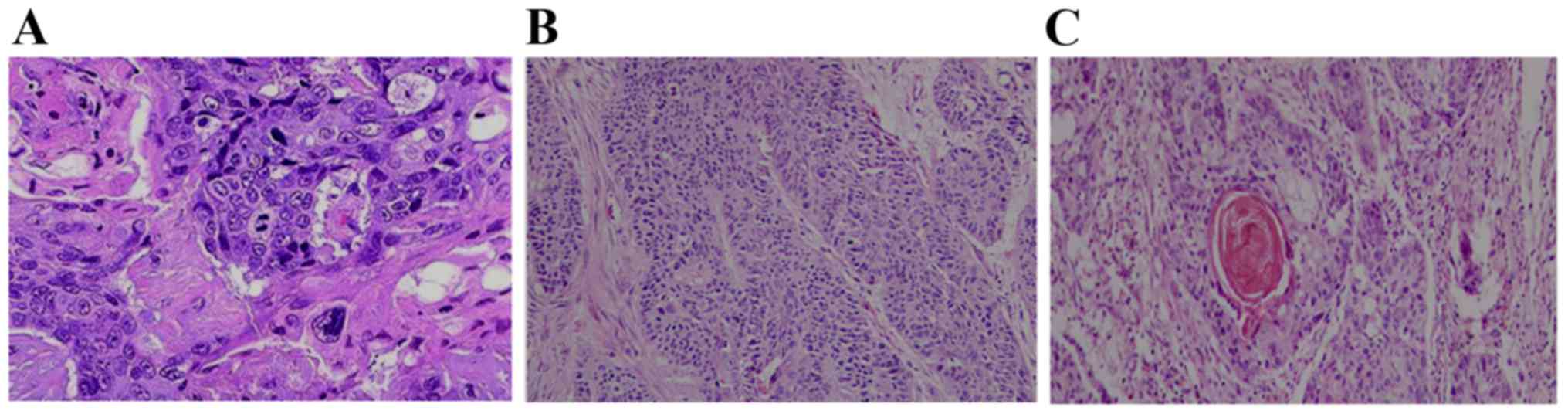
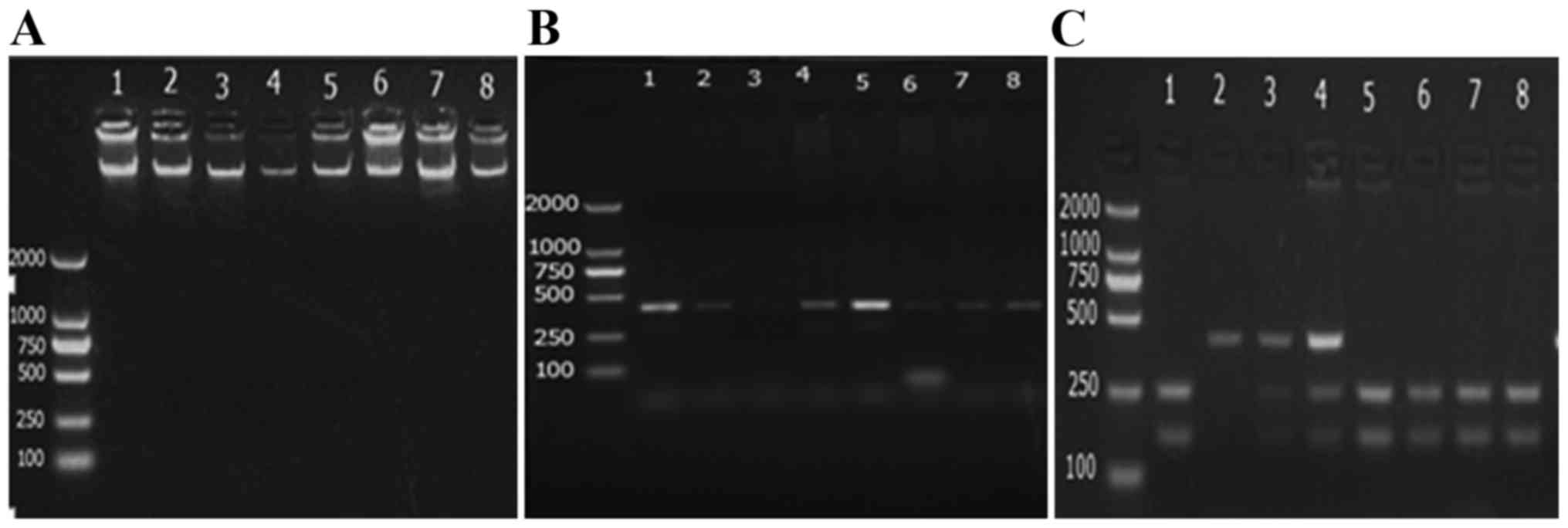
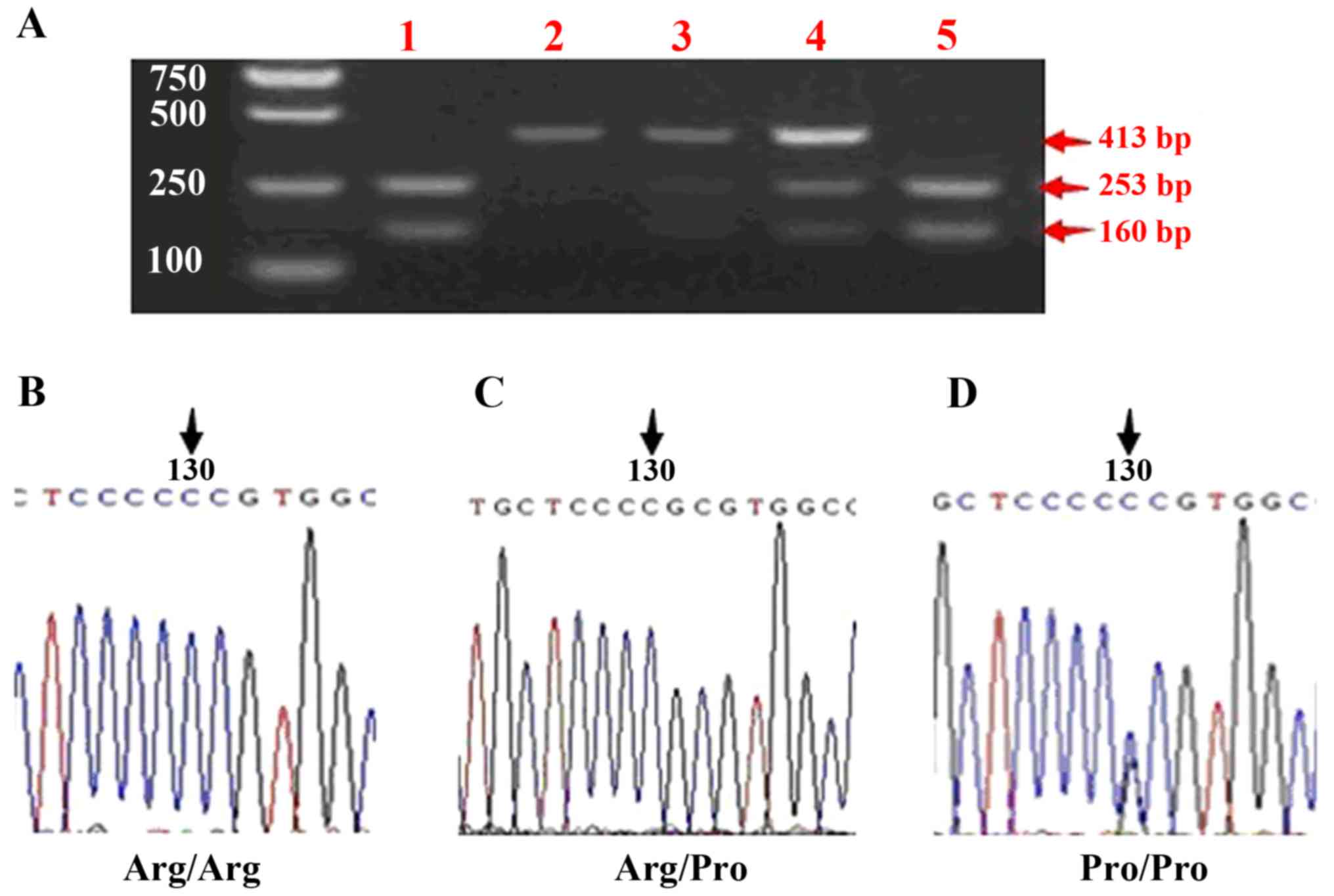
|
1
|
Pennathur A, Gibson MK, Jobe BA and
Luketich JD: Oesophageal carcinoma. Lancet. 381:400–412. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Yang J, Liu B, Li W, Xiong H, Qiu H, Fu Q,
Chen B, Hu G and Yuan X: Association of p53 and MDM2 polymorphisms
with risk of human papillomavirus (HPV)-related esophageal squamous
cell carcinoma (ESCC). Cancer Epidemiol. 37:629–633. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Enzinger PC and Mayer RJ: Esophageal
cancer. N Engl J Med. 349:2241–2252. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Islami F, Boffetta P, Ren JS, Pedoeim L,
Khatib D and Kamangar F: High-temperature beverages and foods and
esophageal cancer risk-a systematic review. Int J Cancer.
125:491–524. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kamangar F, Chow WH, Abnet CC and Dawsey
SM: Environmental causes of esophageal cancer. Gastroenterol Clin
North Am. 38:27–57, vii. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhang HZ, Jin GF and Shen HB:
Epidemiologic differences in esophageal cancer between Asian and
Western populations. Chin J Cancer. 31:281–286. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Gong Jinshan, Ao Shuyun and Ao Qimuge
Deng: Related research of Mongolia national diet and esophageal
cancer in Inner Mongolia area of Tongliao. Chinese Medical Guide.
1–451. 2013.
|
|
9
|
Davidoff AM, Iglehart JD and Marks JR:
Immune response to p53 is dependent upon p53/HSP70 complexes in
breast cancers. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 89:pp. 3439–3442. 1992;
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Vogiatzi P, Vindigni C, Roviello F,
Renieri A and Giordano A: Deciphering the underlying genetic and
epigenetic events leading to gastric carcinogenesis. J Cell
Physiol. 211:287–295. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Li Y: Clinical study of reflux esophagitis
in Mongolian. Inner Mongol J Med. 02:208–209. 2014.
|
|
12
|
Shimada H, Nabeya Y, Okazumi S, Matsubara
H, Funami Y, Shiratori T, Hayashi H, Takeda A and Ochiai T:
Prognostic significance of serum p53 antibody in patients with
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Surgery. 132:41–47. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang Z, Li X, Gao F, et al: Analysis of
the incidence of malignant tumors in Hami area from 2010 to 2012.
Xinjiang Med. 10:1501–1504. 2015.
|
|
14
|
Wu M, Zhao JK, Hu XS, Wang PH, Qin Y, Lu
YC, Yang J, Liu AM, Wu DL, Zhang ZF, et al: Association of smoking,
alcohol drinking and dietary factors with esophageal cancer in
high- and low-risk areas of Jiangsu Province, China. World J
Gastroenterol. 12:1686–1693. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sakata K, Hoshiyama Y, Morioka S,
Hashimoto T, Takeshita T and Tamakoshi A; JACC Study Group, :
Smoking, alcohol drinking and esophageal cancer: Findings from the
JACC Study. J Epidemiol. 15 Suppl 2:S212–S219. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yang CX, Wang HY, Wang ZM, Du HZ, Tao DM,
Mu XY, Chen HG, Lei Y, Matsuo K and Tajima K: Risk factors for
esophageal cancer: A case-control study in South-western China.
Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 6:48–53. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Castelli E, Hrelia P, Maffei F, Fimognari
C, Foschi FG, Caputo F, Cantelli-Forti G, Stefanini GF and
Gasbarrini G: Indicators of genetic damage in alcoholics:
Reversibility after alcohol abstinence. Hepatogastroenterology.
46:1664–1668. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhao Y, Wang F, Shan S, Zhao Y, Qiu X, Li
X, Jiao F, Wang J and Du Y: Genetic polymorphism of p53, but not
GSTP1, is association with susceptibility to esophageal cancer
risk-a meta-analysis. Int J Med Sci. 7:300–308. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Altilia S, Santoro A, Malagoli D,
Lanzarini C, Álvarez JA Ballesteros, Galazzo G, Porter DC, Crocco
P, Rose G, Passarino G, et al: TP53 codon 72 polymorphism affects
accumulation of mtDNA damage in human cells. Aging (Albany NY).
4:28–39. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chen H, Yang X and Wang Z: Association
between p53 Arg72Pro polymorphism and recurrent pregnancy loss: An
updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Reprod Biomed Online.
31:149–153. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Papadakis EN, Dokianakis DN and Spandidos
DA: p53 codon 72 polymorphism as a risk factor in the development
of breast cancer. Mol Cell Biol Res Commun. 3:389–392. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Thomas M, Kalita A, Labrecque S, Pim D,
Banks L and Matlashewski G: Two polymorphic variants of wild-type
p53 differ biochemically and biologically. Mol Cell Biol.
19:1092–1100. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Pereira L, Carvalho MR, Fonseca CG, Lima
SS, Cerqueira EM, Jorge W and Castro MC: Influence of Arg72Pro
polymorphisms of TP53 on the response of buccal cells to
radiotherapy. Genet Mol Res. 10:3552–3558. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Vogelstein B and Kinzler KW: p53 function
and dysfunction. Cell. 70:523–526. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Piao JM, Kim HN, Song HR, Kweon SS, Choi
JS, Yoon JY, Chung IJ, Kim SH and Shin MH: p53 codon 72
polymorphism and the risk of esophageal cancer: A Korean
case-control study. Dis Esophagus. 24:596–600. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hamajima N, Matsuo K, Suzuki T, Nakamura
T, Matsuura A, Hatooka S, Shinoda M, Kodera Y, Yamamura Y, Hirai T,
et al: No associations of p73 G4C14-to-A4T14 at exon 2 and p53
Arg72Pro polymorphisms with the risk of digestive tract cancers in
Japanese. Cancer Lett. 181:81–85. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Liu G, Cescon DW, Zhai R, Zhou W, Kulke
MH, Ma C, Xu W, Su L, Asomaning K, Heist RS, et al: p53 Arg72Pro,
MDM2 T309G and CCND1 G870A polymorphisms are not associated with
susceptibility to esophageal adenocarcinoma. Dis Esophagus.
23:36–39. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Aida J, Yokoyama A, Shimomura N, Nakamura
K, Ishikawa N, Terai M, Poon S, Matsuura M, Fujiwara M, Sawabe M,
et al: Telomere shortening in the esophagus of Japanese alcoholics:
Relationships with chromoendoscopic findings, ALDH2 and ADH1B
genotypes and smoking history. PLoS One. 8:e638602013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Buyru N, Altinisik J, Demokan S and Dalay
N: p53 genotypes and haplotypes associated with risk of breast
cancer. Cancer Detect Prev. 31:207–213. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zehbe I, Voglino G, Wilander E, Genta F
and Tommasino M: Codon 72 polymorphism of p53 and its association
with cervical cancer. Lancet. 354:218–219. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Jee SH, Lee JE and Park JS: Polymorphism
of codon 72 of p53 and environmental factors in the development of
cervical cancer. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 80:69–70. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Buller RE, Sood A, Fullenkamp C, Sorosky
J, Powills K and Anderson B: The influence of the p53 codon 72
polymorphism on ovarian carcinogenesis and prognosis. Cancer Gene
Ther. 4:239–245. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Buller RE, Shahin MS, Holmes RW, Hatterman
M, Kirby PA and Sood AK: p53 Mutations and microsatellite
instability in ovarian cancer: Yin and yang. Am J Obstet Gynecol.
184:891–903. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Cai L, Mu LN, Lu H, Lu QY, You NC, Yu SZ,
Le AD, Zhao J, Zhou XF, Marshall J, et al: Dietary selenium intake
and genetic polymorphisms of the GSTP1 and p53 genes on the risk of
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers
Prev. 15:294–300. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhang L, Xing D, He Z and Lin D: p53 gene
codon 72 polymorphism and susceptibility to esophageal squamous
cell carcinoma in a Chinese population. Zhonghua Yi Xue Yi Chuan
Xue Za Zhi. 19:10–13. 2002.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Hong Y, Miao X, Zhang X, Ding F, Luo A,
Guo Y, Tan W, Liu Z and Lin D: The role of P53 and MDM2
polymorphisms in the risk of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
Cancer Res. 65:9582–9587. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ge H, Cao YY, Chen LQ, Wang YM, Chen ZF,
Wen DG, Zhang XF, Guo W, Wang N, Li Y and Zhang JH: PTEN
polymorphisms and the risk of esophageal carcinoma and gastric
cardiac carcinoma in a high incidence region of China. Dis
Esophagus. 21:409–415. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|