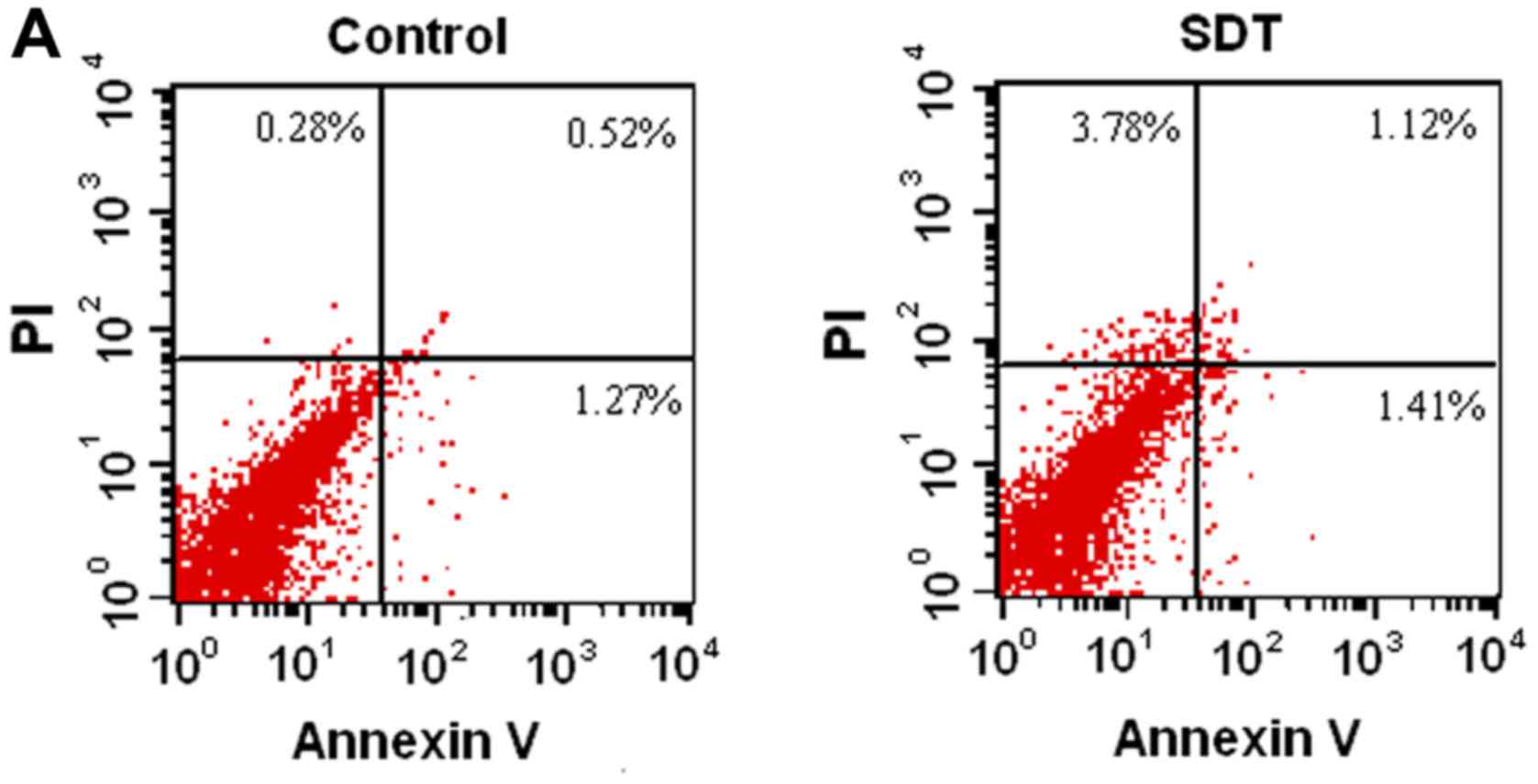
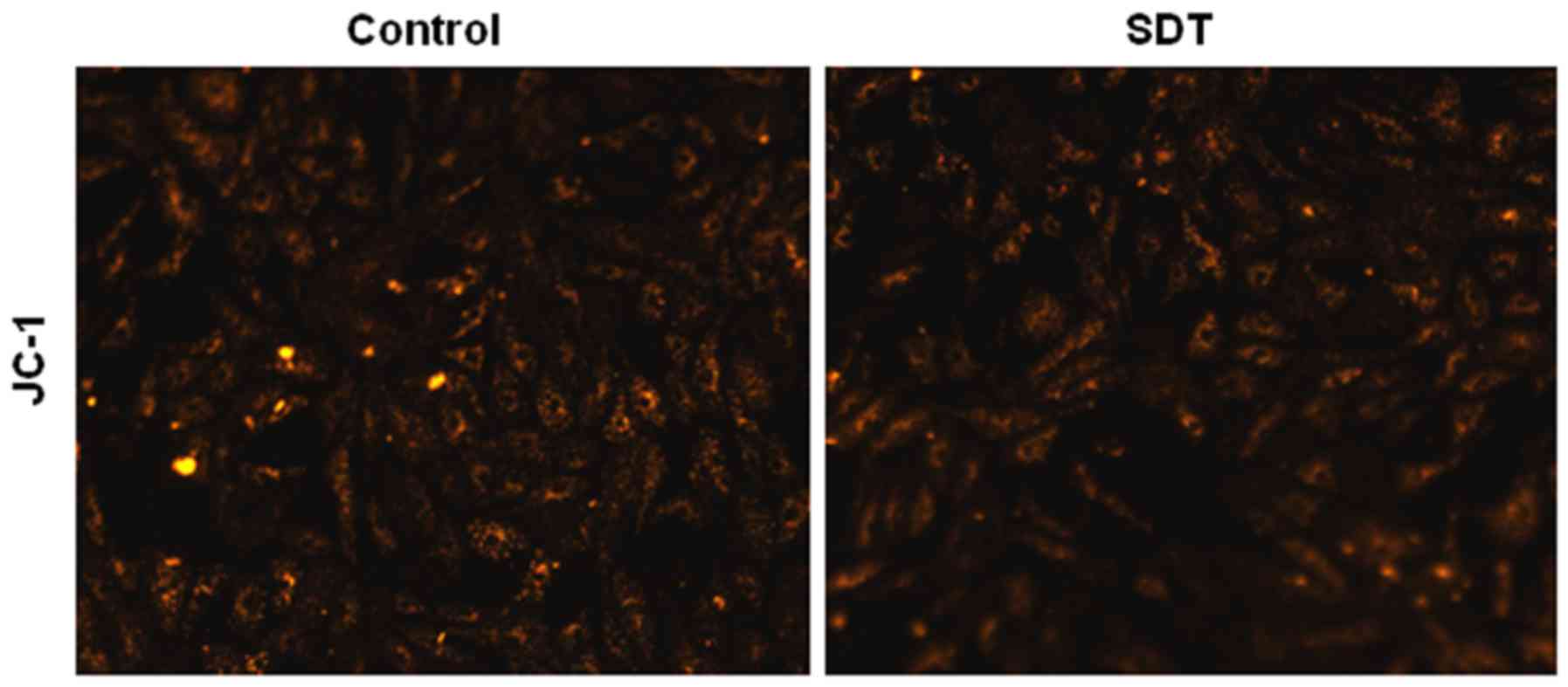
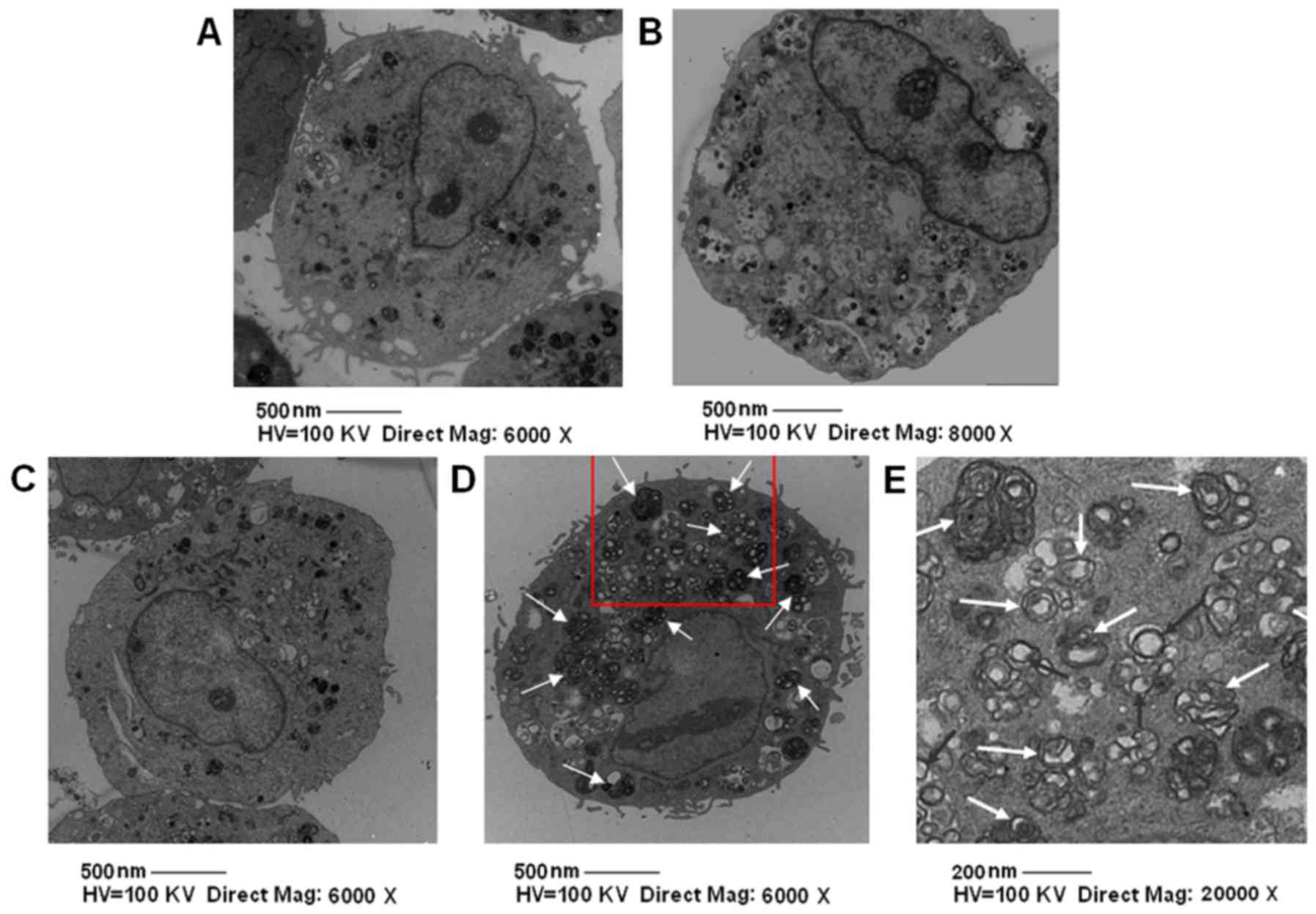
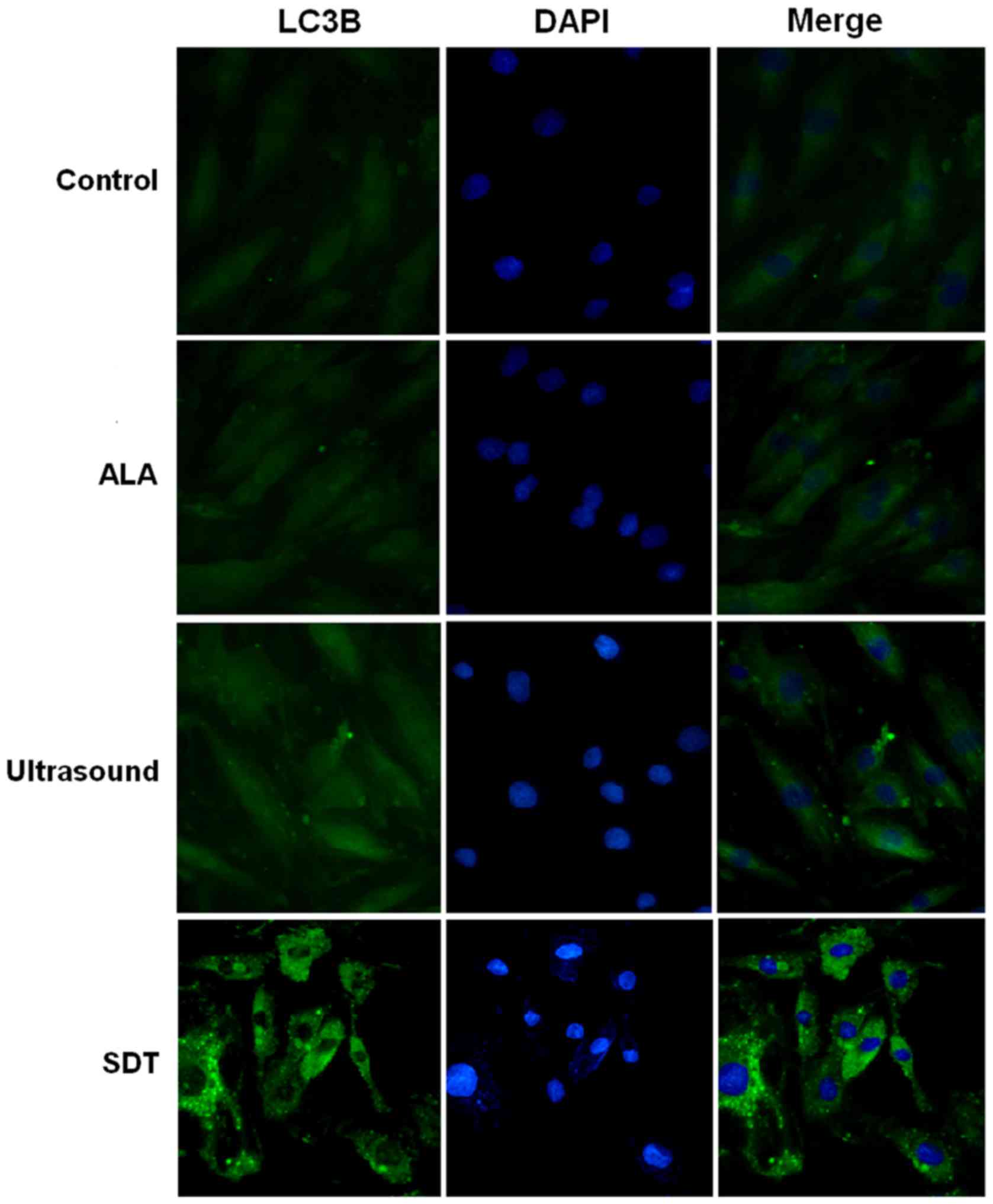
|
1
|
Perelman A, Wachtel C, Cohen M, Haupt S,
Shapiro H and Tzur A: JC-1: Alternative excitation wavelengths
facilitate mitochondrial membrane potential cytometry. Cell Death
Dis. 3:e4302012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chen H, Gao W, Yang Y, Guo S, Wang H, Wang
W, Zhang S, Zhou Q, Xu H, Yao J, et al: Inhibition of VDAC1
prevents Ca2+-mediated oxidative stress and apoptosis
induced by 5-aminolevulinic acid mediated sonodynamic therapy in
THP-1 macrophages. Apoptosis. 19:1712–1726. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Guo S, Sun X, Cheng J, Xu H, Dan J, Shen
J, Zhou Q, Zhang Y, Meng L, Cao W and Tian Y: Apoptosis of THP-1
macrophages induced by protoporphyrin IX-mediated sonodynamic
therapy. Int J Nanomedicine. 8:2239–2246. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Li X, Gao L, Zheng L, Kou J, Zhu X, Jiang
Y, Zhong Z, Dan J, Xu H, Yang Y, et al: The efficacy and mechanism
of apoptosis induction by hypericin-mediated sonodynamic therapy in
THP-1 macrophages. Int J nanomedicine. 10:821–838. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Li Z, Sun X, Guo S, Wang L, Wang T, Peng
C, Wang W, Tian Z, Zhao R, Cao W and Tian Y: Rapid stabilisation of
atherosclerotic plaque with 5-aminolevulinic acid-mediated
sonodynamic therapy. Thromb Haemost. 4:793–803. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Sun X, Xu H, Shen J, Guo S, Shi S, Dan J,
Tian F and Tian Y and Tian Y: Real-time detection of intracellular
reactive oxygen species and mitochondrial membrane potential in
THP-1 macrophages during ultrasonic irradiation for optimal
sonodynamic therapy. Ultrason Sonochem. 22:7–14. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Krammer B and Plaetzer K: ALA and its
clinical impact, from bench to beside. Photochem Photobiol Sci.
7:283–289. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Peng C, Li Y, Liang H, Cheng J, Li Q, Sun
X, Li Z, Wang F, Guo Y, Tian Z, et al: Detection and photodynamic
therapy of inflamed atherosclerotic plaques in the carotid artery
of rabbits. J Photochem Photobiol B. 102:26–31. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Mizushima N, Yoshimori T and Levine B:
Methods in mammalian autophagy research. Cell. 140:313–326. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Martinet W and De Meyer GR: Autophagy in
atherosclerosis. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 10:216–223. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lavandero S, Chiong M, Rothermel BA and
Hill JA: Autophagy in cardiovascular biology. J Clin Invest.
125:55–64. 2015. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ouimet M, Franklin V, Mak E, Liao X, Tabas
I and Marcel YL: Autophagy regulates cholesterol efflux from
macrophage foam cells via lysosomal acid lipase. Cell Metab.
13:655–667. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li BH, Yin YW, Liu Y, Pi Y, Guo L, Cao XJ,
Gao CY, Zhang LL and Li JC: TRPV1 activation impedes foam cell
formation by inducing autophagy in oxLDL-treated vascular smooth
muscle cells. Cell Death Dis. 5:e11822014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Michiels CF, Fransen P, De Munck DG, De
Meyer GR and Martinet W: Defective autophagy in vascular smooth
muscle cells alters contractility and Ca2+ homeostasis
in mice. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 308:H557–H567. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Dan J, Sun X, Li W, Zhang Y, Li X, Xu H,
Li Z, Tian Z, Guo S, Yao J, et al: 5-Aminolevulinic acid-mediated
sonodynamic therapy promotes phenotypic switching from
dedifferentiated to differentiated phenotype via reactive oxygen
species and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase in vascular smooth
muscle cells. Ultrasound Med Biol. 41:1681–1689. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hagiya Y, Fukuhara H, Matsumoto K, Endo Y,
Nakajima M, Tanaka T, Okura I, Kurabayashi A, Furihata M, Inoue K,
et al: Expression levels of PEPT1 and ABCG2 play key roles in
5-aminolevulinic acid (ALA)-induced tumor-specific protoporphyrin
IX (PpIX) accumulation in bladder cancer. Photodiagnosis Photodyn
Ther. 10:288–295. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Uto Y, Tamatani D, Mizuki Y, Endo Y,
Nakanishi I, Ohkubo K, Fukuzumi S, Ishizuka M, Tanaka T, Kuchiike
D, et al: Evaluation of the sonosensitizing activities of
5-aminolevulinic acid and Sn(IV) chlorin e6 in tumor-bearing chick
embryos. Anticancer Res. 34:4583–4587. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Cheng J, Sun X, Guo S, Cao W, Chen H, Jin
Y, Li B, Li Q, Wang H, Wang Z, et al: Effects of 5-aminolevulinic
acid-mediated sonodynamic therapy on macrophages. Int J
Nanomedicine. 8:669–676. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Li Y, Zhou Q, Hu Z, Yang B, Li Q, Wang J,
Zheng J and Cao W: 5-Aminolevulinic acid-based sonodynamic therapy
induces the apoptosis of osteosarcoma in mice. PLoS One.
10:e01320742015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kundu M and Thompson CB: Autophagy: Basic
principles and relevance to disease. Annu Rev Pathol. 3:427–455.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Luo Y, Lu S, Zhou P, Ai QD, Sun GB and Sun
XB: Autophagy: An exposing therapeutic target in atherosclerosis. J
Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 67:266–274. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Perrotta I and Aquila S: The role of
oxidative stress and autophagy in atherosclerosis. Oxid Med Cell
Longev. 2015:1303152015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Liao X, Sluimer JC, Wang Y, Subramanian M,
Brown K, Pattison JS, Robbins J, Martinez J and Tabas I: Macrophage
autophagy plays a protective role in advanced atherosclerosis. Cell
Metab. 15:545–553. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Mehta JL, Chen J, Hermonat PL, Romeo F and
Novelli G: Lectin-like, oxidized low-density lipoprotein receptor-1
(Lox-1): A critical player in the development of atherosclerosis
and related disorders. Cardiovasc Res. 69:36–45. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Xu K, Yang Y, Yan M, Zhan J, Fu X and
Zheng X: Autophagy plays a protective role in free cholesterol
overload-induced death of smooth muscle cells. J Lipid Res.
51:2581–2590. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Salabei JK, Cummins TD, Singh M, Jones SP,
Bhatnagar A and Hill BG: PDGF-mediated autophagy regulates vascular
smooth muscle cell phenotype and resistance to oxidative stress.
Biochem J. 451:375–388. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Mahmoudi MJ, Mahmoudi M, Siassi F, Shokri
F, Eshraghian MR, Zarnani AH, Chahardoli R, Hedayat M, Khoshnoodi
J, Nayeri H, et al: Lymphocyte cytotoxicity of oxLDL in patients
with atherosclerosis. Iran J Immunol. 8:27–33. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Mehta JL, Chen J, Hermonat PL, Romeo F and
Novelli G: Lectin-like, oxidized low-density lipoprotein receptor-1
(LOX-1): A critical player in the development of atherosclerosis
and related disorders. Cardiovasc Res. 69:36–45. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Martinet W and De Meyer GR: Autophagy in
atherosclerosis: A cell survival and death phenomenon with
therapeutic potential. Circ Res. 104:304–317. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kabeya Y, Mizushima N, Ueno T, Yamamoto A,
Kirisako T, Noda T, Kominami E, Ohsumi Y and Yoshimori T: LC3, a
mammalian homogue of yeast Apg8p, is localizing in autophagosome
membranes after processing. EMBO J. 19:5720–5728. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Grootaert MO, da Costa Martins PA, Bitsch
N, Pintelon I, De Meyer GR, Martinet W and Schrijvers DM: Defective
autophagy in vascular smooth muscle cells accelerates senescence
and promotes neointima formation and atherogenesis. Autophagy.
11:2014–2032. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Klionsky DJ, Abeliovich H, Agostinis P,
Agrawal DK, Aliev G, Askew DS, Baba M, Baehrecke EH, Bahr BA,
Ballabio A, et al: Guidelines for the use and interpretation of
assays for monitoring autophagy in higher eukaryotes. Autophagy.
4:151–175. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Salabei JK, Cummins TD, Singh M, Jones SP,
Bhatnagar A and Hill BG: PDGF-mediated autophagy regulates vascular
smooth muscle cell phenotype and resistance to oxidative stress.
Biochem J. 451:375–388. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|