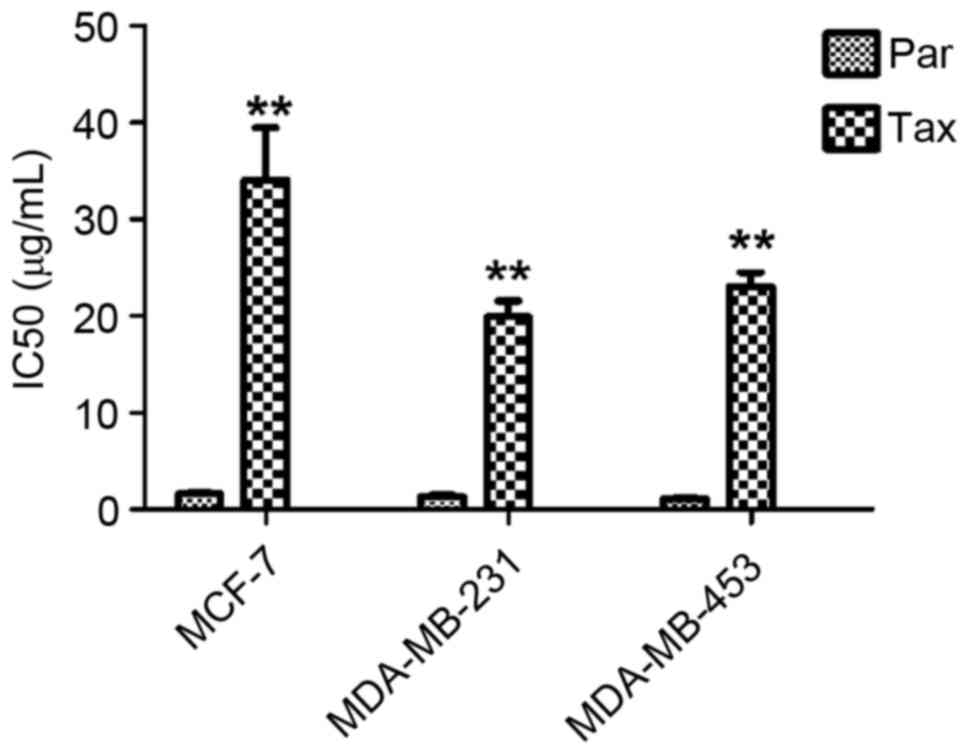
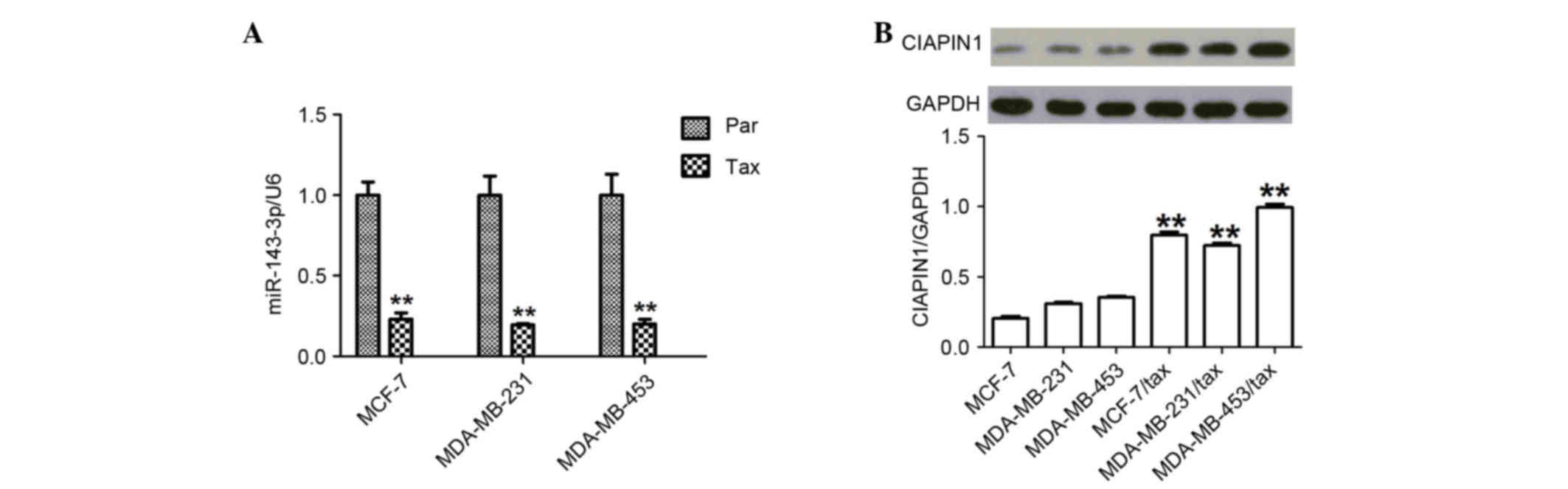
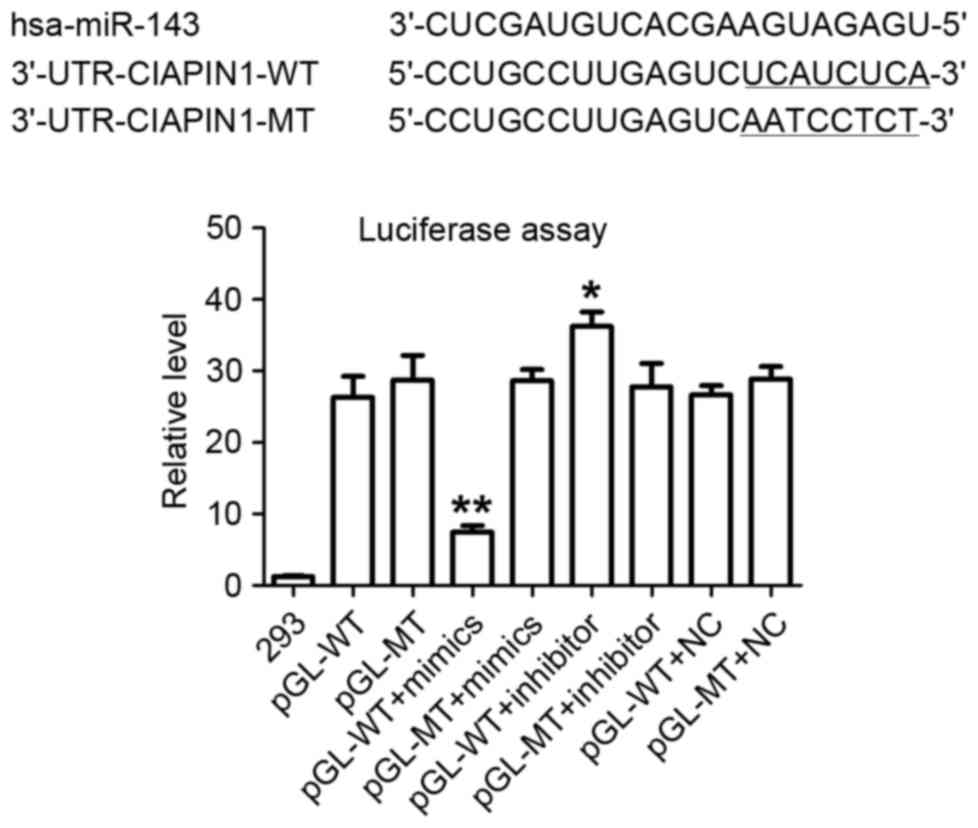
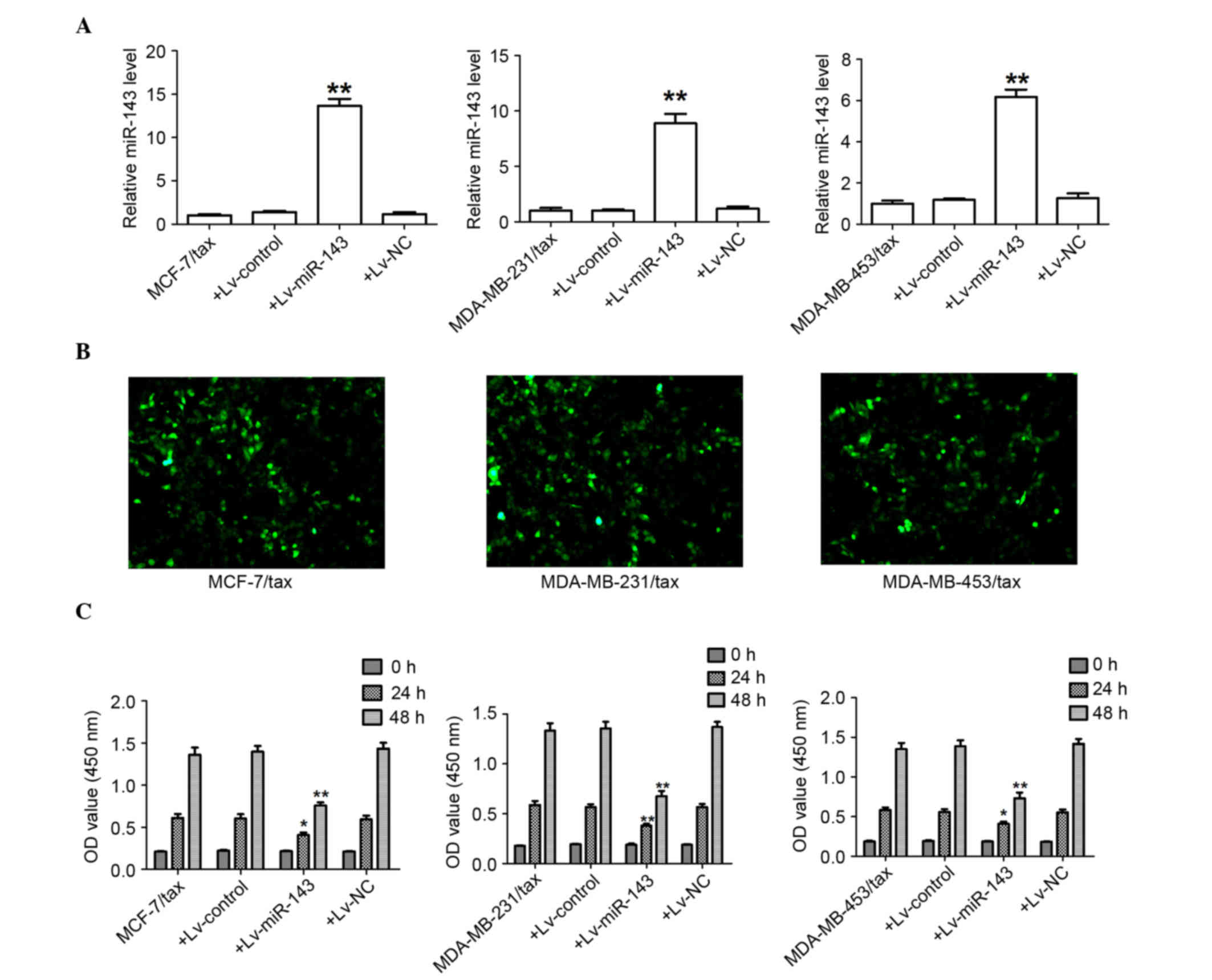
|
1
|
Guo P, Huang ZL, Yu P and Li K: Trends in
cancer mortality in China: An update. Ann Oncol. 23:2755–2762.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Seruga B, Hertz PC, Le LW and Tannock IF:
Global drug development in cancer: A cross-sectional study of
clinical trial registries. Ann Oncol. 21:895–900. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Marquette C and Nabell L:
Chemotherapy-resistant metastatic breast cancer. Curr Treat Options
Oncol. 13:263–275. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Gonzalez-Angulo AM, Morales-Vasquez F and
Hortobagyi GN: Overview of resistance to systemic therapy in
patients with breast cancer. Adv Exp Med Biol. 608:1–22. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kuo MT: Roles of multidrug resistance
genes in breast cancer chemoresistance. Adv Exp Med Biol.
608:23–30. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cascorbi I: Role of pharmacogenetics of
ATP-binding cassette transporters in the pharmacokinetics of drugs.
Pharmacol Ther. 112:457–473. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Shibayama H, Takai E, Matsumura I, Kouno
M, Morii E, Kitamura Y, Takeda J and Kanakura Y: Identification of
a cytokine-induced antiapoptotic molecule anamorsin essential for
definitive hematopoiesis. J Exp Med. 199:581–592. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hao Z, Li X, Qiao T, Du R, Hong L and Fan
D: CIAPIN1 confers multidrug resistance by upregulating the
expression of MDR-1 and MRP-1 in gastric cancer cells. Cancer Biol
Ther. 5:261–266. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Li X, Fan R, Zou X, Hong L, Gao L, Jin H,
Du R, He L, Xia L and Fan D: Reversal of multidrug resistance of
gastric cancer cells by down-regulation of CIAPIN1 with CIAPIN1
siRNA. Mol Biol (Mosk). 42:102–109. 2008.(In Russian). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li X, Hong L, Zhao Y, Jin H, Fan R, Du R,
Xia L, Luo G and Fan D: A new apoptosis inhibitor, CIAPIN1
(cytokine-induced apoptosis inhibitor1), mediates multidrug
resistance in leukemia cells by regulating MDR-1, Bcl-2, and Bax.
Biochem Cell Biol. 85:741–750. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lu D, Xiao Z, Wang W, Xu Y, Gao S, Deng L,
He W, Yang Y, Guo X and Wang X: Down regulation of CIAPIN1 reverses
multidrug resistance in human breast cancer cells by inhibiting
MDR1. Molecules. 17:7595–7611. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Li X, Wu K and Fan D: CIAPIN1 as a
therapeutic target in cancer. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 14:603–610.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Andorfer CA, Necela BM, Thompson EA and
Perez EA: MicroRNA signatures: Clinical biomarkers for the
diagnosis and treatment of breast cancer. Trends Mol Med.
17:313–319. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Shi M and Guo N: MicroRNA expression and
its implications for the diagnosis and therapeutic strategies of
breast cancer. Cancer Treat Rev. 35:328–334. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Jiang S, Zhang LF, Zhang HW, Hu S, Lu MH,
Liang S, Li B, Li Y, Li D, Wang ED and Liu MF: A novel
miR-155/miR-143 cascade controls glycolysis by regulating
hexokinase 2 in breast cancer cells. EMBO J. 31:1985–1998. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yan X, Chen X, Liang H, Deng T, Chen W,
Zhang S, Liu M, Gao X, Liu Y, Zhao C, et al: miR-143 and miR-145
synergistically regulate ERBB3 to suppress cell proliferation and
invasion in breast cancer. Mol Cancer. 13:2202014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Livak and Schmittgen: Analysis of relative
gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the
2-ΔΔCt method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Egerton N: Ixabepilone (ixempra), a
therapeutic option for locally advanced or metastatic breast
cancer. P T. 33:523–531. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang XM, Gao SJ, Guo XF, Sun WJ, Yan ZQ,
Wang WX, Xu YQ and Lu D: CIAPIN1 gene silencing enhances
chemosensitivity in a drug-resistant animal model in vivo. Braz J
Med Biol Res. 47:273–278. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang ZQ, Meng H, Wang N, Liang LN, Liu
LN, Lu SM and Luan Y: Serum microRNA 143 and microRNA 215 as
potential biomarkers for the diagnosis of chronic hepatitis and
hepatocellular carcinoma. Diagn Pathol. 9:1352014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhuang M, Shi Q, Zhang X, Ding Y, Shan L,
Shan X, Qian J, Zhou X, Huang Z, Zhu W, et al: Involvement of
miR-143 in cisplatin resistance of gastric cancer cells via
targeting IGF1R and BCL2. Tumour Biol. 36:2737–2745. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|