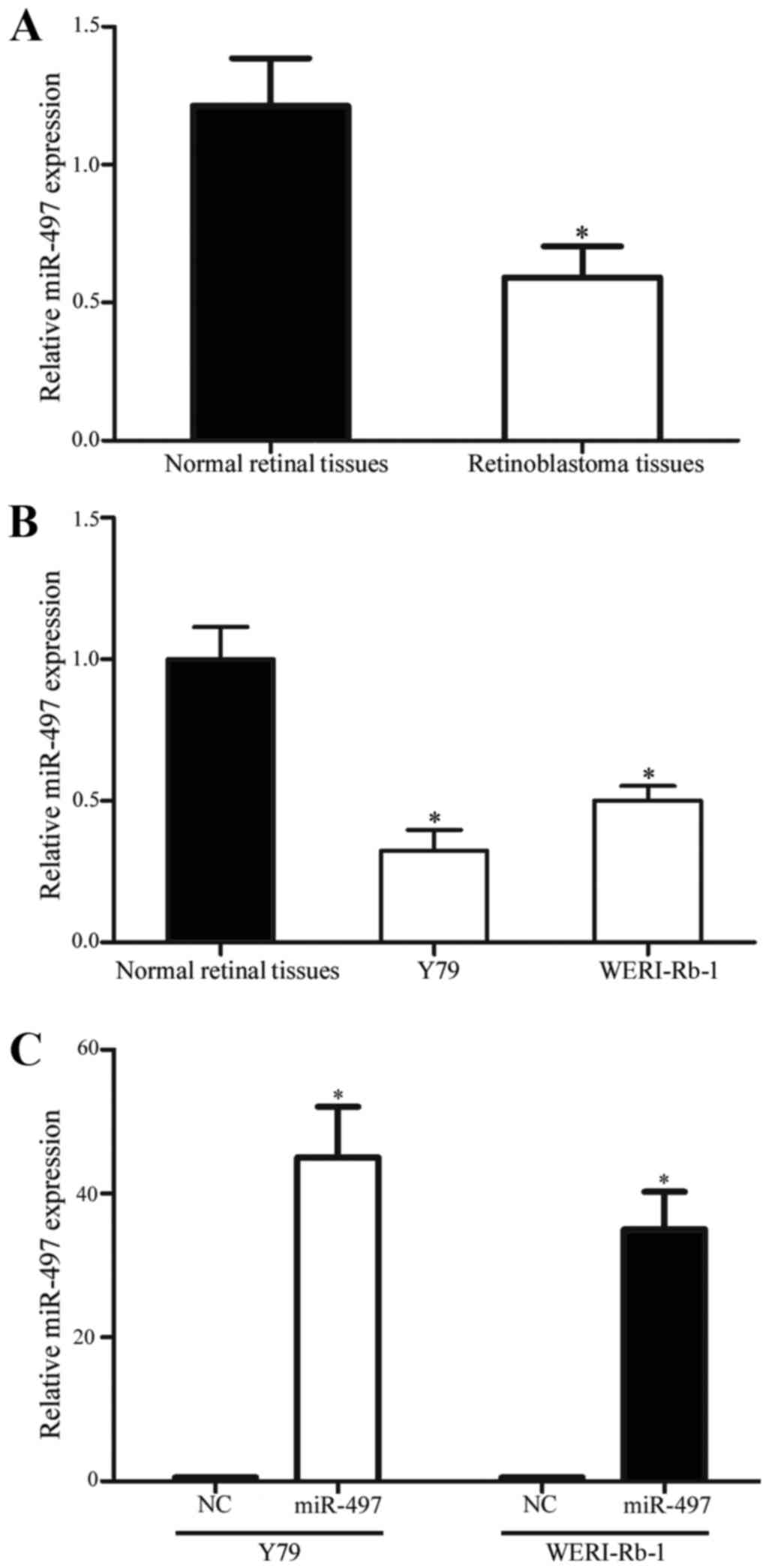
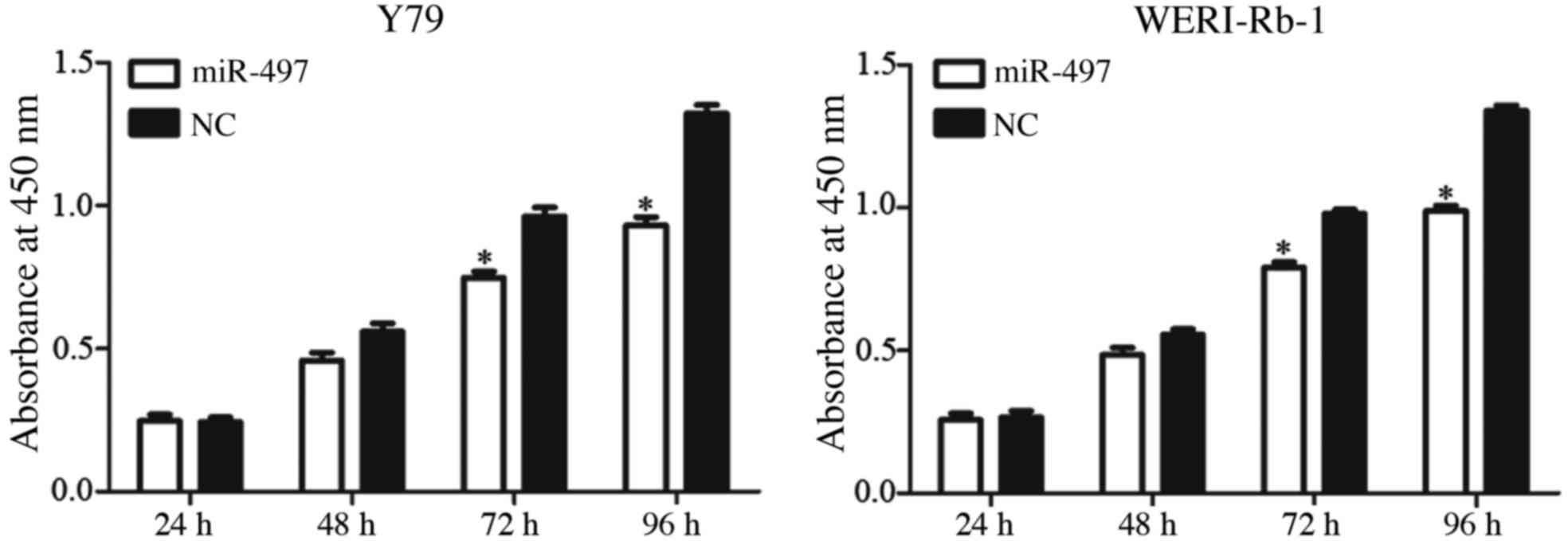
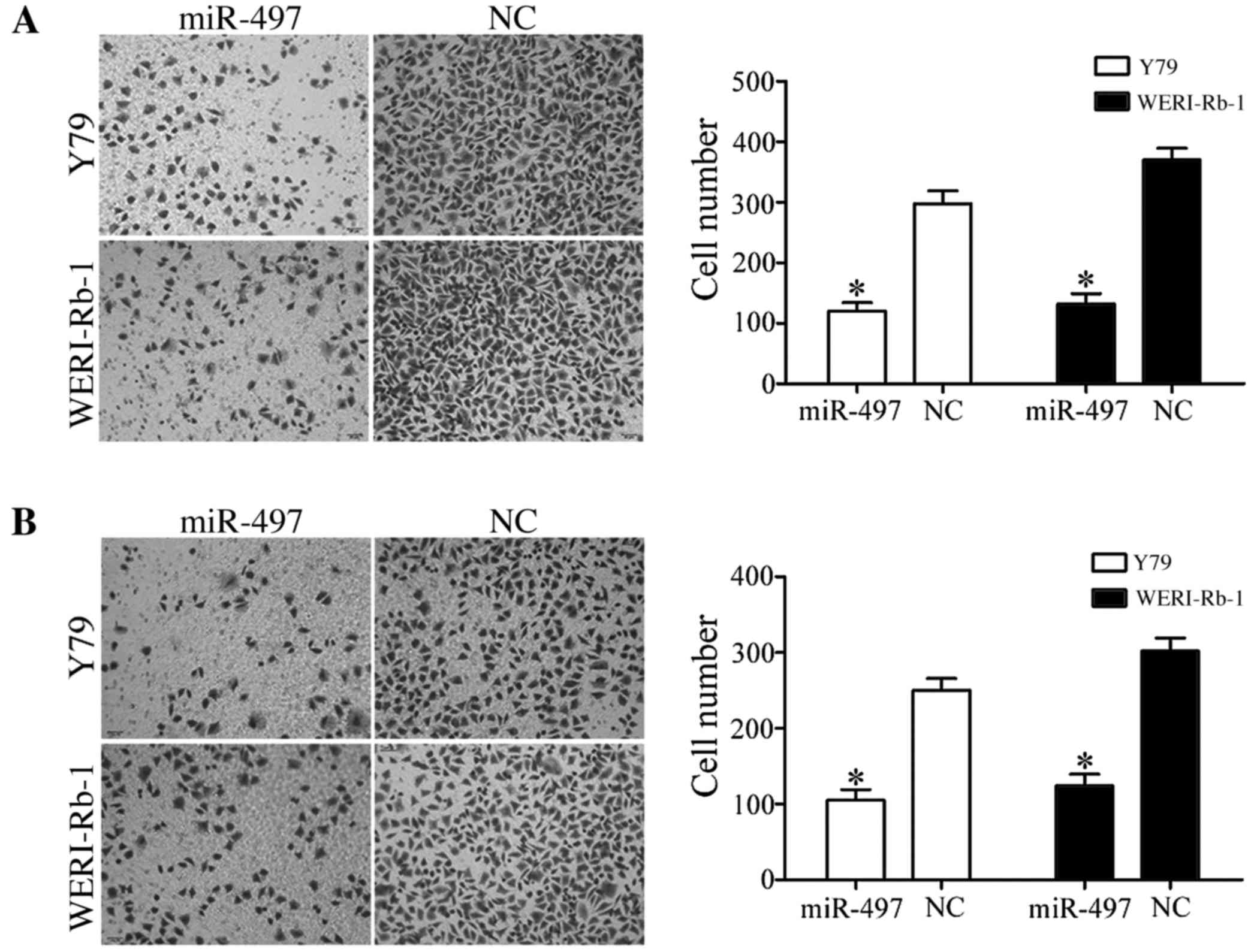
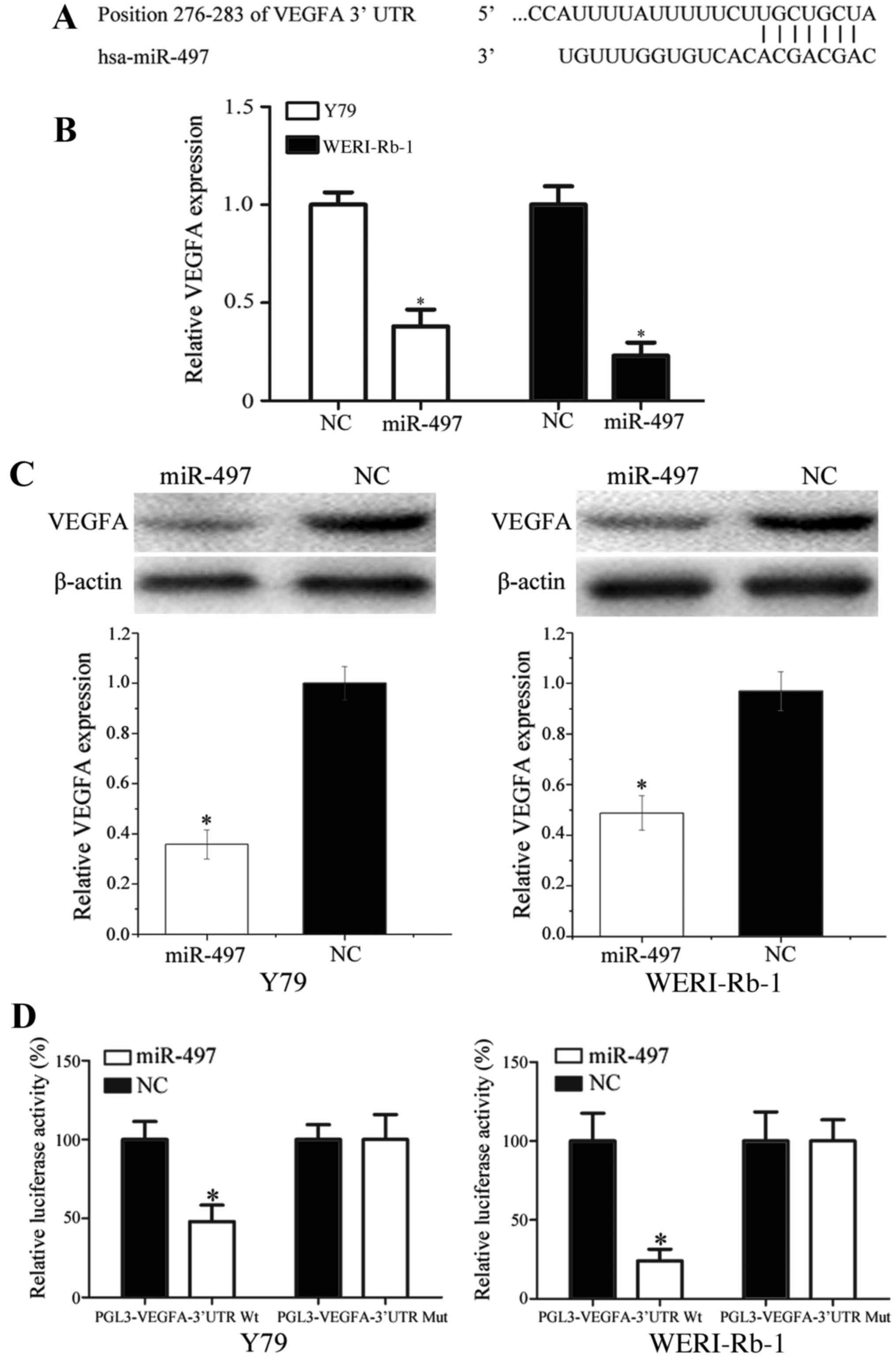
|
1
|
Broaddus E, Topham A and Singh AD:
Incidence of retinoblastoma in the USA: 1975–2004. Br J Ophthalmol.
93:21–23. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
MacCarthy A, Draper GJ, Steliarova-Foucher
E and Kingston JE: Retinoblastoma incidence and survival in
European children (1978–1997). Report from the automated childhood
cancer information system project. Eur J Cancer. 42:2092–2102.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 65:5–29. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Beta M, Venkatesan N, Vasudevan M,
Vetrivel U, Khetan V and Krishnakumar S: Identification and
insilico analysis of retinoblastoma serum microRNA profile and gene
targets towards prediction of novel serum biomarkers. Bioinform
Biol Insights. 7:21–34. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wang J, Wang X, Wu G, Hou D and Hu Q:
MiR-365b-3p, down-regulated in retinoblastoma, regulates cell cycle
progression and apoptosis of human retinoblastoma cells by
targeting PAX6. FEBS Lett. 587:1779–1786. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Shields CL and Shields JA: Diagnosis and
management of retinoblastoma. Cancer Control. 11:317–327.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Xu X, Jia R, Zhou Y, Song X, Wang J, Qian
G, Ge S and Fan X: Microarray-based analysis: Identification of
hypoxia-regulated microRNAs in retinoblastoma cells. Int J Oncol.
38:1385–1393. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Friedman DL, Himelstein B, Shields CL,
Shields JA, Needle M, Miller D, Bunin GR and Meadows AT:
Chemoreduction and local ophthalmic therapy for intraocular
retinoblastoma. J Clin Oncol. 18:12–17. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Mehta M, Sethi S, Pushker N, Kashyap S,
Sen S, Bajaj MS and Ghose S: Retinoblastoma. Singapore Med J.
53:128–135. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Shen F, Mo MH, Chen L, An S, Tan X, Fu Y,
Rezaei K, Wang Z, Zhang L and Fu SW: MicroRNA-21 down-regulates Rb1
expression by targeting PDCD4 in retinoblastoma. J Cancer.
5:804–812. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang J, Wang X, Li Z, Liu H and Teng Y:
MicroRNA-183 suppresses retinoblastoma cell growth, invasion and
migration by targeting LRP6. FEBS J. 281:1355–1365. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Dalgard CL, Gonzalez M, deNiro JE and
O'Brien JM: Differential microRNA-34a expression and tumor
suppressor function in retinoblastoma cells. Invest Ophthalmol Vis
Sci. 50:4542–4551. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ambros V: The functions of animal
microRNAs. Nature. 431:350–355. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hwang HW and Mendell JT: MicroRNAs in cell
proliferation, cell death, and tumorigenesis. Br J Cancer. 96
Suppl:R40–R44. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Calin GA, Ferracin M, Cimmino A, Di Leva
G, Shimizu M, Wojcik SE, Iorio MV, Visone R, Sever NI, Fabbri M, et
al: A MicroRNA signature associated with prognosis and progression
in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 353:1793–1801. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sun YC, Wang J, Guo CC, Sai K, Wang J,
Chen FR, Yang QY, Chen YS, Wang J, To TS, et al: MiR-181b
sensitizes glioma cells to teniposide by targeting MDM2. BMC
Cancer. 14:6112014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ventura A and Jacks T: MicroRNAs and
cancer: Short RNAs go a long way. Cell. 136:586–591. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Finnerty JR, Wang WX, Hébert SS, Wilfred
BR, Mao G and Nelson PT: The miR-15/107 group of microRNA genes:
Evolutionary biology, cellular functions, and roles in human
diseases. J Mol Biol. 402:491–509. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Harries LW: Long non-coding RNAs and human
disease. Biochem Soc Trans. 40:902–906. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Guo ST, Jiang CC, Wang GP, Li YP, Wang CY,
Guo XY, Yang RH, Feng Y, Wang FH, Tseng HY, et al: MicroRNA-497
targets insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor and has a tumour
suppressive role in human colorectal cancer. Oncogene.
32:1910–1920. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bailey-Wilson JE, Amos CI, Pinney SM,
Petersen GM, de Andrade M, Wiest JS, Fain P, Schwartz AG, You M,
Franklin W, et al: A major lung cancer susceptibility locus maps to
chromosome 6q23-25. Am J Hum Genet. 75:460–474. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Tseng RC, Chang JW, Hsien FJ, Chang YH,
Hsiao CF, Chen JT, Chen CY, Jou YS and Wang YC: Genomewide loss of
heterozygosity and its clinical associations in non small cell lung
cancer. Int J Cancer. 117:241–247. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Han Z, Zhang Y, Yang Q, Liu B, Wu J, Zhang
Y, Yang C and Jiang Y: miR-497 and miR-34a retard lung cancer
growth by co-inhibiting cyclin E1 (CCNE1). Oncotarget.
6:13149–13163. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhao X, Zhao Z, Xu W, Hou J and Du X:
Down-regulation of miR-497 is associated with poor prognosis in
renal cancer. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:758–764. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Xu J, Wang T, Cao Z, Huang H, Li J, Liu W,
Liu S, You L, Zhou L, Zhang T and Zhao Y: MiR-497 downregulation
contributes to the malignancy of pancreatic cancer and associates
with a poor prognosis. Oncotarget. 5:6983–6993. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Xie Y, Wei RR, Huang GL, Zhang MY, Yuan YF
and Wang HY: Checkpoint kinase 1 is negatively regulated by miR-497
in hepatocellular carcinoma. Med Oncol. 31:8442014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hiroki E, Akahira J, Suzuki F, Nagase S,
Ito K, Suzuki T, Sasano H and Yaegashi N: Changes in microRNA
expression levels correlate with clinicopathological features and
prognoses in endometrial serous adenocarcinomas. Cancer Sci.
101:241–249. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chen HC, Chen GH, Chen YH, Liao WL, Liu
CY, Chang KP, Chang YS and Chen SJ: MicroRNA deregulation and
pathway alterations in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Br J Cancer.
100:1002–1011. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Li D, Zhao Y, Liu C, Chen X, Qi Y, Jiang
Y, Zou C, Zhang X, Liu S, Wang X, et al: Analysis of MiR-195 and
MiR-497 expression, regulation and role in breast cancer. Clin
Cancer Res. 17:1722–1730. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Guo J, Miao Y, Xiao B, Huan R, Jiang Z,
Meng D and Wang Y: Differential expression of microRNA species in
human gastric cancer versus non-tumorous tissues. J Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 24:652–657. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wang L, Li B, Li L and Wang T:
MicroRNA-497 suppresses proliferation and induces apoptosis in
prostate cancer cells. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 14:3499–3502. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kong XJ, Duan LJ, Qian XQ, Xu D, Liu HL,
Zhu YJ and Qi J: Tumor-suppressive microRNA-497 targets IKKb to
regulate NF-κB signaling pathway in human prostate cancer cells. Am
J Cancer Res. 5:1795–1804. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wang W, Ren F, Wu Q, Jiang D, Li H and Shi
H: MicroRNA-497 suppresses angiogenesis by targeting vascular
endothelial growth factor A through the PI3K/AKT and MAPK/ERK
pathways in ovarian cancer. Oncol Rep. 32:2127–2133.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Han J, Huo M, Mu M, Liu J and Zhang J:
miR-497 suppresses proliferation of human cervical carcinoma HeLa
cells by targeting cyclin E1. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi.
30:597–600. 2014.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Luo M, Shen D, Zhou X, Chen X and Wang W:
MicroRNA-497 is a potential prognostic marker in human cervical
cancer and functions as a tumor suppressor by targeting the
insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor. Surgery. 153:836–847. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Fan L, Wu Q, Xing X, Wei Y and Shao Z:
MicroRNA-145 targets vascular endothelial growth factor and
inhibits invasion and metastasis of osteosarcoma cells. Acta
Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 44:407–414. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Youssef NS and Said AM:
Immunohistochemical expression of CD117 and vascular endothelial
growth factor in retinoblastoma: Possible targets of new therapies.
Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 7:5725–5737. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zhuang Y and Wei M: Impact of vascular
endothelial growth factor expression on overall survival in
patients with osteosarcoma: A meta-analysis. Tumour Biol.
35:1745–1749. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Liu Y, Zheng Q, Wu H, Guo X, Li J and Hao
S: Rapamycin increases pCREB, Bcl-2, and VEGF-A through ERK under
normoxia. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 45:259–267. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Wiszniak S, Mackenzie FE, Anderson P,
Kabbara S, Ruhrberg C and Schwarz Q: Neural crest cell-derived VEGF
promotes embryonic jaw extension. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 112:pp.
6086–6091. 2015; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Yang X, Chen BB, Zhang MH and Wang XR:
MicroRNA-126 inhibits the proliferation of lung cancer cell line
A549. Asian Pac J Trop Med. 8:239–242. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Zhang Z, Zhang Y, Sun XX, Ma X and Chen
ZN: microRNA-146a inhibits cancer metastasis by downregulating VEGF
through dual pathways in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Cancer.
14:52015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Wang R, Tian S, Wang HB, Chu DP, Cao JL,
Xia HF and Ma X: MiR-185 is involved in human breast carcinogenesis
by targeting Vegfa. FEBS Lett. 588:4438–4447. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Zhao D, Jia P, Wang W and Zhang G:
VEGF-mediated suppression of cell proliferation and invasion by
miR-410 in osteosarcoma. Mol Cell Biochem. 400:87–95. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|