadruplex oligonucleotides and reversal of
paclitaxel resistance in human ovarian cancer cells. Tumour Biol.
36:6433–6443. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhang H, Wang J, Cai K, Jiang L, Zhou D,
Yang C, Chen J, Chen D and Dou J: Downregulation of gene MDR1 by
shRNA to reverse multidrug-resistance of ovarian cancer A2780
cells. J Cancer Res Ther. 8:226–231. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|