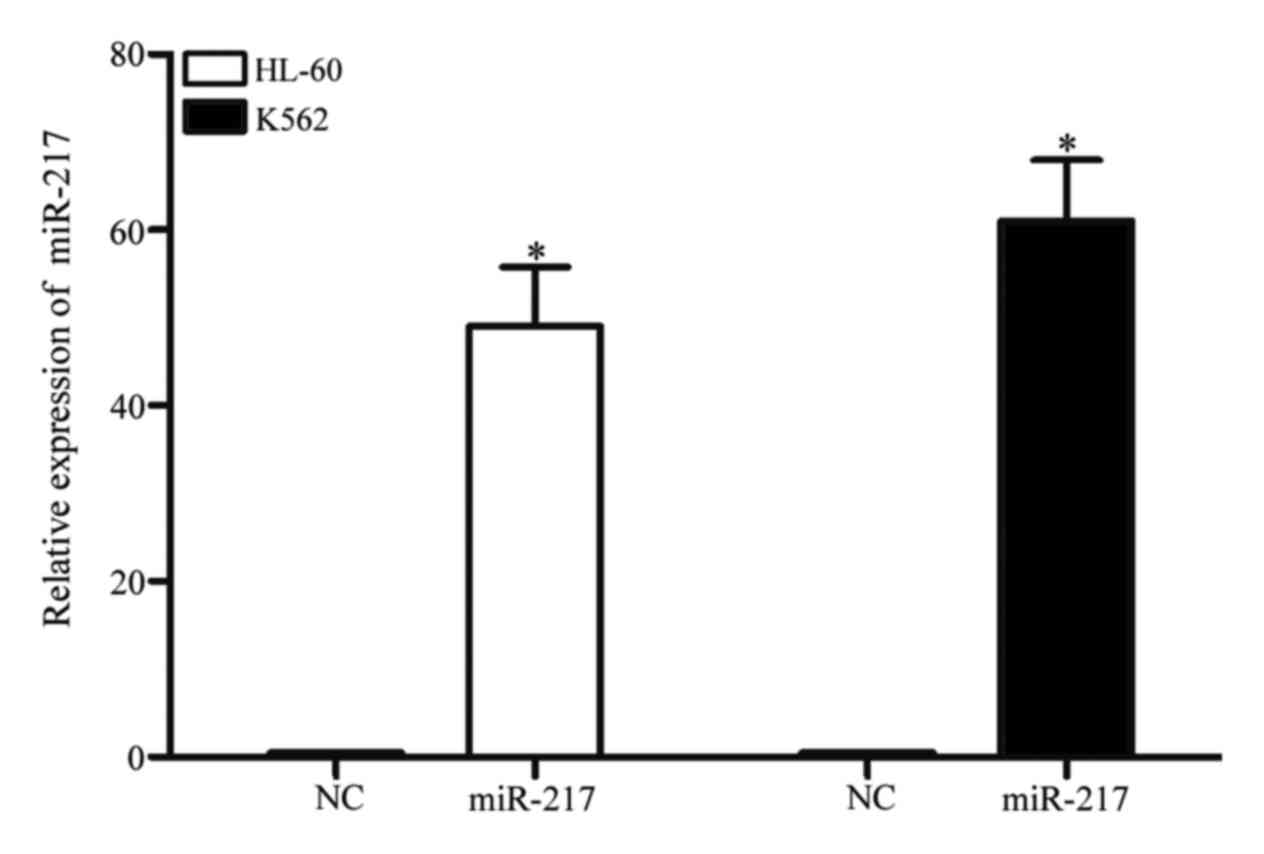
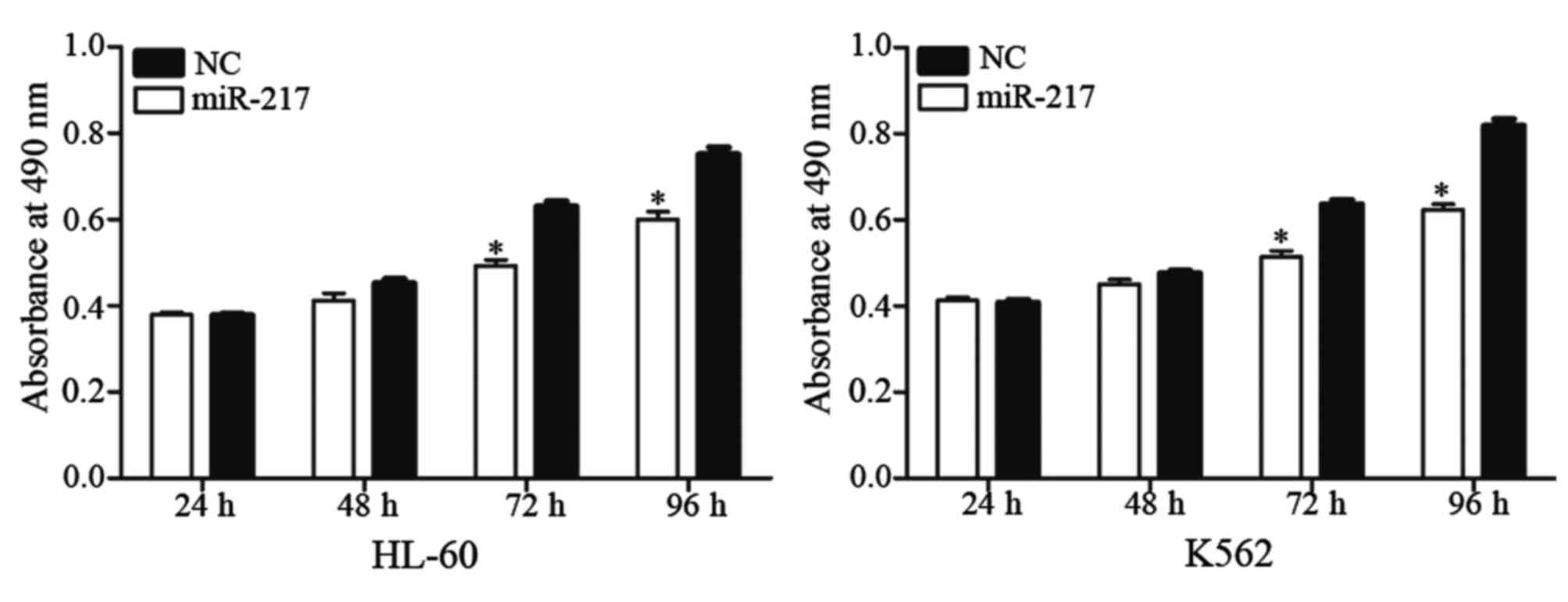
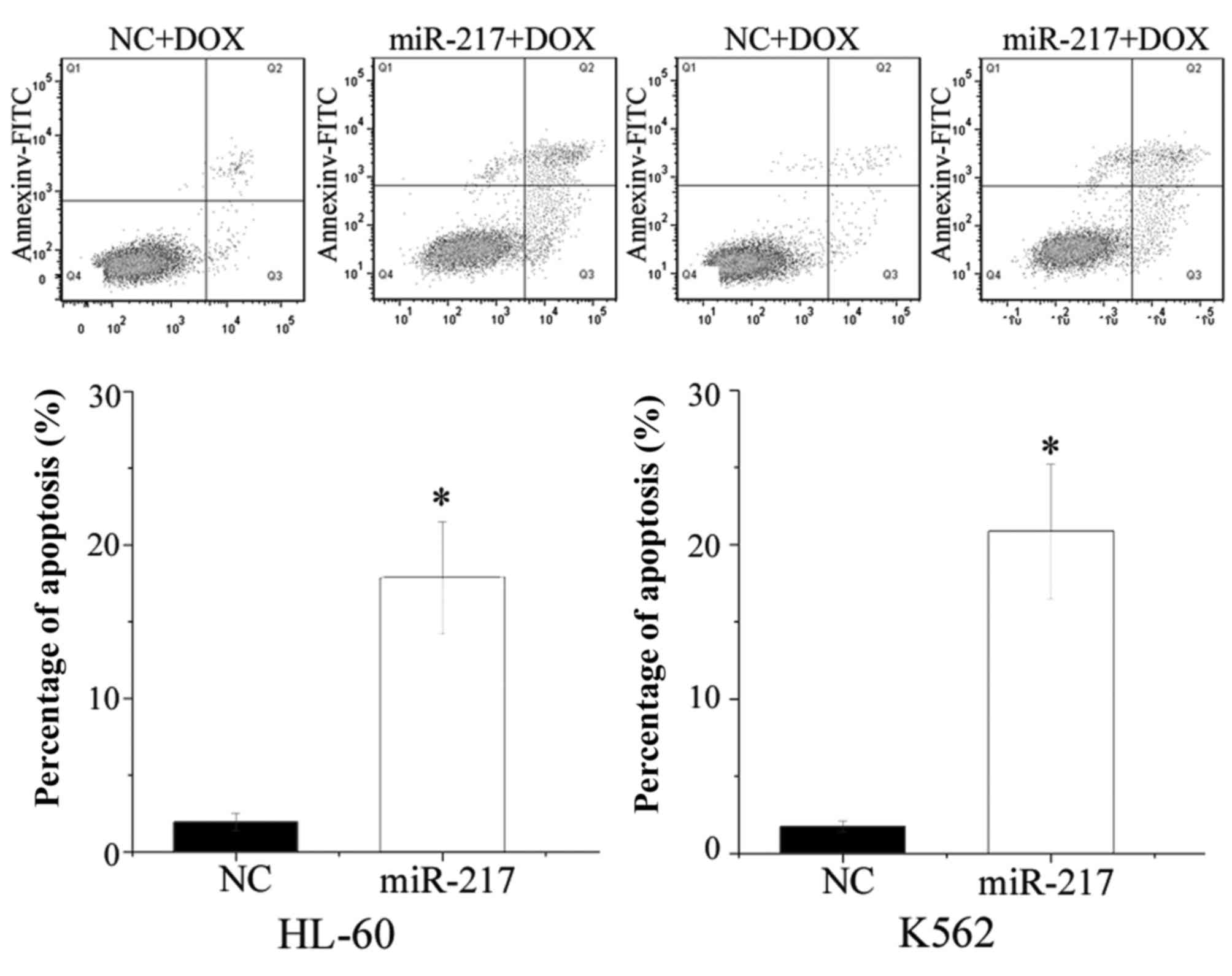
|
1
|
Das RP, Konkimalla VB, Rath SN, Hansa J
and Jagdeb M: Elucidation of the molecular interaction between
miRNAs and the HOXA9 gene, involved in acute myeloid leukemia, by
the assistance of argonaute protein through a computational
approach. Genomics Inform. 13:45–52. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Estey EH: Acute myeloid leukemia: 2013
update on risk-stratification and management. Am J Hematol.
88:318–327. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ferrara F and Schiffer CA: Acute myeloid
leukaemia in adults. Lancet. 381:484–495. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 65:5–29. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Gregory TK, Wald D, Chen Y, Vermaat JM,
Xiong Y and Tse W: Molecular prognostic markers for adult acute
myeloid leukemia with normal cytogenetics. J Hematol Oncol.
2:232009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Burnett A, Wetzler M and Löwenberg B:
Therapeutic advances in acute myeloid leukemia. J Clin Oncol.
29:487–494. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Stanisic S and Kalaycio M: Treatment of
refractory and relapsed acute myelogenous leukemia. Expert Rev
Anticancer Ther. 2:287–295. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
He L and Hannon GJ: MicroRNAs: Small RNAs
with a big role in gene regulation. Nat Rev Genet. 5:522–531. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ameres SL and Zamore PD: Diversifying
microRNA sequence and function. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 14:475–488.
2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Berindan-Neagoe I, Pdel C Monroig,
Pasculli B and Calin GA: MicroRNAome genome: A treasure for cancer
diagnosis and therapy. CA Cancer J Clin. 64:311–336. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ueda T, Volinia S, Okumura H, Shimizu M,
Taccioli C, Rossi S, Alder H, Liu CG, Oue N, Yasui W, et al:
Relation between microRNA expression and progression and prognosis
of gastric cancer: A microRNA expression analysis. Lancet Oncol.
11:136–146. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Braun J and Hüttelmaier S: Pathogenic
mechanisms of deregulated microRNA expression in thyroid carcinomas
of follicular origin. Thyroid Res. 4 Suppl 1:S12011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhang B, Pan X, Cobb GP and Anderson TA:
microRNAs as oncogenes and tumor suppressors. Dev Biol. 302:1–12.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Esquela-Kerscher A and Slack FJ:
Oncomirs-microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer.
6:259–269. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bhardwaj A, Singh S and Singh AP:
MicroRNA-based cancer therapeutics: Big hope from small RNAs. Mol
Cell Pharmacol. 2:213–219. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ryan BM, Robles AI and Harris CC: Genetic
variation in microRNA networks: The implications for cancer
research. Nat Rev Cancer. 10:389–402. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lu F, Zhang J, Ji M, Li P, Du Y, Wang H,
Zang S, Ma D, Sun X and Ji C: miR-181b increases drug sensitivity
in acute myeloid leukemia via targeting HMGB1 and Mcl-1. Int J
Oncol. 45:383–392. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Nagano H, Tomimaru Y, Eguchi H, Hama N,
Wada H, Kawamoto K, Kobayashi S, Mori M and Doki Y: MicroRNA-29a
induces resistance to gemcitabine through the Wnt/β-catenin
signaling pathway in pancreatic cancer cells. Int J Oncol.
43:1066–1072. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wu D, Niu X, Pan H, Zhang Z, Zhou Y, Qu P
and Zhou J: MicroRNA-497 targets hepatoma-derived growth factor and
suppresses human prostate cancer cell motility. Mol Med Rep.
13:2287–2292. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sun B, Yang M, Li M and Wang F: The
microRNA-217 functions as a tumor suppressor and is frequently
downregulated in human osteosarcoma. Biomed Pharmacother. 71:58–63.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wei R, Deng Z and Su J: miR-217 targeting
Wnt5a in osteosarcoma functions as a potential tumor suppressor.
Biomed Pharmacother. 72:158–164. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang H, Dong X, Gu X, Qin R, Jia H and Gao
J: The MicroRNA-217 functions as a potential tumor suppressor in
gastric cancer by targeting GPC5. PLoS One. 10:e01254742015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang B, Shen ZL, Jiang KW, Zhao G, Wang
CY, Yan YC, Yang Y, Zhang JZ, Shen C, Gao ZD, et al: MicroRNA-217
functions as a prognosis predictor and inhibits colorectal cancer
cell proliferation and invasion via an AEG-1 dependent mechanism.
BMC Cancer. 15:4372015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Guo J, Feng Z, Huang Z, Wang H and Lu W:
MicroRNA-217 functions as a tumour suppressor gene and correlates
with cell resistance to cisplatin in lung cancer. Mol Cells.
37:664–671. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Su J, Wang Q, Liu Y and Zhong M: miR-217
inhibits invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells through direct
suppression of E2F3. Mol Cell Biochem. 392:289–296. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Li H, Zhao J, Zhang JW, Huang QY, Huang
JZ, Chi LS, Tang HJ, Liu GQ, Zhu DJ and Ma WM: MicroRNA-217,
down-regulated in clear cell renal cell carcinoma and associated
with lower survival, suppresses cell proliferation and migration.
Neoplasma. 60:511–515. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Vychytilova-Faltejskova P, Kiss I, Klusova
S, Hlavsa J, Prochazka V, Kala Z, Mazanec J, Hausnerova J, Kren L,
Hermanova M, et al: MiR-21, miR-34a, miR-198 and miR-217 as
diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers for chronic pancreatitis and
pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Diagn Pathol. 10:382015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhang Q, Yuan Y, Cui J, Xiao T and Jiang
D: MiR-217 promotes tumor proliferation in breast cancer via
targeting DACH1. J Cancer. 6:184–191. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Shen L, Wang P, Yang J and Li X:
MicroRNA-217 regulates WASF3 expression and suppresses tumor growth
and metastasis in osteosarcoma. PLoS One. 9:e1091382014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zuber J, Tchernitsa OI, Hinzmann B,
Schmitz AC, Grips M, Hellriegel M, Sers C, Rosenthal A and Schäfer
R: A genome-wide survey of RAS transformation targets. Nat Genet.
24:144–152. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Crespo P and León J: Ras proteins in the
control of the cell cycle and cell differentiation. Cell Mol Life
Sci. 57:1613–1636. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wu Y, Zhuang Y, Han M, Xu T and Deng K:
Ras promotes cell survival by antagonizing both JNK and Hid signals
in the Drosophila eye. BMC Dev Biol. 9:532009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Lagadinou ED, Ziros PG, Tsopra OA, Dimas
K, Kokkinou D, Thanopoulou E, Karakantza M, Pantazis P,
Spyridonidis A and Zoumbos NC: c-Jun N-terminal kinase activation
failure is a new mechanism of anthracycline resistance in acute
myeloid leukemia. Leukemia. 22:1899–1908. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kweon SH, Song JH and Kim TS:
Resveratrol-mediated reversal of doxorubicin resistance in acute
myeloid leukemia cells via downregulation of MRP1 expression.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 395:104–110. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Tao J, Lu Q, Wu D, Li P, Xu B, Qing W,
Wang M, Zhang Z and Zhang W: ΜicroRNA-21 modulates cell
proliferation and sensitivity to doxorubicin in bladder cancer
cells. Oncol Rep. 25:1721–1729. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|