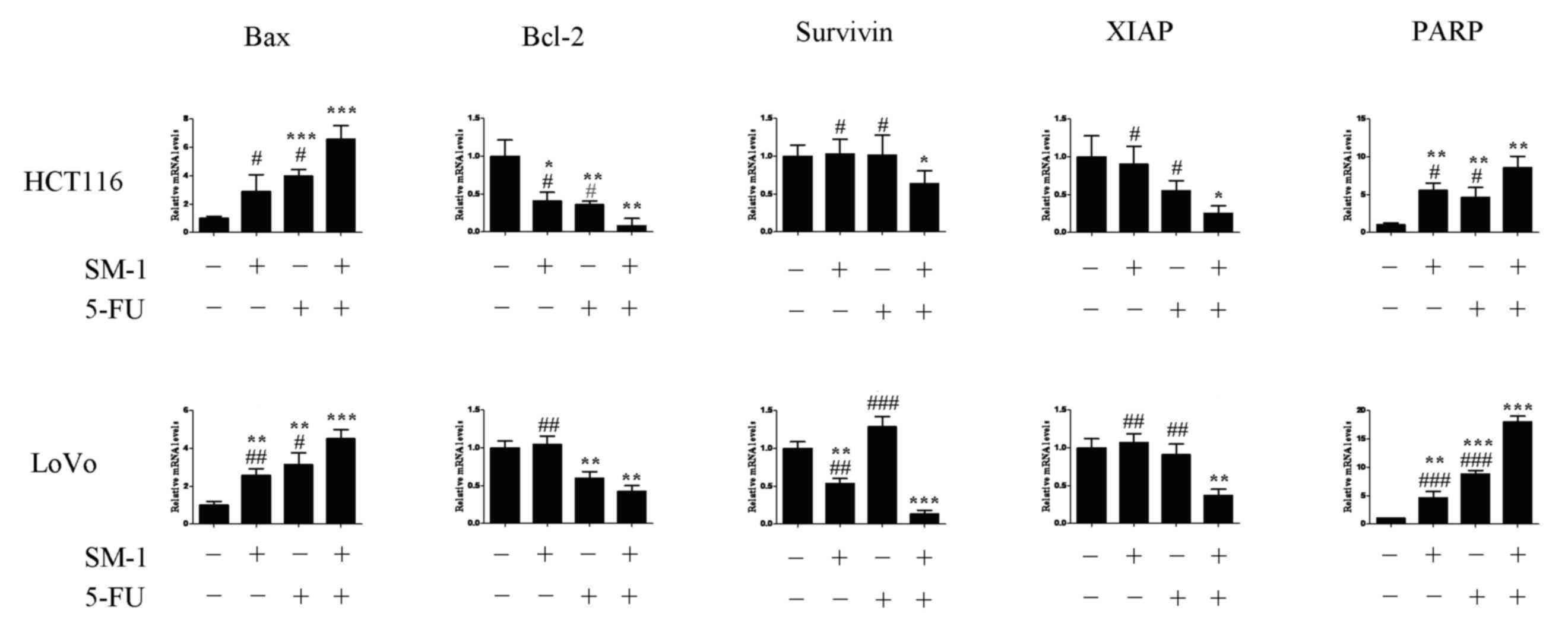
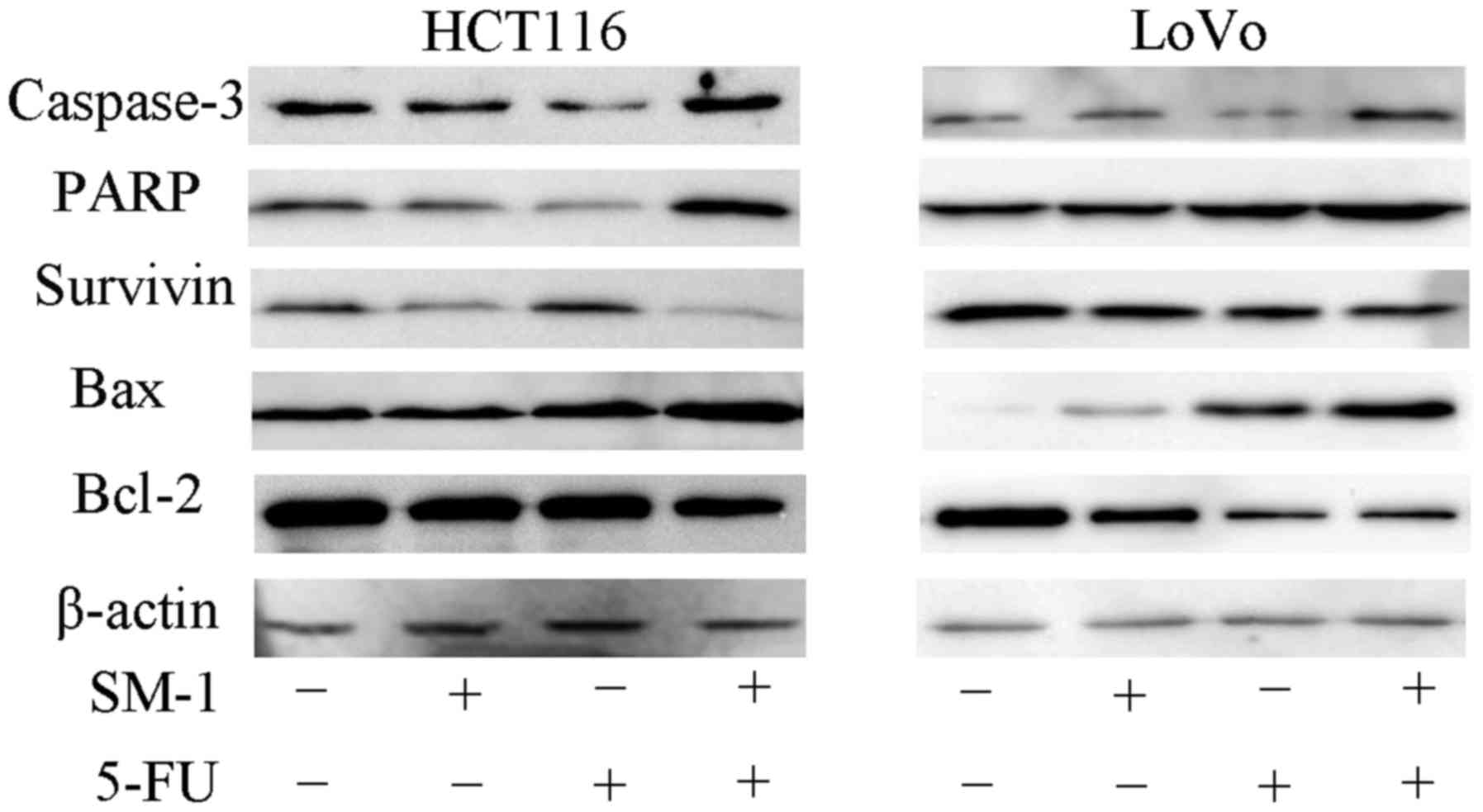
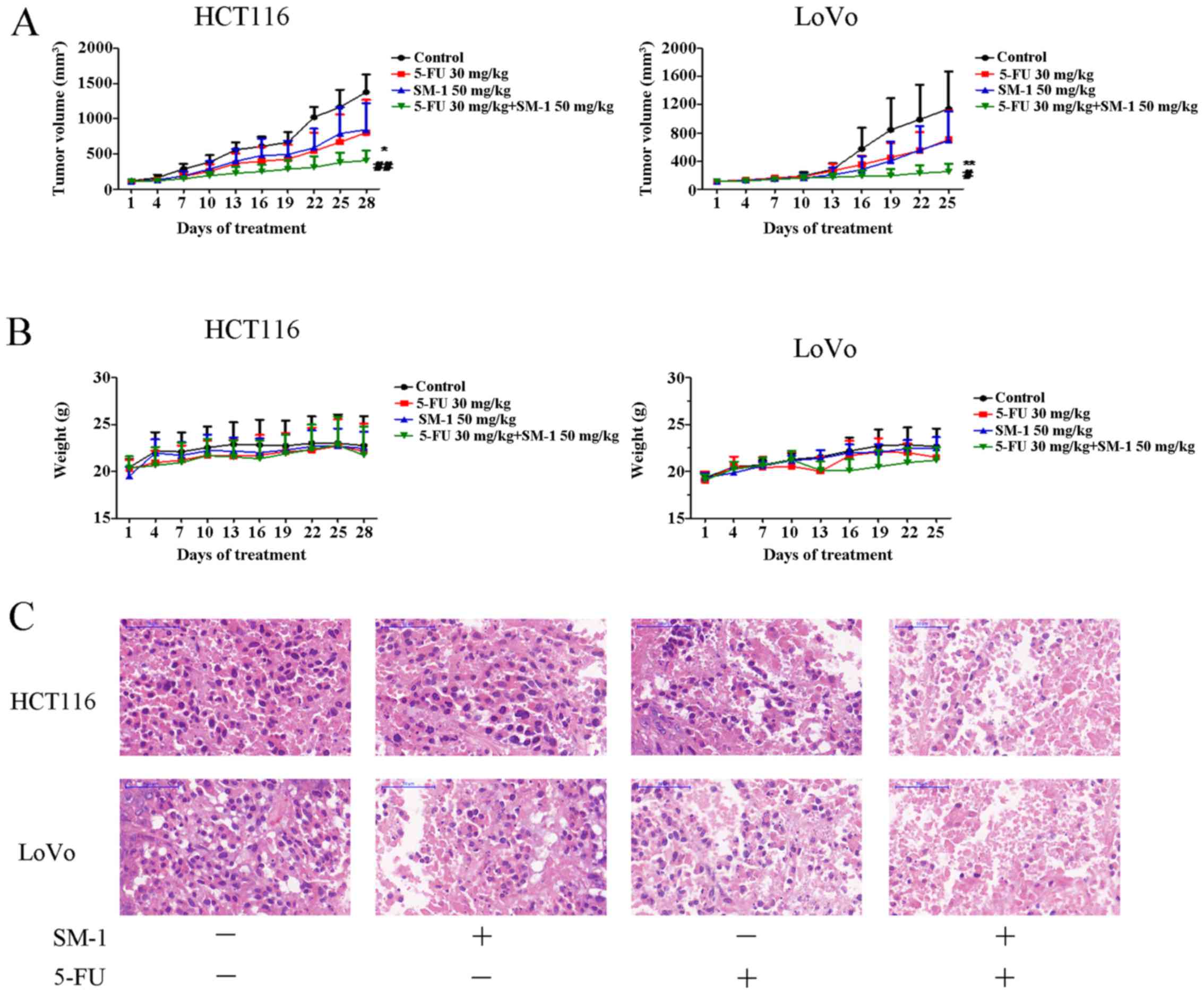
|
1
|
Siegel R, DeSantis C and Jemal A:
Colorectal cancer statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 64:104–117.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wolpin BM and Mayer RJ: Systemic treatment
of colorectal cancer. Gastroenterolog. 134:1296–1310. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Longley DB, Harkin DP and Johnston PG:
5-Fluorouracil: Mechanisms of action and clinical strategies. Nat
Rev Cancer. 3:330–338. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sobrero A, Guglielmi A, Grossi F, Puglisi
F and Aschele C: Mechanism of action of fluoropyrimidines:
Relevance to the new developments in colorectal cancer
chemotherapy. Semin Oncol. 27 5 Suppl 10:S72–S77. 2000.
|
|
5
|
Pardini B, Kumar R, Naccarati A, Novotny
J, Prasad RB, Forsti A, Hemminki K, Vodicka P and Bermejo J
Lorenzo: 5-Fluorouracil based chemotherapy for colorectal cancer
and MTHFR/MTRR genotypes. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 72:162–163. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Macdonald JS: Toxicity of 5-fluorouracil.
Oncology (Williston Park). 13 7 Suppl 3:S33–S34. 1999.
|
|
7
|
Lee SY and Oh SC: Advances of targeted
therapy in treatment of unresectable metastatic colorectal cancer.
Biomed Res Int. 2016:75902452016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Patel BB, Sengupta R, Qazi S, Vachhani H,
Yu Y, Rishi AK and Majumdar AP: Curcumin enhances the effects of
5-fluorouracil and oxaliplatin in mediating growth inhibition of
colon cancer cells by modulating EGFR and IGF-1R. Int J Cancer.
122:267–273. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lee MS, Helms TL, Feng N, Gay J, Chang QE,
Tian F, Wu JY, Toniatti C, Heffernan TP, Powis G, et al: Efficacy
of the combination of MEK and CDK4/6 inhibitors in vitro and in
vivo in KRAS mutant colorectal cancer models. Oncotarget.
7:39595–39608. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Pohl M and Schmiegel W: Colorectal
cancer-personalized, stage-adjusted tumour therapy. Dtsch Med
Wochenschr. 138:1790–1795. 2013.(In German). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kumar S: Caspase function in programmed
cell death. Cell Death Differ. 14:32–43. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Green DR: Apoptotic pathways: Paper wraps
stone blunts scissors. Cell. 102:1–4. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Peterson QP, Hsu DC, Goode DR, Novotny CJ,
Totten RK and Hergenrother PJ: Procaspase-3 activation as an
anti-cancer strategy: Structure-activity relationship of
procaspase-activating compound 1 (PAC-1) and its cellular
co-localization with caspase-3. J Med Chem. 52:5721–5731. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Putt KS, Chen GW, Pearson JM, Sandhorst
JS, Hoagland MS, Kwon JT, Hwang SK, Jin H, Churchwell MI, Cho MH,
et al: Small-molecule activation of procaspase-3 to caspase-3 as a
personalized anticancer strategy. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2:543–550.
2006.
|
|
15
|
Chen Y, Sun M, Ding J and Zhu Q: SM-1, a
novel PAC-1 derivative, activates procaspase-3 and causes cancer
cell apoptosis. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 78:643–654. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yuan HZ, Cao YT, Li LN, Wang SS, Yang DX,
Zhong XB, Tang SB and Yuan SJ: SM-1 induces apoptosis of BGC-823
cells by activating procaspase-3 and exerts antitumor effect.
Military Medical Sciences. 40:326–330. 2016.(In Chinese).
|
|
17
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Demchenko AP: The change of cellular
membranes on apoptosis: Fluorescence detection. Exp Oncol.
34:263–268. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sgonc R and Gruber J: Apoptosis detection:
An overview. Exp Gerontol. 33:525–533. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Bedner E, Li X, Gorczyca W, Melamed MR and
Darzynkiewicz Z: Analysis of apoptosis by laser scanning cytometry.
Cytometry. 35:181–195. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gustavsson B, Carlsson G, Machover D,
Petrelli N, Roth A, Schmoll HJ, Tveit KM and Gibson F: A review of
the evolution of systemic chemotherapy in the anagement of
colorectal cancer. Clin Colorectal Cancer. 14:1–101. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Meyerhardt JA and Mayer RJ: Systemic
therapy for colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med. 352:476–487. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Fakih MG: Metastatic colorectal cancer:
Current state and future directions. J Clin Oncol. 33:1809–1824.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yang SY, Sales KM, Fuller B, Seifalian AM
and Winslet MC: Apoptosis and colorectal cancer: Implications for
therapy. Trends Mol Med. 15:225–233. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Azrak RG, Cao S, Slocum HK, Tóth K,
Durrani FA, Yin MB, Pendyala L, Zhang W, McLeod HL and Rustum YM:
Terapeutic synergy between irinotecan and 5-fluorouracil against
human tumor xenografs. Clin Cancer Res. 10:1121–1129. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Riedl SJ and Shi Y: Molecular mechanisms
of caspase regulation during apoptosis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
5:897–907. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hengartner MO: The biochemistry of
apoptosis. Nature. 407:770–776. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|