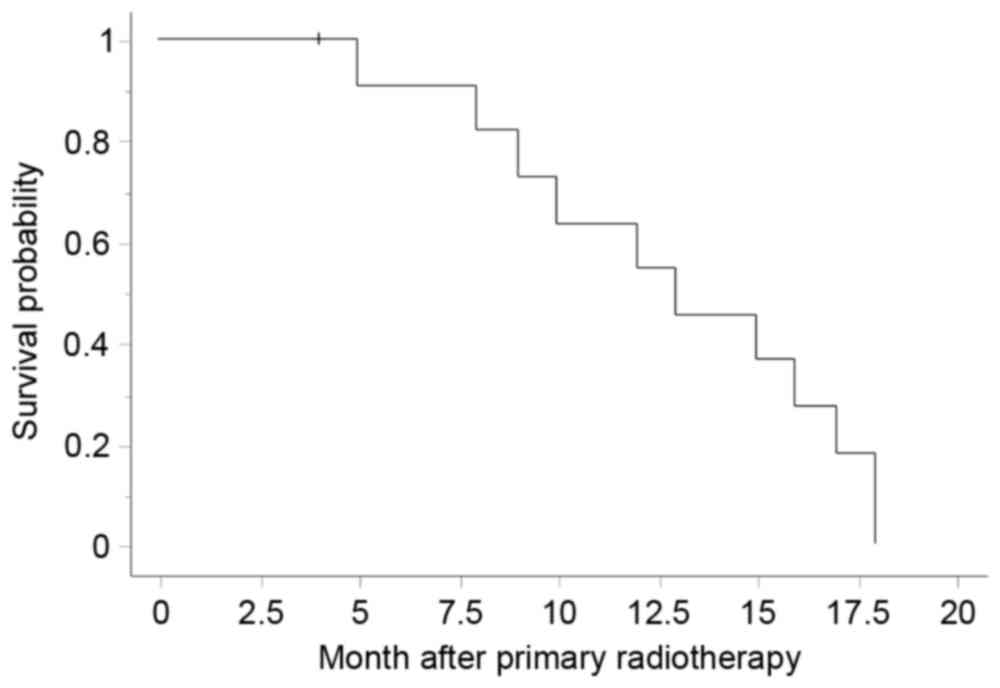
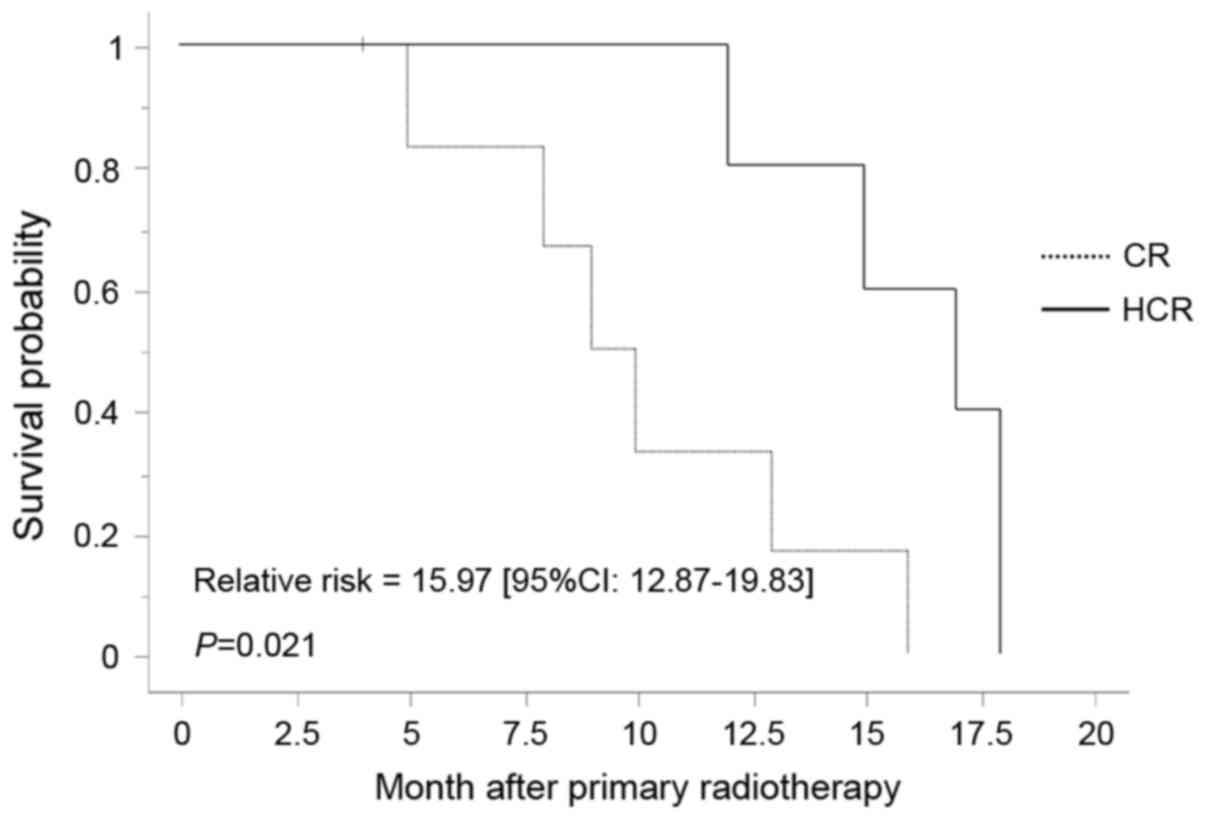
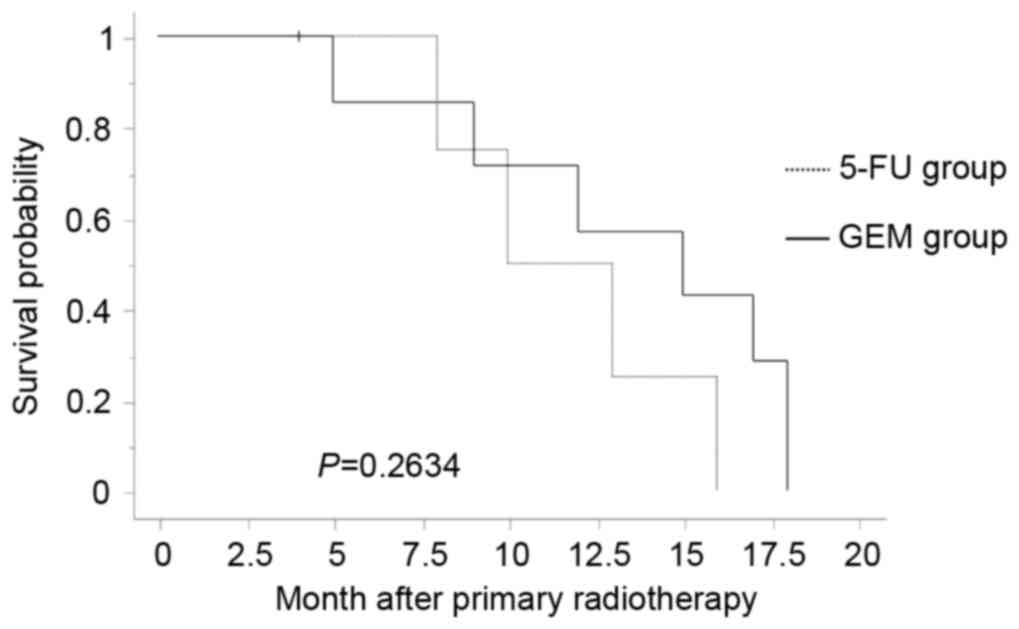
|
1
|
Egawa S, Toma H, Ohigashi H, Okusaka T,
Nakao A, Hatori T, Maguchi H, Yanagisawa A and Tanaka M: Japan
pancreatic cancer registry; 30th year anniversary: Japan pancreas
society. Pancreas. 41:985–992. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Gillen S, Schuster T, Zum Büschenfelde C
Meyer, Friess H and Kleeff J: Preoperative/neoadjuvant therapy in
pancreatic cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis of
response and resection percentages. PLoS Med. 7:e10002672010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hori M, Matsuda T, Shibata A, Katanoda K,
Sobue T and Nishimoto H; Japan Cancer Surveillance Research Group,
: Cancer incidence and incidence rates in Japan in 2009: A study of
32 population-based cancer registries for the Monitoring of Cancer
Incidence in Japan (MCIJ) project. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 45:884–891.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Burris HA III, Moore MJ, Andersen J, Green
MR, Rothenberg ML, Modiano MR, Cripps MC, Portenoy RK, Storniolo
AM, Tarassoff P, et al: Improvements in survival and clinical
benefit with gemcitabine as first-line therapy for patients with
advanced pancreas cancer: A randomized trial. J Clin Oncol.
15:2403–2413. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Li CP, Chao Y, Chi KH, Chan WK, Teng HC,
Lee RC, Chang FY, Lee SD and Yen SH: Concurrent chemoradiotherapy
treatment of locally advanced pancreatic cancer: Gemcitabine versus
5-fluorouracil, a randomized controlled study. Int J Radiat Oncol
Biol Phys. 57:98–104. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yeo CJ, Cameron JL, Lillemoe KD, Sohn TA,
Campbell KA, Sauter PK, Coleman J, Abrams RA and Hruban RH:
Pancreaticoduodenectomy with or without distal gastrectomy and
extended retroperitoneal lymphadenectomy for periampullary
adenocarcinoma, part 2: Randomized controlled trial evaluating
survival, morbidity, and mortality. Ann Surg. 236:355–668. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Riall TS, Cameron JL, Lillemoe KD,
Campbell KA, Sauter PK, Coleman J, Abrams RA, Laheru D, Hruban RH
and Yeo CJ: Pancreaticoduodenectomy with or without distal
gastrectomy and extended retroperitoneal lymphadenectomy for
periampullary adenocarcinoma-part 3: Update on 5-year survival. J
Gastrointest Surg. 9:1191–1206. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Maeda A, Boku N, Fukutomi A, Kondo S,
Kinoshita T, Nagino M and Uesaka K: Randomized phase III trial of
adjuvant chemotherapy with gemcitabine versus S-1 in patients with
resected pancreatic cancer: Japan adjuvant study group of
pancreatic cancer (JASPAC-01). Jpn J Clin Oncol. 38:227–229. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ghorani E, Wong HH, Hewitt C, Calder J,
Corrie P and Basu B: Safety and efficacy of modified FOLFIRINOX for
advanced pancreatic adenocarcinoma: A UK Single-Centre experience.
Oncology. 89:281–287. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
von Hoff DD, Ervin T, Arena FP, Chiorean
EG, Infante J, Moore M, Seay T, Tjulandin SA, Ma WW, Saleh MN, et
al: Increased survival in pancreatic cancer with nab-paclitaxel
plus gemcitabine. N Engl J Med. 369:1691–1703. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Takeda Y, Katsura Y, Ohmura Y, Morimoto Y,
Ishida T, Motoyama Y, Ohneda Y, Sato Y, Kuwahara R, Murakami K, et
al: FOLFIRINOX combination chemotherapy in patients with metastatic
or recurrent pancreatic Cancer-A single institution experience. Gan
To Kagaku Ryoho. 42:2360–2363. 2015.(In Japanese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ueno H, Ikeda M, Ueno M, Mizuno N, Ioka T,
Omuro Y, Nakajima TE and Furuse J: Phase I/II study of
nab-paclitaxel plus gemcitabine for chemotherapy-naive Japanese
patients with metastatic pancreatic cancer. Cancer Chemother
Pharmacol. 77:595–603. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Moertel CG, Frytak S, Hahn RG, O'Connell
MJ, Reitemeier RJ, Rubin J, Schutt AJ, Weiland LH, Childs DS,
Holbrook MA, et al: Therapy of locally unresectable pancreatic
carcinoma: A randomized comparison of high dose (6000 rads)
radiation alone, moderate dose radiation (4000 rads +
5-fluorouracil), and high dose radiation + 5-fluorouracil: The
gastrointestinal tumor study group. Cancer. 48:1705–1710. 1981.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Loehrer PJ Sr, Feng Y, Cardenes H, Wagner
L, Brell JM, Cella D, Flynn P, Ramanathan RK, Crane CH, Alberts SR
and Benson AB III: Gemcitabine alone versus gemcitabine plus
radiotherapy in patients with locally advanced pancreatic cancer:
An eastern cooperative oncology group trial. J Clin Oncol.
29:4105–4112. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chauffert B, Mornex F, Bonnetain F,
Rougier P, Mariette C, Bouché O, Bosset JF, Aparicio T, Mineur L,
Azzedine A, et al: Phase III trial comparing intensive induction
chemoradiotherapy (60 Gy, infusional 5-FU and intermittent
cisplatin) followed by maintenance gemcitabine with gemcitabine
alone for locally advanced unresectable pancreatic cancer.
Definitive results of the 2000-01 FFCD/SFRO study. Ann Oncol.
19:1592–1599. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ueno H, Ioka T, Ikeda M, Ohkawa S,
Yanagimoto H, Boku N, Fukutomi A, Sugimori K, Baba H, Yamao K, et
al: Randomized phase III study of gemcitabine plus S-1, S-1 alone,
or gemcitabine alone in patients with locally advanced and
metastatic pancreatic cancer in Japan and Taiwan: GEST study. J
Clin Oncol. 31:1640–1648. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Crane CH, Abbruzzese JL, Evans DB, Wolff
RA, Ballo MT, Delclos M, Milas L, Mason K, Charnsangavej C, Pisters
PW, et al: Is the therapeutic index better with gemcitabine-based
chemoradiation than with 5-fluorouracil-based chemoradiation in
locally advanced pancreatic cancer? Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys.
52:1293–1302. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Adachi S, Kokura S, Okayama T, Ishikawa T,
Takagi T, Handa O, Naito Y and Yoshikawa T: Effect of hyperthermia
combined with gemcitabine on apoptotic cell death in cultured human
pancreatic cancer cell lines. Int J Hyperthermia. 25:210–219. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ishikawa T, Kokura S, Sakamoto N, Ando T,
Imamoto E, Hattori T, Oyamada H, Yoshinami N, Sakamoto M, Kitagawa
K, et al: Phase II trial of combined regional hyperthermia and
gemcitabine for locally advanced or metastatic pancreatic cancer.
Int J Hyperthermia. 28:597–604. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lutgens LC, Koper PC, Jobsen JJ, van der
Steen-Banasik EM, Creutzberg CL, van den Berg HA, Ottevanger PB,
van Rhoon GC, van Doorn HC, Houben R and van der Zee J: Radiation
therapy combined with hyperthermia versus cisplatin for locally
advanced cervical cancer: Results of the randomized RADCHOC trial.
Radiother Oncol. 120:378–382. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tschoep-Lechner KE, Milani V, Berger F,
Dieterle N, Abdel-Rahman S, Salat C and Issels RD: Gemcitabine and
cisplatin combined with regional hyperthermia as second-line
treatment in patients with gemcitabine-refractory advanced
pancreatic cancer. Int J Hyperthermia. 29:8–16. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Gani C, Schroeder C, Heinrich V, Spillner
P, Lamprecht U, Berger B and Zips D: Long-term local control and
survival after preoperative radiochemotherapy in combination with
deep regional hyperthermia in locally advanced rectal cancer. Int J
Hyperthermia. 32:187–192. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|