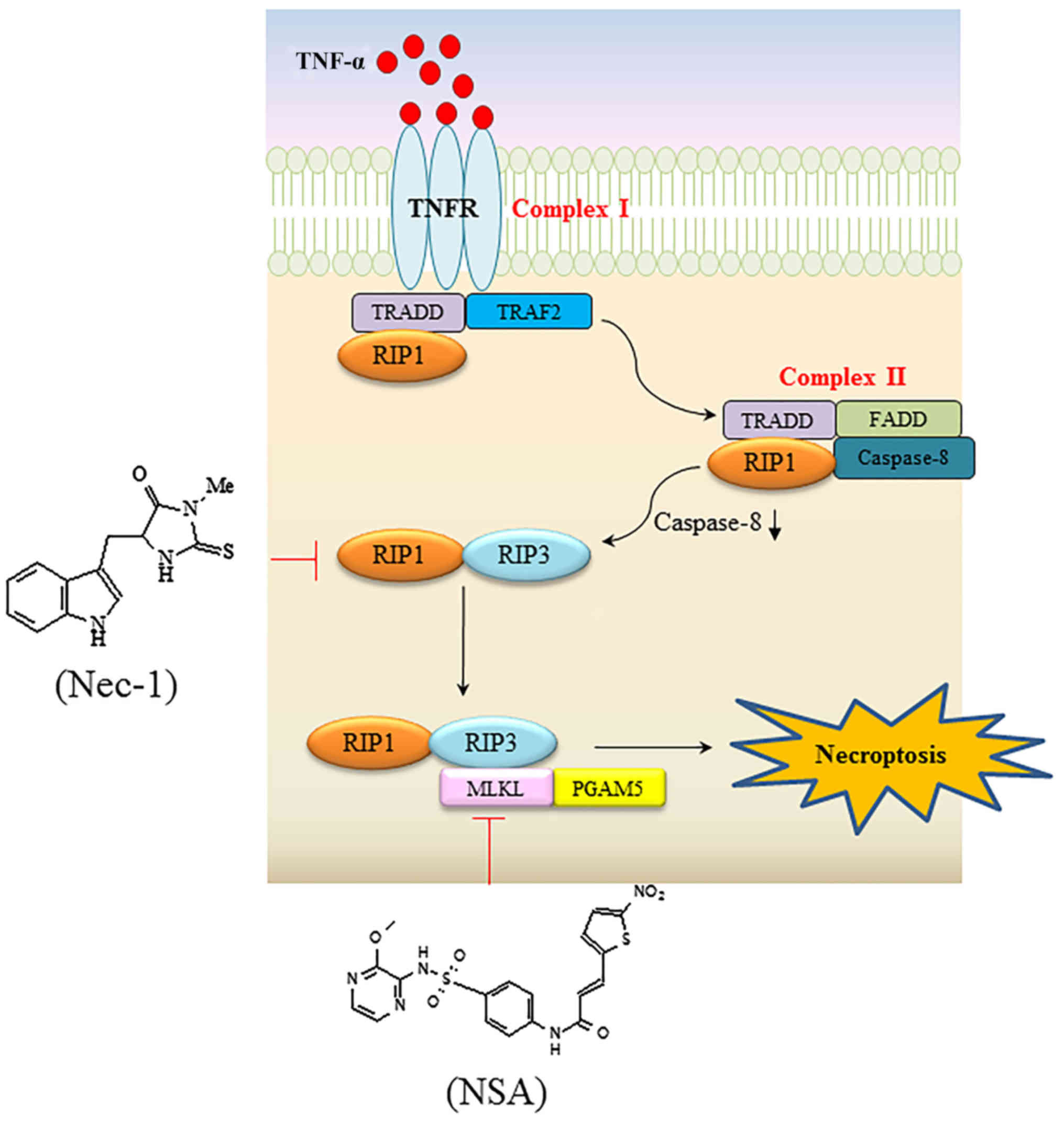
|
1
|
Fulda S, Gorman AM, Hori O and Samali A:
Cellular stress responses: Cell survival and cell death. Int J Cell
Biol. 2010:2140742010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Haanen C and Vermes I: Apoptosis:
Programmed cell death in fetal development. Eur J Obstet Gynecol
Reprod Biol. 64:129–133. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Opferman JT: Apoptosis in the development
of the immune system. Cell Death Differ. 15:234–242. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Duval D, Trouillas M, Thibault C, Dembelé
D, Diemunsch F, Reinhardt B, Mertz AL, Dierich A and Boeuf H:
Apoptosis and differentiation commitment: Novel insights revealed
by gene profiling studies in mouse embryonic stem cells. Cell Death
Differ. 13:564–575. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Elliott MR and Ravichandran KS: Clearance
of apoptotic cells: Implications in health and disease. J Cell
Biol. 189:1059–1070. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Van den Berghe T, Linkermann A,
Jouan-Lanhouet S, Walczak H and Vandenabeele P: Regulated necrosis:
The expanding network of non-apoptotic cell death pathways. Nat Rev
Mol Cell Biol. 15:135–147. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Giampietri C, Starace D, Petrungaro S,
Filippini A and Ziparo E: Necroptosis: Molecular signalling and
translational implications. Int J Cell Biol. 2014:4902752014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lu JV, Chen HC and Walsh CM: Necroptotic
signaling in adaptive and innate immunity. Semin Cell Dev Biol.
35:33–39. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Fulda S: The mechanism of necroptosis in
normal and cancer cells. Cancer Biol Ther. 14:999–1004. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhou W and Yuan J: Necroptosis in health
and diseases. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 35:14–23. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kaczmarek A, Vandenabeele P and Krysko DV:
Necroptosis: The release of damage-associated molecular patterns
and its physiological relevance. Immunity. 38:209–223. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Cho YS, Challa S, Moquin D, Genga R, Ray
TD, Guildford M and Chan FK: Phosphorylation-driven assembly of the
RIP1-RIP3 complex regulates programmed necrosis and virus-induced
inflammation. Cell. 137:1112–1123. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hitomi J, Christofferson DE, Ng A, Yao J,
Degterev A, Xavier RJ and Yuan J: Identification of a molecular
signaling network that regulates a cellular necrotic cell death
pathway. Cell. 135:1311–1323. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Festjens N, Berghe T Vanden, Cornelis S
and Vandenabeele P: RIP1, a kinase on the crossroads of a cell's
decision to live or die. Cell Death Differ. 14:400–410. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Micheau O and Tschopp J: Induction of TNF
receptor I-mediated apoptosis via two sequential signaling
complexes. Cell. 114:181–190. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Han J, Zhong CQ and Zhang DW: Programmed
necrosis: Backup to and competitor with apoptosis in the immune
system. Nat Immunol. 12:1143–1149. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Moquin DM, McQuade T and Chan FK: CYLD
deubiquitinates RIP1 in the TNFα-induced necrosome to facilitate
kinase activation and programmed necrosis. PLoS One. 8:e768412013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Moriwaki K and Chan FK: RIP3: A molecular
switch for necrosis and inflammation. Genes Dev. 27:1640–1649.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sun L, Wang H, Wang Z, He S, Chen S, Liao
D, Wang L, Yan J, Liu W, Lei X and Wang X: Mixed lineage kinase
domain-like protein mediates necrosis signaling downstream of RIP3
kinase. Cell. 148:213–227. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhao J, Jitkaew S, Cai Z, Choksi S, Li Q,
Luo J and Liu ZG: Mixed lineage kinase domain-like is a key
receptor interacting protein 3 downstream component of TNF-induced
necrosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 109:pp. 5322–5327. 2012;
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang Z, Jiang H, Chen S, Du F and Wang X:
The mitochondrial phosphatase PGAM5 functions at the convergence
point of multiple necrotic death pathways. Cell. 148:228–243. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Remijsen Q, Goossens V, Grootjans S, Van
den Haute C, Vanlangenakker N, Dondelinger Y, Roelandt R, Bruggeman
I, Goncalves A, Bertrand MJ, et al: Depletion of RIPK3 or MLKL
blocks TNF-driven necroptosis and switches towards a delayed RIPK1
kinase-dependent apoptosis. Cell Death Dis. 5:e10042014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Degterev A, Hitomi J, Germscheid M, Ch'en
IL, Korkina O, Teng X, Abbott D, Cuny GD, Yuan C, Wagner G, et al:
Identification of RIP1 kinase as a specific cellular target of
necrostatins. Nat Chem Biol. 4:313–321. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Liao D, Sun L, Liu W, He S, Wang X and Lei
X: Necrosulfonamide inhibits necroptosis by selectively targeting
the mixed lineage kinase domain-like protein. Med Chem Comm.
5:333–337. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Christofferson DE and Yuan J: Necroptosis
as an alternative form of programmed cell death. Curr Opin Cell
Biol. 22:263–268. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Bohgaki T, Mozo J, Salmena L,
Matysiak-Zablocki E, Bohgaki M, Sanchez O, Strasser A, Hakem A and
Hakem R: Caspase-8 inactivation in T cells increases necroptosis
and suppresses autoimmunity in Bim-/-mice. J Cell Biol.
195:277–291. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Upton JW, Kaiser WJ and Mocarski ES: Virus
inhibition of RIP3-dependent necrosis. Cell Host Microbe.
7:302–313. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Desvignes L, Wolf AJ and Ernst JD: Dynamic
roles of type I and type II IFNs in early infection with
Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Immunol. 188:6205–6215. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Robinson N, McComb S, Mulligan R, Dudani
R, Krishnan L and Sad S: Type I interferon induces necroptosis in
macrophages during infection with Salmonella enterica serovar
Typhimurium. Nat Immunol. 13:954–962. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
He S, Wang L, Miao L, Wang T, Du F, Zhao L
and Wang X: Receptor interacting protein kinase-3 determines
cellular necrotic response to TNF-alpha. Cell. 137:1100–1111. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Gunther C, Martini E, Wittkopf N, Amann K,
Weigmann B, Neumann H, Waldner MJ, Hedrick SM, Tenzer S, Neurath MF
and Becker C: Caspase-8 regulates TNF-α-induced epithelial
necroptosis and terminal ileitis. Nature. 477:335–339. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Trichonas G, Murakami Y, Thanos A,
Morizane Y, Kayama M, Debouck CM, Hisatomi T, Miller JW and Vavvas
DG: Receptor interacting protein kinases mediate retinal
detachment-induced photoreceptor necrosis and compensate for
inhibition of apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 107:pp.
21695–21700. 2010; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Linkermann A, De Zen F, Weinberg J,
Kunzendorf U and Krautwald S: Programmed necrosis in acute kidney
injury. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 27:3412–3419. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ramachandran A, McGill MR, Xie Y, Ni HM,
Ding WX and Jaeschke H: Receptor interacting protein kinase 3 is a
critical early mediator of acetaminophen-induced hepatocyte
necrosis in mice. Hepatology. 58:2099–2108. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ofengeim D, Ito Y, Najafov A, Zhang Y,
Shan B, DeWitt JP, Ye J, Zhang X, Chang A, Vakifahmetoglu-Norberg
H, et al: Activation of necroptosis in multiple sclerosis. Cell
Rep. 10:1836–1849. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kitur K, Parker D, Nieto P, Ahn DS, Cohen
TS, Chung S, Wachtel S, Bueno S and Prince A: Toxin-induced
necroptosis is a major mechanism of Staphylococcus aureus lung
damage. PLoS Pathog. 11:e10048202015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Su Z, Yang Z, Xie L, DeWitt JP and Chen Y:
Cancer therapy in the necroptosis era. Cell Death Differ.
23:748–756. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Meng MB, Wang HH, Cui YL, Wu ZQ, Shi YY,
Zaorsky NG, Deng L, Yuan ZY, Lu Y and Wang P: Necroptosis in
tumorigenesis, activation of anti-tumor immunity, and cancer
therapy. Oncotarget. 7:57391–57413. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Liu P, Xu B, Shen W, Zhu H, Wu W, Fu Y,
Chen H, Dong H, Zhu Y, Miao K, et al: Dysregulation of TNFα-induced
necroptotic signaling in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: Suppression
of CYLD gene by LEF1. Leukemia. 26:1293–1300. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Wu W, Liu P and Li J: Necroptosis: An
emerging form of programmed cell death. Crit Rev Oncol Hemato.
82:249–258. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Housman G, Byler S, Heerboth S, Lapinska
K, Longacre M, Snyder N and Sarkar S: Drug resistance in cancer: An
overview. Cancers (Basel). 6:1769–1792. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
McCabe KE, Bacos K, Lu D, Delaney JR,
Axelrod J, Potter MD, Vamos M, Wong V, Cosford ND, Xiang R and
Stupack DG: Triggering necroptosis in cisplatin and IAP
antagonist-resistant ovarian carcinoma. Cell Death Dis.
5:e14962014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Basit F, Cristofanon S and Fulda S:
Obatoclax (GX15-070) triggers necroptosis by promoting the assembly
of the necrosome on autophagosomal membranes. Cell Death Differ.
20:1161–1173. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Dunai ZA, Imre G, Barna G, Korcsmaros T,
Petak I, Bauer PI and Mihalik R: Staurosporine induces necroptotic
cell death under caspase-compromised conditions in U937 cells. PLoS
One. 7:e419452012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Deeraksa A, Pan J, Sha Y, Liu XD, Eissa
NT, Lin SH and Yu-Lee LY: Plk1 is upregulated in
androgen-insensitive prostate cancer cells and its inhibition leads
to necroptosis. Oncogene. 32:2973–2983. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Kaku Y, Tsuchiya A, Kanno T and Nishizaki
T: HUHS1015 induces necroptosis and caspase-independent apoptosis
of MKN28 human gastric cancer cells in association with AMID
accumulation in the nucleus. Anticancer Agents Med Chem.
15:242–247. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Pasupuleti N, Leon L, Carraway KL III and
Gorin F: 5-Benzylglycinyl-amiloride kills proliferating and
nonproliferating malignant glioma cells through caspase-independent
necroptosis mediated by apoptosis-inducing factor. J Pharmacol Exp
Ther. 344:600–615. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Huang C, Luo Y, Zhao J, Yang F, Zhao H,
Fan W and Ge P: Shikonin kills glioma cells through necroptosis
mediated by RIP-1. PLoS One. 8:e663262013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Fu Z, Deng B, Liao Y, Shan L, Yin F, Wang
Z, Zeng H, Zuo D, Hua Y and Cai Z: The anti-tumor effect of
shikonin on osteosarcoma by inducing RIP1 and RIP3 dependent
necroptosis. BMC Cancer. 13:5802013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Tian W, Deng Y, Li L, He H, Sun J and Xu
D: Honokiol synergizes chemotherapy drugs in multidrug resistant
breast cancer cells via enhanced apoptosis and additional
programmed necrotic death. Int J Oncol. 42:721–732. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Miki Y, Akimoto J, Moritake K, Hironaka C
and Fujiwara Y: Photodynamic therapy using talaporfin sodium
induces concentration-dependent programmed necroptosis in human
glioblastoma T98G cells. Lasers Med Sci. 30:1739–1745. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Nehs MA, Lin CI, Kozono DE, Whang EE, Cho
NL, Zhu K, Moalem J, Moore FD Jr and Ruan DT: Necroptosis is a
novel mechanism of radiation-induced cell death in anaplastic
thyroid and adrenocortical cancers. Surgery. 150:1032–1039. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Liu T, Bao YH, Wang Y and Jiang JY: The
role of necroptosis in neurosurgical diseases. Braz J Med Biol Res.
48:292–298. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Yamanaka K, Saito Y, Yamamori T, Urano Y
and Noguchi N: 24(S)-hydroxycholesterol induces neuronal cell death
through necroptosis, a form of programmed necrosis. J Biol Chem.
286:24666–24673. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Luedde M, Lutz M, Carter N, Sosna J,
Jacoby C, Vucur M, Gautheron J, Roderburg C, Borg N, Reisinger F,
et al: RIP3, a kinase promoting necroptotic cell death, mediates
adverse remodelling after myocardial infarction. Cardiovasc Res.
103:206–216. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
King MD, Whitaker-Lea WA, Campbell JM,
Alleyne CH Jr and Dhandapani KM: Necrostatin-1 reduces
neurovascular injury after intracerebral hemorrhage. Int J Cell
Biol. 2014:4958172014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Wang H, Sun L, Su L, Rizo J, Liu L, Wang
LF, Wang FS and Wang X: Mixed lineage kinase domain-like protein
MLKL causes necrotic membrane disruption upon phosphorylation by
RIP3. Mol Cell. 54:133–146. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|