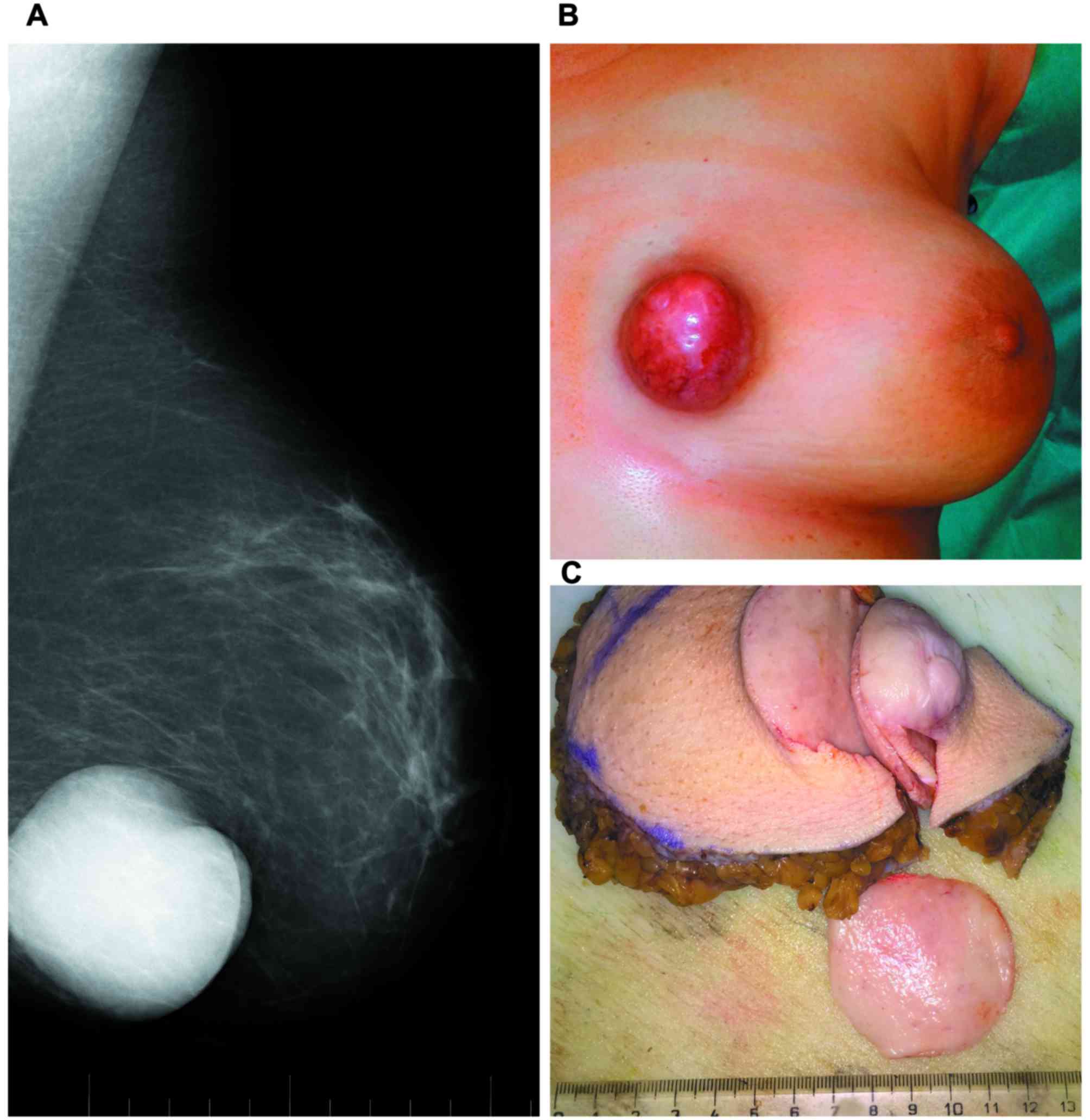
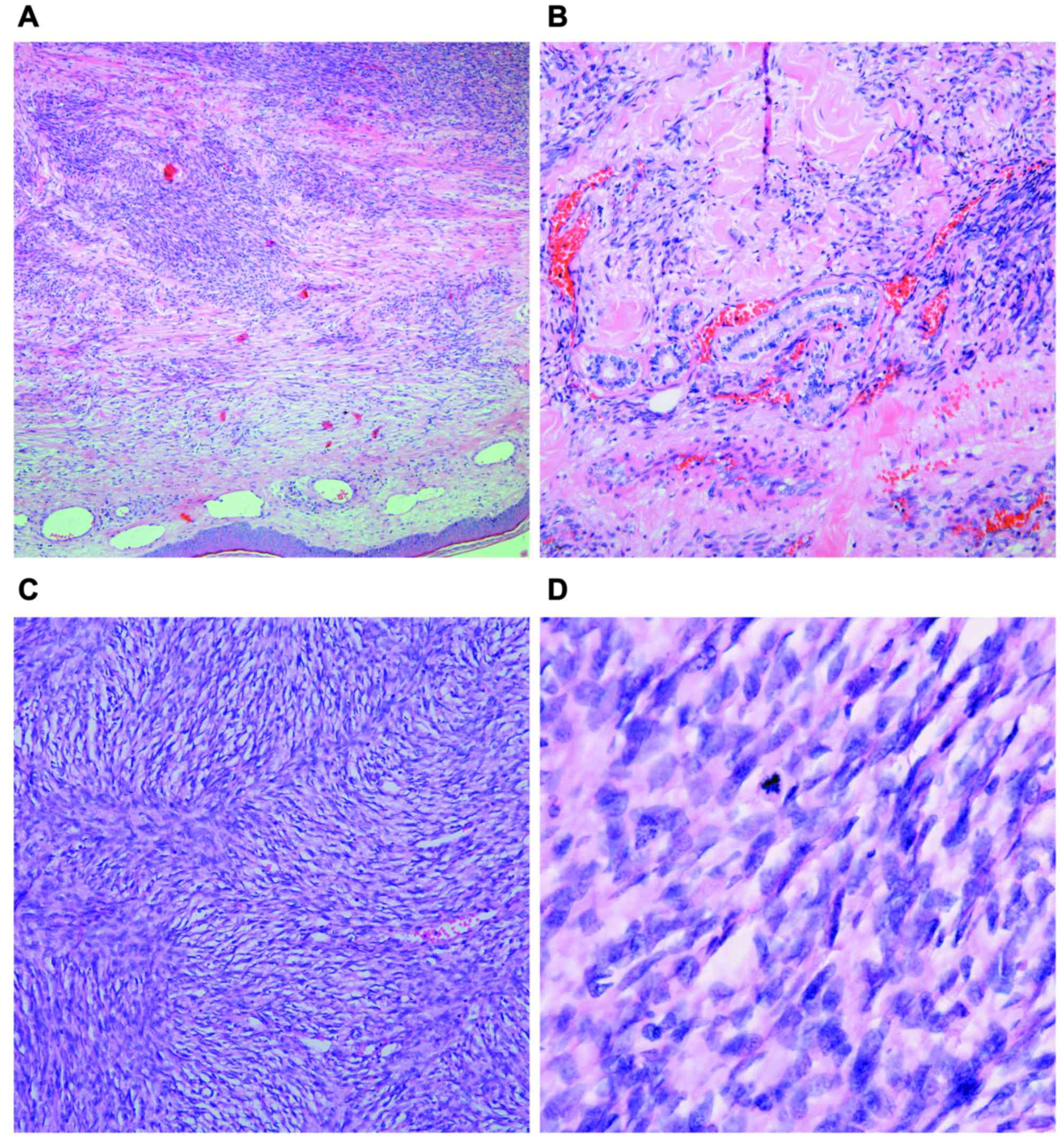
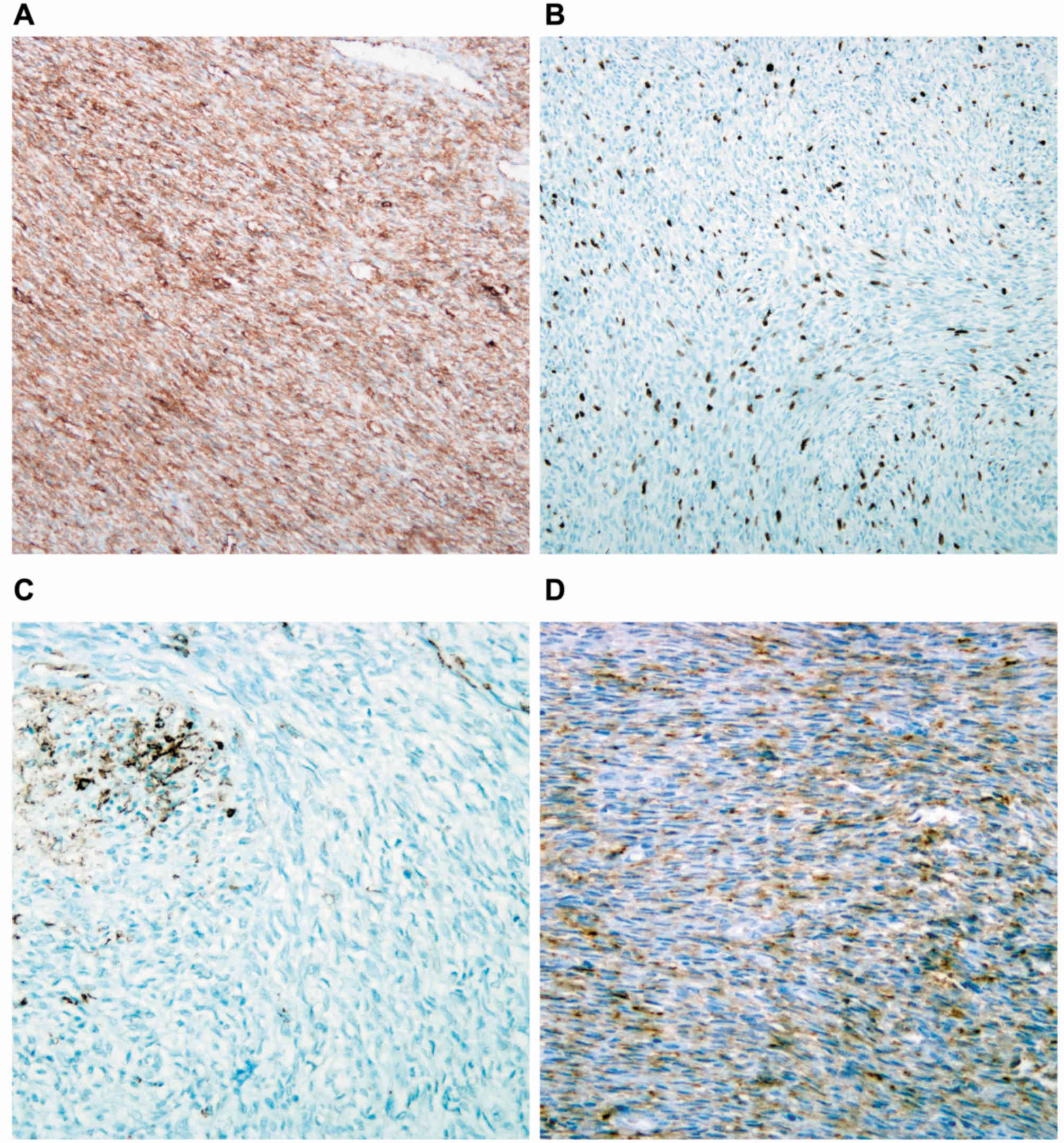
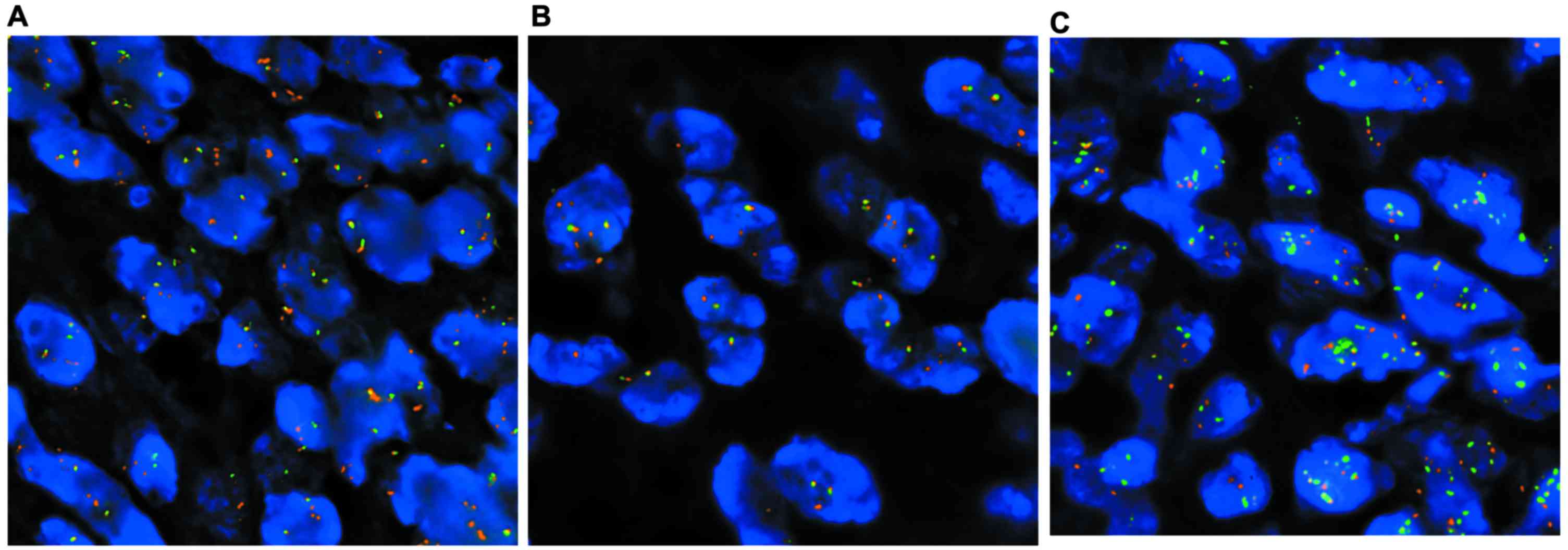
|
1
|
Lemm D, Mügge LO, Mentzel T and Höffken K:
Current treatment options in dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans. J
Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 135:653–665. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jiang J, Huang Z, Wang LH, Shen SD and Lu
H: Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans of the breast: A case report.
Oncol Lett. 8:1202–1204. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sin FN and Wong KW: Dermatofibrosarcoma
protuberans of the breast: A case report. Clin Imaging. 35:398–400.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Criscione VD and Weinstock MA: Descriptive
epidemiology of dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans in the United
States, 1973 to 2002. J Am Acad Dermatol. 56:968–973. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Llombart B, Serra-Guillén C, Monteagudo C,
López Guerrero JA and Sanmartín O: Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans:
A comprehensive review and update on diagnosis and management.
Semin Diagn Pathol. 30:13–28. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Knutsvik G, Stefansson IM, Azis S, Arnes
J, Eide J, Collett K and Akslen L: Evaluation of Ki67 expression
across distinct categories of breast cancer specimens: A
population-based study of matched surgical specimens, core needle
biopsies and tissue microarrays. PLoS One. 9:e1121212014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Darier S and Ferrand M: Recurrent or
progressive dermatofibromas and fibrosarcoma of the skin. Ann
Dermatol Venerol. 5:545–562. 1924.(In French).
|
|
8
|
Hoffman E: Ueber das knollentribende
Fibrosarkom der Haut (dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans). Dermatol Z.
43:1–286. 1925.(In German). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Taylor HB and Helwig EB:
Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans. A study of 115 cases. Cancer.
15:717–725. 1962. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chen X, Chen YH, Zhang YL, Guo YM, Bai ZL
and Zhao X: Magnetic resonance imaging and mammographic appearance
of dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans in a male breast: A case report
and literature review. J Med Case Rep. 3:82462009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Serra-Guillén C, Sanmartín O, Llombart B,
Nagore E, Deltoro C, Martín I, Borella-Estrada R, Requena C,
Martorell-Calatayud A, Cervera J and Guillén C: Correlation between
preoperative magnetic resonance imaging and surgical margins with
modified Mohs for dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans. Dermatol Surg.
37:1638–1645. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Millare GG, Guha-Thakurta N, Sturgis EM,
El-Naggar AK and Debnam JM: Imaging findings of head and neck
dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 35:373–378.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhang L, Liu QY, Cao Y, Zhong JS and Zhang
WD: Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans: Computed tomography and
magnetic resonance imaging findings. Medicine (Baltimore).
94:e10012015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chang GK, Jacobs IA and Salti GI: Outcomes
of surgery for dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans. Eur J Surg Oncol.
30:341–345. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Li N, McNiff J, Hui P, Manfioletti G and
Tallini G: Differential expression of HMGA1 and HMGA2 in
dermatofibroma and dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans: Potential
diagnostic applications and comparison with histologic findings,
CD34, and factor XIIIa immunoreactivity. Am J Dermatopathol.
26:267–272. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Thway K, Ng W, Noujaim J, Jones RL and
Fisher C: The current status of solitary fibrous tumor: Diagnostic
features, variants and genetics. Int J Surg Pathol. 24:281–292.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Stacchiotti S, Pedeutour F, Negri T, Conca
E, Marrari A, Palassini E, Collini P, Keslair F, Morosi C, Gronchi
A, et al: Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans-derived fibrosarcoma:
Clinical history, biological profile and sensitivity to imatinib.
Int J Cancer. 129:1761–1772. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kuzel P, Mahmood MN, Metelitsa AI and
Salopek TG: A clinicopathologic review of a case series of
dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans with fibrosarcomatous
differentiation. J Cutan Med Surg. 19:28–34. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lim SZ, Ong KW, Tee Tan BK, Selvarajan S
and Tan P Hoon: Sarcoma of the breast: An update on a rare entity.
J Clin Pathol. 69:373–381. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Al Barwani AS, Taif S, Al Mazrouai RA, Al
Muzahmi KS and Alrawi A: Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans: Insights
into a rare soft tissue tumor. J Clin Imaging Sci. 6:162016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Llombart B, Monteagudo C, Sanmartín O,
López-Guerrero JA, Serra-Guillén C, Poveda A, Jorda E,
Fernandez-Serra A, Pellín A, Guillén C and Llombart-Bosch A:
Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans: A clinicopathological,
immunohistochemical, genetic (COL1A1-PDGFB), and therapeutic study
of low-grade versus high-grade (fibrosarcomatous) tumors. J Am Acad
Dermatol. 65:564–575. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Simon MP, Navarro M, Roux D and Pouysségur
J: Structural and functional analysis of a chimeric protein
COL1A1-PDGFB generated by the translocation t(17; 22)(q22;q13.1) in
dematofibrosarcoma protubrans (DP). Oncogene. 20:2965–2975. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Giacchero D, Maire G, Nuin PA, Berthier F,
Ebran N, Carlotti A, Celerier P, Coindre JM, Esteve E, Fraitag S,
et al: No correlation between the molecular subtype of COL1A1-PDGFB
fusion gene and the clinicohistopathological features of
dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans. J Invest Dermatol. 130:904–907.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
McArthur GA, Demetri GD, van Oosterom A,
Heinrich MC, Debiec-Rychter M, Corless CL, Nikolova Z, Dimitrijevic
S and Fletcher JA: Molecular and clinical analysis of locally
advanced dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans treated with imatinib:
Imatinib target exploration consortium study B2225. J Clin Oncol.
23:866–873. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Snow SN, Gordon EM, Larson PO, Bagheri MM,
Bentz ML and Sable DB: Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans: A report on
29 patients treated by Mohs micrographic surgery with long-term
follow-up and review of the literature. Cancer. 101:28–38. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Farma JM, Ammori JB, Zager JS, Marzban SS,
Bui MM, Bichakjian CK, Johnson TM, Lowe L, Sabel MS, Wong SL, et
al: Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans: How wide should we resect? Ann
Surg Oncol. 17:2112–2118. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Fields RC, Hameed M, Qin LX, Moraco N, Jia
X, Maki RG, Singer S and Brennan MF: Dermatofibrosarcoma
protuberans (DFSP): Predictors of recurrence and the use of
systemic therapy. Ann Surg Oncol. 18:328–336. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Williams N, Morris CG, Kirwan JM, Dagan R
and Mendenhall WM: Radiotherapy for dermatofibrosarcoma
protuberans. Am J Clin Oncol. 37:430–432. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Eilers G, Czaplinski JT, Mayeda M, Bahri
N, Tao D, Zhu M, Hornick JL, Lindeman NI, Sicinska E, Wagner AJ, et
al: CDKN2A/p16 Loss implicates CDK4 as a therapeutic target in
imatinib-resistant dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans. Mol Cancer
Ther. 14:1346–1353. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|