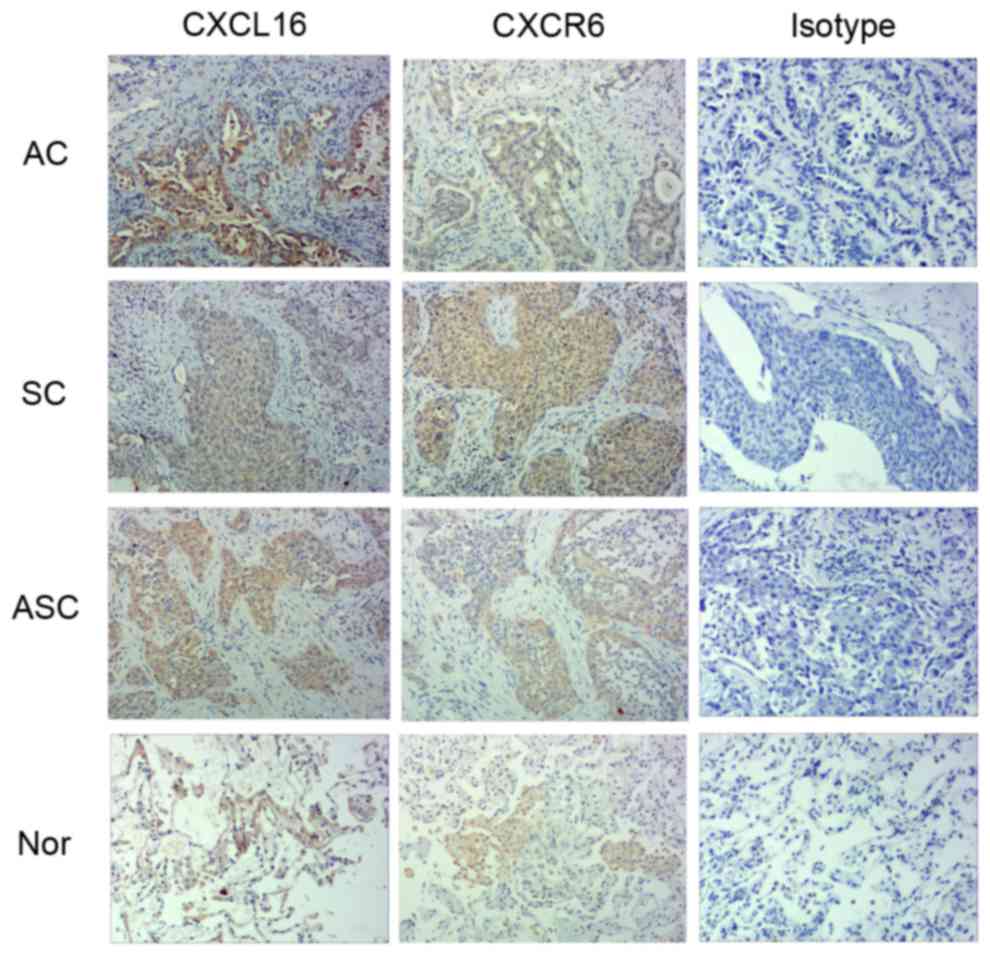
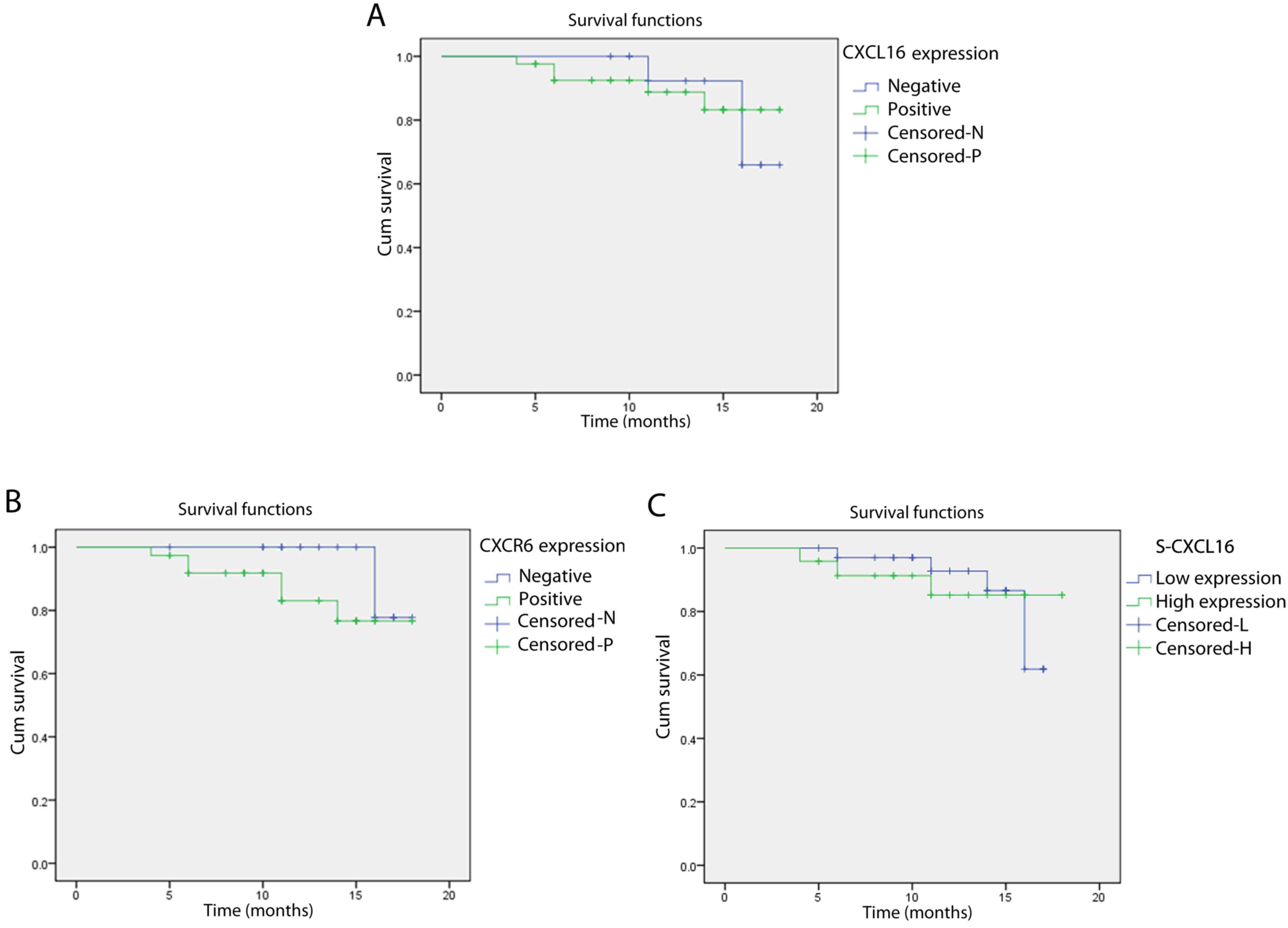
|
1
|
Bray F, Ren JS, Masuyer E and Ferlay J:
Global estimates of cancer prevalence for 27 sites in the adult
population in 2008. Int J Cancer. 132:1133–1145. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 64:9–29. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wood SL, Pernemalm M, Crosbie PA and
Whetton AD: The role of the tumor-microenvironment in lung
cancer-metastasis and its relationship to potential therapeutic
targets. Cancer Treat Rev. 40:558–566. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Gerber PA, Hippe A, Buhren BA, Müller A
and Homey B: Chemokines in tumour associated angiogenesis. Biol
Chem. 390:1213–1223. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Raman D, Baugher PJ, Thu YM and Richmond
A: Role of chemokines in tumor growth. Cancer Lett. 256:137–165.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Vandercappellen J, Van Damme J and Struyf
S: The role of CXC chemokines and their receptors in cancer. Cancer
Lett. 267:226–244. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sarvaiya PJ, Guo D, Ulasov I, Gabikian P
and Lesniak MS: Chemokines in tumor progression and metastasis.
Oncotarget. 4:2171–2185. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Keeley EC, Mehrad B and Strieter RM: CXC
chemokines in cancer angiogenesis and metastases. Adv Cancer Res.
106:91–111. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Matloubian M, David A, Engel S, Ryan JE
and Cyster JG: A transmembrane CXC chemokine is a ligand for
HIV-coreceptor Bonzo. Nat Immunol. 1:298–304. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Shimaoka T, Kume N, Minami M, Hayashida K,
Kataoka H, Kita T and Yonehara S: Molecular cloning of a novel
scavenger receptor for oxidized low density lipoprotein, SR-PSOX,
on macrophages. J Biol Chem. 275:40663–40666. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wilbanks A, Zondlo SC, Murphy K, Mak S,
Soler D, Langdon P, Andrew DP, Wu L and Briskin M: Expression
cloning of the STRL33/BONZO/TYMSTR ligand reveals elements of CC,
CXC and CX3C chemokines. J Immunol. 166:5145–5154. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hattermann K, Ludwig A, Gieselmann V,
Held-Feindt J and Mentlein R: The chemokine CXCL16 induces
migration and invasion of glial precursor cells via its receptor
CXCR6. Mol Cell Neurosci. 39:133–141. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hara T, Katakai T, Lee JH, Nambu Y,
Nakajima-Nagata N, Gonda H, Sugai M and Shimizu A: A transmembrane
chemokine, CXC chemokine ligand 16, expressed by lymph node
fibroblastic reticular cells has the potential to regulate T cell
migration and adhesion. Int Immunol. 18:301–311. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Huang Y, Zhu XY, Du MR, Wu X, Wang MY and
Li DJ: Chemokine CXCL16, a scavenger receptor, induces
proliferation and invasion of firsttrimester human trophoblast
cells in an autocrine manner. Hum Reprod. 21:1083–1091. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Deng L, Chen N, Li Y, Zheng H and Lei Q:
CXCR6/CXCL16 functions as a regulator in metastasis and progression
of cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1806:42–49. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Darash-Yahana M, Gillespie JW, Hewitt SM,
Chen YY, Maeda S, Stein I, Singh SP, Bedolla RB, Peled A, Troyer
DA, et al: The chemokine CXCL16 and its receptor, CXCR6, as markers
and promoters of inflammation-associated cancers. PLoS One.
4:e66952009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hu W, Zhen X, Xiong B, Wang B, Zhang W and
Zhou W: CXCR6 is expressed in human prostate cancer in vivo and is
involved in the in vitro invasion of PC3 and LNCap cells. Cancer
Sci. 99:1362–1369. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Meijer J, Ogink J, Kreike B, Nuyten D, de
Visser KE and Roos E: The chemokine receptor CXCR6 and its ligand
CXCL16 are expressed in carcinomas and inhbit proliferation. Cancer
Res. 68:4701–4708. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Gutwein P, Schramme A, Sinke N,
Abdel-Bakky MS, Voss B, Obermüller N, Doberstein K, Koziolek M,
Fritzsche F, Johannsen M, et al: Tumoural CXCL16 expression is a
novel prognostic marker of longer survival times in renal cell
cancer patients. Eur J Cancer. 45:478–489. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ou DL, Chen CL, Lin SB, Hsu CH and Lin LI:
Chemokine receptor expression profiles in nasopharyngeal carcinoma
and their association with metastasis and radiotherapy. J Pathol.
210:363–373. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lee JT, Lee SD, Lee JZ, Chung MK and Ha
HK: Expression analysis and clinical significance of CXCL16/CXCR6
in patients with bladder cancer. Oncol Lett. 5:229–235.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hu W, Liu Y, Zhou W, Si L and Ren L:
CXCL16 and CXCR6 are coexpressed in human lung cancer in vivo and
mediate the invasion of lung cancer cell lines in vitro. PLoS One.
9:e990562014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Groome PA, Bolejack V, Crowley JJ, Kennedy
C, Krasnik M, Sobin LH and Goldstraw P; IASLC International Staging
Committee, : Cancer Research and Biostatistics; Observers to the
Committee; Participating Institutions: The IASLC lung cancer
staging project: Validation of the proposals for revision of the T
N and M descriptors and consequent stage groupings in the
forthcoming (seventh) edition of the TNM classification of
malignant tumours. J Thorac Oncol. 2:694–705. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Day C, Patel R, Guillen C and Wardlaw AJ:
The chemokine CXCL16 is highly and constitutively expressed by
human bronchial epithelial cells. Exp Lung Res. 35:272–283. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sallusto F, Mackay CR and Lanzavecchia A:
The role of chemokine receptors in primary, effector, and memory
immune responses. Annu Rev Immunol. 18:593–620. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kamp DW, Shacter E and Weitzman SA:
Chronic inflammation and cancer: The role of the mitochondria.
Oncology (Williston Park). 25:400–410, 413. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Pikarsky E, Porat RM, Stein I, Abramovitch
R, Amit S, Kasem S, Gutkovich-Pyest E, Urieli-Shoval S, Galun E and
Ben-Neriah Y: NF-kappaB functions as a tumour promoter in
inflammation-associated cancer. Nature. 431:461–466. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hald SM, Kiselev Y, Al-Saad S, Richardsen
E, Johannessen C, Eilertsen M, Kilvaer TK, Al-Shibli K, Andersen S,
Busund LT, et al: Prognostic impact of CXCL16 and CXCR6 in
non-small cell lung cancer: Combined high CXCL16 expression in
tumor stroma and cancer cells yields improved survival. BMC Cancer.
15:4412015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|