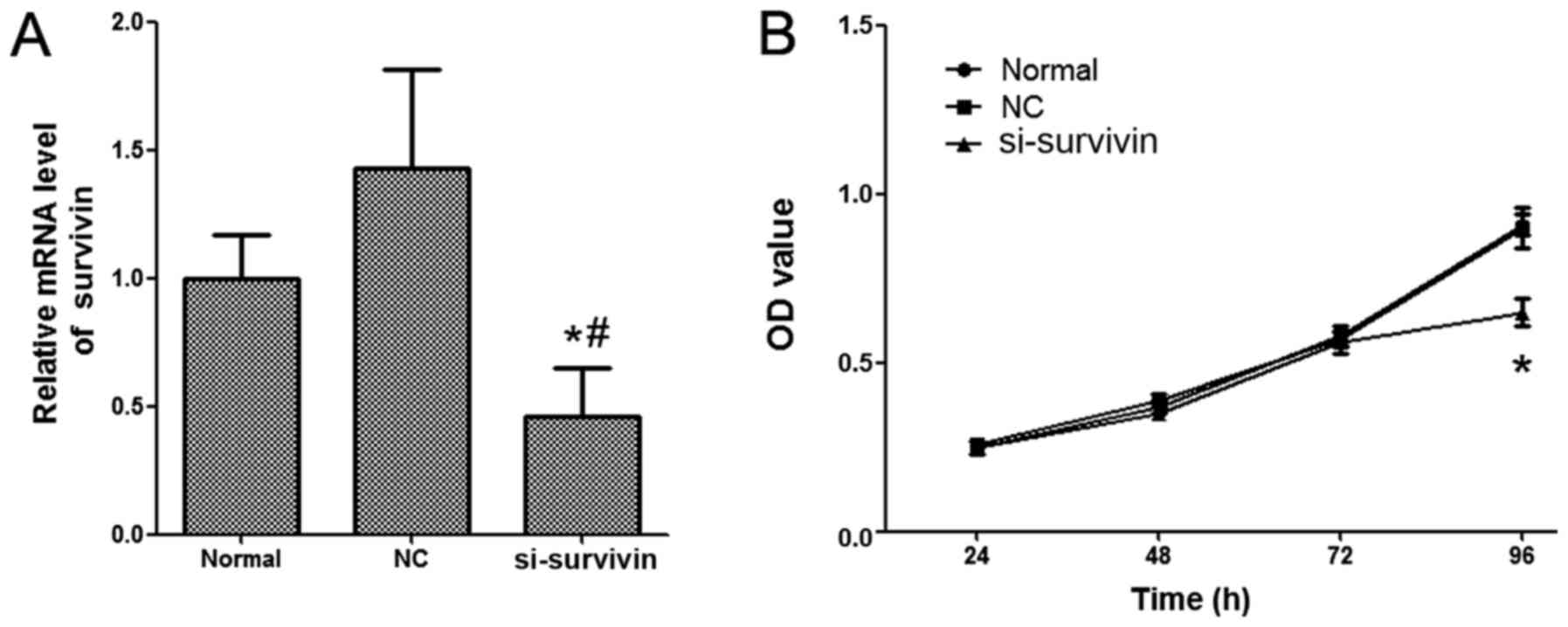
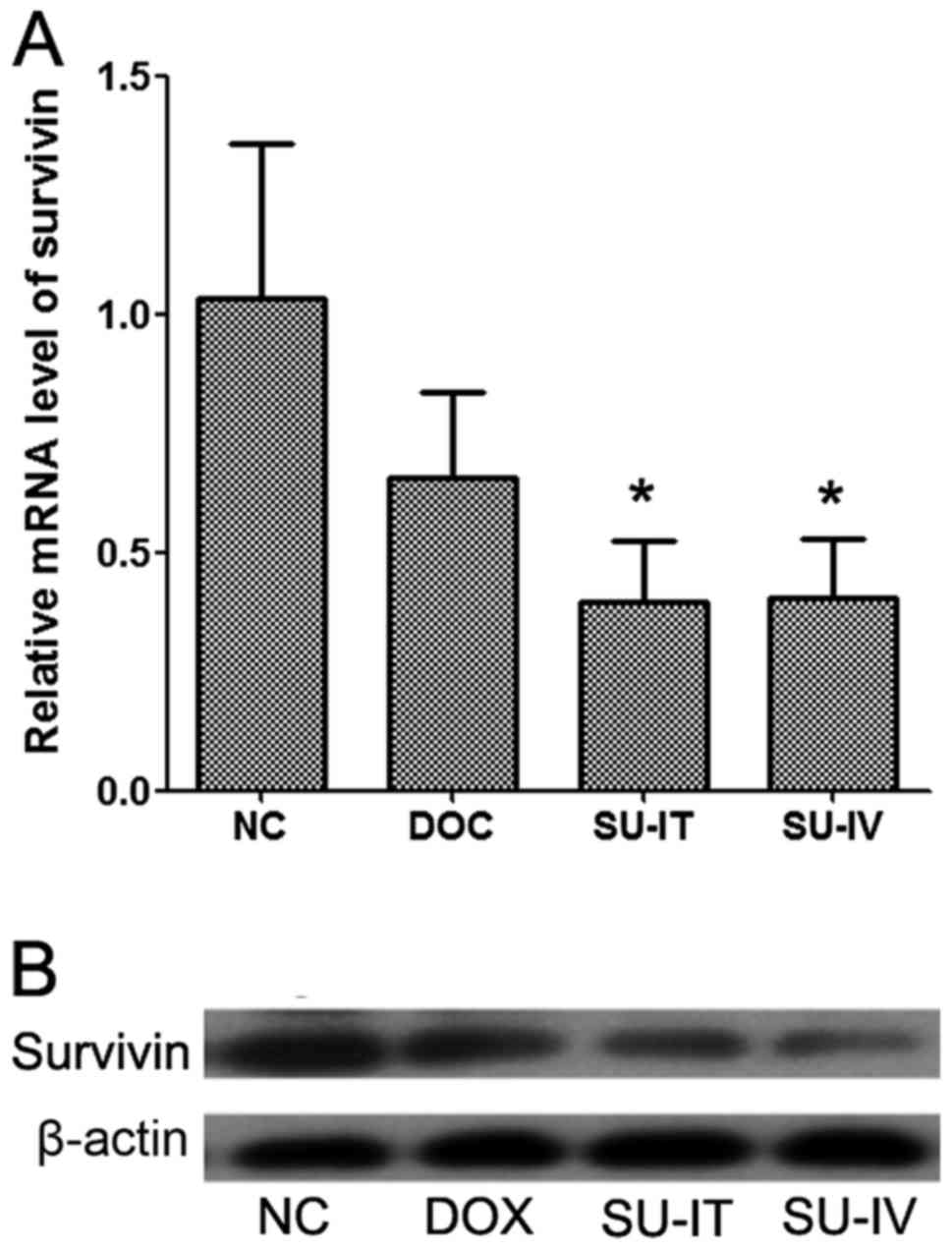
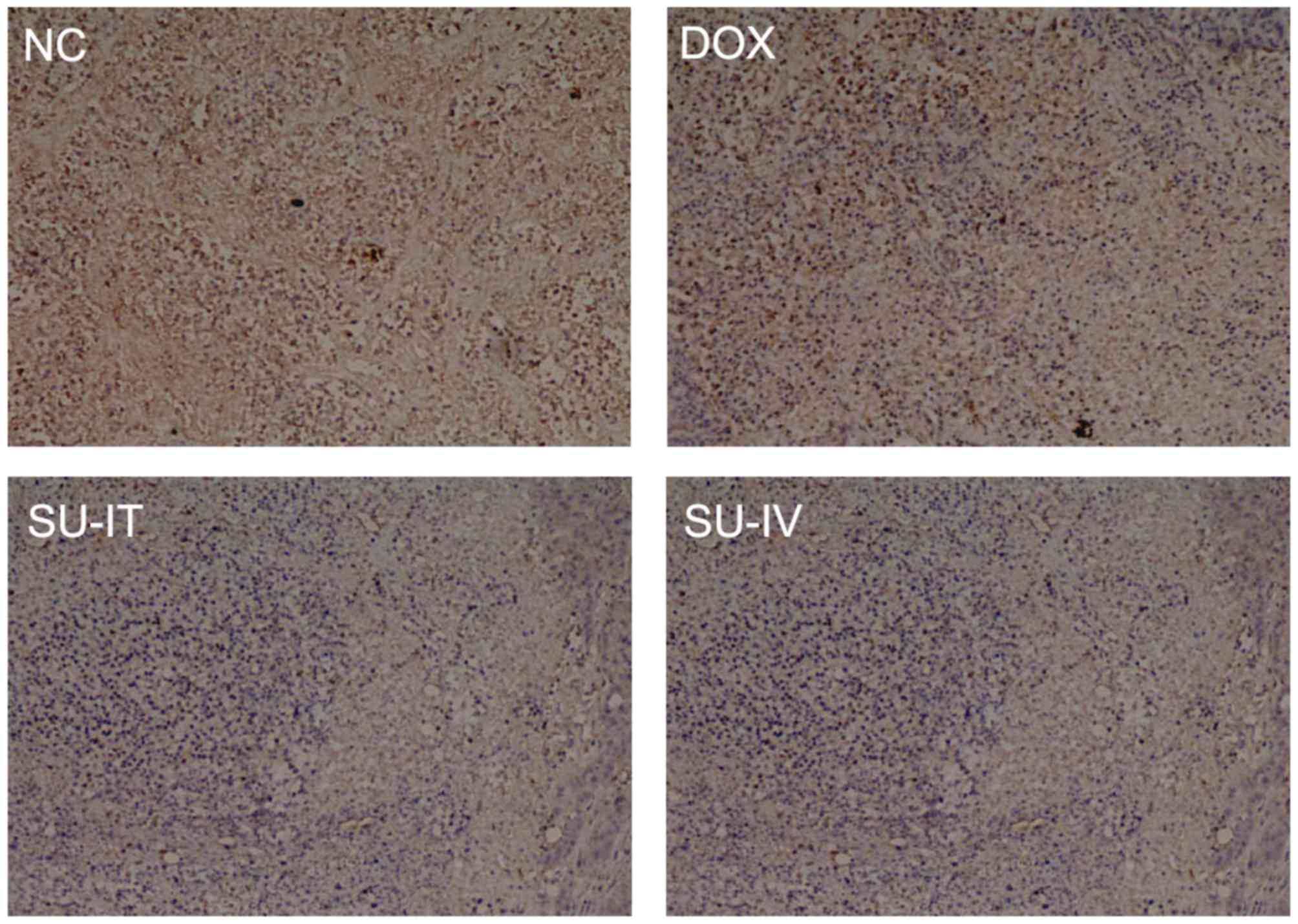
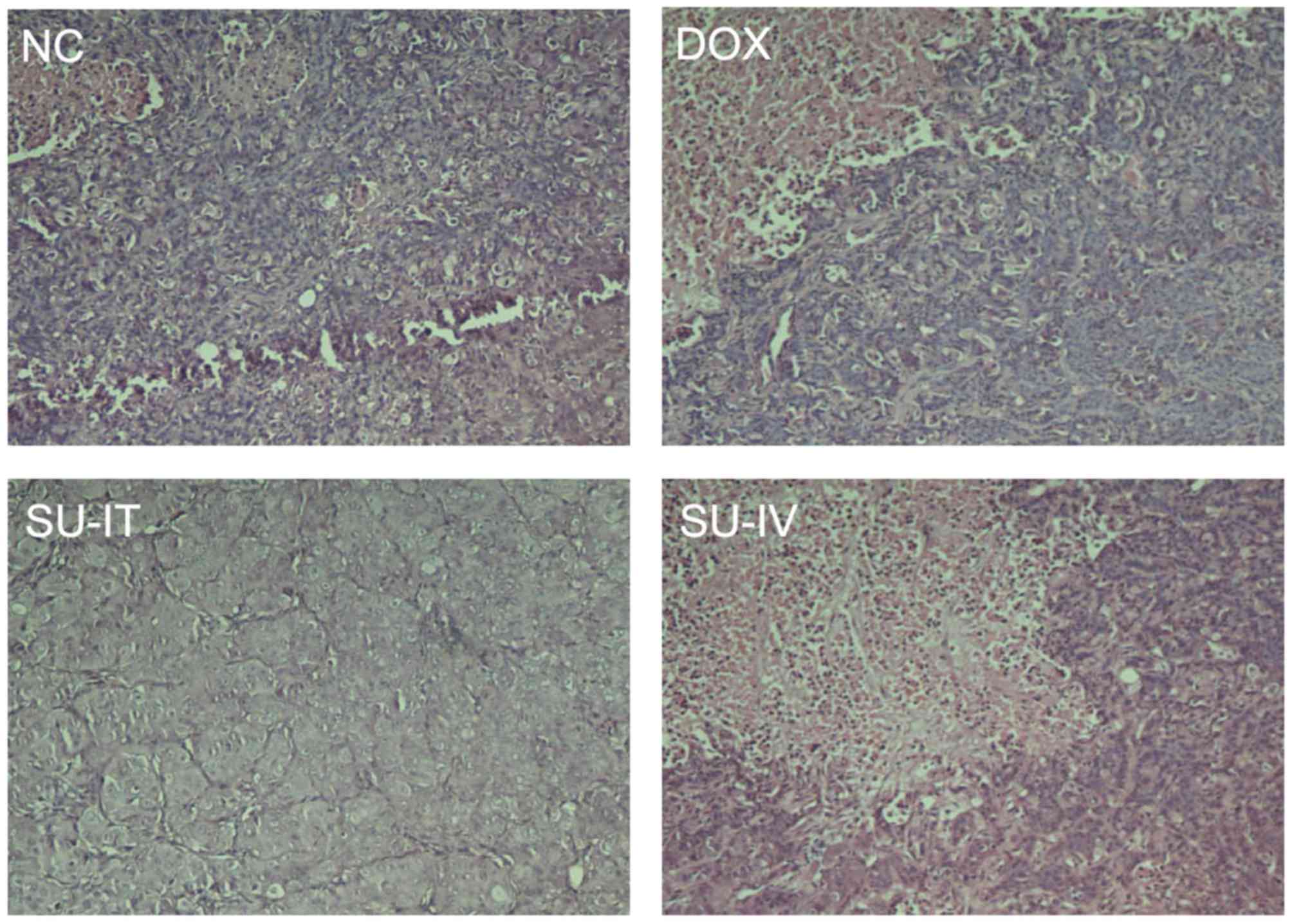
|
1
|
Ambrosini G, Adida C and Altieri DC: A
novel anti-apoptosis gene, survivin, expressed in cancer and
lymphoma. Nat Med. 3:917–921. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Li F, Ambrosini G, Chu EY, Plescia J,
Tognin S, Marchisio PC and Altieri DC: Control of apoptosis and
mitotic spindle checkpoint by survivin. Nature. 396:580–584. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sah NK, Khan Z, Khan GJ and Bisen PS:
Structural, functional and therapeutic biology of survivin. Cancer
Lett. 244:164–171. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zaffaroni N and Daidone MG: Survivin
expression and resistance to anticancer treatments: Perspectives
for new therapeutic interventions. Drug Resist Updat. 5:65–72.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Moriai R, Asanuma K, Kobayashi D, Yajima
T, Yagihashi A, Yamada M and Watanabe N: Quantitative analysis of
the anti-apoptotic gene survivin expression in malignant
haematopoietic cells. Anticancer Res. 21:595–600. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Notarbartolo M, Cervello M, Dusonchet L,
Cusimano A and D'Alessandro N: Resistance to diverse apoptotic
triggers in multidrug resistant HL60 cells and its possible
relationship to the expression of P-glycoprotein, Fas and of the
novel anti-apoptosis factors IAP (inhibitory of apoptosis
proteins). Cancer Lett. 180:91–101. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Troeger A, Siepermann M, Escherich G,
Meisel R, Willers R, Gudowius S, Moritz T, Laws HJ, Hanenberg H,
Goebel U, et al: Survivin and its prognostic significance in
pediatric acute B-cell precursor lymphoblastic leukemia.
Haematologica. 92:1043–1050. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Moriyama M, Kano R, Maruyama H, Hasegawa A
and Kamata H: Small interfering RNA (siRNA) against the survivin
gene increases apoptosis in a canine melanoma cell line. J Vet Med
Sci. 72:1643–1646. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Cai M, Wang G, Tao K and Cai C: Induction
of apoptosis of human colon cancer cells by siRNA recombinant
expression vector targeting survivin gene. J Huazhong Univ Sci
Technolog Med Sci. 29:45–49. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li J, Yue M, Shi X, Feng S, Tang R, Zhang
X, Liu R, Liu Z and Wang T: Evaluation of anti-cancer activity of
survivin siRNA delivered by folate receptor-targeted
polyethylene-glycol liposomes in K562-bearing xenograft mice.
Biomed Eng. 26:14500262014.
|
|
11
|
Hannon GJ and Rossi JJ: Unlocking the
potential of the human genome with RNA interference. Nature.
431:371–378. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Merritt WM, Lin YG, Han LY, Kamat AA,
Spannuth WA, Schmandt R, Urbauer D, Pennacchio LA, Cheng JF, Nick
AM, et al: Dicer, Drosha, and outcomes in patients with ovarian
cancer. N Engl J Med. 359:2641–2650. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Petros RA and DeSimone JM: Strategies in
the design of nanoparticles for therapeutic applications. Nat Rev
Drug Discov. 9:615–627. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Burnett JC and Rossi JJ: RNA-based
therapeutics: Current progress and future prospects. Chem Biol.
19:60–71. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tabernero J, Shapiro GI, LoRusso PM,
Cervantes A, Schwartz GK, Weiss GJ, Paz-Ares L, Cho DC, Infante JR,
Alsina M, et al: First-in-humans trial of an RNA interference
therapeutic targeting VEGF and KSP in cancer patients with liver
involvement. Cancer Discov. 3:406–417. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ozpolat B, Sood AK and Lopez-Berestein G:
Liposomal siRNA nanocarriers for cancer therapy. Adv Drug Deliv
Rev. 66:110–116. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ozpolat B, Sood AK and Lopez-Berestein G:
Nanomedicine based approaches for the delivery of siRNA in cancer.
J Intern Med. 267:44–53. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhou J, Shum KT, Burnett JC and Rossi JJ:
Nanoparticle-based delivery of RNAi therapeutics: Progress and
challenges. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 6:85–107. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Allémann E, Rousseau J, Brasseur N,
Kudrevich SV, Lewis K and van Lier JE: Photodynamic therapy of
tumours with hexadecafluoro zinc phthalocyanine formulated in
PEG-coated poly (lactic acid) nanoparticles. Int J Cancer.
66:821–824. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yu B, Wang X, Zhou C, Teng L, Ren W, Yang
Z, Shih CH, Wang T, Lee RJ, Tang S and Lee LJ: Insight into
mechanisms of cellular uptake of lipid nanoparticles and
intracellular release of small RNAs. Pharm Res. 31:2685–2695. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang Y, Xu Z, Guo S, Zhang L, Sharma A,
Robertson GP and Huang L: Intravenous delivery of siRNA targeting
CD47 effectively inhibits melanoma tumor growth and lung
metastasis. Mol Ther. 21:1919–1929. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Paduano F, Villa R, Pennati M, Folini M,
Binda M, Daidone MG and Zaffaroni N: Silencing of survivin gene by
small interfering RNAs produces supra-additive growth suppression
in combination with 17-allylamino-17-demethoxygeldanamycin in human
prostate cancer cells. Mol Cancer Ther. 5:179–186. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kingston EF, Goulding H and Bateman AC:
Vascular invasion is underrecognized in colorectal cancer using
conventional hematoxylin and eosin staining. Dis Colon Rectum.
50:1867–1872. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Shamsabadi FT, Eidgahi MR, Mehrbod P,
Daneshvar N, Allaudin ZN, Yamchi A and Shahbazi M: Survivin, a
promising gene for targeted cancer treatment. Asian Pac J Cancer
Prev. 17:3711–3719. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Cheung CH, Huang CC, Tsai FY, Lee JY,
Cheng SM, Chang YC, Huang YC, Chen SH and Chang JY:
Survivin-biology and potential as a therapeutic target in oncology.
Onco Targets Ther. 6:1453–1462. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Mobahat M, Narendran A and Riabowol K:
Survivin as a preferential target for cancer therapy. Int J Mol
Sci. 15:2494–2516. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chen XQ, Yang S, Kang MQ, Li ZY, Lu HS and
Lin TY: Survivin expression in human lung cancer and the influence
of its downregulation on the biological behavior of human lung
cancer cells. Exp Ther Med. 3:1010–1014. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Cao C, Mu Y, Hallahan DE and Lu B: XIAP
and survivin as therapeutic targets for radiation sensitization in
preclinical models of lung cancer. Oncogene. 23:7047–7052. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sharma H, Sen S, Lo Muzio L, Mariggiò A
and Singh N: Antisense-mediated downregulation of anti-apoptotic
proteins induces apoptosis and sensitizes head and neck squamous
cell carcinoma cells to chemotherapy. Cancer Biol Ther. 4:720–727.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Fuessel S, Kueppers B, Ning S, Kotzsch M,
Kraemer K, Schmidt U, Meye A and Wirth MP: Systematic in vitro
evaluation of survivin directed antisense oligodeoxynucleotides in
bladder cancer cells. J Urol. 171:2471–2476. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Li Z, Yang S, Chang T, Cao X, Shi L and
Fang G: Anti-angiogenesis and anticancer effects of a plasmid
expressing both ENDO-VEGI151 and small interfering RNA against
survivin. Int J Mol Med. 29:485–490. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Li Z, Yin PH, Yang SS, Li QY, Chang T,
Fang L, Shi LX and Fang GE: Recombinant attenuated Salmonella
typhimurium carrying a plasmid co-expressing ENDO-VEGI151 and
survivin siRNA inhibits the growth of breast cancer in vivo. Mol
Med Rep. 7:1215–1222. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Carvalho A, Carmena M, Sambade C, Earnshaw
WC and Wheatley SP: Survivin is required for stable checkpoint
activation in taxol-treated HeLa cells. J Cell Sci. 116:2987–2998.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yang Z, Xie J, Zhu J, Kang C, Chiang C,
Wang X, Wang X, Kuang T, Chen F, Chen Z, et al: Functional
exosome-mimic for delivery of siRNA to cancer: In vitro and in vivo
evaluation. J Control Release. 243:160–171. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Bonnet S, Archer SL, Allalunis-Turner J,
Haromy A, Beaulieu C, Thompson R, Lee CT, Lopaschuk GD, Puttagunta
L, Bonnet S, et al: A mitochondria-K+ channel axis is suppressed in
cancer and its normalization promotes apoptosis and inhibits cancer
growth. Cancer Cell. 11:37–51. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Siu RW, Fragkoudis R, Simmonds P, Donald
CL, Chase-Topping ME, Barry G, Attarzadeh-Yazdi G, Rodriguez-Andres
J, Nash AA, Merits A, et al: Antiviral RNA interference responses
induced by Semliki Forest virus infection of mosquito cells:
Characterization, origin and frequency-dependent functions of
virus-derived small interfering RNAs. J Virol. 85:2907–2917. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Semple SC, Akinc A, Chen J, Sandhu AP, Mui
BL, Cho CK, Sah DW, Stebbing D, Crosley EJ, Yaworski E, et al:
Rational design of cationic lipids for siRNA delivery. Nat
Biotechnol. 28:172–176. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Yu B, Hsu SH, Zhou C, Wang X, Terp MC, Wu
Y, Teng L, Mao Y, Wang F, Xue W, et al: Lipid nanoparticles for
hepatic delivery of small interfering RNA. Biomaterials.
33:5924–5934. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|