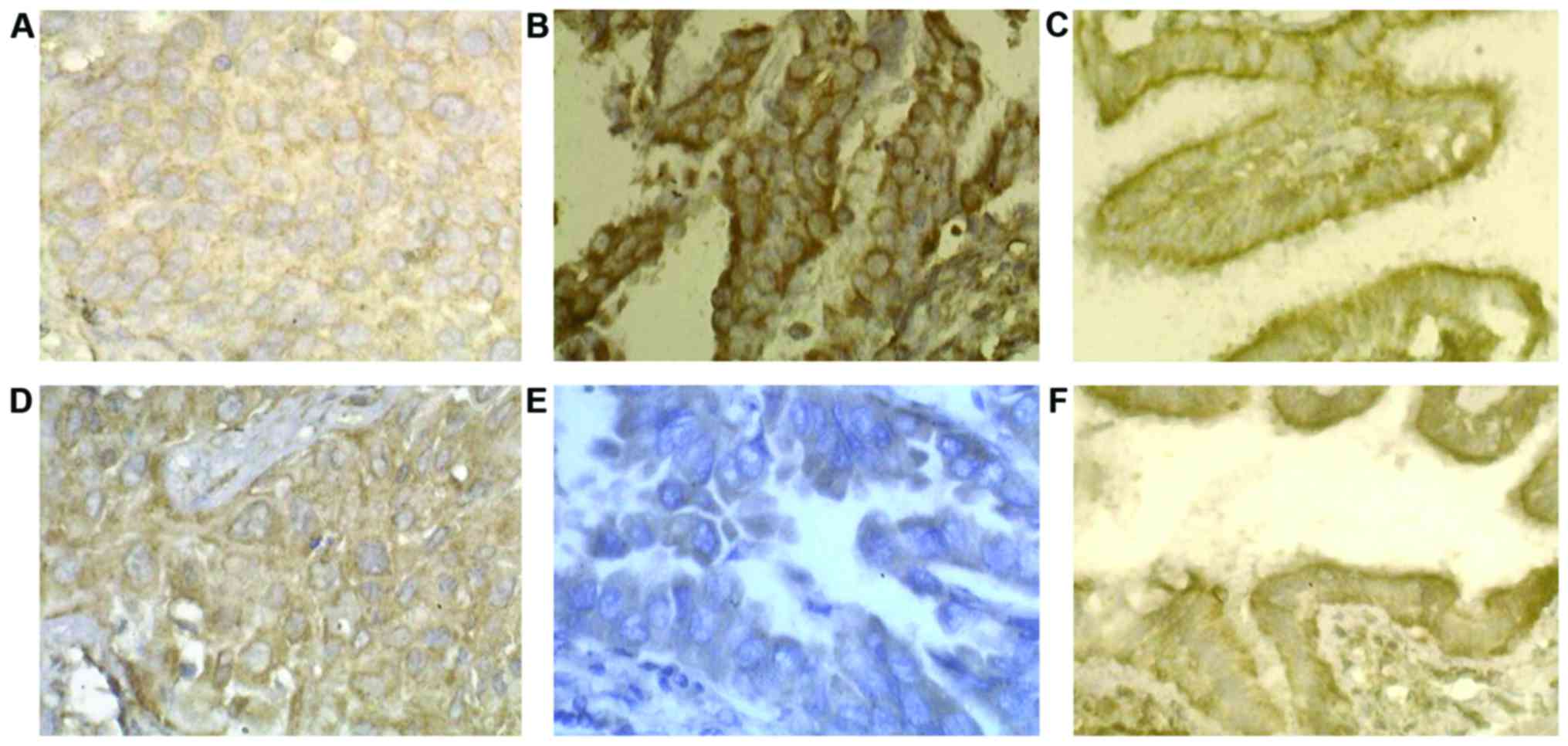
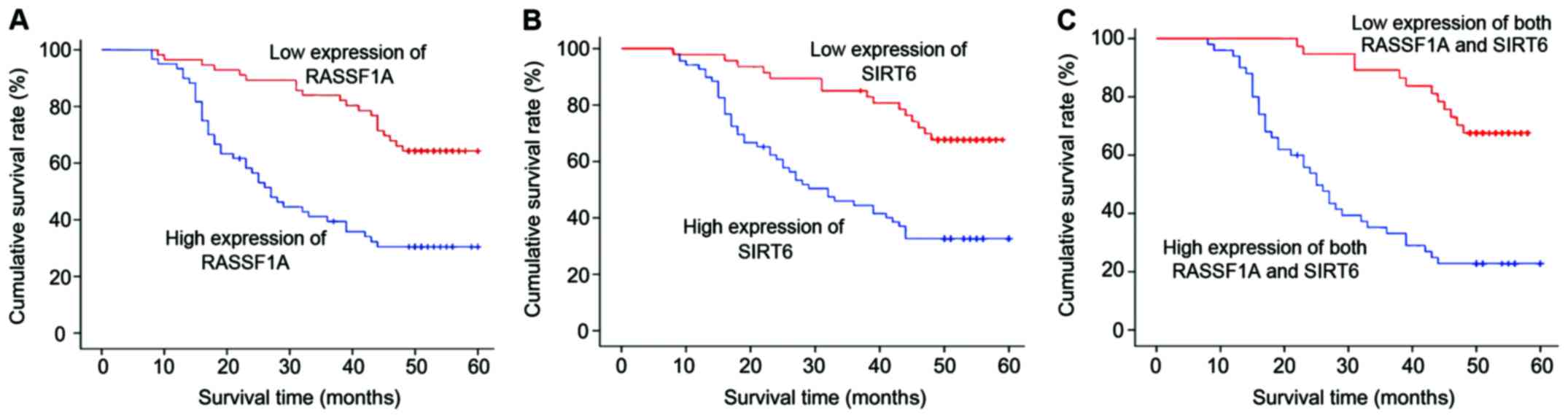
|
1
|
Leong D, Rai R, Nguyen B, Lee A and Yip D:
Advances in adjuvant systemic therapy for non-small-cell lung
cancer. World J Clin Oncol. 5:633–645. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jing W, Li N, Wang Y, Liu X, Liao S, Chai
H and Tu J: The prognostic significance of long noncoding RNAs in
non-small cell lung cancer: A meta-analysis. Oncotarget.
8:3957–3968. 2016.
|
|
3
|
Ettinger DS, Wood DE, Akerley W, Bazhenova
LA, Borghaei H, Camidge DR, Cheney RT, Chirieac LR, DAmico TA,
Dilling TJ, et al: NCCN guidelines insights: Non-small cell lung
cancer, version 4.2016. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 14:255–264. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Douillard JY, Lehur PA, Vignoud J,
Blottière H, Maurel C, Thedrez P, Kremer M and Le Mevel B:
Monoclonal antibodies specific immunotherapy of gastrointestinal
tumors. Hybridoma. 5 Suppl 1:S139–S149. 1986.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Dallol A, Agathanggelou A, Tommasi S,
Pfeifer GP, Maher ER and Latif F: Involvement of the RASSF1A
tumor suppressor gene in controlling cell migration. Cancer Res.
65:7653–7659. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Deng ZH, Zhou JH, Cao HQ, Sheng M and Weng
JF: Proliferation inhibition of human lung adenocarcinoma cell line
A549 transfected by RASSF1A gene. J Cent South Univ (Med
Sci). 30:193–196. 2005.
|
|
7
|
Han Z, Liu L, Liu Y and Li S: Sirtuin
SIRT6 suppresses cell proliferation through inhibition of Twist1
expression in non-small cell lung cancer. Int J Clin Exp Pathol.
7:4774–4781. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Fukatsu A, Ishiguro F, Tanaka I, Kudo T,
Nakagawa K, Shinjo K, Kondo Y, Fujii M, Hasegawa Y, Tomizawa K, et
al: RASSF3 downregulation increases malignant phenotypes of
non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 83:23–29. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Avruch J, Praskova M, Ortiz-Vega S, Liu M
and Zhang XF: Nore1 and RASSF1 regulation of cell proliferation and
of the MST1/2 kinases. Methods Enzymol. 407:290–310. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Dubois F, Keller M, Calvayrac O, Soncin F,
Hoa L, Hergovich A, Parrini MC, Mazières J, Vaisse-Lesteven M,
Camonis J, et al: RASSF1A suppresses the invasion and metastatic
potential of human non-small cell lung cancer cells by inhibiting
YAP activation through the GEF-H1/RhoB pathway. Cancer Res.
76:1627–1640. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Whang YM, Park KH, Jung HY, Jo UH and Kim
YH: Microtubule-damaging agents enhance RASSF1A-induced cell death
in lung cancer cell lines. Cancer. 115:1253–1266. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chen K, Li BK, Xu K, Xu A, Liu C, Zheng S,
Xu Y, Jia C, Liu Q, Li Η, et al: Effect of stable DNA
methyltransferase 3b knockdown on proliferation and apoptosis in
bladder cancer cells in vitro. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao.
35:1524–1529. 2015.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Huang YZ, Wu W, Wu K, Xu XN and Tang WR:
Association of RASSF1A promoter methylation with lung cancer risk:
A meta-analysis. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 15:10325–10328. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Fu L and Zhang S: RASSF1A promotes
apoptosis and suppresses the proliferation of ovarian cancer cells.
Int J Mol Med. 33:1153–1160. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ko E, Lee BB, Kim Y, Lee EJ, Cho EY, Han
J, Shim YM, Park J and Kim DH: Association of RASSF1A and p63 with
poor recurrence-free survival in node-negative stage I–II non-small
cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 19:1204–1212. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Dittfeld C, Richter AM, Steinmann K,
Klagge-Ulonska A and Dammann RH: The SARAH domain of RASSF1A and
its tumor suppressor function. Mol Biol Int. 2012:1967152012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Pastuszak-Lewandoska D, Kordiak J,
Migdalska-Sęk M, Czarnecka KH, Antczak A, Górski P, Nawrot E,
Kiszałkiewicz JM, Domańska D and Brzeziańska-Lasota E: Quantitative
analysis of mRNA expression levels and DNA methylation profiles of
three neighboring genes: FUS1, NPRL2/G21 and
RASSF1A in non-small cell lung cancer patients. Respir Res.
16:762015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bai L, Lin G, Sun L, Liu Y, Huang X, Cao
C, Guo Y and Xie C: Upregulation of SIRT6 predicts poor prognosis
and promotes metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer via the
ERK1/2/MMP9 pathway. Oncotarget. 7:40377–40386. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Azuma Y, Yokobori T, Mogi A, Altan B,
Yajima T, Kosaka T, Onozato R, Yamaki E, Asao T, Nishiyama M, et
al: SIRT6 expression is associated with poor prognosis and
chemosensitivity in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. J
Surg Oncol. 112:231–237. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Cai Y, Sheng ZY and Liang SX:
Radiosensitization effect of overexpression of adenovirus-mediated
SIRT6 on A549 non-small cell lung cancer cells. Asian Pac J Cancer
Prev. 15:7297–7301. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bae JS, Park SH, Jamiyandorj U, Kim KM,
Noh SJ, Kim JR, Park HJ, Kwon KS, Jung SH, Park HS, et al:
CK2α/CSNK2A1 phosphorylates SIRT6 and is involved in the
progression of breast carcinoma and predicts shorter survival of
diagnosed patients. Am J Pathol. 186:3297–3315. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bhardwaj A and Das S: SIRT6 deacetylates
PKM2 to suppress its nuclear localization and oncogenic functions.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 113:E538–E547. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Demir IE, Ceyhan GO and Friess H:
Epigenomic therapies: The potential of targeting SIRT6 for the
treatment of pancreatic cancer. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 21:1–3.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lee N, Ryu HG, Kwon JH, Kim DK, Kim SR,
Wang HJ, Kim KT and Choi KY: SIRT6 depletion suppresses tumor
growth by promoting cellular senescence induced by DNA damage in
HCC. PLoS One. 11:e01658352016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wolf K and Strand S: Assessing the histone
deacetylase activity of SIRT6 in primary murine hepatocytes via
proximity ligation assay. Methods Mol Biol. 1510:149–158. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Thaler S, Hähnel PS, Schad A, Dammann R
and Schuler M: RASSF1A mediates p21Cip1/Waf1-dependent
cell cycle arrest and senescence through modulation of the
Raf-MEK-ERK pathway and inhibition of Akt. Cancer Res.
69:1748–1757. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Romano D, Matallanas D, Weitsman G,
Preisinger C, Ng T and Kolch W: Proapoptotic kinase MST2
coordinates signaling crosstalk between RASSF1A, Raf-1, and Akt.
Cancer Res. 70:1195–1203. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sundaresan NR, Vasudevan P, Zhong L, Kim
G, Samant S, Parekh V, Pillai VB, Ravindra PV, Gupta M, Jeevanandam
V, et al: The sirtuin SIRT6 blocks IGF-Akt signaling and
development of cardiac hypertrophy by targeting c-Jun. Nat Med.
18:1643–1650. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|