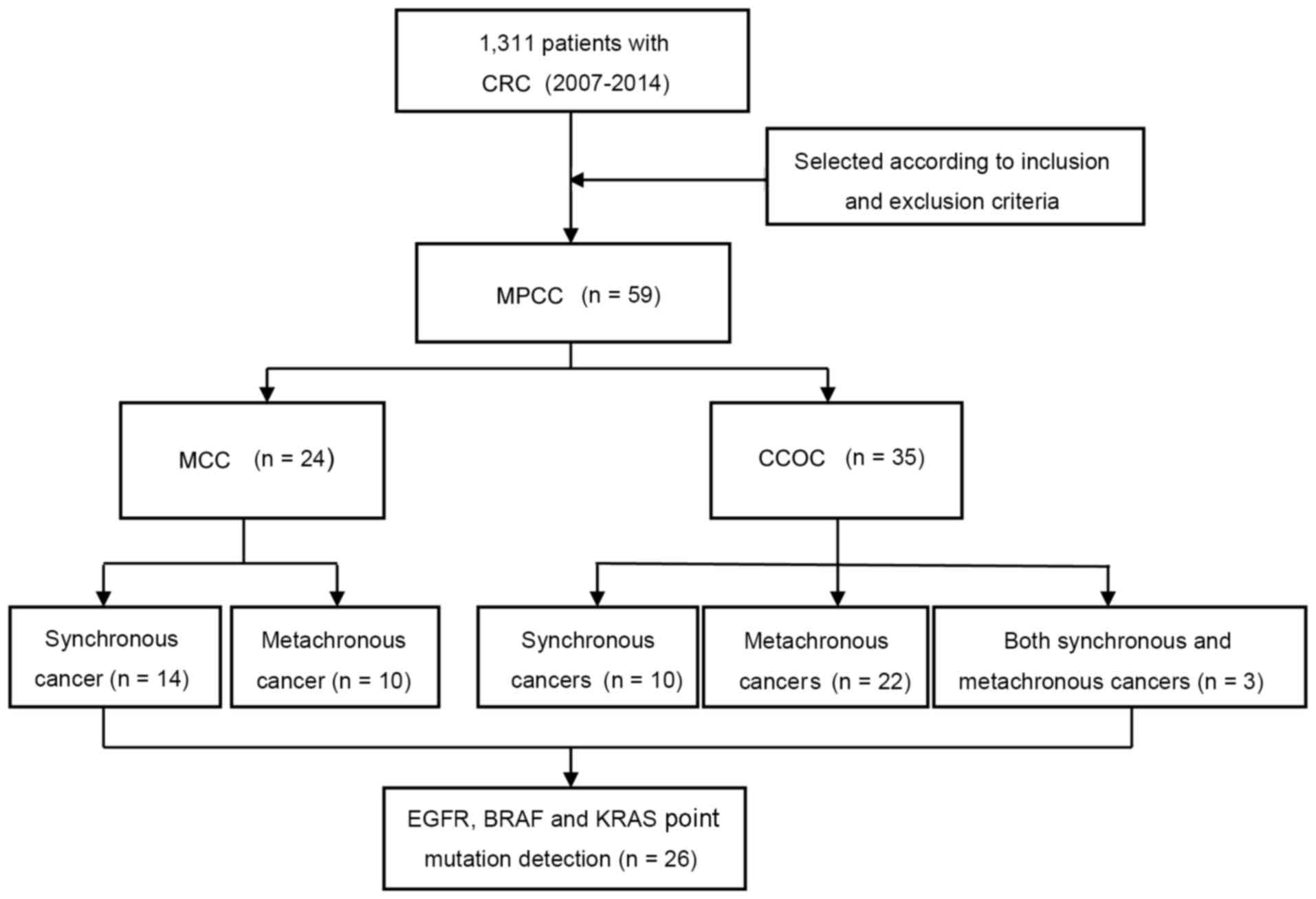
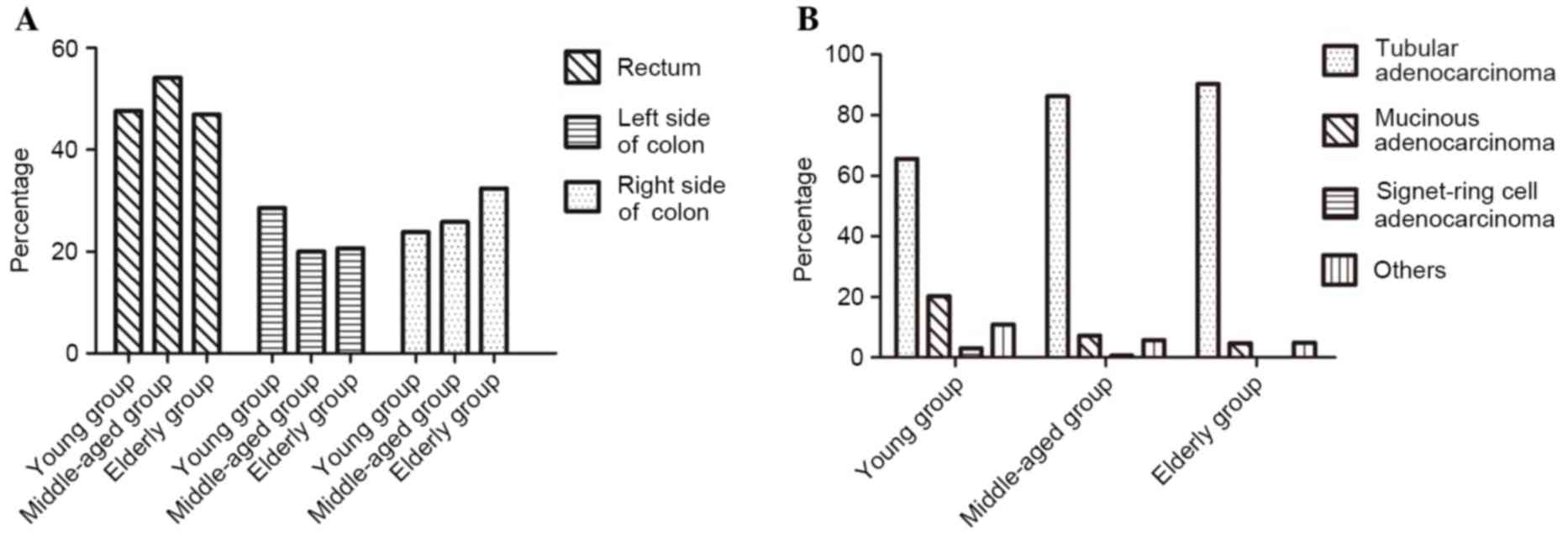
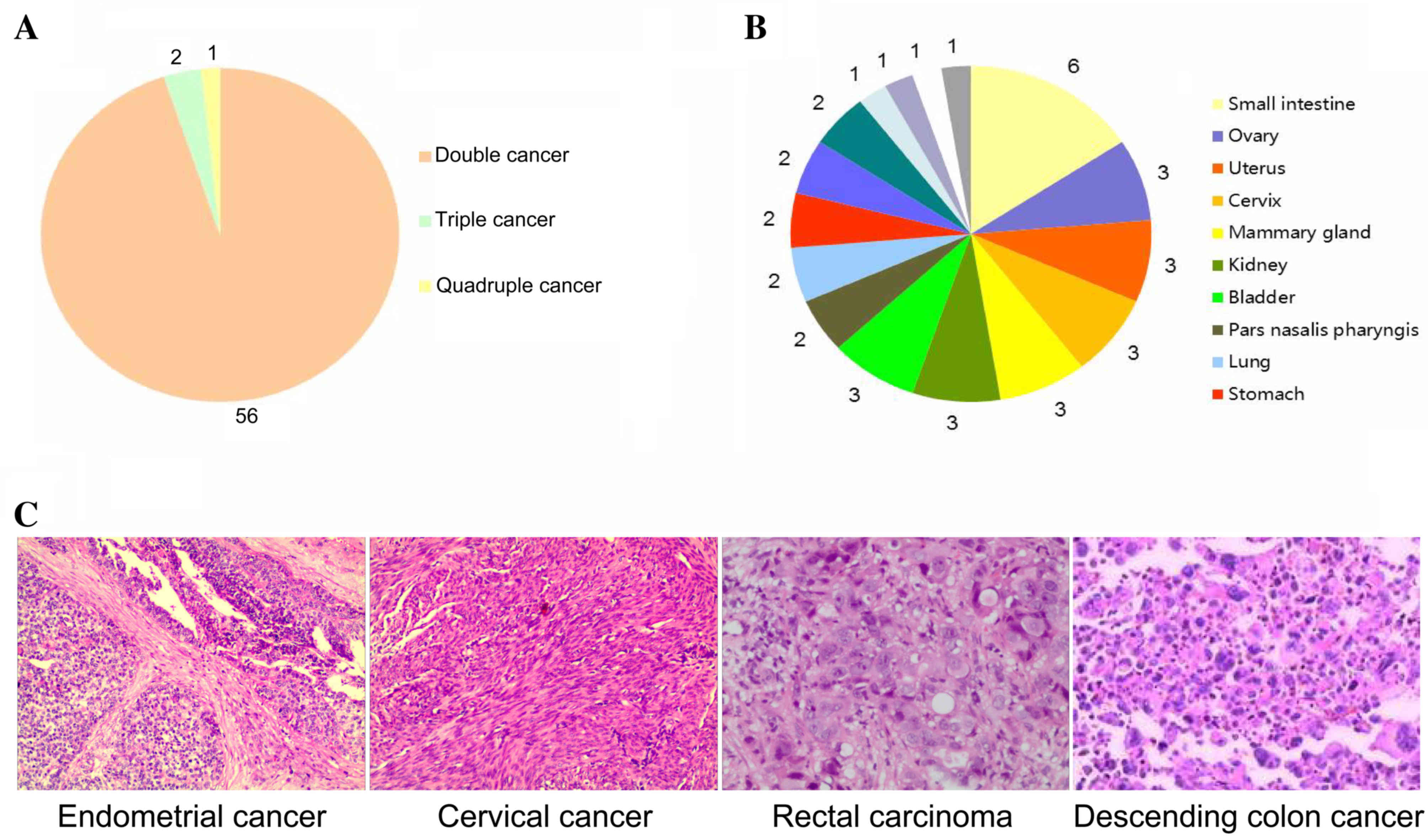
|
1
|
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser
S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D and Bray F: Cancer
incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major
patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 136:E359–E386. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Zeng H, Zhang S and He J:
Annual report on status of cancer in China, 2011. Chin J Cancer
Res. 27:2–12. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Dai Z, Zheng RS, Zou XN, Zhang SW, Zeng
HM, Li N and Chen WQ: Analysis and prediction of colorectal cancer
incidence trend in China. Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zh.
46:598–603. 2012.(In Chinese).
|
|
4
|
Shen Y, Han X, Wang J, Wang S, Yang H, Lu
SH and Shi Y: Prognostic impact of mutation profiling in patients
with stage II and III colon cancer. Sci Rep. 6:243102016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kriegsmann M, Arens N, Endris V, Weichert
W and Kriegsmann J: Detection of KRAS NRAS and BRAF by mass
spectrometry-a sensitive, reliable, fast and cost-effective
technique. Diagn Pathol. 10:1322015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ueno M, Muto T, Oya M, Ota H, Azekura K
and Yamaguchi T: Multiple primary cancer: An experience at the
Cancer Institute Hospital with special reference to colorectal
cancer. Int J Clin Oncol. 8:162–167. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Warren S and Gates O: Carcinoma of
ceruminous gland. Am J Pathol. 17:821–826.3. 1941.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lee TK, Barringer M, Myers RT and Sterchi
JM: Multiple primary carcinomas of the colon and associated
extracolonic primary malignant tumors. Ann Surg. 195:501–507. 1982.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Li M and Gu J: Changing patterns of
colorectal cancer in China over a period of 20 years. World J
Gastroenterol. 11:4685–4688. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
McCashland TM, Brand R, Lyden E and de
Garmo P: CORI Research Project: Gender differences in colorectal
polyps and tumors. Am J Gastroenterol. 96:882–886. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lacopetta B: Are there two sides to
colorectal cancer? Int J Cancer. 101:403–408. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Stewart SL, Wike JM, Kato I, Lewis DR and
Michaud F: A population-based study of colorectal cancer histology
in the United States, 1998–2001. Cancer. 107 5 Suppl:S1128–S1141.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Morton LM, Swerdlow AJ, Schaapveld M,
Ramadan S, Hodgson DC, Radford J and van Leeuwen FE: Current
knowledge and future research directions in treatment-related
second primary malignancies. EJC Suppl. 12:S5–S17. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Morton LM, Onel K, Curtis RE, Hungate EA
and Armstrong GT: The rising incidence of second cancers: Patterns
of occurrence and identification of risk factors for children and
adults. Am Soc Clin Oncol Educ Book. e57–e67. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
da Silva SD, Morand GB, Alobaid FA, Hier
MP, Mlynarek AM, Alaoui-Jamali MA and Kowalski LP:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) markers have prognostic
impact in multiple primary oral squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Exp
Metastasis. 32:55–63. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Jung YS, Lim J, Jung KW, Ryu J and Won YJ:
Metachronous second primary malignancies after head and neck cancer
in a Korean cohort (1993–2010). PLoS One. 10:e01341602015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chen HS and Sheen-Chen SM: Synchronous and
‘early’ metachronous colorectal adenocarcinoma: Analysis of
prognosis and current trends. Dis Colon Rectum. 43:1093–1099. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Takeuchi H, Toda T, Nagasaki S, Kawano T,
Minamisono Y, Maehara Y and Sugimachi K: Synchronous multiple
colorectal adenocarcinomas. J Surg Oncol. 64:304–307. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Bertolaccini L and Olivero G: Hereditary
non polyposis colorectal cancer (HNPCC). A clinical and genetic
entity. Minerva Chir. 57:63–72. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hodadoostan MK, Reza F, Elham M, Alizade
AH Mohammad, Molaie M, Mashaiekhy R, Doagoo SZ, Moosavy M, Malek FN
and Zali MR: Clinical and pathology characteristics of colorectal
polyps in Iranian population. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 11:557–560.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yoshida D, Kono S, Moore MA, Toyomura K,
Nagano J, Mizoue T, Mibu R, Tanaka M, Kakeji Y, Maehara Y, et al:
Colorectal polypectomy and risk of colorectal cancer by subsite:
The Fukuoka colorectal cancer study. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 37:597–602.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Papadopoulos V, Michalopoulos A, Baanis G,
Papapolychroniadis K, Paramythiotis D, Fotiadis P, Berovalis P and
Harlaftis N: Synchronous and metachronous colorectal carcinoma.
Tech Coloproctol. 8 Suppl 1:s97–s100. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Brown SR, Finan PJ, Hall NR and Bishop DT:
Incidence of DNA replication errors in patients with multiple
primary cancers. Dis Colon Rectum. 41:765–769. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wood LD, Parsons DW, Jones S, Lin J,
Sjöblom T, Leary RJ, Shen D, Boca SM, Barber T, Ptak J, et al: The
genomic landscapes of human breast and colorectal cancers. Science.
318:1108–1113. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Liang YH, Shao YY, Chen HM, Lai CL, Lin
ZZ, Kuo RN, Cheng AL, Yeh KH and Lai MS: Young patients with
colorectal cancer have increased risk of second primary cancers.
Jpn J Clin Oncol. 45:1029–1035. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Negru S, Papadopoulou E, Apessos A,
Stanculeanu DL, Ciuleanu E, Volovat C, Croitoru A, Kakolyris S,
Aravantinos G, Ziras N, et al: KRAS, NRAS and BRAF mutations in
Greek and Romanian patients with colorectal cancer: A cohort study.
BMJ Open. 4:e0046522014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Haley L, Tseng LH, Zheng G, Dudley J,
Anderson DA, Azad NS, Gocke CD, Eshleman JR and Lin MT: Performance
characteristics of next-generation sequencing in clinical mutation
detection of colorectal cancers. Mod Pathol. 28:1390–1399. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|