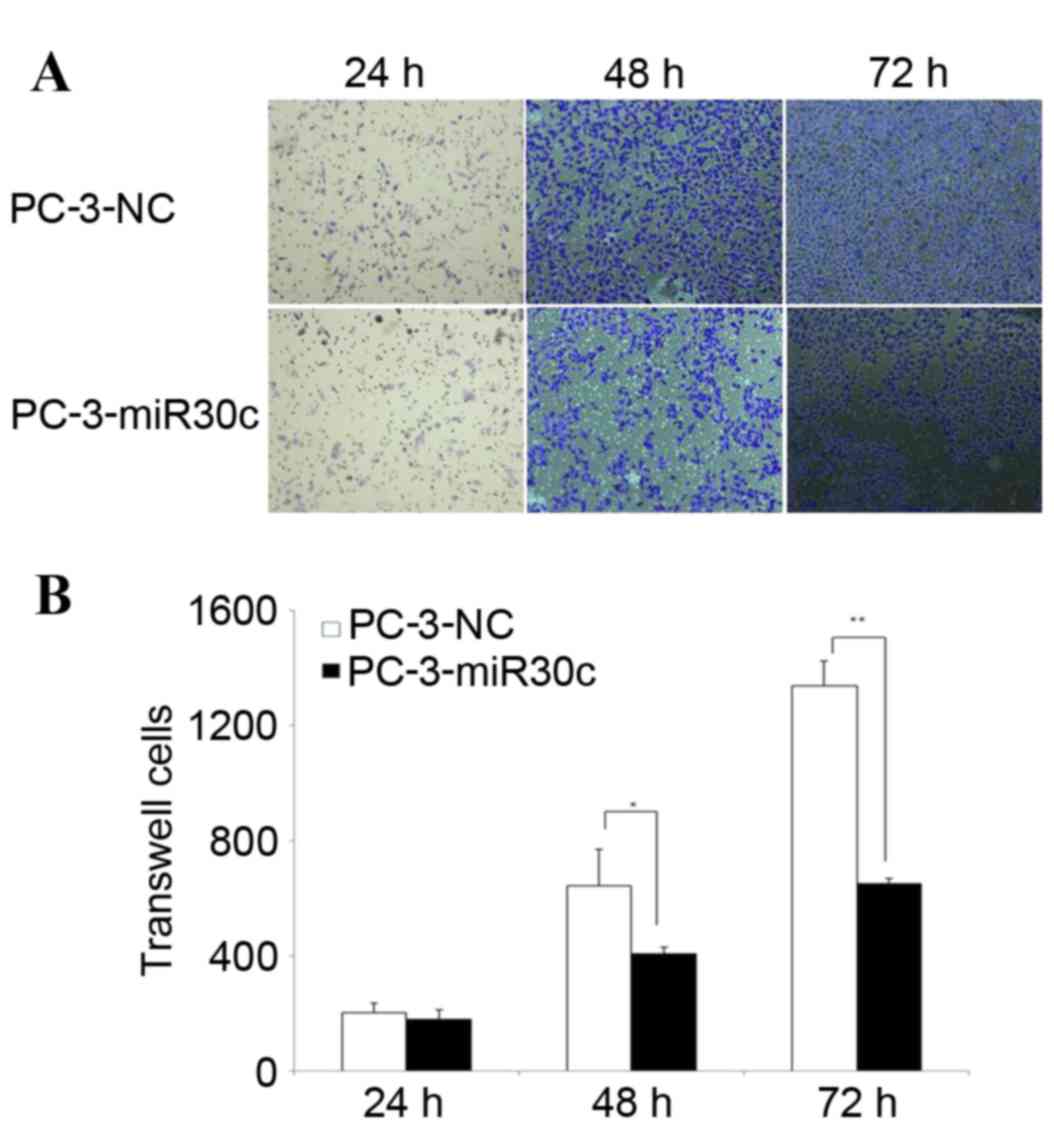
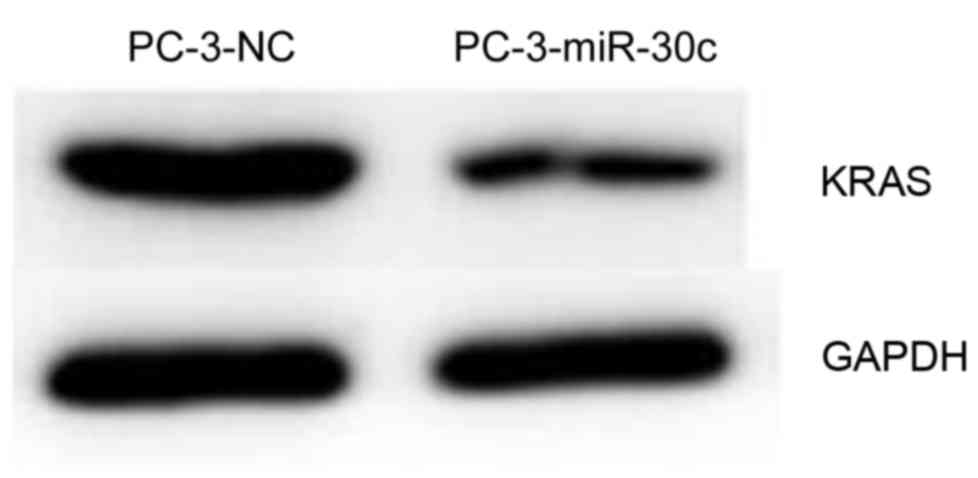
|
1
|
Peyromaure EM, Mao K, Sun Y, Xia S, Jiang
N, Zhang S, Wang G, Liu Z and Debré B: A comparative study of
prostate cancer detection and management in China and in France.
Can J Urol. 16:4472–4477. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zeigler-Johnson CM, Rennert H, Mittal RD,
Jalloh M, Sachdeva R, Malkowicz SB, Mandhani A, Mittal B, Gueye SM
and Rebbeck TR: Evaluation of prostate cancer characteristics in
four populations worldwide. Can J Urol. 15:4056–4064.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Torre LA, Siegel RL, Ward EM and Jemal A:
Global cancer incidence and mortality rates and Trends-An update.
Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 25:16–27. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Shi XB, Tepper CG and White RW deVere:
Cancerous miRNAs and their regulation. Cell Cycle. 7:1529–1538.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Porkka KP, Pfeiffer MJ, Waltering KK,
Vessella RL, Tammela TL and Visakorpi T: MicroRNA expression
profiling in prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 67:6130–6135. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ambs S, Prueitt RL, Yi M, Hudson RS, Howe
TM, Petrocca F, Wallace TA, Liu CG, Volinia S, Calin GA, et al:
Genomic profiling of microRNA and messenger RNA reveals deregulated
microRNA expression in prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 68:6162–6170.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chen ZH, Zhang GL, Li HR, Luo JD, Li ZX,
Chen GM and Yang J: A panel of five circulating microRNAs as
potential biomarkers for prostate cancer. Prostate. 72:1443–1452.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kachakova D, Mitkova A, Popov E, Popov I,
Vlahova A, Dikov T, Christova S, Mitev V, Slavov C and Kaneva R:
Combinations of serum prostate-specific antigen and plasma
expression levels of let-7c, miR-30c, miR-141 and miR-375 as
potential better diagnostic biomarkers for prostate cancer. DNA
Cell Biol. 34:189–200. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Cochetti G, Poli G, Guelfi G, Boni A,
Egidi MG and Mearini E: Different levels of serum microRNAs in
prostate cancer and benign prostatic hyperplasia: Evaluation of
potential diagnostic and prognostic role. Onco Targets Ther.
9:7545–7553. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sylvestre Y, De Guire V, Querido E,
Mukhopadhyay UK, Bourdeau V, Major F, Ferbeyre G and Chartrand P:
An E2F/miR-20a autoregulatory feedback loop. J Biol Chem.
282:2135–2143. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Dhar S, Kumar A, Rimando AM, Zhang X and
Levenson AS: Resveratrol and pterostilbene epigenetically restore
PTEN expression by targeting oncomiRs of the miR-17 family in
prostate cancer. Oncotarget. 6:27214–27226. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Qin W, Shi Y, Zhao B, Yao C, Jin L, Ma J
and Jin Y: miR-24 regulates apoptosis by targeting the open reading
frame (ORF) region of FAF1 in cancer cells. PLoS One. 5:e94292010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Xu B, Wang N, Wang X, Tong N, Shao N, Tao
J, Li P, Niu X, Feng N, Zhang L, et al: MiR-146a suppresses tumor
growth and progression by targeting EGFR pathway and in a
p-ERK-dependent manner in castration-resistant prostate cancer.
Prostate. 72:1171–1178. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lee H, Park CS, Deftereos G, Morihara J,
Stern JE, Hawes SE, Swisher E, Kiviat NB and Feng Q: MicroRNA
expression in ovarian carcinoma and its correlation with
clinicopathological features. World J Surg Oncol. 10:1742012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhou H, Xu X, Xun Q, Yu D, Ling J, Guo F,
Yan Y, Shi J and Hu Y: microRNA-30c negatively regulates
endometrial cancer cells by targeting metastasis-associated gene-1.
Oncol Rep. 27:807–812. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhong Z, Xia Y, Wang P, Liu B and Chen Y:
Low expression of microRNA-30c promotes invasion by inducing
epithelial mesenchymal transition in non-small cell lung cancer.
Mol Med Rep. 10:2575–2579. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wu W, Zhang X, Liao Y, Zhang W, Cheng H,
Deng Z, Shen J, Yuan Q, Zhang Y and Shen W: miR-30c negatively
regulates the migration and invasion by targeting the immediate
early response protein 2 in SMMC-7721 and HepG2 cells. Am J Cancer
Res. 5:1435–1446. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Rodríguez-González FG, Sieuwerts AM, Smid
M, Look MP, Meijer-van Gelder ME, De Weerd V, Sleijfer S, Martens
JW and Foekens JA: MicroRNA-30c expression level is an independent
predictor of clinical benefit of endocrine therapy in advanced
estrogen receptor positive breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat.
127:43–51. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Dobson JR, Taipaleenmäki H, Hu YJ, Hong D,
van Wijnen AJ, Stein JL, Stein GS, Lian JB and Pratap J:
hsa-mir-30c promotes the invasive phenotype of metastatic breast
cancer cells by targeting NOV/CCN3. Cancer Cell Int. 14:732014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chen ZH, Zhang GL, Li HR, Luo JD, Li ZX,
Chen GM and Yang J: A panel of five circulating microRNAs as
potential biomarkers for prostate cancer. Prostate. 72:1443–1452.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Tanic M, Yanowsky K, Rodriguez-Antona C,
Andrés R, Márquez-Rodas I, Osorio A, Benitez J and Martinez-Delgado
B: Deregulated miRNAs in hereditary breast cancer revealed a role
for miR-30c in regulating KRAS oncogene. PLoS One. 7:e388472012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Jay C, Nemunaitis J, Chen P, Fulgham P and
Tong AW: miRNA profiling for diagnosis and prognosis of human
cancer. DNA Cell Biol. 26:293–300. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lu J, Getz G, Miska EA, Alvarez-Saavedra
E, Lamb J, Peck D, Sweet-Cordero A, Ebert BL, Mak RH, Ferrando AA,
et al: MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature.
435:834–838. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yen MC, Shih YC, Hsu YL, Lin ES, Lin YS,
Tsai EM, Ho YW, Hou MF and Kuo PL: Isolinderalactone enhances the
inhibition of SOCS3 on STAT3 activity by decreasing miR-30c in
breast cancer. Oncol Rep. 35:1356–1364. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|