|
1
|
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser
S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D and Bray F: Cancer
incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major
patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 136:E359–E386. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Faivre J, Lepage C and Viguier J: Cancer
colorectal: Du diagnostic au dépistage. Gastroentérologie Clin
Biol. 33:660–671. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Institut National Du Cancer (INCA), . Les
traitements du cancer du côlon, collection Guides patients Cancer
info. INCA. 2010, http://www.e-cancer.fr/Patients-et-proches/Les-cancers/Cancer-du-colon/Points-cles
|
|
4
|
Rawson JB and Bapat B: Epigenetic
biomarkers in colorectal cancer diagnostics. Expert Rev Mol Diagn.
12:499–509. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hatakeyama K, Wakabayashi-Nakao K, Ohshima
K, Sakura N, Yamaguchi K and Mochizuki T: Novel protein isoforms of
carcinoembryonic antigen are secreted from pancreatic, gastric and
colorectal cancer cells. BMC Res Notes. 6:3812013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Gold P and Freedman SO: Specific
carcinoembryonic antigens of the human digestive system. J Exp Med.
122:467–481. 1965. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bast RC Jr, Ravdin P, Hayes DF, Bates S,
Fritsche H Jr, Jessup JM, Kemeny N, Locker GY, Mennel RG and
Somerfield MR: American Society of Clinical Oncology Tumor Markers
Expert Panel: 2000, Update of recommendations for the use of tumor
markers in breast and colorectal cancer: Clinical practice
guidelines of the American society of clinical oncology. J Clin
Oncol. 19:1865–1878. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yörüker EE, Holdenrieder S and Gezer U:
Blood-based biomarkers for diagnosis, prognosis and treatment of
colorectal cancer. Clin Chim Acta. 455:26–32. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Fan F, Samuel S, Evans KW, Lu J, Xia L,
Zhou Y, Sceusi E, Tozzi F, Ye XC, Mani SA and Ellis LM:
Overexpression of Snail induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition
and a cancer stem cell-like phenotype in human colorectal cancer
cells. Cancer Med. 1:5–16. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Newton KF, Newman W and Hill J: Review of
biomarkers in colorectal cancer. Colorectal Dis. 14:3–17. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang B and Zhang Q: The expression and
clinical significance of circulating microRNA-21 in serum of five
solid tumors. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 138:1659–1666. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Cohen SJ, Punt CJA, Iannotti N, Saidman
BH, Sabbath KD, Gabrail NY, Picus J, Morse MA, Mitchell E, Miller
MC, et al: Prognostic significance of circulating tumor cells in
patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Ann Oncol.
20:1223–1229. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Taback B, Saha S and Hoon DS: Comparative
analysis of mesenteric and peripheral blood circulating tumor DNA
in colorectal cancer patients. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1075:197–203.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bazan V, Bruno L, Augello C, Agnese V,
Calò V, Corsale S, Gargano G, Terrasi M, Schirò V, Di Fede G, et
al: Molecular detection of TP53, Ki-Ras and p16INK4A promoter
methylation in plasma of patients with colorectal cancer and its
association with prognosis. Results of a 3-year GOIM (Gruppo
Oncologico dell'Italia Meridionale) prospective study. Ann Oncol.
17(Suppl 7): vii84–vii90. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Rahbari NN, Aigner M, Thorlund K, Mollberg
N, Motschall E, Jensen K, Diener MK, Büchler MW, Koch M and Weitz
J: Meta-analysis shows that detection of circulating tumor cells
indicates poor prognosis in patients with colorectal cancer.
Gastroenterology. 138:1714–1726. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Abdallah EA, Fanelli MF, Buim ME, Netto MC
Machado, Junior JL Gasparini, Souza E, Silva V, Dettino AL, Mingues
NB, Romero JV, Ocea LM, et al: Thymidylate synthase expression in
circulating tumor cells: A new tool to predict 5-fluorouracil
resistance in metastatic colorectal cancer patients. Int J Cancer.
137:1397–1405. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lecomte T, Berger A, Zinzindohoué F,
Micard S, Landi B, Blons H, Beaune P, Cugnenc PH and Laurent-Puig
P: Detection of free-circulating tumor-associated DNA in plasma of
colorectal cancer patients and its association with prognosis. Int
J Cancer. 100:542–548. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Locker GY, Hamilton S, Harris J, Jessup
JM, Kemeny N, Macdonald JS, Somerfield MR, Hayes DF and Bast RC Jr:
ASCO: ASCO 2006 update of recommendations for the use of tumor
markers in gastrointestinal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 24:5313–5327.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
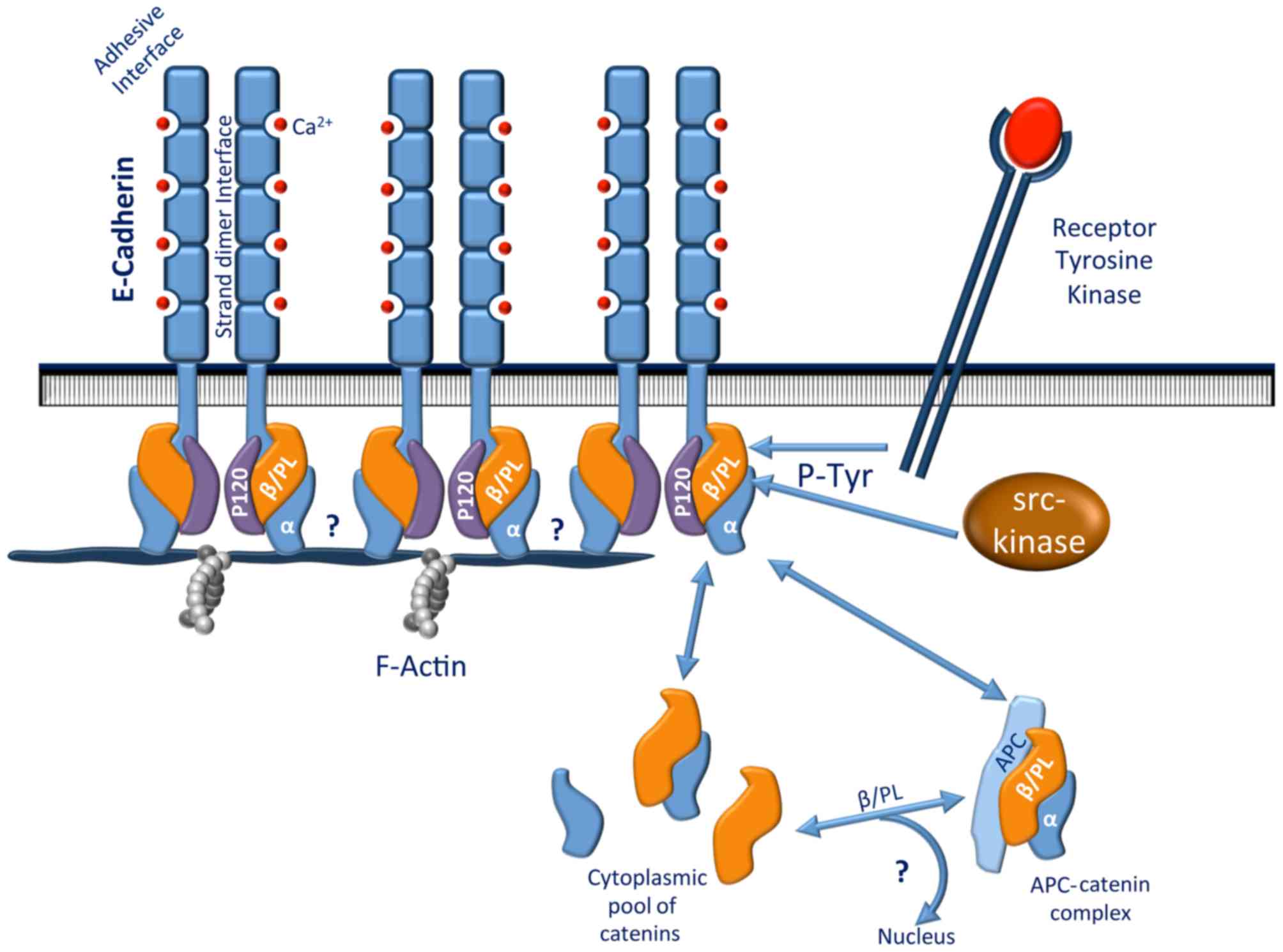
Behrens J: The role of cell adhesion
molecules in cancer invasion and metastasis. Breast Cancer Res
Treat. 24:175–184. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Shiozaki H, Oka H, Inoue M, Tamura S and
Monden M: E-cadherin mediated adhesion system in cancer cells.
Cancer. 77:1605–1613. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Nagar B, Overduin M, Ikura M and Rini JM:
Structural basis of calcium-induced E-cadherin rigidification and
dimerization. Nature. 380:360–364. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Van Roya F and Berxb G: The cell-cell
adhesion molecule E-cadherin. Cell Mol Life Sci. 65:3756–3788.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Aberle H, Schwartz H and Kemler R:
Cadherin-catenin complex: Protein interactions and their
implications for cadherin function. J Cell Biochem. 61:514–523.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Shapiro L, Fannon AM, Kwong PD, Thompson
A, Lehmann MS, Grübel G, Legrand JF, Als-Nielsen J, Colman DR and
Hendrickson WA: Structural basis of cell-cell adhesion by
cadherins. Nature. 374:327–337. 1995. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Canel M, Serrels A, Frame MC and Brunton
VG: E-cadherin-integrin crosstalk in cancer invasion and
metastasis. J Cell Sci. 126:393–401. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Liu DS, Hoefnagel SJM, Fisher OM,
Krishnadath KK, Montgomery KG, Busuttil RA, Colebatch AJ, Read M,
Duong CP, Phillips WA and Clemons NJ: Novel metastatic models of
esophageal adenocarcinoma derived from FLO-1 cells highlight the
importance of E-cadherin in cancer metastasis. Oncotarget.
7:83342–83358. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Strathdee G: Epigenetic versus genetic
alterations in the inactivation of E-cadherin. Semin Cancer Biol.
12:373–379. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Vécsey-Semjén B, Becker KF, Sinski A,
Blennow E, Vietor I, Zatloukal K, Beug H, Wagner E and Huber LA:
Novel colon cancer cell lines leading to better understanding of
the diversity of respective primary cancers. Oncogene.
21:4646–4662. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kanazawa T, Watanabe T, Kazama S, Tada T,
Koketsu S and Nagawa H: Poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma and
mucinous carcinoma of the colon and rectum show higher rates of
loss of heterozygosity and loss of E-cadherin expression due to
methylation of promoter region. Int J Cancer. 102:225–229. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Cheng CW, Wu PE, Yu JC, Huang CS, Yue CT,
Wu CW and Shen CY: Mechanisms of inactivation of E-cadherin in
breast carcinoma: Modification of the two-hit hypothesis of tumor
suppressor gene. Oncogene. 20:3814–3823. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
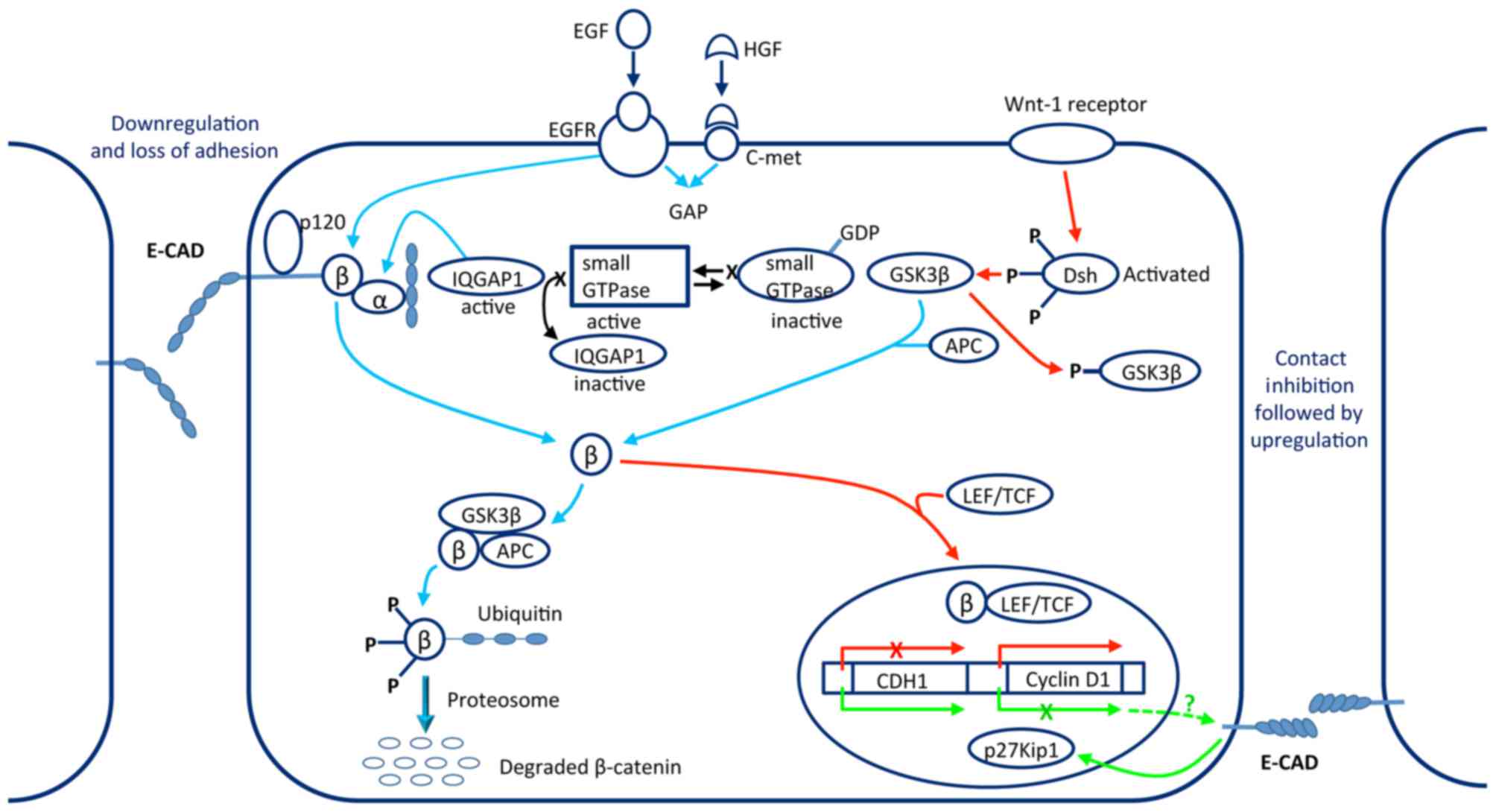
|
Shen Y, Hirsch DS, Sasiela CA and Wu WJ:
Cdc42 Regulates E-cadherin ubiquitination and degradation through
an epidermal growth factor receptor to Src-mediated pathway. J Biol
Chem. 283:5127–5137. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
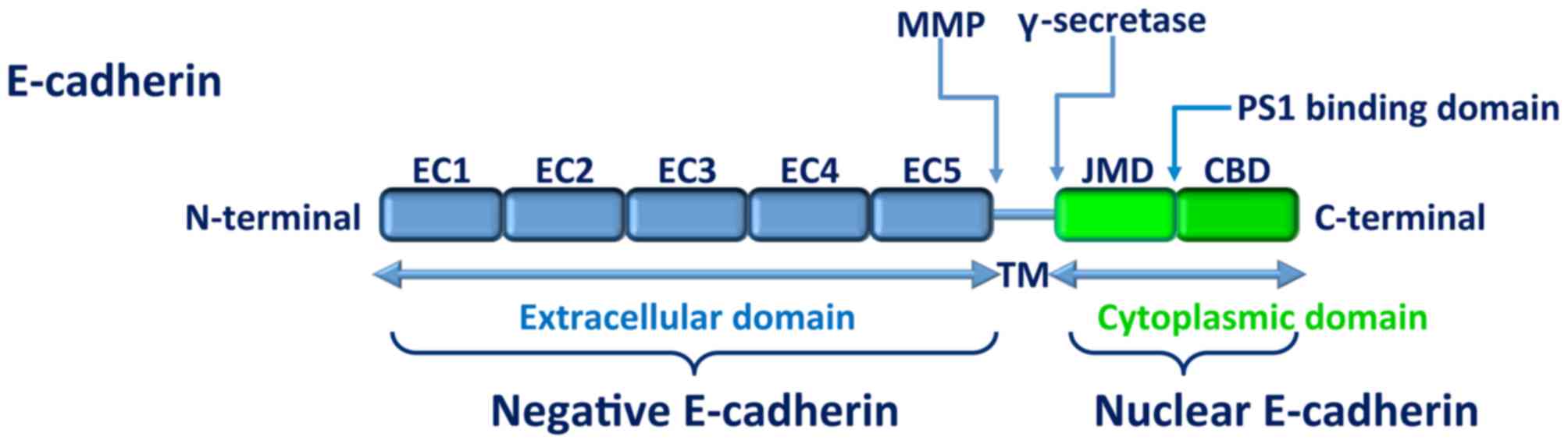
Symowicz J, Adley BP, Gleason KJ, Johnson
JJ, Ghosh S, Fishman DA, Hudson LG and Stack MS: Engagement of
collagen-binding integrins promotes matrix
metalloproteinase-9-dependent E-cadherin ectodomain shedding in
ovarian carcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 67:2030–2039. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Johnson SK, Ramani VC, Hennings L and Haun
RS: Kallikrein 7 enhances pancreatic cancer cell invasion by
shedding E-cadherin. Cancer. 109:1811–1820. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Trillsch F, Kuerti S, Eulenburg C, Burandt
E, Woelber L, Prieske K, Eylmann K, Oliveira-Ferrer L,
Milde-Langosch K and Mahner S: E-cadherin fragments as potential
mediators for peritoneal metastasis in advanced epithelial ovarian
cancer. Br J Cancer. 114:213–220. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Jang B, Jung H, Chung H, Moon BI and Oh
ES: Syndecan-2 enhances E-cadherin shedding and fibroblast-like
morphological changes by inducing MMP-7 expression in colon cancer
cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 477:47–53. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Carvalho S, Oliveira T, Bartels MF,
Miyoshi E, Pierce M, Taniguchi N, Carneiro F, Seruca R, Reis CA,
Strahl S and Pinho SS: O-mannosylation and N-glycosylation: Two
coordinated mechanisms regulating the tumour suppressor functions
of E-cadherin in cancer. Oncotarget. 7:65231–652446.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Petrova YI, Schecterson L and Gumbiner BM:
Roles for E-cadherin cell surface regulation in cancer. Mol Biol
Cell. 27:3233–3244. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Okugawa Y, Toiyama Y, Inoue Y, Iwata T,
Fujikawa H, Saigusa S, Konishi N, Tanaka K, Uchida K and Kusunoki
M: Clinical significance of serum soluble E-cadherin in colorectal
carcinoma1. J Surg Res. 175:e67–e73. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Efstathiou JA, Liu D, Wheeler JM, Kim HC,
Beck NE, Ilyas M, Karayiannakis AJ, Mortensen NJ, Kmiot W, Playford
RJ, et al: Mutated epithelial cadherin is associated with increased
tumorigenicity and loss of adhesion and of responsiveness to the
motogenic trefoil factor 2 in colon carcinoma cells. Proc Natl Acad
Sci. 96:pp. 2316–2321. 1999; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Kitadai Y, Bucana CD, Ellis LM, Anzai H,
Tahara E and Fidler IJ: In situ mRNA hybridization technique for
analysis of metastases related genes in human colon carcinoma.
cells. 147:1238–1247. 1995.
|
|
41
|
Gofuku J, Shiozaki H, Tsujinaka T, Inoue
M, Tamura S, Doki Y, Matsui S, Tsukita S, Kikkawa N and Monden M:
Expression of E-cadherin and alpha-catenin in patients with
colorectal carcinoma. Correlation with cancer invasion and
metastasis. Am J Clin Pathol. 111:29–37. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Velikova G, Banks RE, Gearing A, Hemingway
I, Forbes MA, Preston SR, Hall NR, Jones M, Wyatt J, Miller K, et
al: Serum concentrations of soluble adhesion molecules in patients
with colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer. 77:1857–1863. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Wilmanns C, Grossmann J, Steinhauer S,
Manthey G, Weinhold B, Schmitt-Gräff A and von Specht BU: Soluble
serum E-cadherin as a marker of tumour progression in colorectal
cancer patients. Clin Exp Metastasis. 21:75–78. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Weiss JV, Klein-Scory S, Kübler S,
Reinacher-Schick A, Stricker I, Schmiegel W and Schwarte-Waldhoff
I: Soluble E-cadherin as a serum biomarker candidate: Elevated
levels in patients with late-stage colorectal carcinoma and FAP.
Int J Cancer. 128:1384–1392. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Cao H, Xu E, Liu H, Wan L and Lai M:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in colorectal cancer metastasis:
A system review. Pathol Res Pract. 211:557–569. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Wang R, Ma X, Li Y, He Y, Huang D, Cai S
and Peng J: The characteristics and prognostic effect of E-cadherin
expression in colorectal signet ring cell carcinoma. PLOS One.
11:e01605272016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Gao M, Zhang X, Li D, He P, Tian W and
Zeng B: Expression analysis and clinical significance of eIF4E,
VEGF-C, E-cadherin and MMP-2 in colorectal adenocarcinoma.
Oncotarget. 7:85502–85514. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Chen D, Dai F, Chen Z, Wang S, Cheng X,
Sheng Q, Lin J and Chen W: Dimethoxy curcumin induces apoptosis by
suppressing survivin and inhibits invasion by enhancing E-cadherin
in colon cancer cells. Med Sci Monit. 22:3215–3222. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Nguyen L, Fifis T and Christophi C:
Vascular disruptive agent OXi4503 and anti-angiogenic agent
Sunitinib combination treatment prolong survival of mice with CRC
liver metastasis. BMC Cancer. 16:5332016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Fan LC, Teng HW, Shiau CW, Tai WT, Hung
MH, Yang SH, Jiang JK and Chen KF: Regorafenib (Stivarga)
pharmacologically targets epithelial-mesenchymal transition in
colorectal cancer. Oncotarget. 7:64136–64147. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Liu S, Barry EL, Baron JA, Rutherford RE,
Seabrook ME and Bostick RM: Effects of supplemental calcium and
vitamin D on the APC/β-catenin pathway in the normal colorectal
mucosa of colorectal adenoma patients. Mol Carcinog. 56:412–424.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|