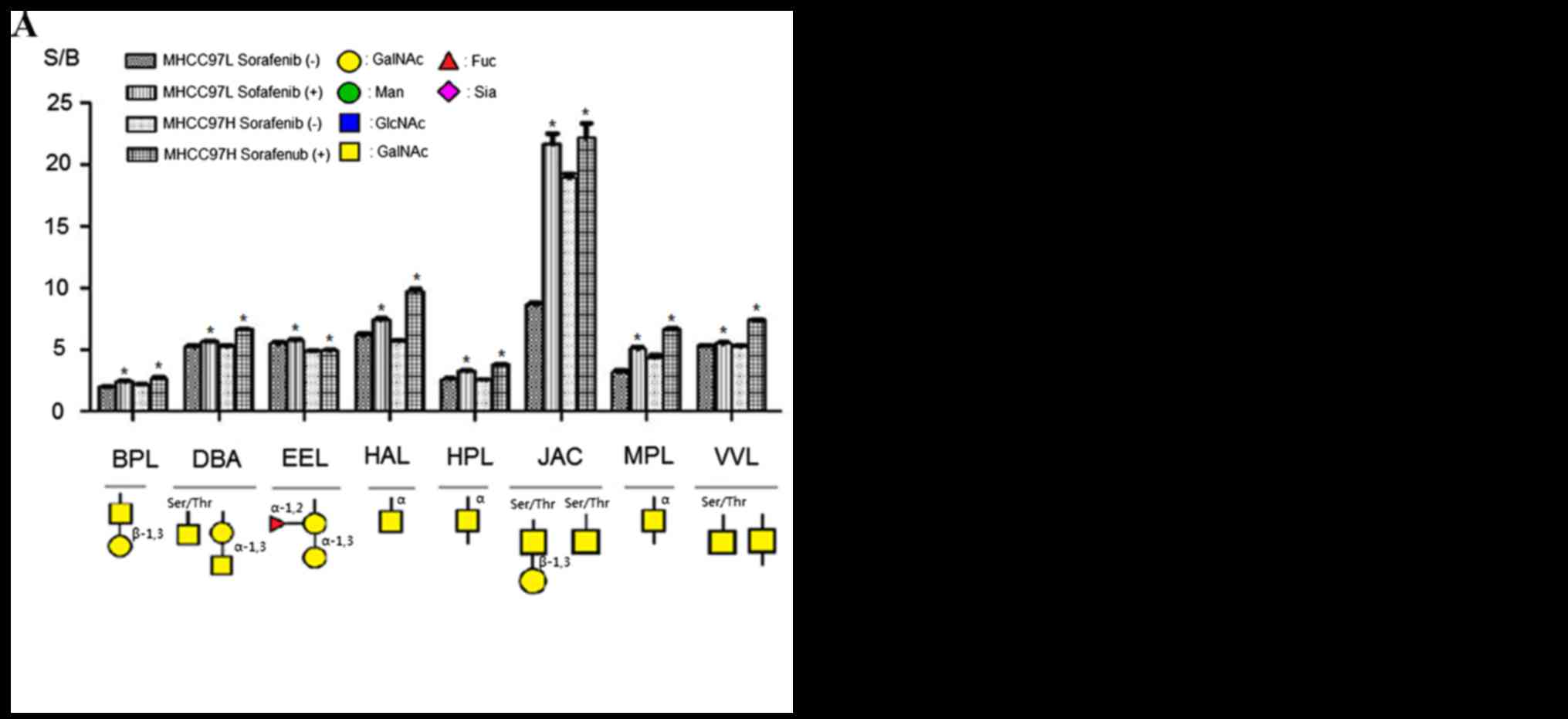
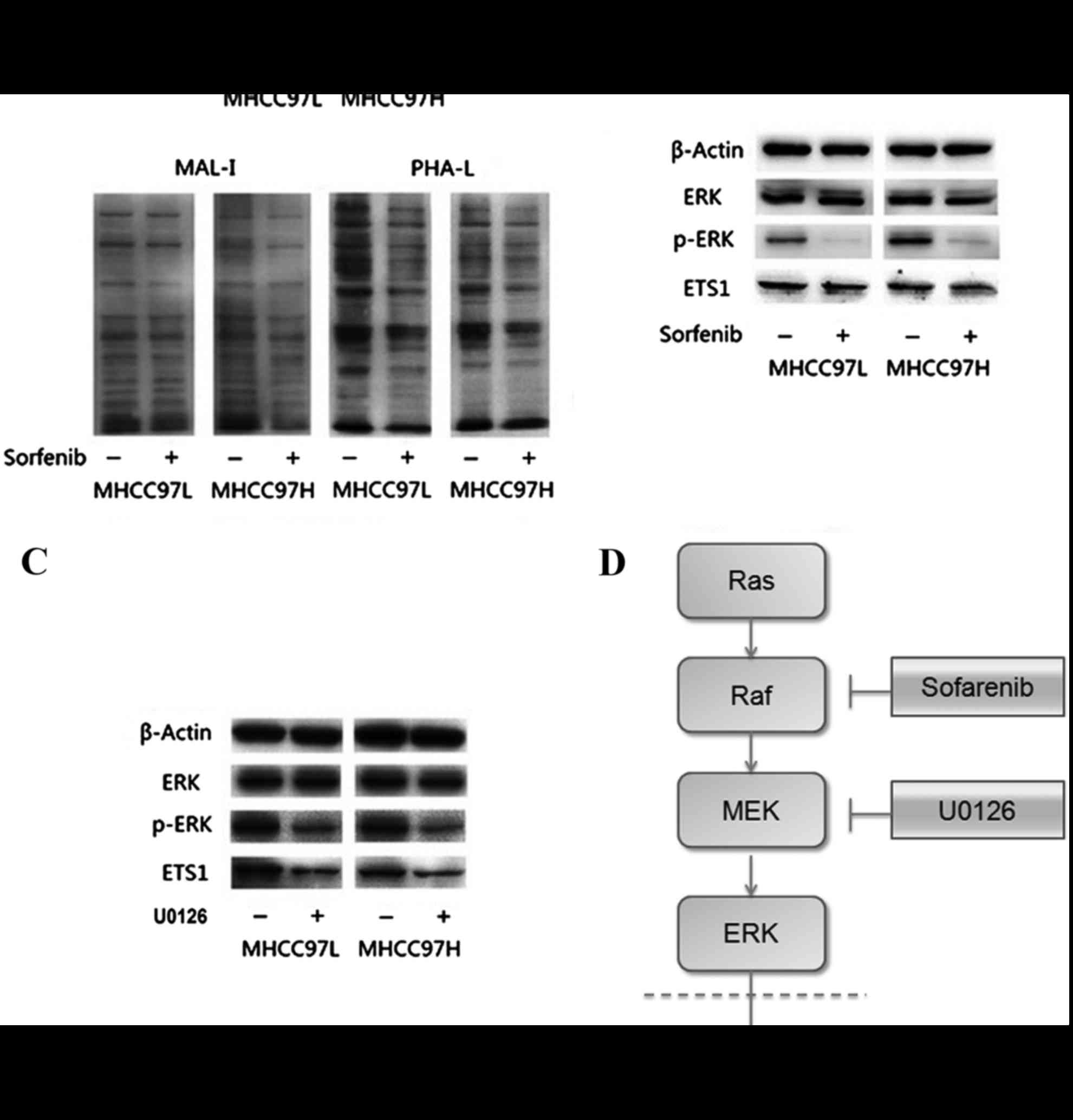
|
1
|
Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D,
Mathers C and Parkin DM: Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in
2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 127:2893–2917. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Center MM and Jemal A: International
trends in liver cancer incidence rates. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers
Prev. 20:2362–2368. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Nault JC and Zucman-Rossi J: Genetics of
hepatobiliary carcinogenesis. Semin Liver Dis. 31:173–187. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wong CH: Protein glycosylation: New
challenges and opportunities. J Org Chem. 70:4219–4225. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ohtsubo K and Marth JD: Glycosylation in
cellular mechanisms of health and disease. Cell. 126:855–867. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Li M, Song L and Qin X: Glycan changes:
Cancer metastasis and anti-cancer vaccines. J Biosci. 35:665–673.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Comunale MA, Wang M, Hafner J, Krakover J,
Rodemich L, Kopenhaver B, Long RE, Junaidi O, Bisceglie AM, Block
TM and Mehta AS: Identification and development of fucosylated
glycoproteins as biomarkers of primary hepatocellular carcinoma. J
Proteome Res. 8:595–602. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ang IL, Poon TC, Lai PB, Chan AT, Ngai SM,
Hui AY, Johnson PJ and Sung JJ: Study of serum haptoglobin and its
glycoforms in the diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma: A
glycoproteomic approach. J Proteome Res. 5:2691–2700. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chen GQ, Zhang Q, Xu YF, Zhang WZ, Guan M,
Su B, Liang HQ and Lu Y: Changes of alkaline phosphatase sugar
chains in hepatocellular carcinoma tissue. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing
Za Zhi. 11:739–741. 2003.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chow AK, Ng L, Lam CS, Wong SK, Wan TM,
Cheng NS, Yau TC, Poon RT and Pang RW: The Enhanced metastatic
potential of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells with sorafenib
resistance. PloS One. 8:e786752013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wilhelm SM, Carter C, Tang L, Wilkie D,
McNabola A, Rong H, Chen C, Zhang X, Vincent P, McHugh M, et al:
BAY 43–9006 exhibits broad spectrum oral antitumor activity and
targets the RAF/MEK/ERK pathway and receptor tyrosine kinases
involved in tumor progression and angiogenesis. Cancer Res.
64:7099–7109. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Liu L, Cao Y, Chen C, Zhang X, McNabola A,
Wilkie D, Wilhelm S, Lynch M and Carter C: Sorafenib blocks the
RAF/MEK/ERK pathway, inhibits tumor angiogenesis, and induces tumor
cell apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma model PLC/PRF/5. Cancer
Res. 66:11851–11858. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Llovet JM, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V, Hilgard
P, Gane E, Blanc JF, De Oliveira AC, Santoro A, Raoul JL, Forner A,
et al: Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J
Med. 359:378–390. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Deng YR, Liu WB, Lian ZX, Li X and Hou X:
Sorafenib inhibits macrophage-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget. 7:38292–38305.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Fu QH, Zhang Q, Zhang JY, Sun X, Lou Y, Li
GG, Chen ZL, Bai XL and Liang TB: LB-100 sensitizes hepatocellular
carcinoma cells to the effects of sorafenib during hypoxia by
activation of Smad3 phosphorylation. Tumour Biol. 37:7277–7286.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Adjibade P, St-Sauveur VG, Huberdeau M
Quevillon, Fournier MJ, Savard A, Coudert L, Khandjian EW and
Mazroui R: Sorafenib, a multikinase inhibitor, induces formation of
stress granules in hepatocarcinoma cells. Oncotarget.
6:43927–43943. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Xin AJ, Cheng L, Diao H, Wang P, Gu YH, Wu
B, Wu YC, Chen GW, Zhou SM, Guo SJ, et al: Comprehensive profiling
of accessible surface glycans of mammalian sperm using a lectin
microarray. Clin Proteomics. 11:102014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Tan Z, Lu W, Li X, Yang G, Guo J, Yu H, Li
Z and Guan F: Altered N-Glycan expression profile in
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition of NMuMG cells revealed by an
integrated strategy using mass spectrometry and glycogene and
lectin microarray analysis. J Proteome Res. 13:2783–2795. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Li S, Mo C, Peng Q, Kang X, Sun C, Jiang
K, Huang L, Lu Y, Sui J, Qin X and Liu Y: Cell surface glycan
alterations in epithelial mesenchymal transition process of Huh7
hepatocellular carcinoma cell. PloS one. 8:e712732013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Gu Y, Tang Y, Zhou X and Liu Y: Alteration
of the glycan profile of serum glycoproteins during the
seroconversion process in hepatitis B virus-infected patients
treated with antiviral therapy and its clinical significance.
Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 22:660–666. 2014.(In Chinese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Li Y, Tang ZY, Ye SL, Liu YK, Chen J, Xue
Q, Chen J, Gao DM and Bao WH: Establishment of cell clones with
different metastatic potential from the metastatic hepatocellular
carcinoma cell line MHCC97. World J Gastroenterol. 7:630–636.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Blomme B, van Steenkiste C, Callewaert N
and Van Vlierberghe H: Alteration of protein glycosylation in liver
diseases. J Hepatol. 50:592–603. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Dennis JW, Laferte S, Waghorne C, Breitman
ML and Kerbel RS: Beta 1–6 branching of Asn-linked oligosaccharides
is directly associated with metastasis. Science. 236:582–585. 1987.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Shao DM, Wang QH, Chen C, Shen ZH, Yao M,
Zhou XD, Tang ZY and Gu JX: N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase V
activity in metastatic models of human hepatocellular carcinoma in
nude mice. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 18:331–335. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhao Y, Li Y, Ma H, Dong W, Zhou H, Song
X, Zhang J and Jia L: Modification of sialylation mediates the
invasive properties and chemosensitivity of human hepatocellular
carcinoma. Mol Cell Proteomics. 13:520–536. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Watanabe D, Takagi H, Suzuma K, Suzuma I,
Oh H, Ohashi H, Kemmochi S, Uemura A, Ojima T, Suganami E, et al:
Transcription factor Ets-1 mediates ischemia- and vascular
endothelial growth factor-dependent retinal neovascularization. Am
J Pathol. 164:1827–1835. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ko JH, Miyoshi E, Noda K, Ekuni A, Kang R,
Ikeda Y and Taniguchi N: Regulation of the GnT-V promoter by
transcription factor Ets-1 in various cancer cell lines. J Biol
Chem. 274:22941–22948. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Tamagawa H, Inoshita E, Takeshita T,
Takagaki M, Shizukuishi S and Tsunemitsu A: Purification and some
properties of fucosyltransferase in human parotid saliva. J Dent
Res. 66:72–77. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Galili U: Interaction of the natural
anti-Gal antibody with alpha-galactosyl epitopes: A major obstacle
for xenotransplantation in humans. Immunol Today. 14:480–482. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Venkitachalam S, Revoredo L, Varadan V,
Fecteau RE, Ravi L, Lutterbaugh J, Markowitz SD, Willis JE, Gerken
TA and Guda K: Biochemical and functional characterization of
glycosylation-associated mutational landscapes in colon cancer. Sci
Rep. 6:236422016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kizuka Y and Taniguchi N: Enzymes for
N-glycan branching and their genetic and nongenetic regulation in
cancer. Biomolecules. 6:E252016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Taniguchi N and Kizuka Y: Glycans and
cancer: Role of N-glycans in cancer biomarker, progression and
metastasis, and therapeutics. Adv Cancer Res. 126:11–51. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|