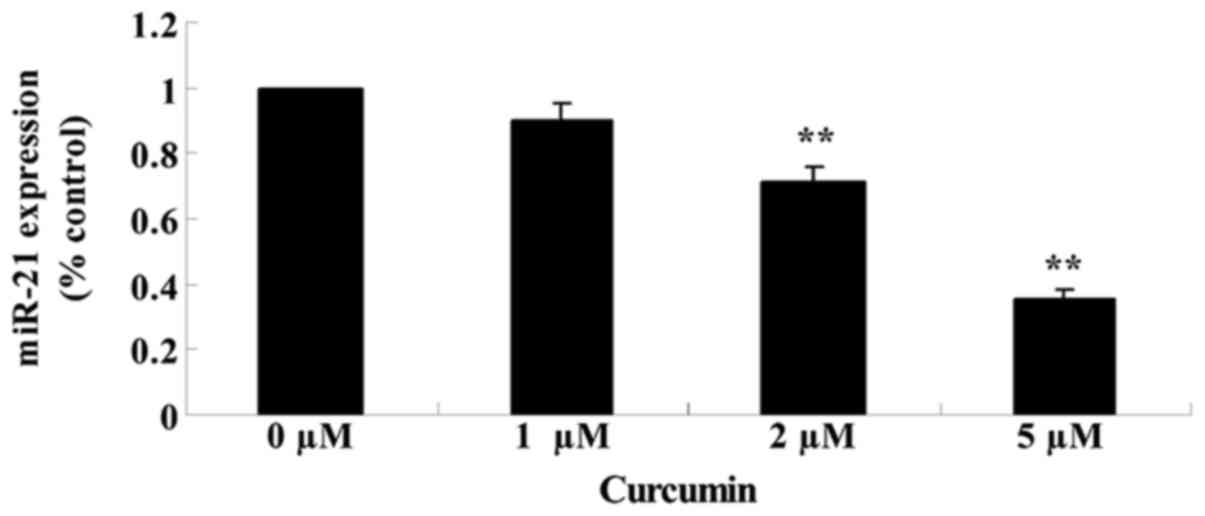
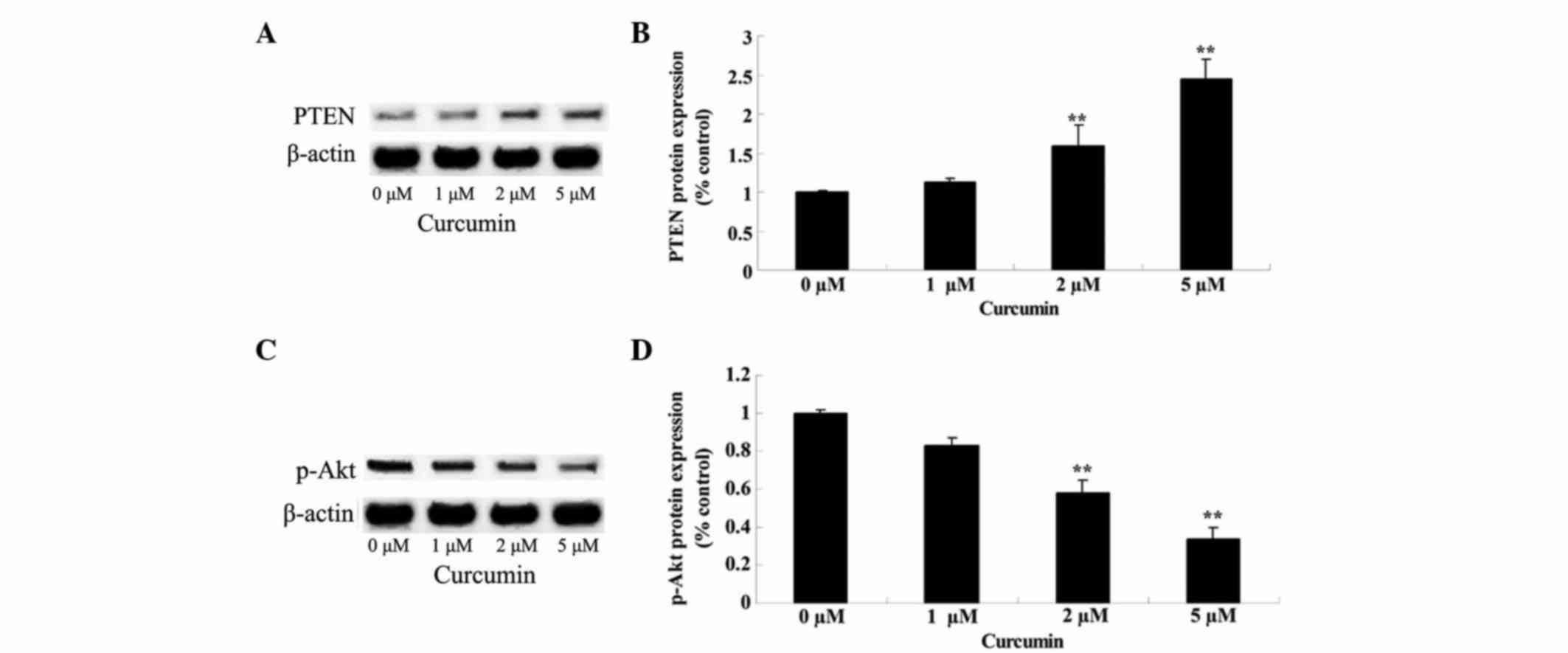
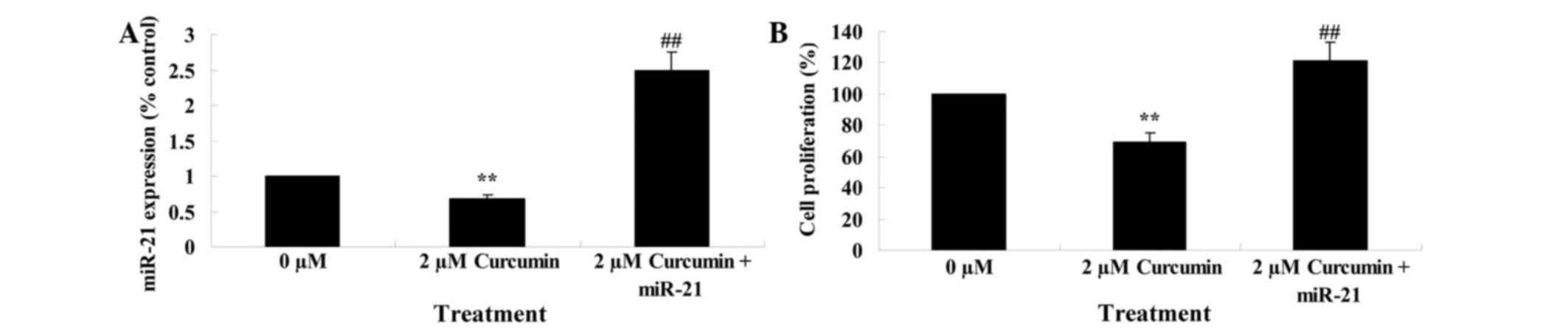
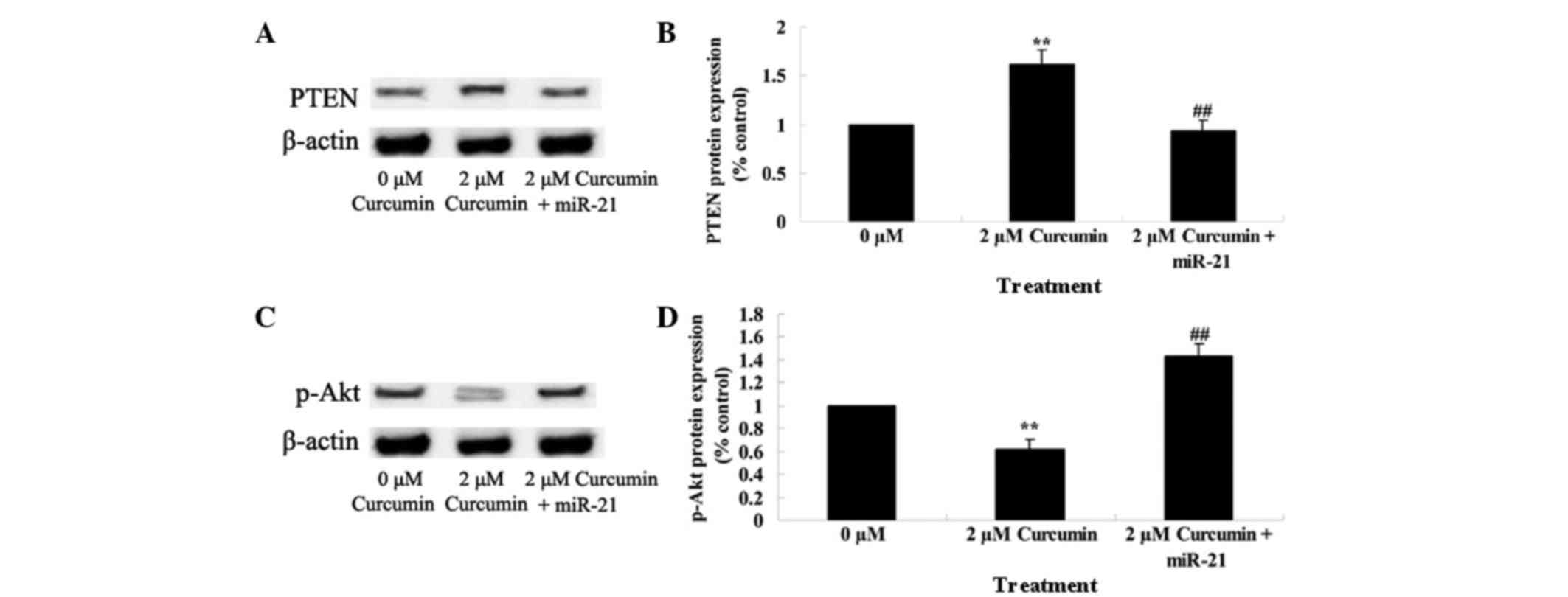
|
1
|
Pu Z, Yuan X, Zhang X, Chen Q and Xie H:
Meta-analysis on the association between CYP2D6*10 gene
polymorphism and disease free survival of breast cancer patients
receiving tamoxifen treatment in Asia. Bangladesh J Pharmacol.
9:652–662. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Rao X, Evans J, Chae H, Pilrose J, Kim S,
Yan P, Huang RL, Lai HC, Lin H, Liu Y, et al: CpG island shore
methylation regulates caveolin-1 expression in breast cancer.
Oncogene. 32:4519–4528. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zhang J, Wang Y, Yin Q, Zhang W, Zhang T
and Niu Y: An associated classification of triple negative breast
cancer: The risk of relapse and the response to chemotherapy. Int J
Clin Exp Pathol. 6:1380–1391. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Moshammer MI, Kalipciyan M, Bartsch R,
Steger GG, Sedivy R and Mader RM: Exosomal microRNA transfer varies
with specific microRNAs functional in colorectal cancer and
cellular differentiation. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 52:87–88.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Catania A, Maira F, Skarmoutsou E, D'Amico
F, Abounader R and Mazzarino MC: Insight into the role of microRNAs
in brain tumors (review). Int J Oncol. 40:605–624. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Osawa S, Shimada Y, Sekine S, Okumura T,
Nagata T, Fukuoka J and Tsukada K: MicroRNA profiling of gastric
cancer patients from formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded samples.
Oncol Lett. 2:613–619. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chiu J, Khan ZA, Farhangkhoee H and
Chakrabarti S: Curcumin prevents diabetes-associated abnormalities
in the kidneys by inhibiting p300 and nuclear factor-kappaB.
Nutrition. 25:964–972. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wang J, Du XX, Jiang H and Xie JX:
Curcumin attenuates 6-hydroxydopamine-induced cytotoxicity by
anti-oxidation and nuclear factor-kappa B modulation in MES23.5
cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 78:178–183. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wu SJ, Tam KW, Tsai YH, Chang CC and Chao
JC: Curcumin and saikosaponin a inhibit chemical-induced liver
inflammation and fibrosis in rats. Am J Chin Med. 38:99–111. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhen L, Fan D, Yi X, Cao X, Chen D and
Wang L: Curcumin inhibits oral squamous cell carcinoma
proliferation and invasion via EGFR signaling pathways. Int J Clin
Exp Pathol. 7:6438–6446. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ye M and Zhang J and Zhang J, Miao Q, Yao
L and Zhang J: Curcumin promotes apoptosis by activating the
p53-miR-192-5p/215-XIAP pathway in non-small cell lung cancer.
Cancer Lett. 357:196–205. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Liu X, Sun K, Song A, Zhang X, Zhang X and
He X: Curcumin inhibits proliferation of gastric cancer cells by
impairing ATP-sensitive potassium channel opening. World J Surg
Oncol. 12:3892014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Livak and Schmittgen: Analysis of relative
gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the
2-ΔΔCt method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Jiang H, Bai X, Zhang C and Zhang X:
Evaluation of HER2 gene amplification in breast cancer using nuclei
microarray in situ hybridization. Int J Mol Sci. 13:5519–5527.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Menendez JA and Lupu R: RNA
interference-mediated silencing of the p53 tumor-suppressor protein
drastically increases apoptosis after inhibition of endogenous
fatty acid metabolism in breast cancer cells. Int J Mol Med.
15:33–40. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Teong B, Lin CY, Chang SJ, Niu GC, Yao CH,
Chen IF and Kuo SM: Enhanced anti-cancer activity by
curcumin-loaded hydrogel nanoparticle derived aggregates on A549
lung adenocarcinoma cells. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 26:53572015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chen QY, Jiao DM, Wang LF, Wang L, Hu HZ,
Song J, Yan J, Wu LJ and Shi JG: Curcumin inhibits
proliferation-migration of NSCLC by steering crosstalk between a
Wnt signaling pathway and an adherens junction via EGR-1. Mol
Biosyst. 11:859–868. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Fan L, Li A, Li W, Cai P, Yang B, Zhang M,
Gu Y, Shu Y, Sun Y, Shen Y, et al: Novel role of Sarco/endoplasmic
reticulum calcium ATPase 2 in development of colorectal cancer and
its regulation by F36, a curcumin analog. Biomed Pharmacother.
68:1141–1148. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Shi J: Considering exosomal miR-21 as a
biomarker for cancer. J Clin Med. 5:422016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Frey MR, Carraro G, Batra RK, Polk DB and
Warburton D: Sprouty keeps bowel kinases regular in colon cancer,
while miR-21 targets Sprouty. Cancer Biol Ther. 11:122–124. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Han M, Liu M, Wang Y, Chen X, Xu J, Sun Y,
Zhao L, Qu H, Fan Y and Wu C: Antagonism of miR-21 reverses
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer stem cell phenotype
through AKT/ERK1/2 inactivation by targeting PTEN. PLoS One.
7:e395202012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yin C, Zhou X, Dang Y, Yan J and Zhang G:
Potential role of circulating miR-21 in the diagnosis and prognosis
of digestive System Cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis.
Medicine (Baltimore). 94:e21232015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Mudduluru G, George-William JN, Muppala S,
Asangani IA, Kumarswamy R, Nelson LD and Allgayer H: Curcumin
regulates miR-21 expression and inhibits invasion and metastasis in
colorectal cancer. Biosci Rep. 31:185–197. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Leslie NR, Kriplani N, Hermida MA,
Alvarez-Garcia V and Wise HM: The PTEN protein: Cellular
localization and post-translational regulation. Biochem Soc Trans.
44:273–278. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yi XP, Han T, Li YX, Long XY and Li WZ:
Simultaneous silencing of XIAP and survivin causes partial
mesenchymal-epithelial transition of human pancreatic cancer cells
via the PTEN/PI3K/Akt pathway. Mol Med Rep. 12:601–608.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
He C, Dong X, Zhai B, Jiang X, Dong D, Li
B, Jiang H, Xu S and Sun X: MiR-21 mediates sorafenib resistance of
hepatocellular carcinoma cells by inhibiting autophagy via the
PTEN/Akt pathway. Oncotarget. 6:28867–28881. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Schwarzenbach H, Milde-Langosch K,
Steinbach B, Müller V and Pantel K: Diagnostic potential of
PTEN-targeting miR-214 in the blood of breast cancer patients.
Breast Cancer Res Treat. 134:933–941. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Khaw AK and Hande MP, Kalthur G and Hande
MP: Curcumin inhibits telomerase and induces telomere shortening
and apoptosis in brain tumour cells. J Cell Biochem. 114:1257–1270.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wong TF, Takeda T, Li B, Tsuiji K,
Kitamura M, Kondo A and Yaegashi N: Curcumin disrupts uterine
leiomyosarcoma cells through AKT-mTOR pathway inhibition. Gynecol
Oncol. 122:141–148. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhang J, Yang Y, Zhang Z, He Y, Liu Z, Yu
Y, Wu S, Cai B and Feng Y: Gankyrin plays an essential role in
estrogen-driven and GPR30-mediated endometrial carcinoma cell
proliferation via the PTEN/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Cancer Lett.
339:279–287. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Xue G, Zippelius A, Wicki A, Mandalà M,
Tang F, Massi D and Hemmings BA: Integrated Akt/PKB signaling in
immunomodulation and its potential role in cancer immunotherapy. J
Natl Cancer Inst. 107:2015
|
|
32
|
Park JH, Lee JY, Shin DH, Jang KS, Kim HJ
and Kong G: Loss of Mel-18 induces tumor angiogenesis through
enhancing the activity and expression of HIF-1alpha mediated by the
PTEN/PI3K/Akt pathway. Oncogene. 30:4578–4589. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhao M, Zhou A, Xu L and Zhang X: The role
of TLR4-mediated PTEN/PI3K/AKT/NF-κB signaling pathway in
neuroinflammation in hippocampal neurons. Neuroscience. 269:93–101.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Li P, Xiao LY and Tan H: Muc-1 promotes
migration and invasion of oral squamous cell carcinoma cells via
PI3K-Akt signaling. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:10365–10374.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yang X, Cheng Y, Li P, Tao J, Deng X,
Zhang X, Gu M, Lu Q and Yin C: A lentiviral sponge for miRNA-21
diminishes aerobic glycolysis in bladder cancer T24 cells via the
PTEN/PI3K/AKT/mTOR axis. Tumour Biol. 36:383–391. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|