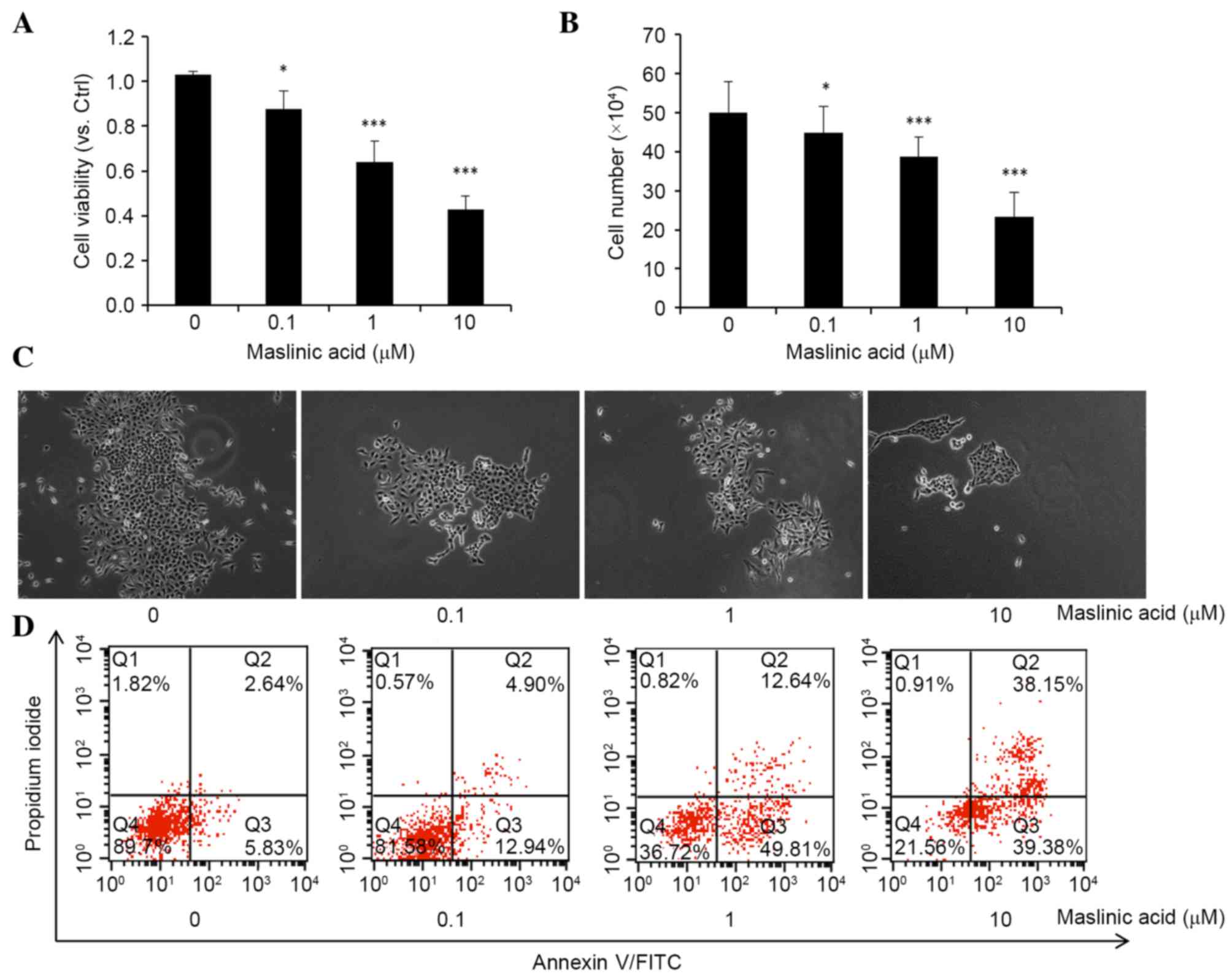
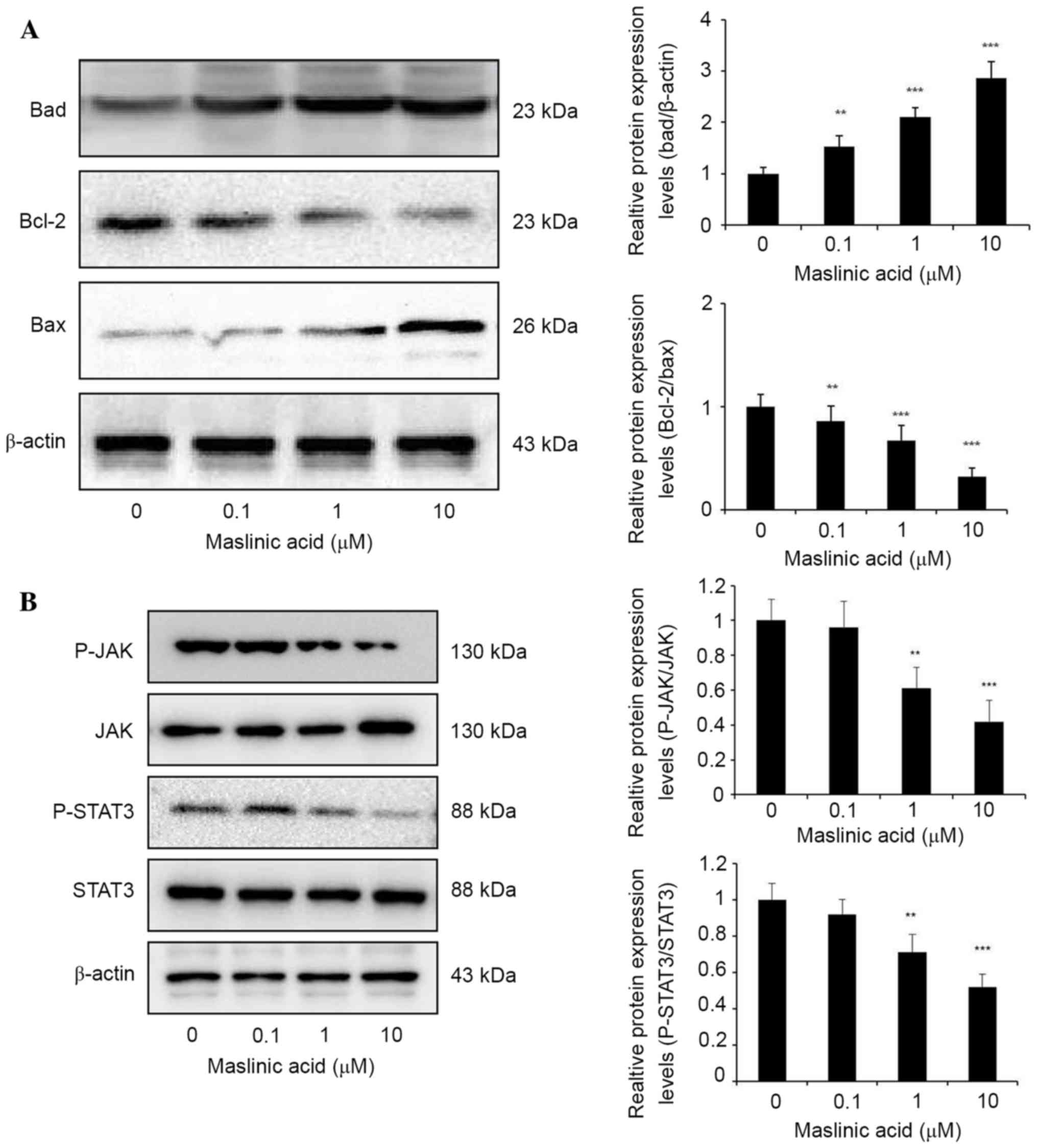
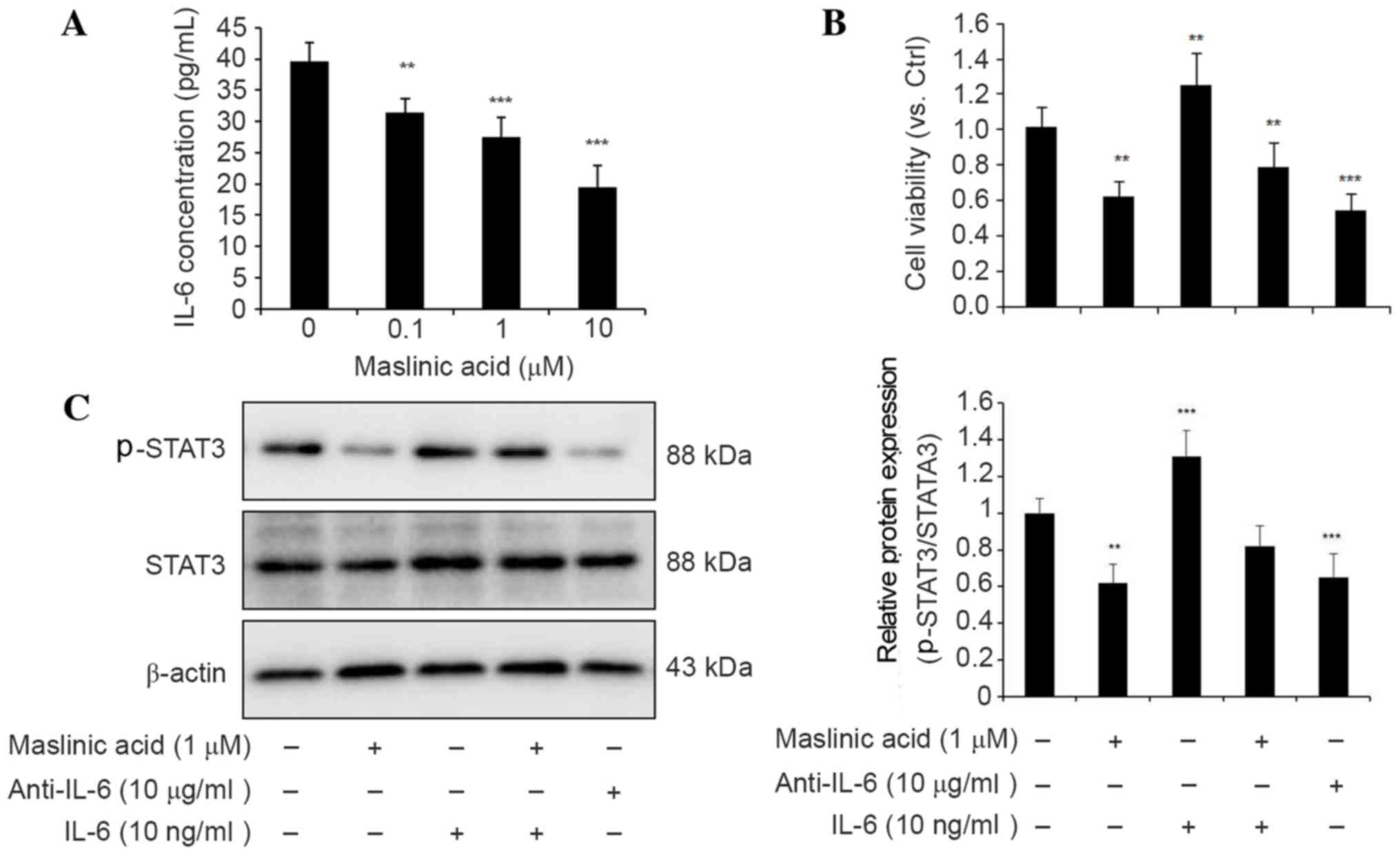
|
1
|
Reyes-Zurita FJ, Rufino-Palomares EE,
Lupiáñez JA and Cascante M: Maslinic acid, a natural triterpene
from Olea europaea L., induces apoptosis in HT29 human colon-cancer
cells via the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway. Cancer Lett.
273:44–54. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Pavel IZ, Danciu C, Oprean C, Dehelean CA,
Muntean D, Csuk R and Muntean DM: In vitro evaluation of the
antimicrobial ability and cytotoxicity on two melanoma cell lines
of a benzylamide derivative of maslinic acid. Anal Cell Pathol
(Amst). 2016:27876232016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Parra A, Rivas F, Lopez PE,
Garcia-Granados A, Martinez A, Albericio F, Marquez N and Muñoz E:
Solution- and solid-phase synthesis and anti-HIV activity of
maslinic acid derivatives containing amino acids and peptides.
Bioorg Med Chem. 17:1139–1145. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Nieto FR, Cobos EJ, Entrena JM, Parra A,
García-Granados A and Baeyens JM: Antiallodynic and analgesic
effects of maslinic acid, a pentacyclic triterpenoid from Olea
europaea. J Nat Prod. 76:737–740. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zhang S, Ding D, Zhang X, Shan L and Liu
Z: Maslinic acid induced apoptosis in bladder cancer cells through
activating p38 MAPK signaling pathway. Mol Cell Biochem.
392:281–287. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Park SY, Nho CW, Kwon DY, Kang YH, Lee KW
and Park JH: Maslinic acid inhibits the metastatic capacity of
DU145 human prostate cancer cells: Possible mediation via
hypoxia-inducible factor-1α signalling. Br J Nutr. 109:210–222.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Rufino-Palomares EE, Reyes-Zurita FJ,
García-Salguero L, Mokhtari K, Medina PP, Lupiáñez JA and Peragón
J: Maslinic acid, a triterpenic anti-tumoural agent, interferes
with cytoskeleton protein expression in HT29 human colon-cancer
cells. J Proteomics. 83:15–25. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Reyes-Zurita FJ, Pachón-Peña G, Lizárraga
D, Rufino-Palomares EE, Cascante M and Lupiáñez JA: The natural
triterpene maslinic acid induces apoptosis in HT29 colon cancer
cells by a JNK-p53-dependent mechanism. BMC Cancer. 11:1542011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Burger R: Impact of interleukin-6 in
hematological malignancies. Transfus Med Hemother. 40:336–343.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Reynaud D, Pietras E, Barry-Holson K, Mir
A, Binnewies M, Jeanne M, Sala-Torra O, Radich JP and Passegué E:
IL-6 controls leukemic multipotent progenitor cell fate and
contributes to chronic myelogenous leukemia development. Cancer
Cell. 20:661–673. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hirano T, Ishihara K and Hibi M: Roles of
STAT3 in mediating the cell growth, differentiation and survival
signals relayed through the IL-6 family of cytokine receptors.
Oncogene. 19:2548–2556. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Heinrich P, Behrmann I, Müller-Newen G,
Schaper F and Graeve L: Interleukin-6-type cytokine signalling
through the gp130/Jak/STAT pathway. Biochem J. 334:297–314. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ogata A, Chauhan D, Teoh G, Treon SP,
Urashima M, Schlossman RL and Anderson KC: IL-6 triggers cell
growth via the Ras-dependent mitogen-activated protein kinase
cascade. J Immunol. 159:2212–2221. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Huang W, Yu LF, Zhong J, Wu W, Zhu JY,
Jiang FX and Wu YL: Stat3 is involved in angiotensin II-induced
expression of MMP2 in gastric cancer cells. Dig Dis Sci.
54:2056–2062. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ding SZ, Cho CH and Lam SK: Regulation of
interleukin 6 production in a human gastric epithelial cell line
MKN-28. Cytokine. 12:1129–1135. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
To KF, Chan MW, Leung WK, Ng EK, Yu J, Bai
AH, Lo AW, Chu SH, Tong JH, Lo KW, et al: Constitutional activation
of IL-6-mediated JAK/STAT pathway through hypermethylation of
SOCS-1 in human gastric cancer cell line. Br J Cancer.
91:1335–1341. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Strober W: Trypan blue exclusion test of
cell viability. Curr Protoc Immunol Appendix. 3:Appendix 3B. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Catlett-Falcone R, Landowski TH, Oshiro
MM, Turkson J, Levitzki A, Savino R, Ciliberto G, Moscinski L,
Fernández-Luna JL, Nuñez G, et al: Constitutive activation of Stat3
signaling confers resistance to apoptosis in human U266 myeloma
cells. Immunity. 10:105–115. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Shain KH, Yarde DN, Meads MB, Huang M,
Jove R, Hazlehurst LA and Dalton WS: Beta1 integrin adhesion
enhances IL-6-mediated STAT3 signaling in myeloma cells:
Implications for microenvironment influence on tumor survival and
proliferation. Cancer Res. 69:1009–1015. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhong Z, Wen Z and Darnell JE Jr: Stat3: A
STAT family member activated by tyrosine phosphorylation in
response to epidermal growth factor and interleukin-6. Science.
264:95–98. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Al Zaid Siddiquee K and Turkson J: STAT3
as a target for inducing apoptosis in solid and hematological
tumors. Cell Res. 18:254–267. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Li C, Yang Z, Zhai C, Qiu W, Li D, Yi Z,
Wang L, Tang J, Qian M, Luo J and Liu M: Maslinic acid potentiates
the anti-tumor activity of tumor necrosis factor alpha by
inhibiting NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Mol Cancer. 9:732010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wu DM, Zhao D, Li DZ, Xu DY, Chu WF and
Wang XF: Maslinic acid induces apoptosis in salivary gland adenoid
cystic carcinoma cells by Ca2+-evoked p38 signaling pathway. Naunyn
Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 383:321–330. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Reyes-Zurita FJ, Rufino-Palomares EE,
Lupiáñez JA and Cascante M: Maslinic acid, a natural triterpene
from Olea europaea L., induces apoptosis in HT29 human colon-cancer
cells via the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway. Cancer Lett.
273:44–54. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hsum YW, Yew WT, Hong PL, Soo KK, Hoon LS,
Chieng YC and Mooi LY: Cancer chemopreventive activity of maslinic
acid: Suppression of COX-2 expression and inhibition of NF-κB and
AP-1 activation in raji cells. Planta Med. 77:152–157. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Coussens LM and Werb Z: Inflammation and
cancer. Nature. 420:860–867. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hodge DR, Hurt EM and Farrar WL: The role
of IL-6 and STAT3 in inflammation and cancer. Eur J Cancer.
41:2502–2512. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Murakami M, Hibi M, Nakagawa N, Nakagawa
T, Yasukawa K, Yamanishi K, Taga T and Kishimoto T: IL-6-induced
homodimerization of gp130 and associated activation of a tyrosine
kinase. Science. 260:1808–1810. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Heinrich PC, Behrmann I, Müller-Newen G,
Schaper F and Graeve L: Interleukin-6-type cytokine signalling
through the gp130/Jak/STAT pathway. Biochem J. 334:297–314. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kanda N, Seno H, Konda Y, Marusawa H,
Kanai M, Nakajima T, Kawashima T, Nanakin A, Sawabu T, Uenoyama Y,
et al: STAT3 is constitutively activated and supports cell survival
in association with survivin expression in gastric cancer cells.
Oncogene. 23:4921–4929. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Endo TA, Masuhara M, Yokouchi M, Suzuki R,
Sakamoto H, Mitsui K, Matsumoto A, Tanimura S, Ohtsubo M, Misawa H,
et al: A new protein containing an SH2 domain that inhibits JAK
kinases. Nature. 387:921–924. 1997. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yadav A, Kumar B, Datta J, Teknos TN and
Kumar P: IL-6 promotes head and neck tumor metastasis by inducing
epithelial-mesenchymal transition via the JAK-STAT3-SNAIL signaling
pathway. Mol Cancer Res. 9:1658–1667. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Sriuranpong V, Park JI, Amornphimoltham P,
Patel V, Nelkin BD and Gutkind JS: Epidermal growth factor
receptor-independent constitutive activation of STAT3 in head and
neck squamous cell carcinoma is mediated by the autocrine/paracrine
stimulation of the interleukin 6/gp130 cytokine system. Cancer Res.
63:2948–2956. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Alas S and Bonavida B: Rituximab
inactivates signal transducer and activation of transcription 3
(STAT3) activity in B-non-Hodgkin's lymphoma through inhibition of
the interleukin 10 autocrine/paracrine loop and results in
down-regulation of Bcl-2 and sensitization to cytotoxic drugs.
Cancer Res. 61:5137–5144. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Sano M, Fukuda K, Kodama H, Takahashi T,
Kato T, Hakuno D, Sato T, Manabe T, Tahara S and Ogawa S:
Autocrine/Paracrine secretion of IL-6 family cytokines causes
angiotensin II-induced delayed STAT3 activation. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 269:798–802. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|