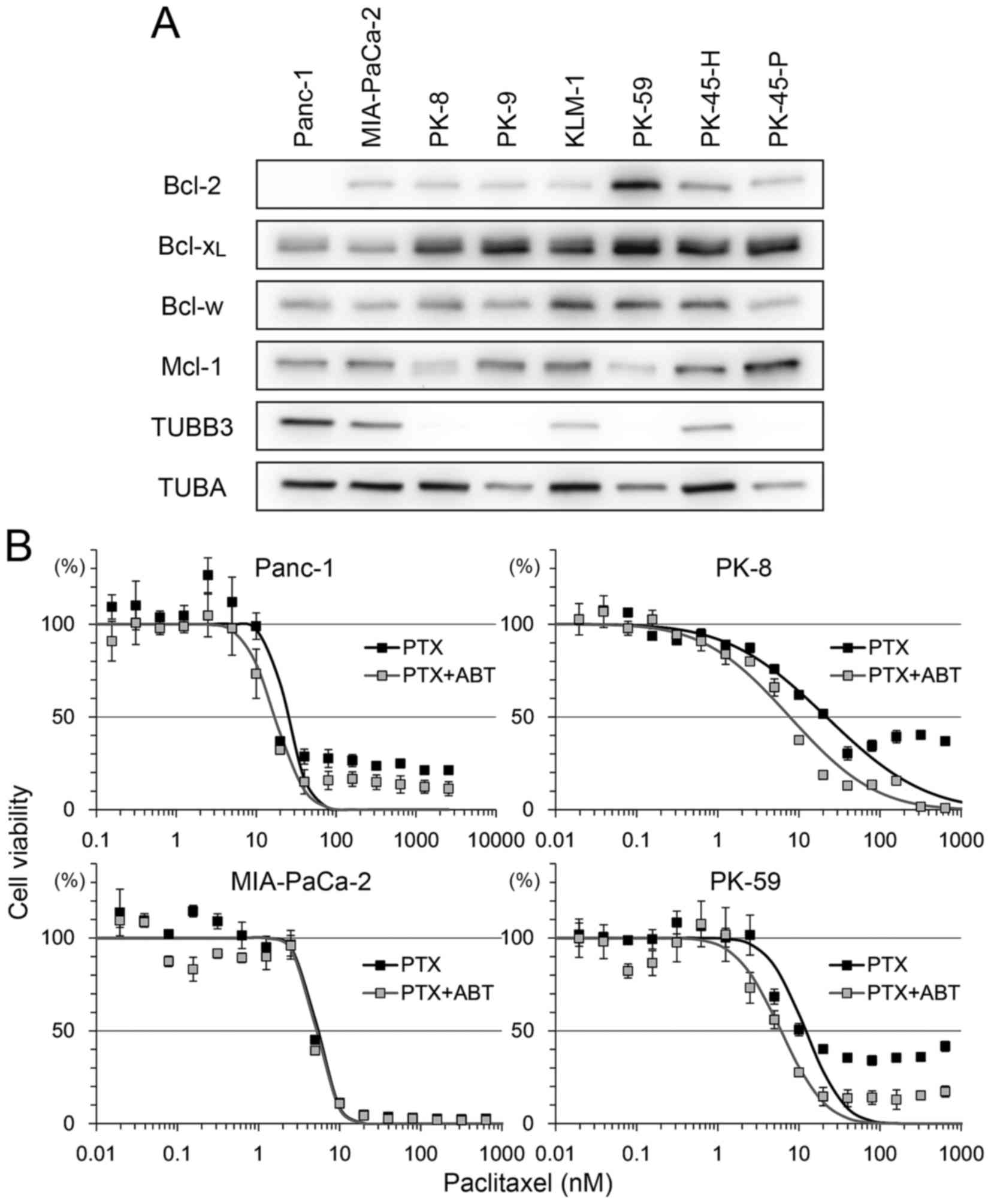
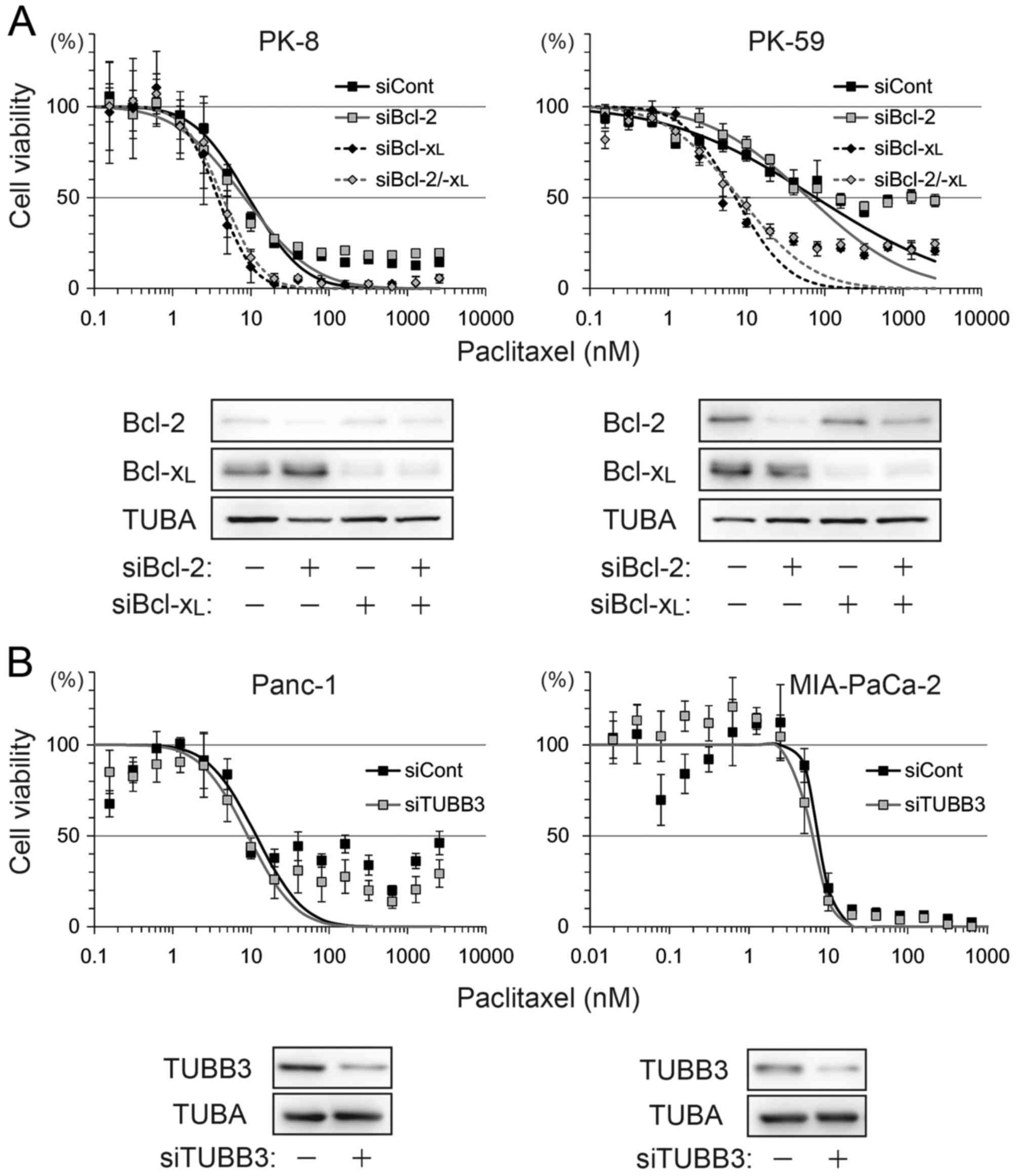
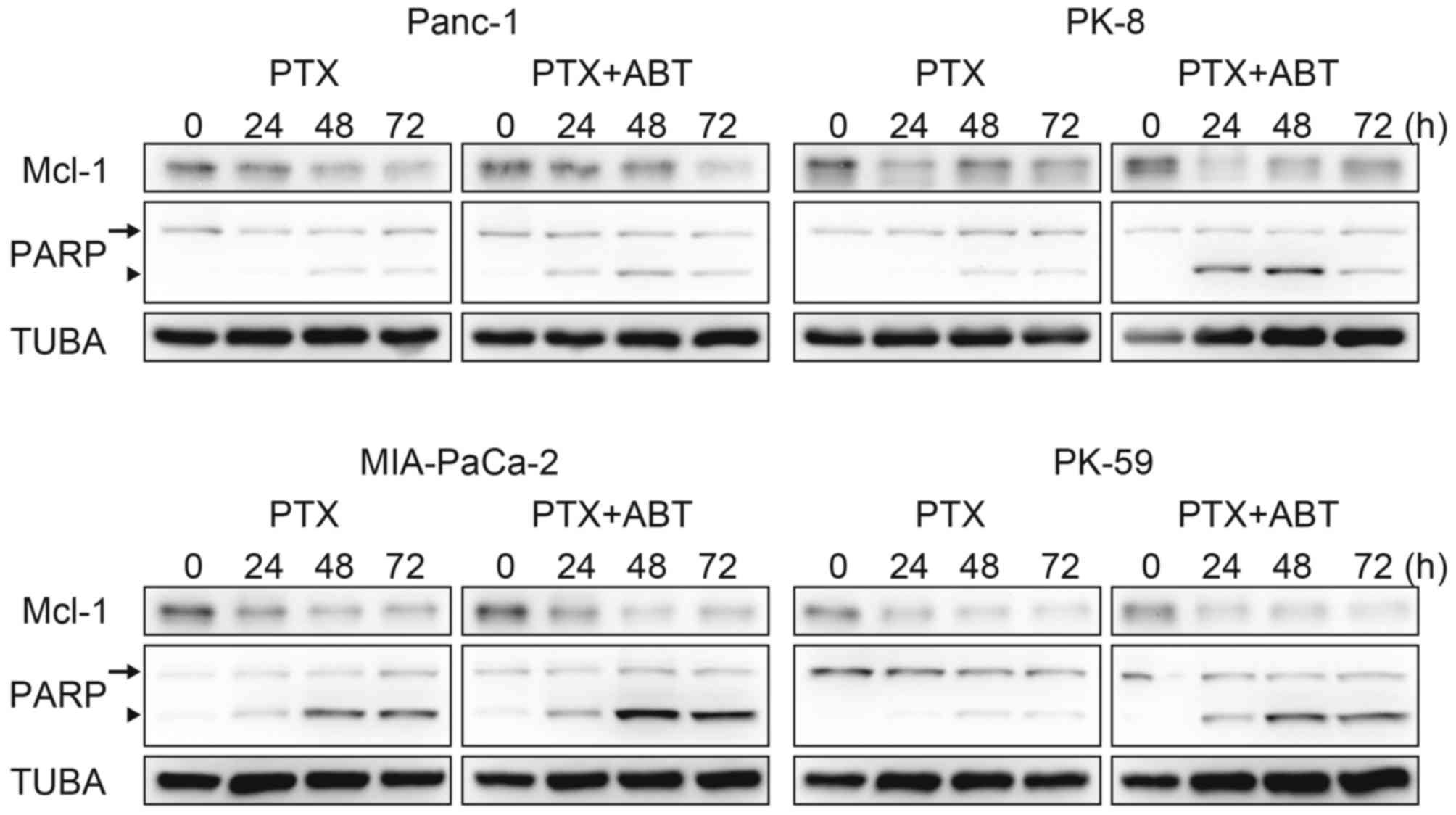
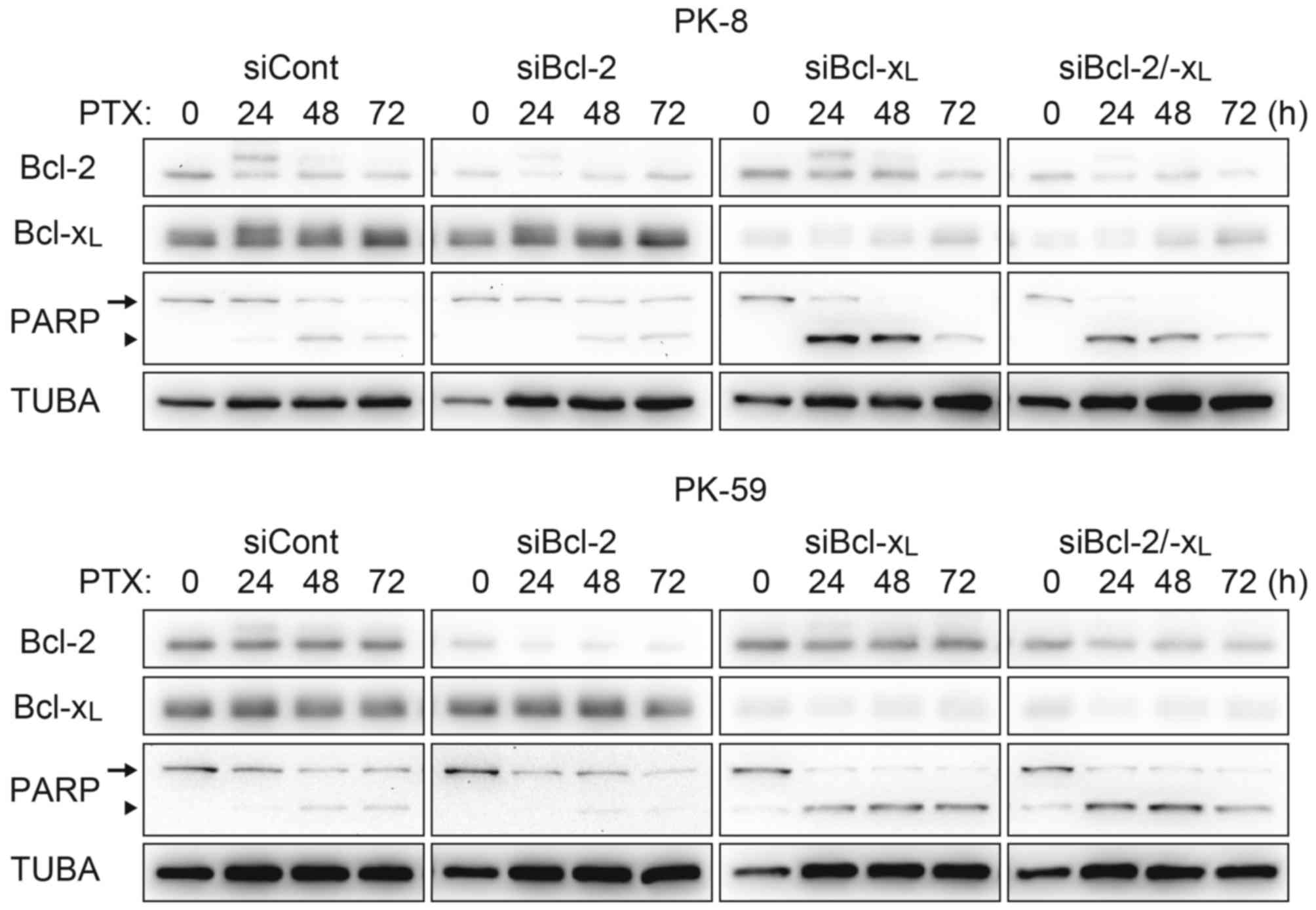
|
1
|
Warshaw AL and Fernández-del Castillo C:
Pancreatic Carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 326:455–465. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Gourgou-Bourgade S, Bascoul-Mollevi C,
Desseigne F, Ychou M, Bouché O, Guimbaud R, Bécouarn Y, Adenis A,
Raoul JL, Boige V, et al: Impact of FOLFIRINOX compared with
gemcitabine on quality of life in patients with metastatic
pancreatic cancer: Results from the PRODIGE 4/ACCORD 11 randomized
trial. J Clin Oncol. 31:23–29. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Burris HA III, Moore MJ, Andersen J, Green
MR, Rothenberg ML, Modiano MR, Cripps MC, Portenoy RK, Storniolo
AM, Tarassoff P, et al: Improvements in survival and clinical
benefit with gemcitabine as first-line therapy for patients with
advanced pancreas cancer: A randomized trial. J Clin Oncol.
15:2403–2413. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Shukuya T, Yasui H, Boku N, Onozawa Y,
Fukutomi A, Yamazaki K, Taku K, Kojima T and Machida N: Weekly
Paclitaxel after failure of gemcitabine in pancreatic cancer
patients with malignant ascites: A retrospective study. Jpn J Clin
Oncol. 40:1135–1138. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Maeda S, Motoi F, Onogawa T, Morikawa T,
Shigeru O, Sakata N, Takadate T, Naitoh T, Rikiyama T, Katayose Y,
et al: Paclitaxel as second-line chemotherapy in patients with
gemcitabine-refractory pancreatic cancer: A retrospective study.
Int J Clin Oncol. 16:539–545. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Saif MW: Advancements in the management of
pancreatic cancer: 2013. JOP. 14:112–118. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhang DS, Wang DS, Wang ZQ, Wang FH, Luo
HY, Qiu MZ, Wang F, Li YH and Xu RH: Phase I/II study of
albumin-bound nab-paclitaxel plus gemcitabine administered to
Chinese patients with advanced pancreatic cancer. Cancer Chemother
Pharmacol. 71:1065–1072. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Blagosklonny MV: Mitotic arrest and cell
fate: Why and how mitotic inhibition of transcription drives
mutually exclusive events. Cell Cycle. 6:70–74. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Rowinsky EK: The development and clinical
utility of the taxane class of antimicrotubule chemotherapy agents.
Annu Rev Med. 48:353–374. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hari M, Loganzo F, Annable T, Tan X, Musto
S, Morilla DB, Nettles JH, Snyder JP and Greenberger LM:
Paclitaxel-resistant cells have a mutation in the
paclitaxel-binding region of beta-tubulin (Asp26Glu) and less
stable microtubules. Mol Cancer Ther. 5:270–278. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Mozzetti S, Ferlini C, Concolino P,
Filippetti F, Raspaglio G, Prislei S, Gallo D, Martinelli E,
Ranelletti FO, Ferrandina G and Scambia G: Class III beta-tubulin
overexpression is a prominent mechanism of paclitaxel resistance in
ovarian cancer patients. Clin Cancer Res. 11:298–305.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Derry WB, Wilson L, Khan IA, Luduena RF
and Jordan MA: Taxol differentially modulates the dynamics of
microtubules assembled from unfractionated and purified
beta-tubulin isotypes. Biochemistry. 36:3554–3562. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kavallaris M, Kuo DY, Burkhart CA, Regl
DL, Norris MD, Haber M and Horwitz SB: Taxol-resistant epithelial
ovarian tumors are associated with altered expression of specific
beta-tubulin isotypes. J Clin Invest. 100:1282–1293. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lee KM, Cao D, Itami A, Pour PM, Hruban
RH, Maitra A and Ouellette MM: Class III beta-tubulin, a marker of
resistance to paclitaxel, is overexpressed in pancreatic ductal
adenocarcinoma and intraepithelial neoplasia. Histopathology.
51:539–546. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Youle RJ and Strasser A: The BCL-2 protein
family: Opposing activities that mediate cell death. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 9:47–59. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wertz IE, Kusam S, Lam C, Okamoto T,
Sandoval W, Anderson DJ, Helgason E, Ernst JA, Eby M, Liu J, et al:
Sensitivity to antitubulin chemotherapeutics is regulated by MCL1
and FBW7. Nature. 471:110–114. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Inuzuka H, Shaik S, Onoyama I, Gao D,
Tseng A, Maser RS, Zhai B, Wan L, Gutierrez A, Lau AW, et al: SCF
(FBW7) regulates cellular apoptosis by targeting MCL1 for
ubiquitylation and destruction. Nature. 471:104–109. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Oltersdorf T, Elmore SW, Shoemaker AR,
Armstrong RC, Augeri DJ, Belli BA, Bruncko M, Deckwerth TL, Dinges
J, Hajduk PJ, et al: An inhibitor of Bcl-2 family proteins induces
regression of solid tumours. Nature. 435:677–681. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wilson WH, O'Connor OA, Czuczman MS,
LaCasce AS, Gerecitano JF, Leonard JP, Tulpule A, Dunleavy K, Xiong
H, Chiu YL, et al: Safety, pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and
activity of navitoclax, a targeted high affinity inhibitor of
BCL-2, in lymphoid malignancies. Lancet Oncol. 11:1149–1159. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Tse C, Shoemaker AR, Adickes J, Anderson
MG, Chen J, Jin S, Johnson EF, Marsh KC, Mitten MJ, Nimmer P, et
al: ABT-263: A potent and orally bioavailable Bcl-2 family
inhibitor. Cancer Res. 68:3421–3428. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gandhi L, Camidge DR, de Oliveira M
Ribeiro, Bonomi P, Gandara D, Khaira D, Hann CL, McKeegan EM,
Litvinovich E, Hemken PM, et al: Phase I study of Navitoclax
(ABT-263), a novel Bcl-2 family inhibitor, in patients with
small-cell lung cancer and other solid tumors. J Clin Oncol.
29:909–916. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wong M, Tan N, Zha J, Peale FV, Yue P,
Fairbrother WJ and Belmont LD: Navitoclax (ABT-263) reduces
Bcl-x(L)-mediated chemoresistance in ovarian cancer models. Mol
Cancer Ther. 11:1026–35. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Tan N, Malek M, Zha J, Yue P, Kassees R,
Berry L, Fairbrother WJ, Sampath D and Belmont LD: Navitoclax
enhances the efficacy of taxanes in non-small cell lung cancer
models. Clin Cancer Res. 17:1394–1404. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Stamelos V, Robinson E, Redman CW and
Richardson A: Navitoclax augments the activity of carboplatin and
paclitaxel combinations in ovarian cancer cells. Gynecol Oncol.
128:377–382. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Watanabe A, Yasuhira S, Inoue T, Kasai S,
Shibazaki M, Takahashi K, Akasaka T, Masuda T and Maesawa C: BCL2
and BCLxL are key determinants of resistance to antitubulin
chemotherapeutics in melanoma cells. Exp Dermatol. 22:518–523.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sonnichsen DS and Relling MV: Clinical
pharmacokinetics of paclitaxel. Clin Pharmacokinet. 27:256–269.
1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Jain HV, Richardson A, Meyer-Hermann M and
Byrne HM: Exploiting the synergy between carboplatin and ABT-737 in
the treatment of ovarian carcinomas. PLoS One. 9:e815822014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Tan N, Wong M, Nannini MA, Hong R, Lee LB,
Price S, Williams K, Savy PP, Yue P, Sampath D, et al: Bcl-2/Bcl-xL
inhibition increases the efficacy of MEK inhibition alone and in
combination with PI3 kinase inhibition in lung and pancreatic tumor
models. Mol Cancer Ther. 12:853–864. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Infante JR, Matsubayashi H, Sato N,
Tonascia J, Klein AP, Riall TA, Yeo C, Iacobuzio-Donahue C and
Goggins M: Peritumoral fibroblast SPARC expression and patient
outcome with resectable pancreatic adenocarcinoma. J Clin Oncol.
25:319–325. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hidalgo M and Von Hoff DD: Translational
therapeutic opportunities in ductal adenocarcinoma of the pancreas.
Clin Cancer Res. 18:4249–4256. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Oikonomopoulos GM, Syrigos KN and Saif MW:
Prognostic factors in pancreatic cancer. JOP. 14:322–324.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
von Hoff DD, Ramanathan RK, Borad MJ,
Laheru DA, Smith LS, Wood TE, Korn RL, Desai N, Trieu V, Iglesias
JL, et al: Gemcitabine plus nab-paclitaxel is an active regimen in
patients with advanced pancreatic cancer: A phase I/II trial. J
Clin Oncol. 29:4548–4554. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|