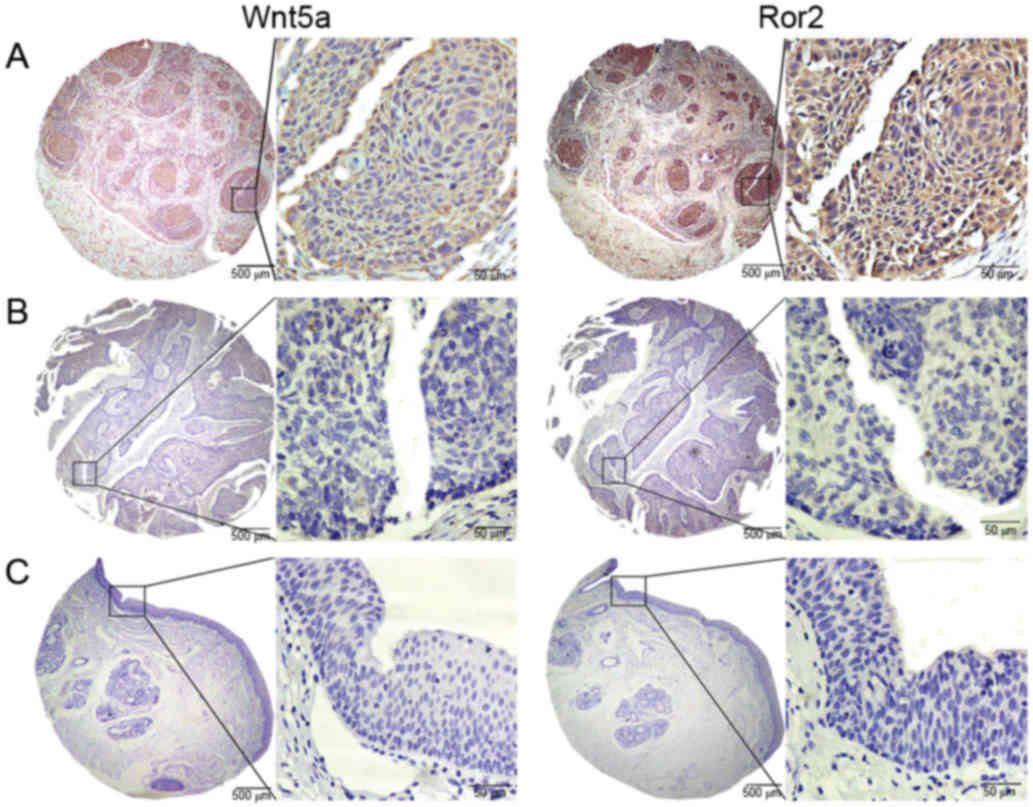
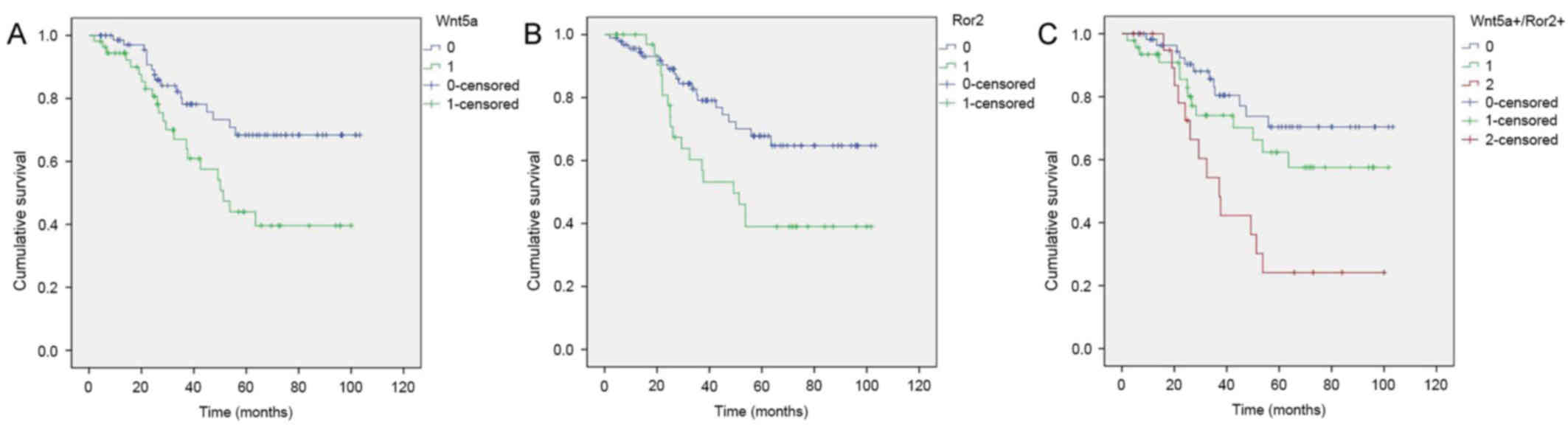
|
1
|
Siegel R, Naishadham D and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 62:10–29. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hoffman HT, Porter K, Karnell LH, Cooper
JS, Weber RS, Langer CJ, Ang KK, Gay G, Stewart A and Robinson RA:
Laryngeal cancer in the United States: Changes in demographics,
patterns of care and survival. Laryngoscope. 116 Suppl 111:S1–S13.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Papadas TA, Alexopoulos EC, Mallis A,
Jelastopulu E, Mastronikolis NS and Goumas P: Survival after
laryngectomy: A review of 133 patients with laryngeal carcinoma.
Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 267:1095–1101. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Logan CY and Nusse R: The Wnt signaling
pathway in development and disease. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol.
20:781–810. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Veeman MT, Axelrod JD and Moon RT: A
second canon. Functions and mechanisms of beta-catenin-independent
Wnt signaling. Dev Cell. 5:367–377. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Korinek V, Barker N, Willert K, Molenaar
M, Roose J, Wagenaar G, Markman M, Lamers W, Destree O and Clevers
H: Two members of the Tcf family implicated in Wnt/beta-catenin
signaling during embryogenesis in the mouse. Mol Cell Biol.
18:1248–1256. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Molinolo AA, Amornphimoltham P, Squarize
CH, Castilho RM, Patel V and Gutkind JS: Dysregulated molecular
networks in head and neck carcinogenesis. Oral Oncol. 45:324–334.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Qian D, Jones C, Rzadzinska A, Mark S,
Zhang X, Steel KP, Dai X and Chen P: Wnt5a functions in planar cell
polarity regulation in mice. Dev Biol. 306:121–133. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Slusarski DC, Corces VG and Moon RT:
Interaction of Wnt and a Frizzled homologue triggers
G-protein-linked phosphatidylinositol signalling. Nature.
390:410–413. 1997. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Pandur P, Maurus D and Kuhl M:
Increasingly complex: New players enter the Wnt signaling network.
Bioessays. 24:881–884. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Prado SM Diaz, Villaamil V Medina, Gallego
G Aparicio, Calvo M Blanco, López Cedrún JL, Soliva S Sironvalle,
Ayerbes M Valladares, García Campelo R and Antón Aparicio LM:
Expression of Wnt gene family and frizzled receptors in head and
neck squamous cell carcinomas. Virchows Arch. 455:67–75. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Rhee CS, Sen M, Lu D, Wu C, Leoni L, Rubin
J, Corr M and Carson DA: Wnt and frizzled receptors as potential
targets for immunotherapy in head and neck squamous cell
carcinomas. Oncogene. 21:6598–6605. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Giles RH, van Es JH and Clevers H: Caught
up in a Wnt storm: Wnt signaling in cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1653:1–24. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Pukrop T and Binder C: The complex
pathways of Wnt 5a in cancer progression. J Mol Med (Berl).
86:259–266. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
McDonald SL and Silver A: The opposing
roles of Wnt-5a in cancer. Br J Cancer. 101:209–214. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Mikels AJ and Nusse R: Purified Wnt5a
protein activates or inhibits beta-catenin-TCF signaling depending
on receptor context. PLoS Biol. 4:e1152006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
MacLeod RJ, Hayes M and Pacheco I: Wnt5a
secretion stimulated by the extracellular calcium-sensing receptor
inhibits defective Wnt signaling in colon cancer cells. Am J
Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 293:G403–G411. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Forrester WC: The Ror receptor tyrosine
kinase family. Cell Mol Life Sci. 59:83–96. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yoda A, Oishi I and Minami Y: Expression
and function of the Ror-family receptor tyrosine kinases during
development: Lessons from genetic analyses of nematodes, mice, and
humans. J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 23:1–15. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wright TM, Brannon AR, Gordan JD, Mikels
AJ, Mitchell C, Chen S, Espinosa I, van de Rijn M, Pruthi R, Wallen
E, et al: Ror2, a developmentally regulated kinase, promotes tumor
growth potential in renal cell carcinoma. Oncogene. 28:2513–2523.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kobayashi M, Shibuya Y, Takeuchi J, Murata
M, Suzuki H, Yokoo S, Umeda M, Minami Y and Komori T: Ror2
expression in squamous cell carcinoma and epithelial dysplasia of
the oral cavity. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod.
107:398–406. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
O'Connell MP, Fiori JL, Xu M, Carter AD,
Frank BP, Camilli TC, French AD, Dissanayake SK, Indig FE, Bernier
M, et al: The orphan tyrosine kinase receptor, ROR2, mediates Wnt5A
signaling in metastatic melanoma. Oncogene. 29:34–44. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Geng M, Cao YC, Chen YJ, Jiang H, Bi LQ
and Liu XH: Loss of Wnt5a and Ror2 protein in hepatocellular
carcinoma associated with poor prognosis. World J Gastroenterol.
18:1328–1338. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lee SE, Lim SD, Kang SY, Suh SB and Suh
YL: Prognostic significance of Ror2 and Wnt5a expression in
medulloblastoma. Brain Pathol. 23:445–453. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lara E, Calvanese V, Huidobro C, Fernández
AF, Moncada-Pazos A, Obaya AJ, Aguilera O, González-Sancho JM,
Sánchez L, Astudillo A, et al: Epigenetic repression of ROR2 has a
Wnt-mediated, pro-tumourigenic role in colon cancer. Mol Cancer.
9:1702010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Thompson L: World Health Organization
classification of tumours: Pathology and genetics of head and neck
tumours. Ear Nose Throat J. 85:742006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wu H, Xu H, Zhang S, Wang X, Zhu H, Zhang
H, Zhu J and Huang J: Potential therapeutic target and independent
prognostic marker of TROP2 in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma.
Head Neck. 35:1373–1378. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Feng J, Xu L, Ni S, Gu J, Zhu H, Wang H,
Zhang S, Zhang W and Huang J: Involvement of FoxQ1 in NSCLC through
regulating EMT and increasing chemosensitivity. Oncotarget.
5:9689–9702. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wang Q, Ni Q, Wang X, Zhu H, Wang Z and
Huang J: High expression of RAB27A and TP53 in pancreatic cancer
predicts poor survival. Med Oncol. 32:3722015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ni S, Xu L, Huang J, Feng J, Zhu H, Wang G
and Wang X: Increased ZO-1 expression predicts valuable prognosis
in non-small cell lung cancer. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 6:2887–2895.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sun R, Wang X, Zhu H, Mei H, Wang W, Zhang
S and Huang J: Prognostic value of LAMP3 and TP53 overexpression in
benign and malignant gastrointestinal tissues. Oncotarget.
5:12398–12409. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Clark CC, Cohen I, Eichstetter I,
Cannizzaro LA, McPherson JD, Wasmuth JJ and Iozzo RV: Molecular
cloning of the human proto-oncogene Wnt-5A and mapping of the gene
(WNT5A) to chromosome 3p14-p21. Genomics. 18:249–260. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Topol L, Jiang X, Choi H, Garrett-Beal L,
Carolan PJ and Yang Y: Wnt-5a inhibits the canonical Wnt pathway by
promoting GSK-3-independent beta-catenin degradation. J Cell Biol.
162:899–908. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Chen S, Wang J, Gou WF, Xiu YL, Zheng HC,
Zong ZH, Takano Y and Zhao Y: The involvement of RhoA and Wnt-5a in
the tumorigenesis and progression of ovarian epithelial carcinoma.
Int J Mol Sci. 14:24187–24199. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Hudson BD, Kulp KS and Loots GG: Prostate
cancer invasion and metastasis: Insights from mining genomic data.
Brief Funct Genomics. 12:397–410. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Weeraratna AT, Jiang Y, Hostetter G,
Rosenblatt K, Duray P, Bittner M and Trent JM: Wnt5a signaling
directly affects cell motility and invasion of metastatic melanoma.
Cancer Cell. 1:279–288. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kurayoshi M, Oue N, Yamamoto H, Kishida M,
Inoue A, Asahara T, Yasui W and Kikuchi A: Expression of Wnt-5a is
correlated with aggressiveness of gastric cancer by stimulating
cell migration and invasion. Cancer Res. 66:10439–10448. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kremenevskaja N, von Wasielewski R, Rao
AS, Schöfl C, Andersson T and Brabant G: Wnt-5a has tumor
suppressor activity in thyroid carcinoma. Oncogene. 24:2144–2154.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ying J, Li H, Yu J, Ng KM, Poon FF, Wong
SC, Chan AT, Sung JJ and Tao Q: WNT5A exhibits tumor-suppressive
activity through antagonizing the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling, and
is frequently methylated in colorectal cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
14:55–61. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Oishi I, Suzuki H, Onishi N, Takada R,
Kani S, Ohkawara B, Koshida I, Suzuki K, Yamada G, Schwabe GC, et
al: The receptor tyrosine kinase Ror2 is involved in non-canonical
Wnt5a/JNK signalling pathway. Genes Cells. 8:645–654. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Masiakowski P and Yancopoulos GD: The Wnt
receptor CRD domain is also found in MuSK and related orphan
receptor tyrosine kinases. Curr Biol. 8:R4071998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Rehn M, Pihlajaniemi T, Hofmann K and
Bucher P: The frizzled motif: In how many different protein
families does it occur? Trends Biochem Sci. 23:415–417. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
He X, Saint-Jeannet JP, Wang Y, Nathans J,
Dawid I and Varmus H: A member of the Frizzled protein family
mediating axis induction by Wnt-5A. Science. 275:1652–1654. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Matsuda T, Nomi M, Ikeya M, Kani S, Oishi
I, Terashima T, Takada S and Minami Y: Expression of the receptor
tyrosine kinase genes, Ror1 and Ror2, during mouse development.
Mech Dev. 105:153–156. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
DeChiara TM, Kimble RB, Poueymirou WT,
Rojas J, Masiakowski P, Valenzuela DM and Yancopoulos GD: Ror2,
encoding a receptor-like tyrosine kinase, is required for cartilage
and growth plate development. Nat Genet. 24:271–274. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Takeuchi S, Takeda K, Oishi I, Nomi M,
Ikeya M, Itoh K, Tamura S, Ueda T, Hatta T, Otani H, et al: Mouse
Ror2 receptor tyrosine kinase is required for the heart development
and limb formation. Genes Cells. 5:71–78. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Oldridge M, Fortuna AM, Maringa M,
Propping P, Mansour S, Pollitt C, DeChiara TM, Kimble RB,
Valenzuela DM, Yancopoulos GD and Wilkie AO: Dominant mutations in
ROR2, encoding an orphan receptor tyrosine kinase, cause
brachydactyly type B. Nat Genet. 24:275–278. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Schwabe GC, Tinschert S, Buschow C,
Meinecke P, Wolff G, Gillessen-Kaesbach G, Oldridge M, Wilkie AO,
Kömec R and Mundlos S: Distinct mutations in the receptor tyrosine
kinase gene ROR2 cause brachydactyly type B. Am J Hum Genet.
67:822–831. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Afzal AR, Rajab A, Fenske CD, Oldridge M,
Elanko N, Ternes-Pereira E, Tüysüz B, Murday VA, Patton MA, Wilkie
AO and Jeffery S: Recessive Robinow syndrome, allelic to dominant
brachydactyly type B, is caused by mutation of ROR2. Nat Genet.
25:419–422. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Mikels A, Minami Y and Nusse R: Ror2
receptor requires tyrosine kinase activity to mediate Wnt5A
signaling. J Biol Chem. 284:30167–30176. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Lyashenko N, Weissenböck M, Sharir A,
Erben RG, Minami Y and Hartmann C: Mice lacking the orphan receptor
ror1 have distinct skeletal abnormalities and are growth retarded.
Dev Dyn. 239:2266–2277. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Person AD, Beiraghi S, Sieben CM,
Hermanson S, Neumann AN, Robu ME, Schleiffarth JR, Billington CJ
Jr, van Bokhoven H, Hoogeboom JM, et al: WNT5A mutations in
patients with autosomal dominant Robinow syndrome. Dev Dyn.
239:327–337. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Minami Y, Oishi I, Endo M and Nishita M:
Ror-family receptor tyrosine kinases in noncanonical Wnt signaling:
Their implications in developmental morphogenesis and human
diseases. Dev Dyn. 239:1–15. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|