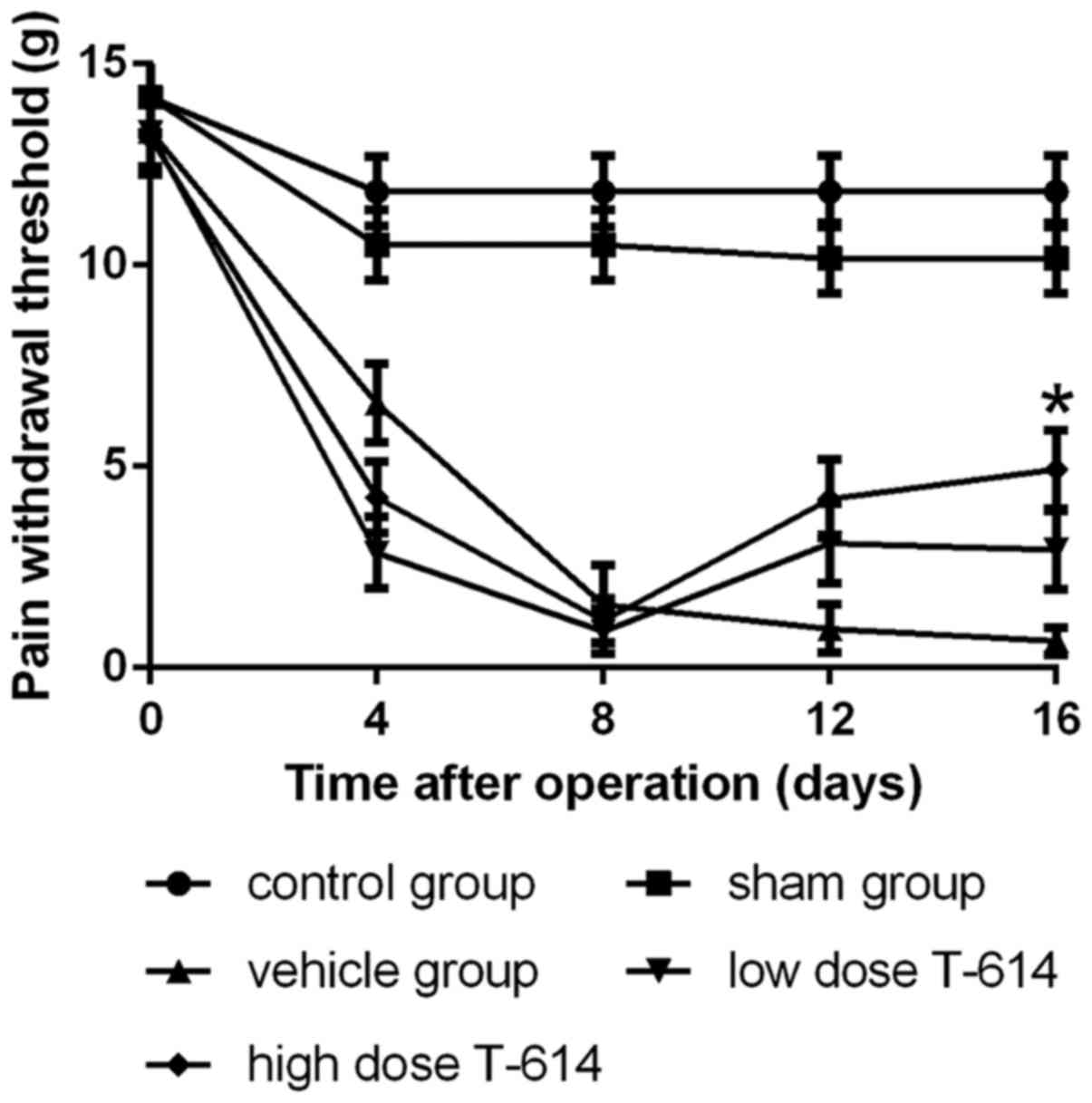
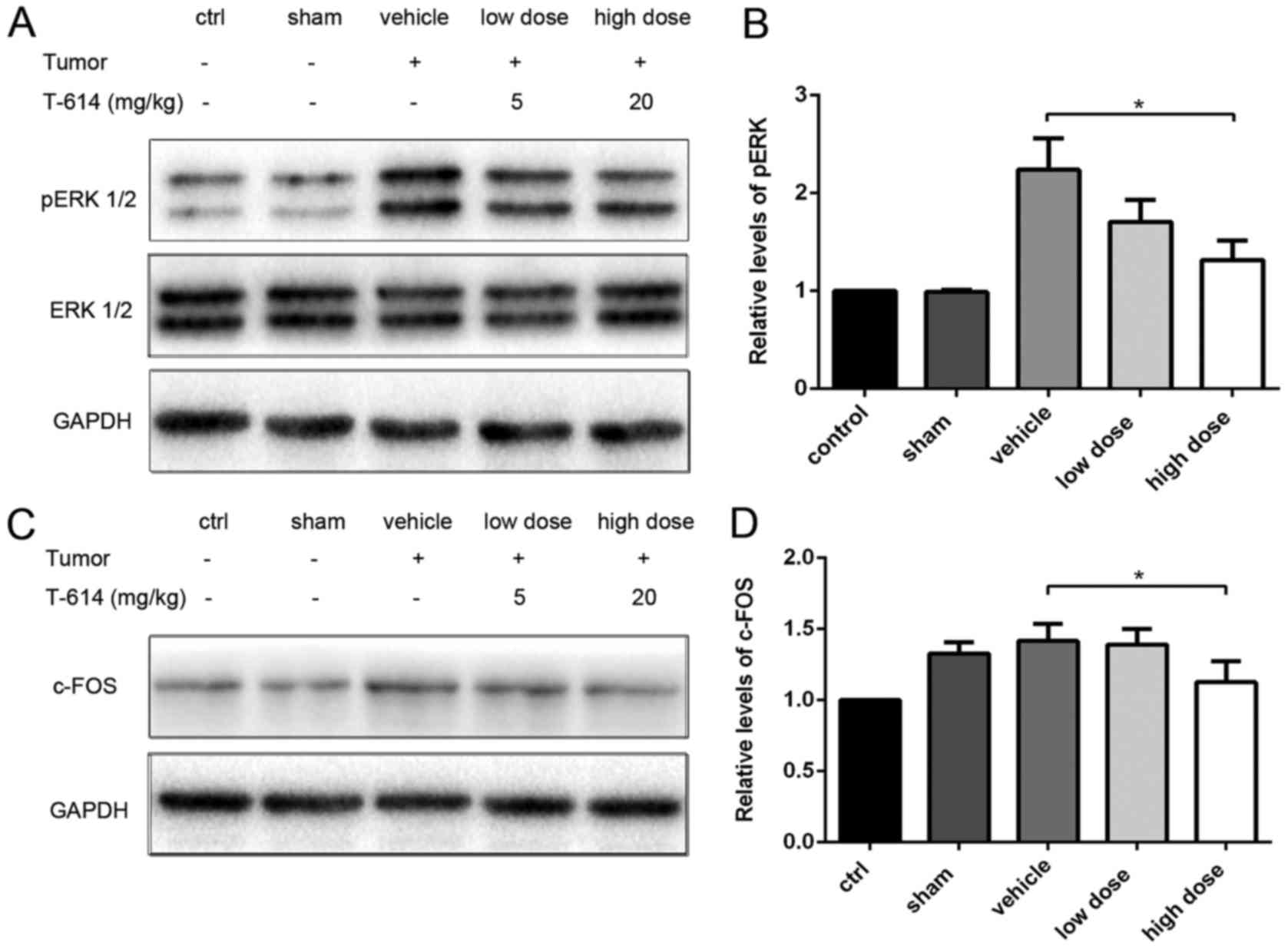
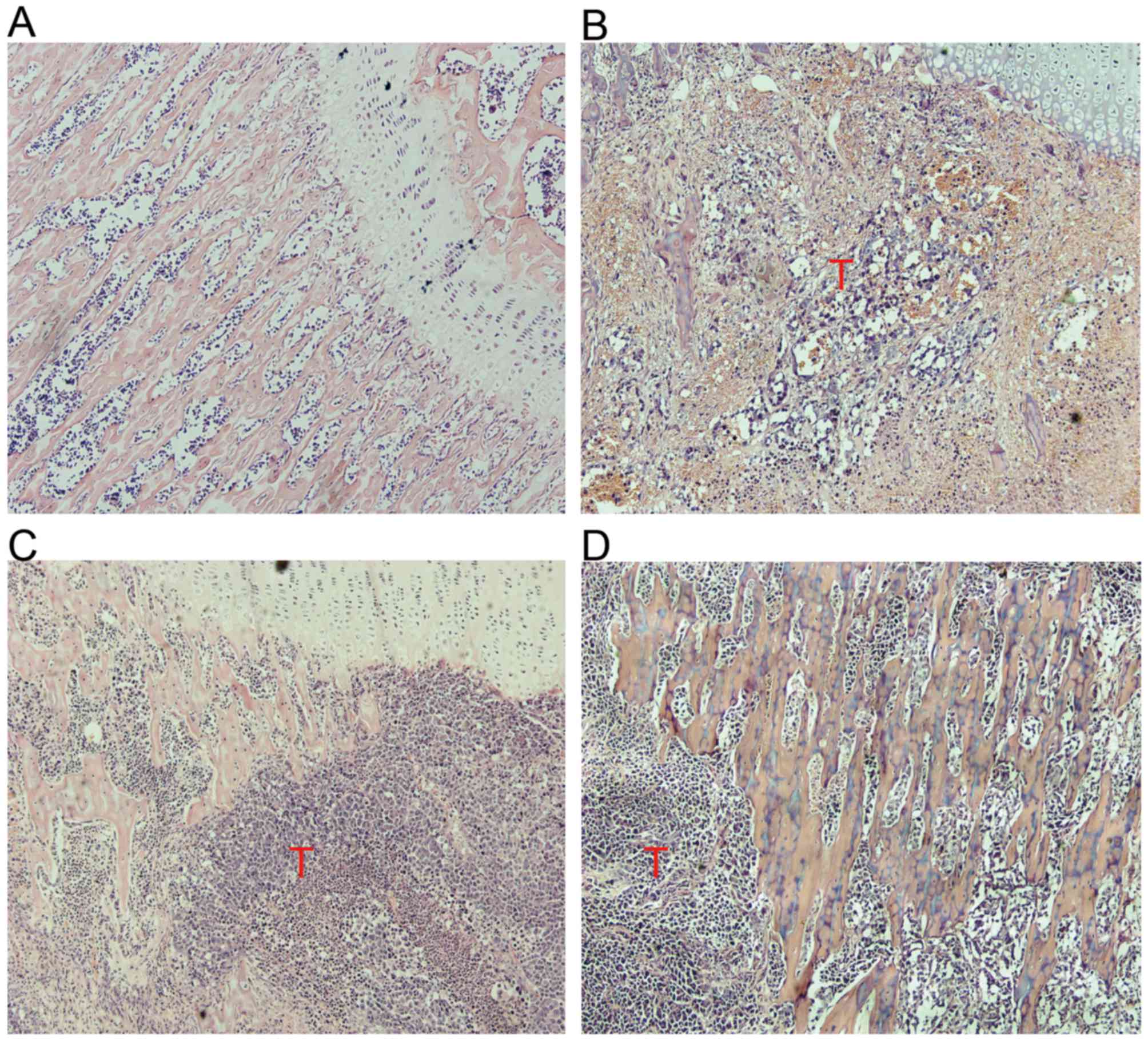
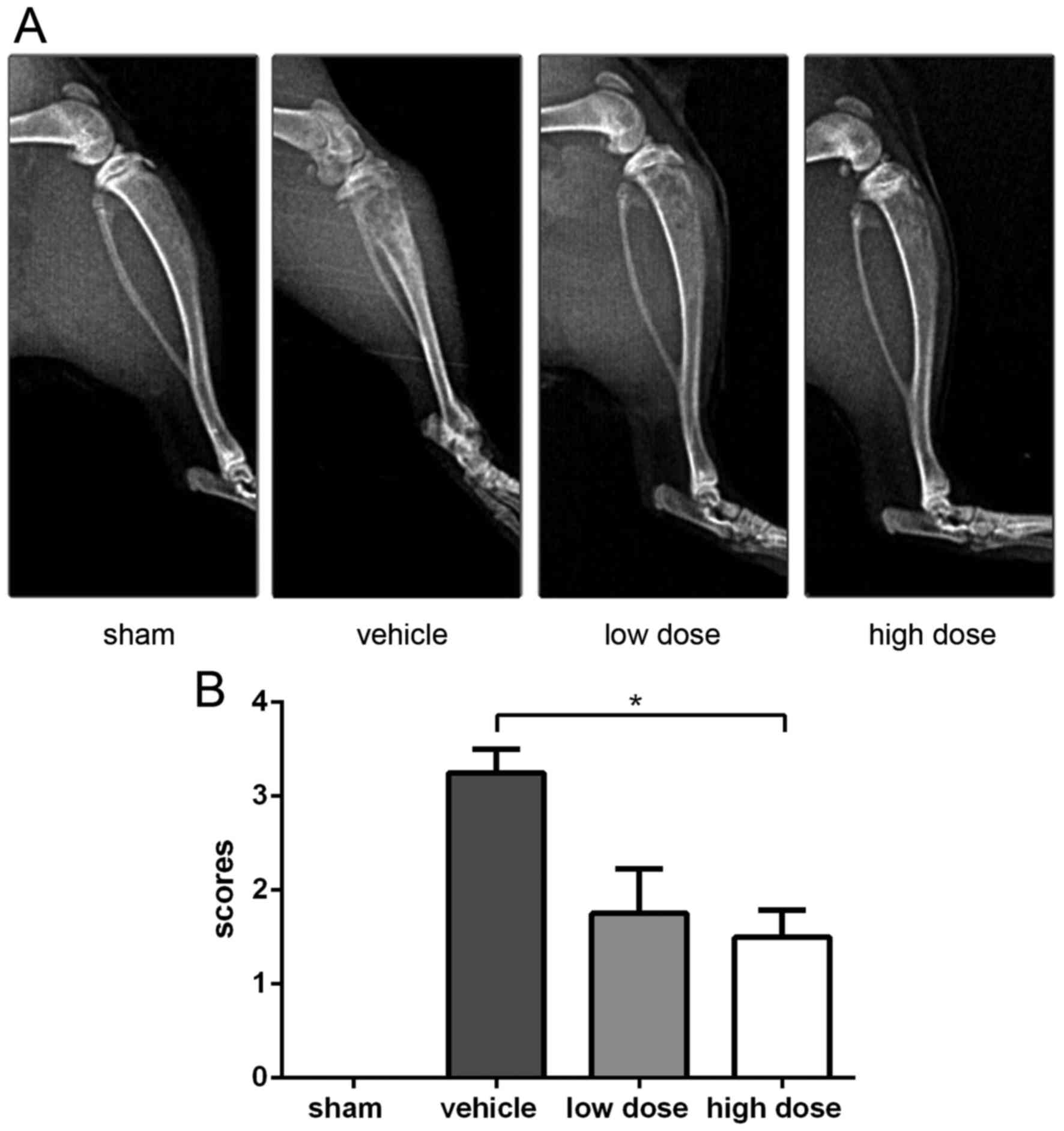
|
1
|
Roodman GD: Genes associate with abnormal
bone cell activity in bone metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev.
31:569–578. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Holland PM, Miller R, Jones J, Douangpanya
H, Piasecki J, Roudier M and Dougall WC: Combined therapy with the
RANKL inhibitor RANK-Fc and rhApo2L/TRAIL/dulanermin reduces bone
lesions and skeletal tumor burden in a model of breast cancer
skeletal metastasis. Cancer Biol Ther. 9:539–550. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zinonos I, Luo KW, Labrinidis A, Liapis V,
Hay S, Panagopoulos V, Denichilo M, Ko CH, Yue GG, Lau CB, et al:
Pharmacologic inhibition of bone resorption prevents cancer-induced
osteolysis but enhances soft tissue metastasis in a mouse model of
osteolytic breast cancer. Int J Oncol. 45:532–540. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Gui Q, Xu C, Zhuang L, Xia S, Chen Y, Peng
P and Yu S: A new rat model of bone cancer pain produced by rat
breast cancer cells implantation of the shaft of femur at the third
trochanter level. Cancer Biol Ther. 14:193–199. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kane CM, Hoskin P and Bennett MI: Cancer
induced bone pain. BMJ. 350:h3152015. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Vahtsevanos K, Kyrgidis A, Verrou E,
Katodritou E, Triaridis S, Andreadis CG, Boukovinas I, Koloutsos
GE, Teleioudis Z, Kitikidou K, et al: Longitudinal cohort study of
risk factors in cancer patients of bisphosphonate-related
osteonecrosis of the jaw. J Clin Oncol. 27:5356–5362. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Stopeck AT, Lipton A, Body JJ, Steger GG,
Tonkin K, de Boer RH, Lichinitser M, Fujiwara Y, Yardley DA,
Viniegra M, et al: Denosumab compared with zoledronic acid for the
treatment of bone metastases in patients with advanced breast
cancer: A randomized, double-blind study. J Clin Oncol.
28:5132–5139. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Koo HJ, Yoon WJ, Sohn EH, Ham YM, Jang SA,
Kwon JE, Jeong YJ, Kwak JH, Sohn E, Park SY, et al: The analgesic
and anti-inflammatory effects of Litsea japonica fruit are mediated
via suppression of NF-κB and JNK/p38 MAPK activation. Int
Immunopharmacol. 22:84–97. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yin JJ, Pollock CB and Kelly K: Mechanisms
of cancer metastasis to the bone. Cell Res. 15:57–62. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bussard KM, Venzon DJ and Mastro AM:
Osteoblasts are a major source of inflammatory cytokines in the
tumor microenvironment of bone metastatic breast cancer. J Cell
Biochem. 111:1138–1148. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Takiguchi S, Korenaga N, Inoue K, Sugi E,
Kataoka Y, Matsusue K, Futagami K, Li YJ, Kukita T, Teramoto N and
Iguchi H: Involvement of CXCL14 in osteolytic bone metastasis from
lung cancer. Int J Oncol. 44:1316–1324. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Luo Q, Sun Y, Liu W, Qian C, Jin B, Tao F,
Gu Y, Wu X, Shen Y and Xu Q: A novel disease-modifying
antirheumatic drug, iguratimod, ameliorates murine arthritis by
blocking IL-17 signaling, distinct from methotrexate and
leflunomide. J Immunol. 191:4969–4978. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Okamura K, Yonemoto Y, Okura C, Kobayashi
T and Takagishi K: Efficacy of the clinical use of iguratimod
therapy in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Mod Rheumatol.
25:235–240. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Guan XH, Fu QC, Shi D, Bu HL, Song ZP,
Xiong BR, Shu B, Xiang HB, Xu B, Manyande A, et al: Activation of
spinal chemokine receptor CXCR3 mediates bone cancer pain through
an Akt-ERK crosstalk pathway in rats. Exp Neurol. 263:39–49. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Mao-Ying QL, Zhao J, Dong ZQ, Wang J, Yu
J, Yan MF, Zhang YQ, Wu GC and Wang YQ: A rat model of bone cancer
pain induced by intra-tibia inoculation of Walker 256 mammary gland
carcinoma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 345:1292–1298. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Du F, Lü LJ, Fu Q, Dai M, Teng JL, Fan W,
Chen SL, Ye P, Shen N, Huang XF, et al: T-614, a novel
immunomodulator, attenuates joint inflammation and articular damage
in collagen-induced arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 10:R1362008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Xu B, Guan XH, Yu JX, Lv J, Zhang HX, Fu
QC, Xiang HB, Bu HL, Shi D, Shu B, et al: Activation of spinal
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B mediates pain
behavior induced by plantar incision in mice. Exp Neurol.
255:71–82. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Pogatzki EM and Raja SN: A mouse model of
incisional pain. Anesthesiology. 99:1023–1027. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Bloom AP, Jimenez-Andrade JM, Taylor RN,
Castañeda-Corral G, Kaczmarska MJ, Freeman KT, Coughlin KA,
Ghilardi JR, Kuskowski MA and Mantyh PW: Breast cancer-induced bone
remodeling, skeletal pain, and sprouting of sensory nerve fibers. J
Pain. 12:698–711. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Medhurst SJ, Walker K, Bowes M, Kidd BL,
Glatt M, Muller M, Hattenberger M, Vaxelaire J, O'Reilly T,
Wotherspoon G, et al: A rat model of bone cancer pain. Pain.
96:129–140. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gao YJ and Ji RR: c-Fos and pERK, which is
a better marker for neuronal activation and central sensitization
after noxious stimulation and tissue injury? Open Pain J. 2:11–17.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang LN, Yao M, Yang JP, Peng J, Peng Y,
Li CF, Zhang YB, Ji FH, Cheng H, Xu QN, et al: Cancer-induced bone
pain sequentially activates the ERK/MAPK pathway in different cell
types in the rat spinal cord. Mol Pain. 7:482011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang XW, Li TT, Zhao J, Mao-Ying QL, Zhang
H, Hu S, Li Q, Mi WL, Wu GC, Zhang YQ and Wang YQ: Extracellular
signal-regulated kinase activation in spinal astrocytes and
microglia contributes to cancer-induced bone pain in rats.
Neuroscience. 217:172–181. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Doré-Savard L, Otis V, Belleville K,
Lemire M, Archambault M, Tremblay L, Beaudoin JF, Beaudet N,
Lecomte R, Lepage M, et al: Behavioral, medical imaging and
histopathological features of a new rat model of bone cancer pain.
PLoS One. 5:e137742010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kingsley LA, Fournier PG, Chirgwin JM and
Guise TA: Molecular biology of bone metastasis. Mol Cancer Ther.
6:2609–2617. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sterling JA, Edwards JR, Martin TJ and
Mundy GR: Advances in the biology of bone metastasis: How the
skeleton affects tumor behavior. Bone. 48:6–15. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Siclari VA, Guise TA and Chirgwin JM:
Molecular interactions between breast cancer cells and the bone
microenvironment drive skeletal metastases. Cancer Metastasis Rev.
25:621–633. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Mantyh P: Bone cancer pain: Causes,
consequences, and therapeutic opportunities. Pain. 154 Suppl
1:S54–S62. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Sosnoski DM, Krishnan V, Kraemer WJ,
Dunn-Lewis C and Mastro AM: Changes in cytokines of the bone
microenvironment during breast cancer metastasis. Int J Breast
Cancer. 2012:1602652012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Jimenez-Andrade JM, Mantyh WG, Bloom AP,
Ferng AS, Geffre CP and Mantyh PW: Bone cancer pain. Ann N Y Acad
Sci. 1198:173–181. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yoneda T, Hata K, Nakanishi M, Nagae M,
Nagayama T, Wakabayashi H, Nishisho T, Sakurai T and Hiraga T:
Involvement of acidic microenvironment in the pathophysiology of
cancer-associated bone pain. Bone. 48:100–105. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Clark AK, Old EA and Malcangio M:
Neuropathic pain and cytokines: Current perspectives. J Pain Res.
6:803–814. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ellis A and Bennett DL: Neuroinflammation
and the generation of neuropathic pain. Br J Anaesth. 111:26–37.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Falk S and Dickenson AH: Pain and
nociception: Mechanisms of cancer-induced bone pain. J Clin Oncol.
32:1647–1654. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Du F, Lü LJ, Teng JL, Shen N, Ye P and Bao
CD: T-614 alters the production of matrix metalloproteinases (MMP-1
andMMP-3) and inhibits the migratory expansion of rheumatoid
synovial fibroblasts, in vitro. Int Immunopharmacol. 13:54–60.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
David Roodman G: Role of stromal-derived
cytokines and growth factors in bone metastasis. Cancer. 97 3
Suppl:S733–S738. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Ara T and Declerck YA: Interleukin-6 in
bone metastasis and cancer progression. Eur J Cancer. 46:1223–1231.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ara T, Song L, Shimada H, Keshelava N,
Russell HV, Metelitsa LS, Groshen SG, Seeger RC and DeClerck YA:
Interleukin-6 in the bone marrow microenvironment promotes the
growth and survival of neuroblastoma cells. Cancer Res. 69:329–337.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Paice JA and Ferrell B: The management of
cancer pain. CA Cancer J Clin. 61:157–182. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Aikawa Y, Yamamoto M, Yamamoto T, Morimoto
K and Tanaka K: An anti-rheumatic agent T-614 inhibits NF-kappaB
activation in LPS- and TNF-alpha-stimulated THP-1 cells without
interfering with IkappaBalpha degradation. Inflamm Res. 51:188–194.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Okamura K, Yonemoto Y, Suto T, Okura C and
Takagishi K: Efficacy at 52 weeks of daily clinical use of
iguratimod in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Mod Rheumatol.
25:534–539. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Hara M, Abe T, Sugawara S, Mizushima Y,
Hoshi K, Irimajiri S, Hashimoto H, Yoshino S, Matsui N and Nobunaga
M: Long-term safety study of iguratimod in patients with rheumatoid
arthritis. Mod Rheumatol. 17:10–16. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Hara M, Ishiguro N, Katayama K, Kondo M,
Sumida T, Mimori T, Soen S, Nagai K, Yamaguchi T and Yamamoto K;
Iguratimod-Clinical Study Group, : Safety and efficacy of
combination therapy of iguratimod with methotrexate for patients
with active rheumatoid arthritis with an inadequate response to
methotrexate: An open-label extension of a randomized,
double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Mod Rheumatol. 24:410–418.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|