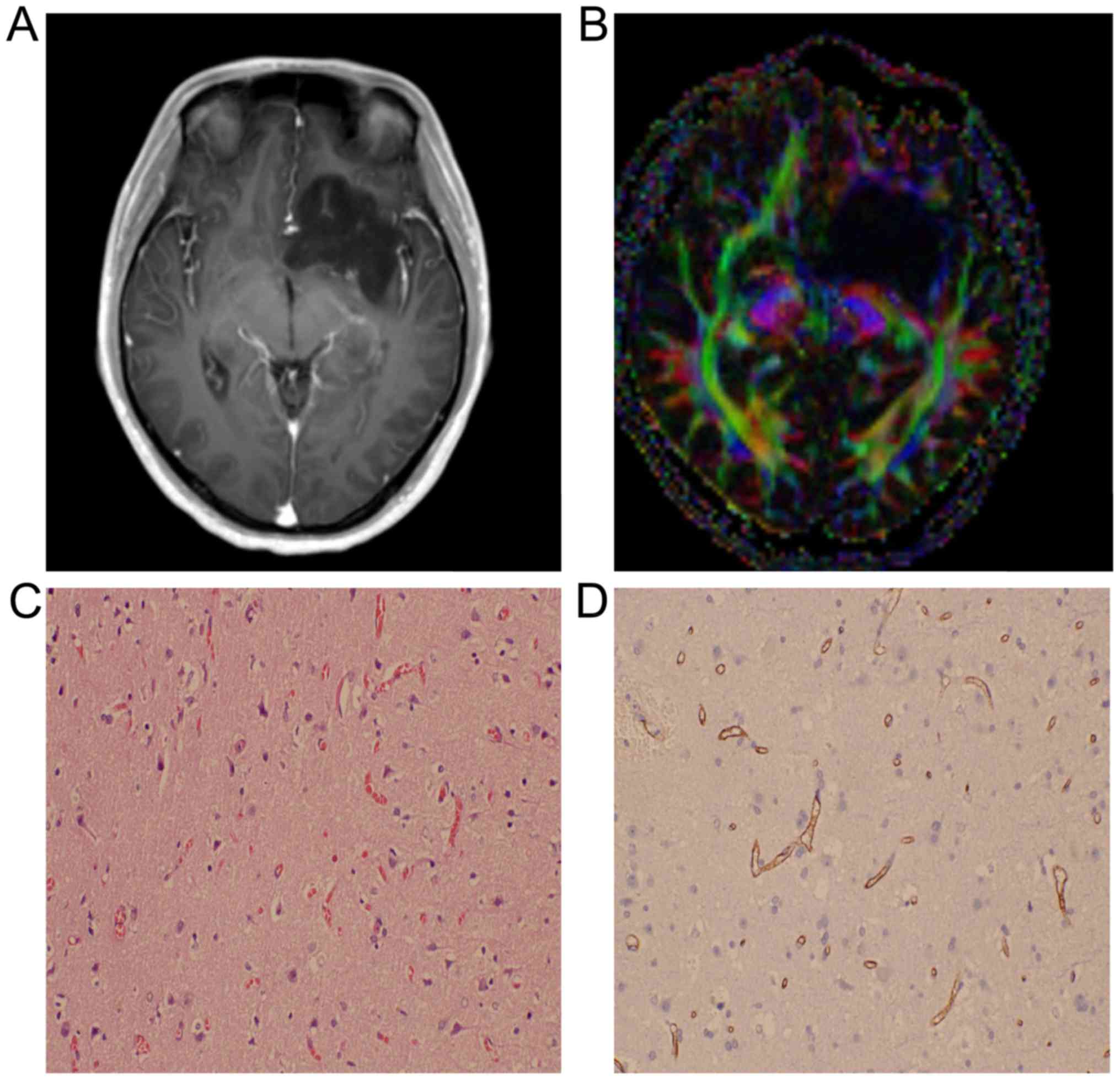
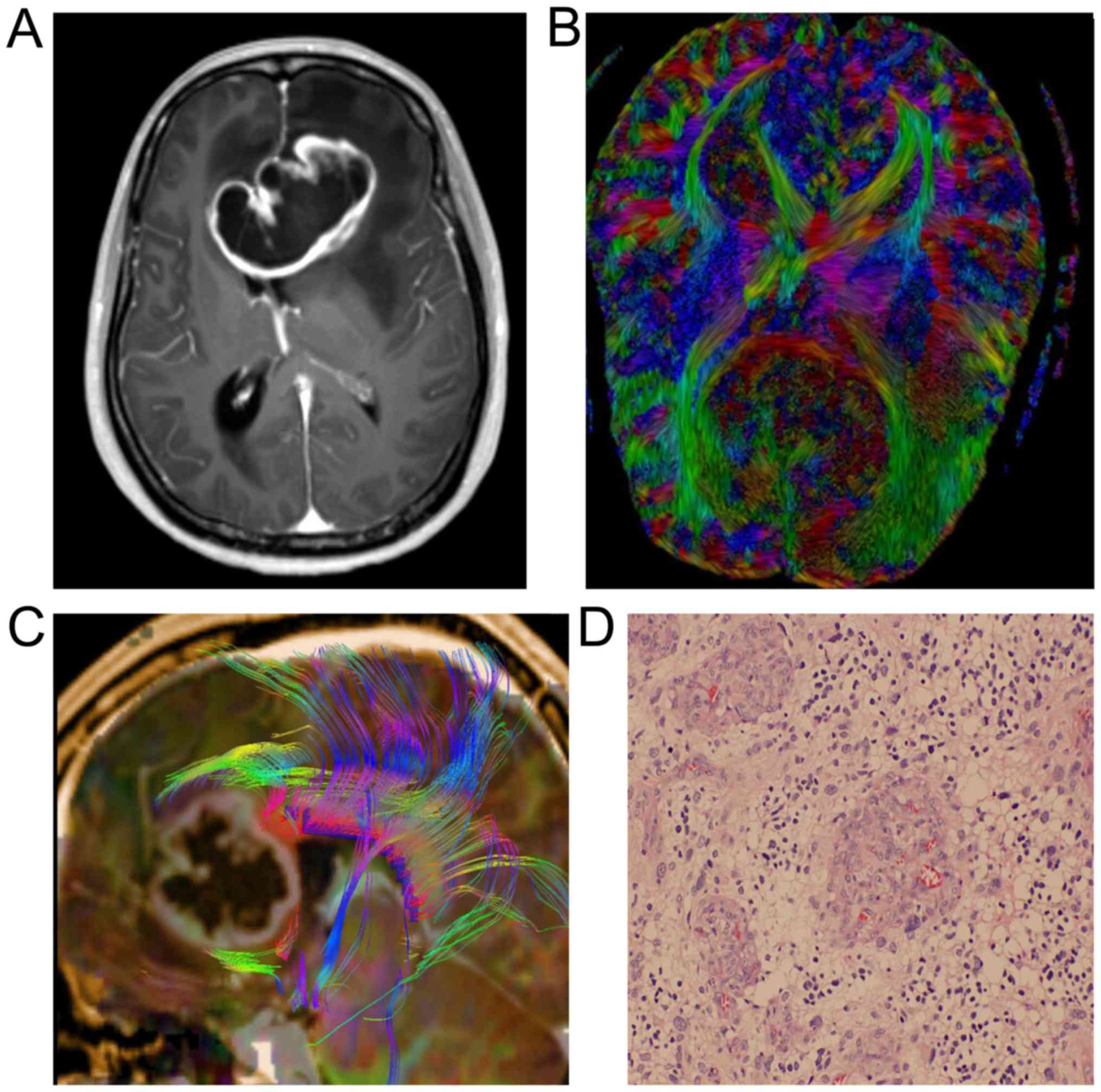
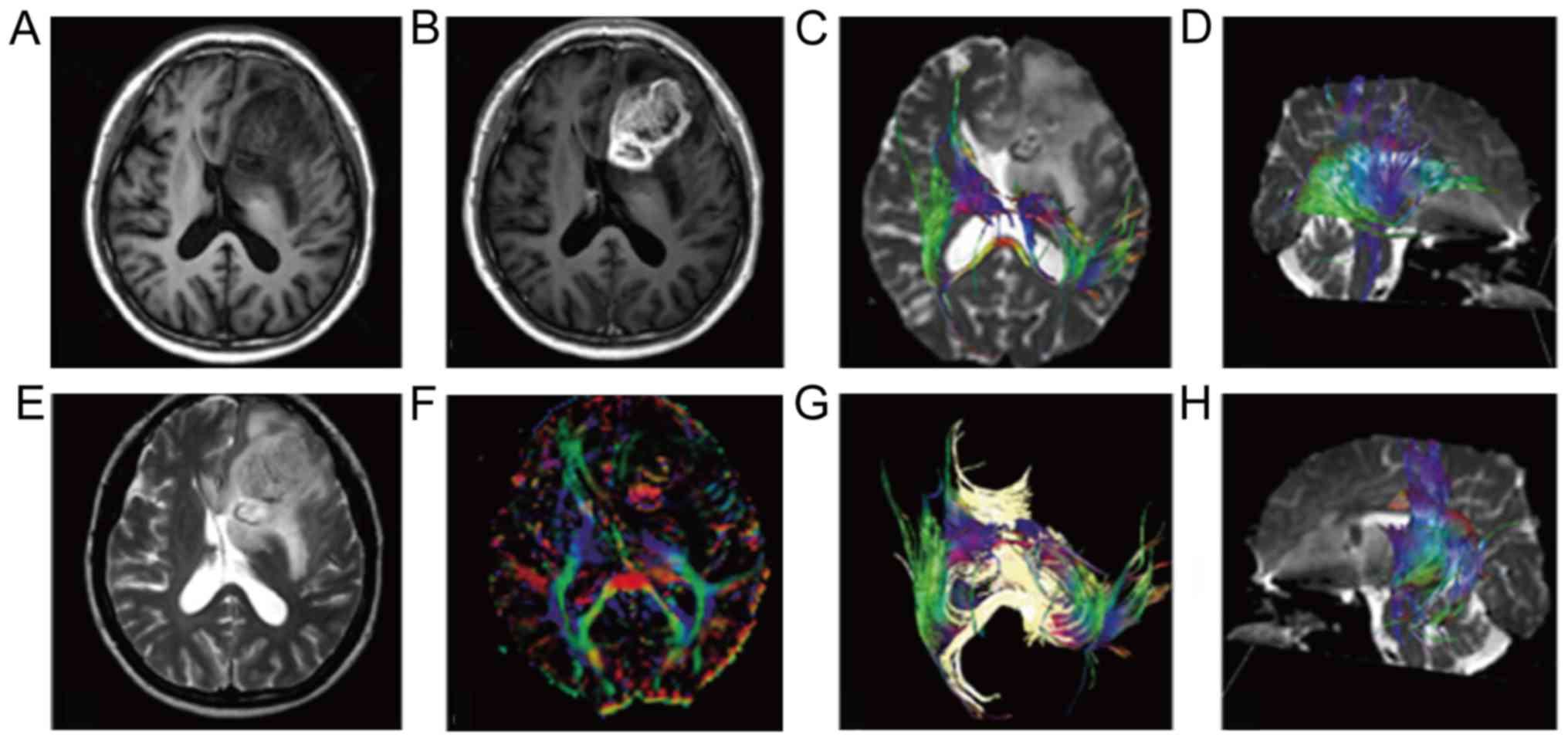
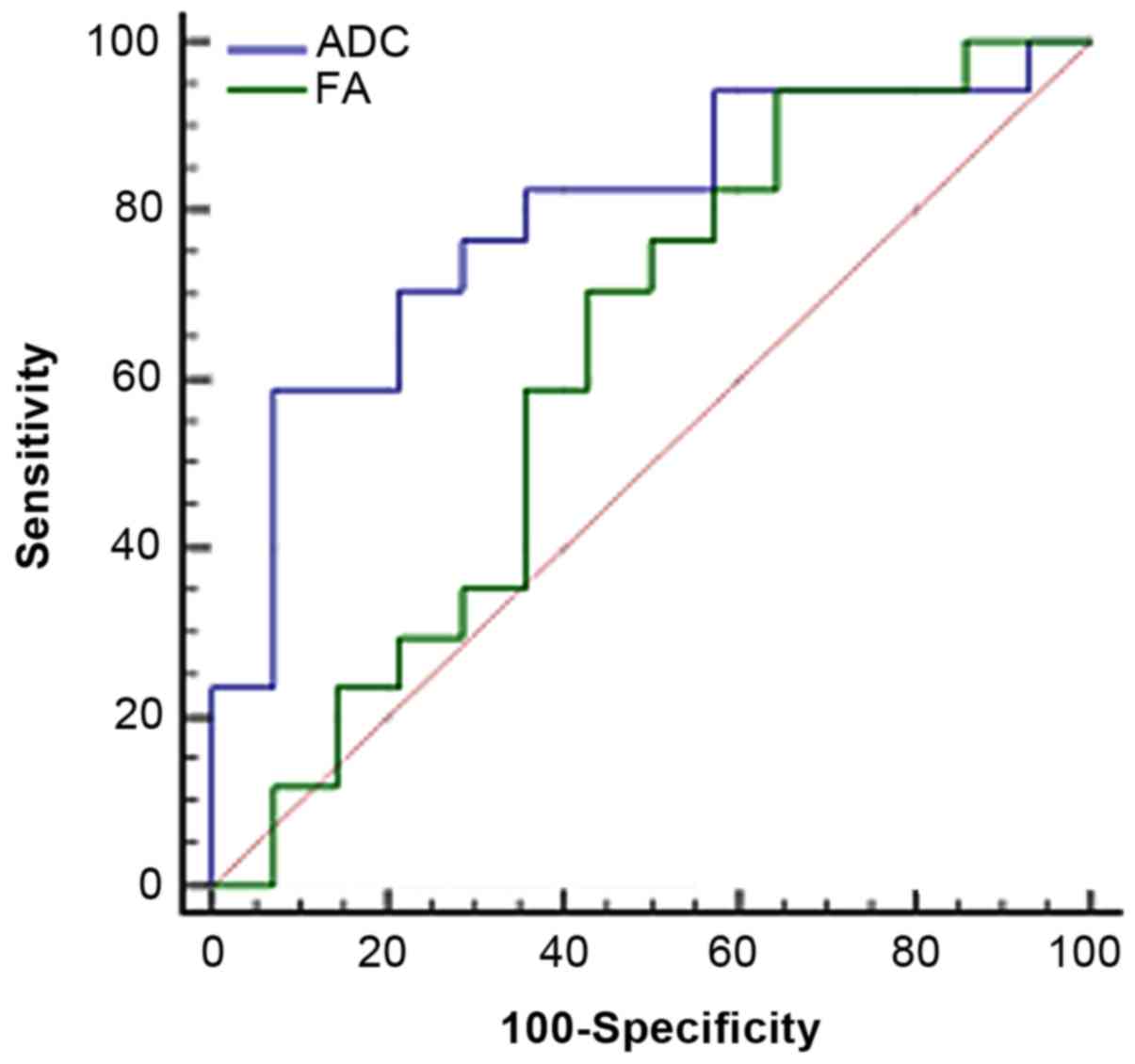
|
1
|
Inoue T, Ogasawara K, Beppu T, Ogawa A and
Kabasawa H: Diffusion tensor imaging for preoperative evaluation of
tumor grade in gliomas. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 107:174–180. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Rousseau A, Mokhtari K and Duyckaerts C:
The 2007 WHO classification of tumors of the central nervous system
- what has changed? Curr Opin Neurol. 21:720–727. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Field AS and Alexander AL: Diffusion
tensor imaging in cerebral tumor diagnosis and therapy. Top Magn
Reson Imaging. 15:315–324. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Nimsky C, Ganslandt O, Hastreiter P, Wang
R, Benner T, Sorensen AG and Fahlbusch R: Preoperative and
intraoperative diffusion tensor imaging-based fiber tracking in
glioma surgery. Neurosurgery. 61:178–185; discussion 186. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hadziahmetovic M, Shirai K and Chakravarti
A: Recent advancements in multimodality treatment of gliomas.
Future Oncol. 7:1169–1183. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yao K, Wang H, Duan Z, Bian Y, Xia L, Ma Z
and Qi X: Mixed granular cell astrocytoma and fibrosarcoma of the
brain: A case report. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 7:4473–4478.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Leestma JE: Brain tumors. Am J Pathol.
100:239–316. 1980.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wang H, Li XT, Wu C, Wu ZW, Li YY, Yang
TQ, Chen GL, Xie XS, Huang YL, Du ZW, et al: miR-132 can inhibit
glioma cells invasion and migration by target MMP16 in vitro. Onco
Targets Ther. 8:3211–3218. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Doblas S, He T, Saunders D, Pearson J,
Hoyle J, Smith N, Lerner M and Towner RA: Glioma morphology and
tumor-induced vascular alterations revealed in seven rodent glioma
models by in vivo magnetic resonance imaging and angiography. J
Magn Reson Imaging. 32:267–275. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bokacheva L, Ackerstaff E, LeKaye HC,
Zakian K and Koutcher JA: High-field small animal magnetic
resonance oncology studies. Phys Med Biol. 59:R65–R127. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lohrke J, Frenzel T, Endrikat J, Alves FC,
Grist TM, Law M, Lee JM, Leiner T, Li KC, Nikolaou K, et al: 25
years of Contrast-Enhanced MRI: Developments, current challenges
and future perspectives. Adv Ther. 33:1–28. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gutova M, Frank JA, D'Apuzzo M,
Khankaldyyan V, Gilchrist MM, Annala AJ, Metz MZ, Abramyants Y,
Herrmann KA, Ghoda LY, et al: Magnetic resonance imaging tracking
of ferumoxytol-labeled human neural stem cells: Studies leading to
clinical use. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2:766–775. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kalpathy-Cramer J, Gerstner ER, Emblem KE,
Andronesi OC and Rosen B: Advanced magnetic resonance imaging of
the physical processes in human glioblastoma. Cancer Res.
74:4622–4637. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhou J, Tryggestad E, Wen Z, Lal B, Zhou
T, Grossman R, Wang S, Yan K, Fu DX, Ford E, et al: Differentiation
between glioma and radiation necrosis using molecular magnetic
resonance imaging of endogenous proteins and peptides. Nat Med.
17:130–134. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|